Abstract
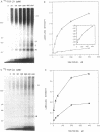
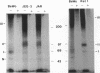
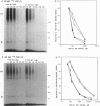
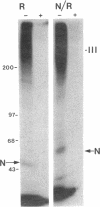
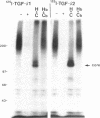
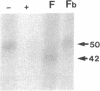
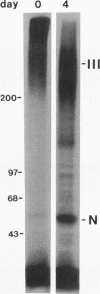
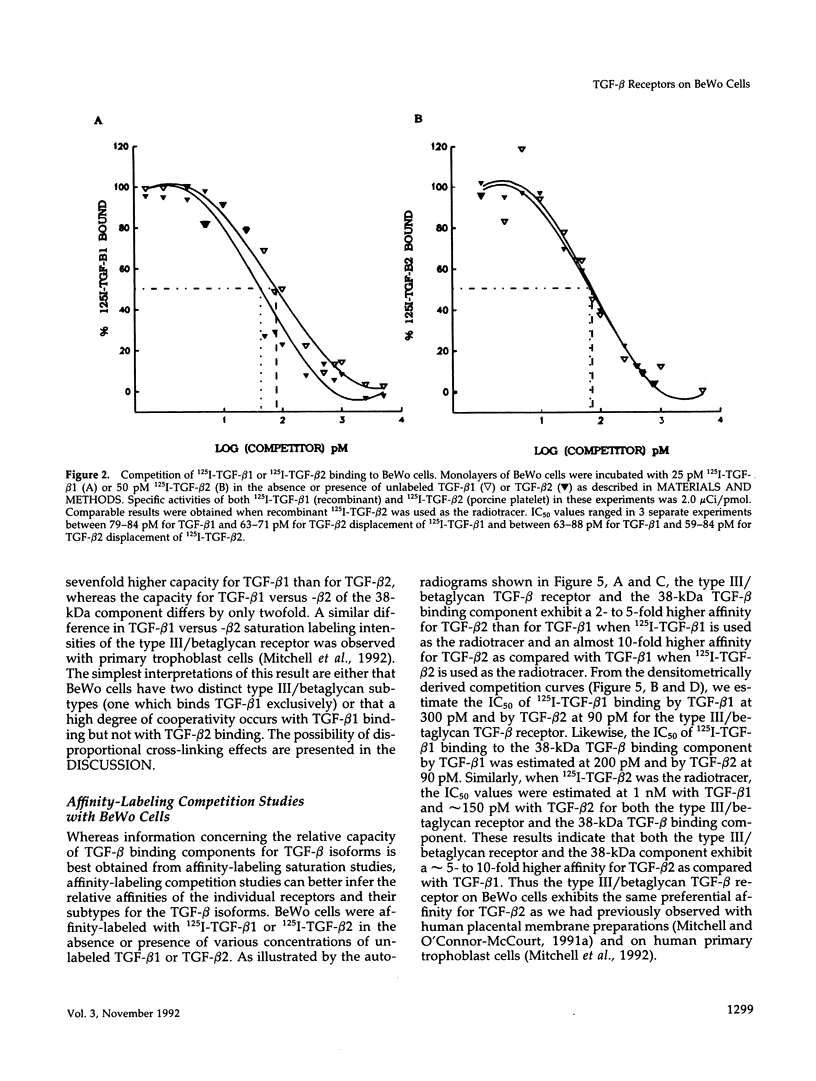
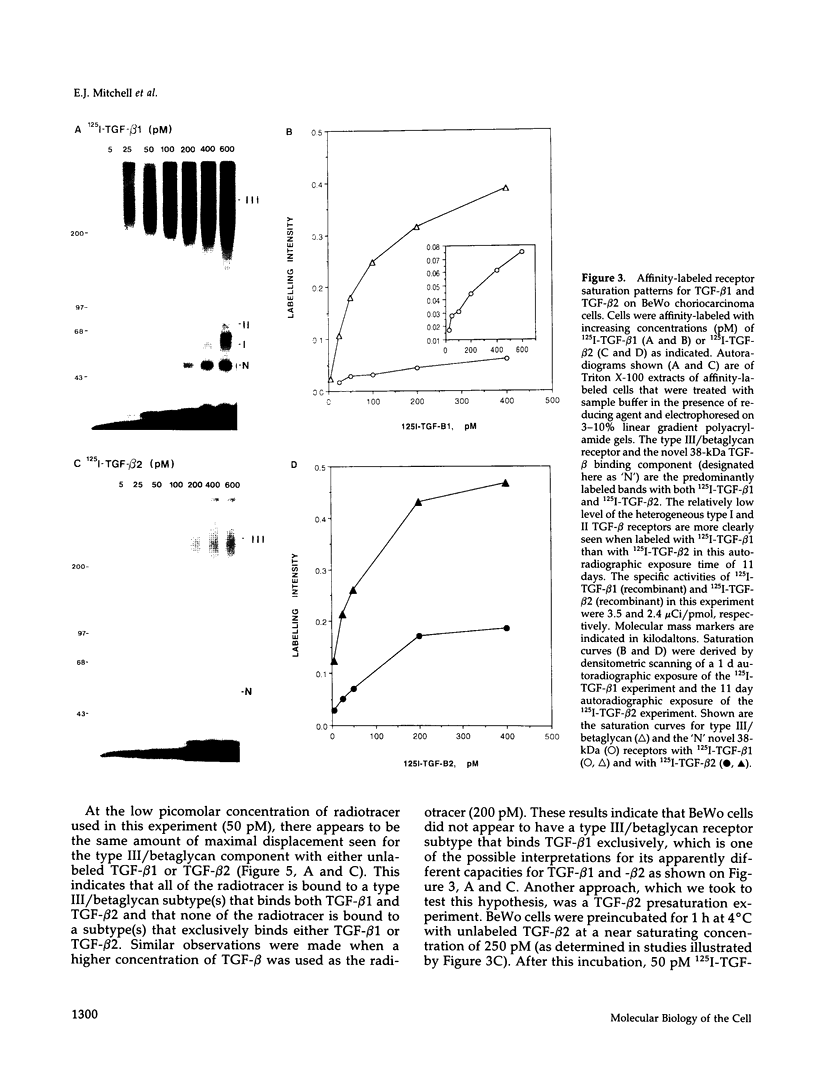
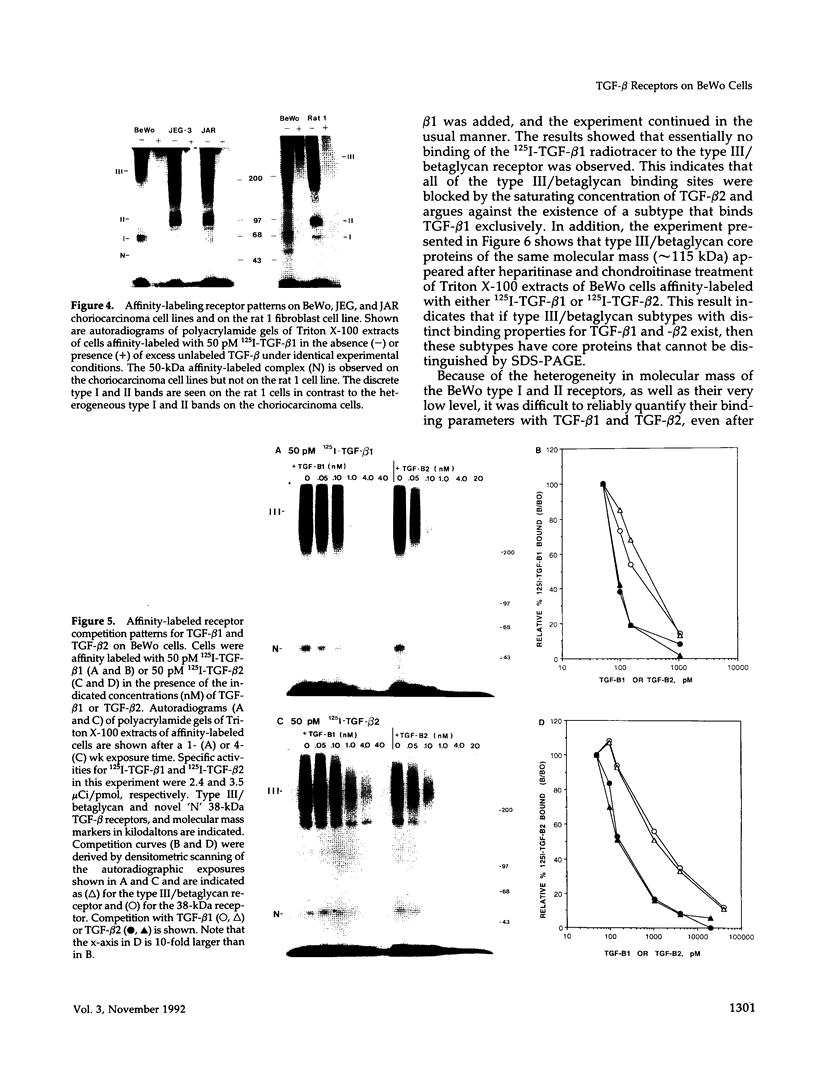
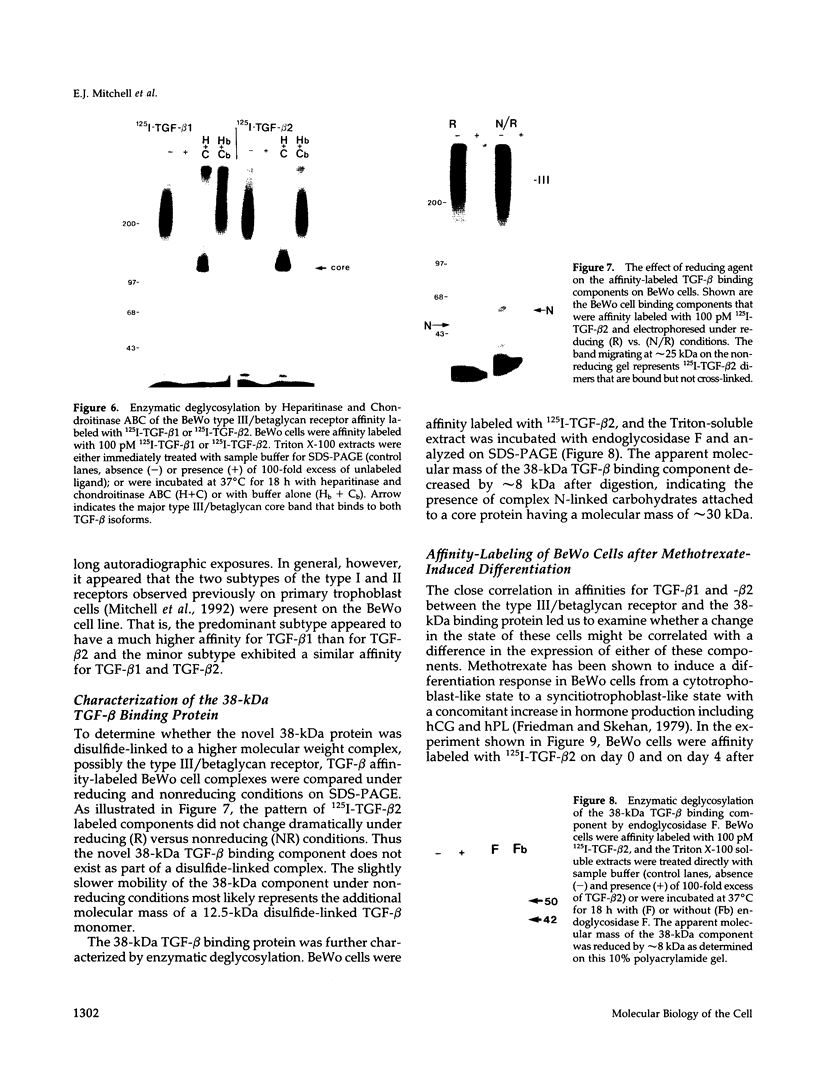
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) is a potential mediator of placental trophoblast functions, including differentiation, hormone production, endometrial invasion, and immunosuppression. Equilibrium binding and affinity-labeling assays were used to investigate the binding characteristics of TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 on an established human choriocarcinoma trophoblastic cell line (BeWo). The equilibrium binding experiments indicated that the BeWo cells exhibited similar average affinities and total number of binding sites for TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2. The Kd values obtained from Scatchard analyses were approximately 65 pM for 125I-TGF-beta 1 and approximately 40 pM for 125I-TGF-beta 2, with 70,000 and 85,000 sites per cell, respectively. Competitive equilibrium binding experiments indicated that TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 were equipotent (apparent half maximal inhibition [IC50] approximately 70 pM) and that all binding sites were capable of recognizing both isoforms. Affinity-labeling studies with 125I-TGF-beta 1 and 125I-TGF-beta 2 and the chemical cross-linking agent bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate (BS3) revealed a predominant type III/betaglycan receptor, a low level of apparently heterogeneous type I and II receptors and an additional novel 38-kDa TGF-beta binding glycoprotein that was present both under reducing and nonreducing conditions on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Affinity-labeling saturation and competition studies indicated that the type III/betaglycan component appears to have a 7-fold higher capacity for TGF-beta 1 than for -beta 2 yet exhibits a 5- to 10-fold higher affinity for TGF-beta 2 than for -beta 1. The 38-kDa TGF-beta binding component, an N-linked glycoprotein, exhibits a higher affinity for TGF-beta 2 than for -beta 1 that is strikingly similar to that of the type III/betaglycan receptor. This 38-kDa binding protein appears to be upregulated after methotrexate-induced differentiation of the BeWo cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman D. J., Schneider S. L., Thompson D. A., Cheng H. L., Tomasi T. B. A transforming growth factor beta 2 (TGF-beta 2)-like immunosuppressive factor in amniotic fluid and localization of TGF-beta 2 mRNA in the pregnant uterus. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1391–1401. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres J. L., Stanley K., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3137–3145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Novel activin receptors: distinct genes and alternative mRNA splicing generate a repertoire of serine/threonine kinase receptors. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90209-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Hollenberg M. D. The nature and function of polypeptide growth factor receptors in the human placenta. J Dev Physiol. 1989 Nov;12(5):237–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd F. T., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibition of epithelial cell proliferation linked to the expression of a 53-kDa membrane receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2272–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burres N. S., Cass C. E. Inhibition of methotrexate-induced differentiation of cultured human choriocarcinoma (BeWo) cells by thymidine. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 1;47(19):5059–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerneus D. P., van der Ende A. Apical and basolateral transferrin receptors in polarized BeWo cells recycle through separate endosomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1149–1158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Andres J. L., Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta receptor type III is a membrane proteoglycan. Domain structure of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16984–16991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Hernandez H., Laiho M., ten Dijke P., Iwata K. K., Massagué J. Distinct transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptor subsets as determinants of cellular responsiveness to three TGF-beta isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20533–20538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Isoform-specific transforming growth factor-beta binding proteins with membrane attachments sensitive to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20767–20772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. A., Flanders K. C., Banwatt D., Millar-Book W., Manuel J., Stedronska-Clark J., Rowley B. Murine pregnancy decidua produces a unique immunosuppressive molecule related to transforming growth factor beta-2. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3008–3014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. A., Lea R. G., Podor T., Daya S., Banwatt D., Harley C. Cytokines determining the success or failure of pregnancy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;626:524–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb37944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. J., Cui T. Y., Zhang L., Hartman L., Grahl K., Zhang G. Y., Tarpey J., Damsky C. H. Adhesive and degradative properties of human placental cytotrophoblast cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):891–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. J., Skehan P. Morphological differentiation of human choriocarcinoma cells induced by methotrexate. Cancer Res. 1979 Jun;39(6 Pt 1):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Dart L. L., Meyers C. A., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Purification and initial characterization of a type beta transforming growth factor from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3676–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Characterization of a membrane receptor for transforming growth factor-beta in normal rat kidney fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10995–11000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham C. H., Lala P. K. Mechanism of control of trophoblast invasion in situ. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Aug;148(2):228–234. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham C. H., Lysiak J. J., McCrae K. R., Lala P. K. Localization of transforming growth factor-beta at the human fetal-maternal interface: role in trophoblast growth and differentiation. Biol Reprod. 1992 Apr;46(4):561–572. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod46.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichijo H., Rönnstrand L., Miyagawa K., Ohashi H., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Purification of transforming growth factor-beta 1 binding proteins from porcine uterus membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22459–22464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis F. M., Boyd F. T., Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Responsiveness to transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) restored by genetic complementation between cells defective in TGF-beta receptors I and II. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9108–9112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis M. B., Massagué J. Concomitant loss of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptor types I and II in TGF-beta-resistant cell mutants implicates both receptor types in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18518–18524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lala P. K., Graham C. H. Mechanisms of trophoblast invasiveness and their control: the role of proteases and protease inhibitors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Dec;9(4):369–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00049525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea R. G., Flanders K. C., Harley C. B., Manuel J., Banwatt D., Clark D. A. Release of a transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 2-related suppressor factor from postimplantation murine decidual tissue can be correlated with the detection of a subpopulation of cells containing RNA for TGF-beta 2. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):778–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Cheifetz S., Doody J., Andres J. L., Lane W. S., Massagué J. Structure and expression of the membrane proteoglycan betaglycan, a component of the TGF-beta receptor system. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Danielpour D., Miller D., Border W. A., Robbins A. R. The 260-kDa transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta binding protein in rat glomeruli is a complex comprised of 170- and 85-kDa TGF-beta binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11449–11454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Danielpour D. Novel 150- and 180-kDa glycoproteins that bind transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 1 but not TGF-beta 2 are present in several cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9907–9911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Robbins A. R., Bruce M. D., Danielpour D. Identification of disulfide-linked transforming growth factor-beta 1-specific binding proteins in rat glomeruli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9351–9356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Receptors for the TGF-beta family. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90627-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Lee A., Pelton R. W., Chen E. Y., Moses H. L., Derynck R. Murine transforming growth factor-beta 2 cDNA sequence and expression in adult tissues and embryos. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;3(7):1108–1114. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-7-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. J., Fitz-Gibbon L., O'Connor-McCourt M. D. Subtypes of betaglycan and of type I and type II transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptors with different affinities for TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 are exhibited by human placental trophoblast cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Feb;150(2):334–343. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. J., O'Connor-McCourt M. D. A transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) receptor from human placenta exhibits a greater affinity for TGF-beta 2 than for TGF-beta 1. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4350–4356. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrish D. W., Bhardwaj D., Paras M. T. Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibits placental differentiation and human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen secretion. Endocrinology. 1991 Jul;129(1):22–26. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. The molecular and cellular basis of affinity maturation in the antibody response. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90198-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady P., Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Expression of a new type high molecular weight receptor (type V receptor) of transforming growth factor beta in normal and transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91381-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady P., Kuo M. D., Baldassare J. J., Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Purification of a new type high molecular weight receptor (type V receptor) of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) from bovine liver. Identification of the type V TGF-beta receptor in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8583–8589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson R. Growth factors, protooncogenes and human placental development. Cell Differ Dev. 1989 Oct;28(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(89)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paria B. C., Jones K. L., Flanders K. C., Dey S. K. Localization and binding of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in mouse preimplantation embryos and in delayed and activated blastocysts. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelton R. W., Dickinson M. E., Moses H. L., Hogan B. L. In situ hybridization analysis of TGF beta 3 RNA expression during mouse development: comparative studies with TGF beta 1 and beta 2. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):609–620. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelton R. W., Saxena B., Jones M., Moses H. L., Gold L. I. Immunohistochemical localization of TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2, and TGF beta 3 in the mouse embryo: expression patterns suggest multiple roles during embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1091–1105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard J. W. Regulation of polypeptide growth factor synthesis and growth factor-related gene expression in the rat and mouse uterus before and after implantation. J Reprod Fertil. 1990 Mar;88(2):721–731. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0880721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S. W., Burmester J. K., Merwin J. R., Madri J. A., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Identification of a structural domain that distinguishes the actions of the type 1 and 2 isoforms of transforming growth factor beta on endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritvos O., Erämaa M. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and phorbol ester induce transforming growth factor-beta 1 messenger ribonucleic acid levels in choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2240–2245. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Differential expression of the TGF-beta isoforms in embryogenesis suggests specific roles in developing and adult tissues. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992 Jun;32(2):91–98. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080320203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff E., Rizzino A. Preparation and binding of radioactively labeled porcine transforming growth factor type beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):714–719. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80555-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid P., Cox D., Bilbe G., Maier R., McMaster G. K. Differential expression of TGF beta 1, beta 2 and beta 3 genes during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):117–130. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R., Roberts A. B., Rosen D. M., Seyedin S. M. Membrane binding characteristics of two forms of transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14655–14662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R. TGF-beta receptors. Ciba Found Symp. 1991;157:29–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R., Ziman J. M., Kane C. J., Dasch J. R. Two novel patterns of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) binding to cell surface proteins are dependent upon the binding of TGF-beta 1 and indicate a mechanism of positive cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1048–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamada H., McMaster M. T., Flanders K. C., Andrews G. K., Dey S. K. Cell type-specific expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in the mouse uterus during the periimplantation period. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;4(7):965–972. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-7-965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Masui T., Harris C. C., Sporn M. B. Distribution and modulation of the cellular receptor for transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. F., Lin H. Y., Ng-Eaton E., Downward J., Lodish H. F., Weinberg R. A. Expression cloning and characterization of the TGF-beta type III receptor. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagel S., Parhar R. S., Jeffrey J. J., Lala P. K. Normal nonmetastatic human trophoblast cells share in vitro invasive properties of malignant cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):455–462. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Mann D. M., Ruoslahti E. Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta by the proteoglycan decorin. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):281–284. doi: 10.1038/346281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]