Abstract
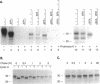
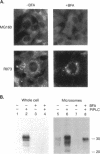
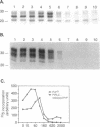
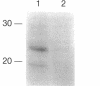
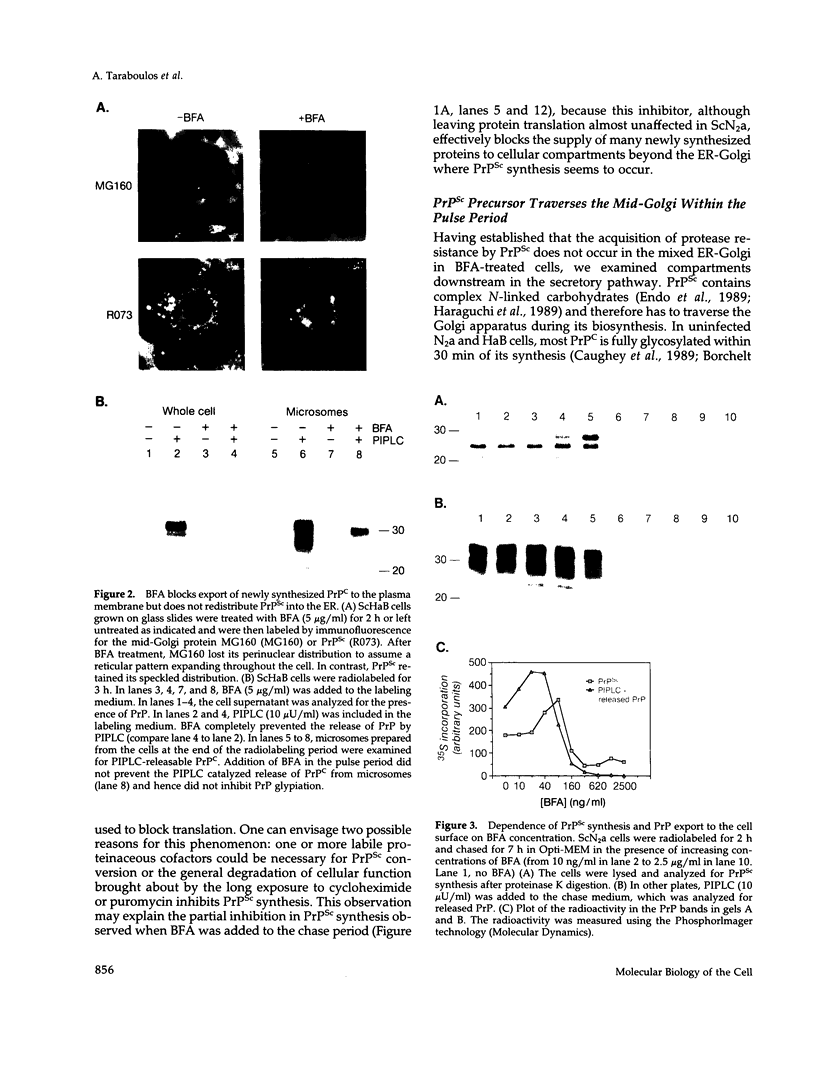
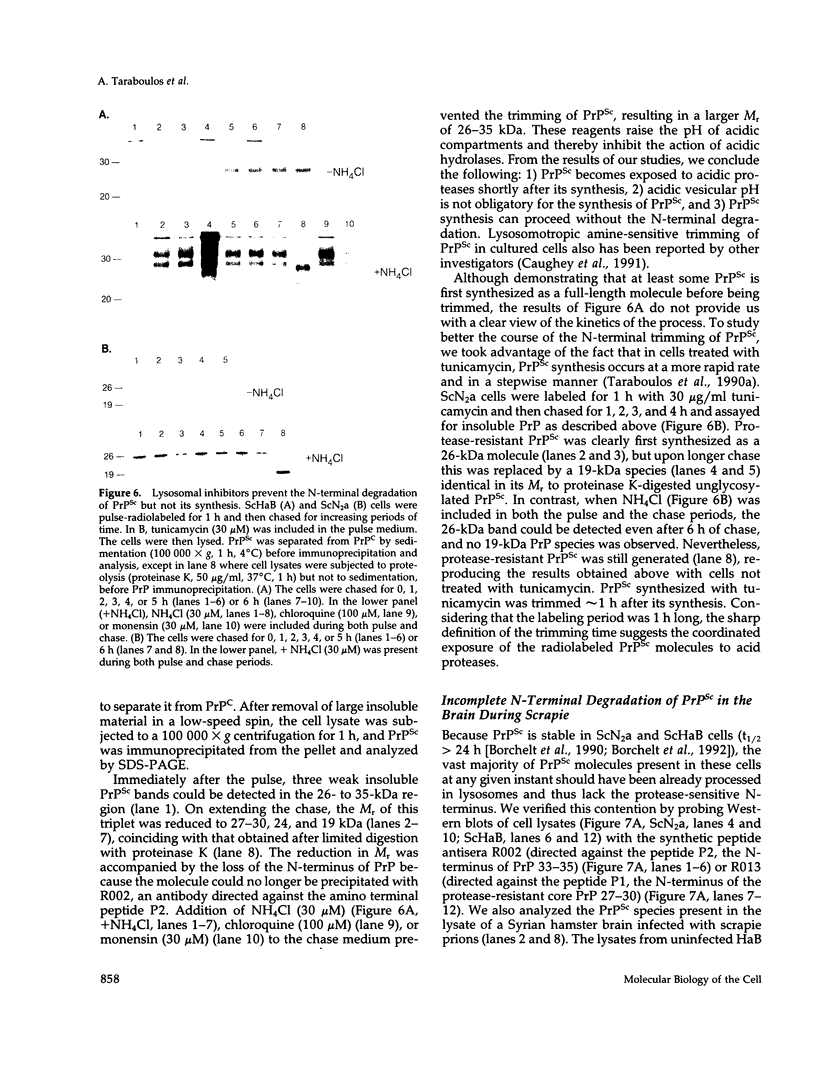
Scrapie prions are composed largely, if not entirely, of the scrapie prion protein (PrPSc) that is encoded by a chromosomal gene. Scrapie-infected mouse neuroblastoma (ScN2a) and hamster brain (ScHaB) cells synthesize PrPSc from the normal PrP isoform (PrPC) or a precursor through a posttranslational process. In pulse-chase radiolabeling experiments, we found that presence of brefeldin A (BFA) during both the pulse and the chase periods prevented the synthesis of PrPSc. Removal of BFA after the chase permitted synthesis of PrPSc to resume. BFA also blocked the export of nascent PrPC to the cell surface but did not alter the distribution of intracellular deposits of PrPSc. Under the same conditions, BFA caused the redistribution of the Golgi marker MG160 into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Using monensin as an inhibitor of mid-Golgi glycosylation, we determined that PrP traverses the mid-Golgi stack before acquiring protease resistance. About 1 h after the formation of PrPSc, its N-terminus was removed by a proteolytic process that was inhibited by ammonium chloride, chloroquine, and monensin, arguing that this is a lysosomal event. These results suggest that the ER is not competent for the synthesis of PrPSc and that the synthesis of PrPSc occurs during the transit of PrP between the mid-Golgi stack and lysosomes. Presumably, the endocytic pathway features in the synthesis of PrPSc.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry R. A., Vincent M. T., Kent S. B., Hood L. E., Prusiner S. B. Characterization of prion proteins with monospecific antisera to synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1188–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Oesch B., Scott M., Westaway D., Wälchli M., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B., Weissmann C. Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90662-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchelt D. R., Scott M., Taraboulos A., Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and cellular prion proteins differ in their kinetics of synthesis and topology in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):743–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. A., Scott M. R., Bockman J. M., Borchelt D. R., Taraboulos A., Hsiao K. K., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie-infected murine neuroblastoma cells produce protease-resistant prion proteins. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1558–1564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1558-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Fischer M., Lang Y., Bluethmann H., Lipp H. P., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):577–582. doi: 10.1038/356577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Neary K., Buller R., Ernst D., Perry L. L., Chesebro B., Race R. E. Normal and scrapie-associated forms of prion protein differ in their sensitivities to phospholipase and proteases in intact neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1093–1101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1093-1101.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Race R. E., Ernst D., Buchmeier M. J., Chesebro B. Prion protein biosynthesis in scrapie-infected and uninfected neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):175–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.175-181.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Raymond G. J., Ernst D., Race R. E. N-terminal truncation of the scrapie-associated form of PrP by lysosomal protease(s): implications regarding the site of conversion of PrP to the protease-resistant state. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6597–6603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6597-6603.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Raymond G. J. The scrapie-associated form of PrP is made from a cell surface precursor that is both protease- and phospholipase-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18217–18223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chege N. W., Pfeffer S. R. Compartmentation of the Golgi complex: brefeldin-A distinguishes trans-Golgi cisternae from the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):893–899. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diment S., Leech M. S., Stahl P. D. Cathepsin D is membrane-associated in macrophage endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6901–6907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Russ G., Yewdell J. W. Brefeldin A redistributes resident and itinerant Golgi proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):61–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Groth D., Prusiner S. B., Kobata A. Diversity of oligosaccharide structures linked to asparagines of the scrapie prion protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8380–8388. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Oda K., Yokota S., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18545–18552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb L. G., Haltia M., Brown P., Nieto A., Kovanen J., McCombie W. R., Trapp S., Gajdusek D. C. New mutation in scrapie amyloid precursor gene (at codon 178) in Finnish Creutzfeldt-Jakob kindred. Lancet. 1991 Feb 16;337(8738):425–425. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Goldfarb L. G., Brown P., Asher D. M., Brown W. T., Lin S., Teener J. W., Feinstone S. M., Rubenstein R., Kascsak R. J. Mutations in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker's syndrome. Exp Neurol. 1989 Nov;106(2):204–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas J. O., Mezitis S. G., Stieber A., Fleischer B., Gonatas N. K. MG-160. A novel sialoglycoprotein of the medial cisternae of the Golgi apparatus [published eeratum appears in J Biol Chem 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4264]. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):646–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon P. B., Seglen P. O. Prelysosomal convergence of autophagic and endocytic pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):40–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90556-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. A., Kelly R. B. Endocytic membrane traffic to the Golgi apparatus in a regulated secretory cell line. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21269–21278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraguchi T., Fisher S., Olofsson S., Endo T., Groth D., Tarentino A., Borchelt D. R., Teplow D., Hood L., Burlingame A. Asparagine-linked glycosylation of the scrapie and cellular prion proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Barry R. A., Lieberburg I., Prusiner S. B., Lingappa V. R. Biogenesis and transmembrane orientation of the cellular isoform of the scrapie prion protein [published errratum appears in Mol Cell Biol 1987 May;7(5):2035]. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):914–920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemström C., Virtanen A., Bridge E., Ketner G., Pettersson U. Adenovirus E4-dependent activation of the early E2 promoter is insufficient to promote the early-to-late-phase transition. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1440–1449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1440-1449.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. K., Scott M., Foster D., Groth D. F., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Spontaneous neurodegeneration in transgenic mice with mutant prion protein. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1587–1590. doi: 10.1126/science.1980379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K., Baker H. F., Crow T. J., Poulter M., Owen F., Terwilliger J. D., Westaway D., Ott J., Prusiner S. B. Linkage of a prion protein missense variant to Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):342–345. doi: 10.1038/338342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K., Meiner Z., Kahana E., Cass C., Kahana I., Avrahami D., Scarlato G., Abramsky O., Prusiner S. B., Gabizon R. Mutation of the prion protein in Libyan Jews with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 18;324(16):1091–1097. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104183241604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Whitney J. A., Mellman I. Selective inhibition of transcytosis by brefeldin A in MDCK cells. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):617–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90535-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Tonna-DeMasi M., Fersko R., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Mouse polyclonal and monoclonal antibody to scrapie-associated fibril proteins. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3688–3693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3688-3693.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum: disposing of newly synthesized proteins. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Glickman J., Donaldson J. G., Robbins J., Kreis T. E., Seamon K. B., Sheetz M. P., Klausner R. D. Forskolin inhibits and reverses the effects of brefeldin A on Golgi morphology by a cAMP-independent mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):567–577. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L., Tipper C., Amherdt M., Orci L., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):601–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Stiernberg J., Waneck G. L., Flavell R. A., Kincade P. W. Cell-specific heterogeneity in sensitivity of phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane antigens to release by phospholipase C. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 4;113(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Taraboulos A., Kenaga L., Serban D., Stieber A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Gonatas N. Ultrastructural localization of scrapie prion proteins in cytoplasmic vesicles of infected cultured cells. Lab Invest. 1991 Dec;65(6):622–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Misumi Y., Miki K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Hirose S., Takami N., Misumi Y., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A arrests the intracellular transport of a precursor of complement C3 before its conversion site in rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F., Poulter M., Lofthouse R., Collinge J., Crow T. J., Risby D., Baker H. F., Ridley R. M., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Insertion in prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1989 Jan 7;1(8628):51–52. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91713-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Scott M., Foster D., Pan K. M., Groth D., Mirenda C., Torchia M., Yang S. L., Serban D., Carlson G. A. Transgenetic studies implicate interactions between homologous PrP isoforms in scrapie prion replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90134-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M., Taraboulos A., Scott M., Groth D., Prusiner S. B. Intracellular accumulation of the cellular prion protein after mutagenesis of its Asn-linked glycosylation sites. Glycobiology. 1990 Sep;1(1):101–109. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Ying Y. S., Kolhouse J. F., Kamen B. A., Anderson R. G. The glycophospholipid-linked folate receptor internalizes folate without entering the clathrin-coated pit endocytic pathway. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):637–649. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M., Foster D., Mirenda C., Serban D., Coufal F., Wälchli M., Torchia M., Groth D., Carlson G., DeArmond S. J. Transgenic mice expressing hamster prion protein produce species-specific scrapie infectivity and amyloid plaques. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90608-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serban D., Taraboulos A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Rapid detection of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie prion proteins. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):110–117. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider M. D., Rogers O. C. Intracellular movement of cell surface receptors after endocytosis: resialylation of asialo-transferrin receptor in human erythroleukemia cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):826–834. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Prions and prion proteins. FASEB J. 1991 Oct;5(13):2799–2807. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.13.1916104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Rogers M., Borchelt D. R., McKinley M. P., Scott M., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Acquisition of protease resistance by prion proteins in scrapie-infected cells does not require asparagine-linked glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8262–8266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion proteins accumulate in the cytoplasm of persistently infected cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2117–2132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A., Vassalli P., Détraz M. Comparative studies of intracellular transport of secretory proteins. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):694–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C. A 'unified theory' of prion propagation. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):679–683. doi: 10.1038/352679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström L., Lodish H. F. Nonlysosomal, pre-Golgi degradation of unassembled asialoglycoprotein receptor subunits: a TLCK- and TPCK-sensitive cleavage within the ER. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):997–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. A., Park J. E., Brown W. J. Brefeldin A causes a microtubule-mediated fusion of the trans-Golgi network and early endosomes. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]