Abstract
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most frequent cancer worldwide, comprising almost 50% of all malignancies in some developing nations. Our recent work identified protein kinase Cε (PKCε) as a critical and causative player in establishing an aggressive phenotype in HNSCC. In this study, we investigated the specificity and efficacy of HN1-PKCε, a novel bi-functional cancer cell homing, PKCε inhibitory peptide, as a treatment for HNSCC. HN1-PKCε peptide was designed by merging two separate technologies and synthesized as a capped peptide with two functional modules, HN1 (cancer cell homing) and PKCε (specific PKCε inhibitory), connected by a novel linker module. HN1-PKCε preferentially internalized into UMSCC1 and UMSCC36 cells, two HNSCC cell lines, in comparison to oral epithelial cells; 82.1% positive for UMSCC1 and 86.5% positive for UMSCC36 compared to 1.2% positive for oral epithelial cells. In addition, HN1-PKCε penetrated HNSCC cells in a dose-and time-dependent manner. Consistent with these in vitro observations, systemic injection of HN1-PKCε resulted in selective delivery of HN1-PKCε into UMSCC1 xenografts in nude mice. HN1-PKCε blocked the translocation of active PKCε in UMSCC1 cells confirming HN1-PKCε as a PKCε inhibitor. HN1-PKCε inhibited cell invasion by 72 ± 2% (p<0.001, n=12) and cell motility by 56 ± 2% (p<0.001, n=5) in UMSCC1 cells. Moreover, in vivo bioluminescence imaging demonstrated that HN1-PKCε significantly (83 ± 1% inhibition, p<0.02) retards the growth of UMSCC1 xenografts in nude mice. Our work indicates that the bi-functional HN1-PKCε inhibitory peptide represents a promising novel therapeutic strategy for HNSCC.
Keywords: Experimental therapeutics, Head and Neck Cancer, Protein Kinase, and Oncogene
INTRODUCTION
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most frequent cancer worldwide. Nearly 46,000 people will be diagnosed with HNSCC in the United States this year and an estimated 11,000 people will die of the disease (1). Although improvements in local control and survivalhave been achieved with the use of multi-modality regimens, the overall 5 year survival rate for HNSCC has not improved significantly over the past 20 years (2, 3). Local-regional relapse and distant metastasis after definitive therapy remain the major causes of morbidityand mortality in HNSCC patients. This clinical problem has prompted substantial efforts in identifyinggenetic determinants that contribute to aggressive HNSCC.
Evidence has shown that protein kinase Cε (PKCε), a member of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases, is a transforming oncogene and is involved in the development and progression of skin, breast, and prostate cancer (4–6). Our recent results demonstrate that PKCε plays a critical and causative role in establishing an aggressive phenotype in HNSCC. We reported that PKCε is upstream of and directly modulates the Rho GTPase signaling cascade, specifically RhoA and RhoC, to control cell invasion and motility (7). Moreover, specific inhibition of PKCε with RNA interference in HNSCC cells with high endogenous PKCε levels was sufficient to significantly inhibit cell invasion and motility (7). A prospective study showed that elevated PKCε in the primary tumor of HNSCC patients is associated with an increase in disease recurrence and a decrease in overall survival (8). This observation is in agreement with our work that PKCε promotes an aggressive phenotype in HNSCC and suggests that targeting PKCε may be an effective anti-cancer strategy for managing HNSCC patients.
In this study, we determined the effects of a novel cancer cell homing, PKCε inhibitory peptide on HNSCC cells in vitro and in vivo. The bi-functional HN1-PKCε peptide was constructed by connecting two functional motifs, HN1 (cancer cell homing) and PKCε (specific PKCε inhibitory), with a linker peptide. HN1-PKCε preferentially penetrated HNSCC cells in vitro and in vivo and blocked the translocation of active PKCε in HNSCC cells. In addition, HN1-PKCε inhibited cell invasion, motility, and proliferation in vitro and significantly retarded the growth of HNSCC xenografts in nude mice. Our work shows that HN1-PKCε is a novel therapeutic agent with potent anti-tumor efficacy against HNSCC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines
Immortalized normal oral epithelial cells (E6/E7-NOE) were kindly provided by Drs. William Foulkes and Ala-Eddin Al Moustafa from McGill University and cultured in Keratinocyte-SFM medium without supplement. UMSCC1 and UMSCC36 cells were kindly provided by Dr. Thomas Carey from the University of Michigan Medical School and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum.
Peptide synthesis
Unlabeled and FITC-labeled peptides were synthesized and purified (>95%) by the University of Michigan Protein Structure and Peptide Synthesis Facility or by New England Peptides (Gardner, MA). Cy5-labeled HN1-PKCε was synthesized and purified (>95%) by Open Biosystems (Huntsville, AL). Cy5-labeled PKCε was synthesized by standard N-9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) solid phase synthesis on CLEAR amide resin (Peptide International, 0.48 mmol/g). Following Fmoc deprotection of the final residue, 2 equivalents of Cy5-NHS ester (GE Healthcare, United Kingdom) and 4 equivalents of triethylamine were dissolved in NMP and transferred to the resin. The reaction vessel was covered in foil and left to react for 16 hrs. The resin was washed 3 × DMF, 3 × CH2Cl2 and 3 × MeOH. The Cy5-labeled PKCε peptide was cleaved from the resin for two hours in a mixture of 95/2.5/2.5 trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)/triisopropylsilane/water. The crude peptide was precipitated into cold ether and purified by RP-HPLC on a Waters C18 column using water with 0.1% TFA as the A solvent and CH3CN as the B solvent (14%–31%B over 17 minutes). Product molecular weight was confirmed by ESI-MS in both negative ion mode (m−H+, 1479.1) and positive ion mode (M+2H+/2, 740.9).
PKCε translocation
UMSCC1 cells were untreated or treated with HN1-control or HN1-PKCε for 48 hours. Subsequently, cells were stimulated with a general PKC activator, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, 10 nM for 30 minutes), washed withcold phosphate-buffered saline, scraped in homogenization buffer (9), passed through a 25-gauge syringe needle, and spun at 100,000 × g for 30 minutes at 4°C. The cytoplasmic fractions were collected and the pellets (particulate fractions) were resuspended in homogenization buffer with 1% Triton X-100. Western blot analysis using a PKCε-specific antibody (Millipore, Billerica, MA) was performed to assess the translocation of PKCε.
Cell invasion and cell motility
Cell invasion was determined as described from the cell invasion assay kit (Chemicon International, Temecula, CA). Cells were harvested and resuspended in serum-free medium. An aliquot (1 × 105 cells) of the prepared cell suspension was added into the chamber and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C in a 10% CO2 tissue culture incubator. Non-invading cells were gently removed from the interior of the inserts with a cotton-tipped swab. Invasive cells were stained and counted. Random cell motility was determined as described from the motility assay kit (Cellomics, Pittsburgh, PA). Cells were harvested, suspended in medium and plated on top of a field of microscopic fluorescent beads. After a 16-hour incubation period, cells were fixed and areas of clearing in the fluorescent bead field corresponding to phagokinetic cell tracks were quantified using NIH ScionImager.
Cell proliferation
Cells were untreated or treated with cis-platinum (1, 3, or 10 μM), cis-platinum and HN1-control, or cis-platinum and HN1-PKCε for 3 days. Cell proliferation was assessed using the MTT reagent to detect metabolic active cells (Sigma, St. Louis, MO).
Pre-clinical efficacy of HN1-PKCε
UMSCC1-luciferase cells (1 × 106) were implanted into the flank of 10-week old athymic nude mice and tumors were allowed to develop without treatment. At 2-weeks post-implantation, mice with established tumors of approximately 40 mm3 in volume were imaged for bioluminescence intensity using the Xenogen IVIS Spectrum System (Caliper Life Sciences, Hopkinton, MA). Mice were randomly assigned to three treatment arms, untreated (n=9), HN1-control (10 mg/kg, 3X week, n=8) or HN1-PKCε (10 mg/kg, 3X week, n=11), based on bioluminescence intensity to achieve a statistically similar mean bioluminescence intensity at the start of the treatment protocol. Tumor response was assessed on a weekly basis using the in vivo bioluminescence imaging modality.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by Student’s t-test. P-values<0.05 were considered significant
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The excitement over PKCs as therapeutic anti-cancer targets prompted the rapid development of drugs designed to specifically inhibit PKCs. The drugs developed to date can be divided into two main groups; inhibitors that target the C1 regulatory domain and inhibitors that target the kinase domain. Overall, in numerous clinical trials, PKC inhibitors have shown very modest activity, at best, as single agent or in combination with standard chemotherapeutics (10, 11). Bryostatin-1, a PKC modulator that targets the C1 domain, is the most extensively used in clinical trials. Recent phase II clinical trials with bryostatin-1 in combination with cisplatin for cervical squamous cell carcinoma or in combination with interleukin-2 for renal cell carcinoma showed minimal efficacy and perhaps even a possibility of therapeutic antagonism (12, 13). One possible explanation is that C1 domain inhibitors are not isoform specific since the C1 domain is well conserved in the PKC family, with the exception of the atypical isoforms. Therefore, C1 domain inhibitors likely inhibit desired oncogene-like PKC isoforms but also have the undesired side-effect of inhibiting tumor-suppressor-like PKC isoforms resulting in no net response or possibly a tumor stimulatory response. The kinase domain inhibitors are not specific PKC inhibitors since the kinase inhibitors target other serine/threonine kinases with higher specificity. Taken together, there remains a critical need to develop isoform specific PKC inhibitors.
The activation of the PKCε signaling cascade is a critical genetic event resulting in an aggressive HNSCC phenotype. Our laboratory reported that RhoA and RhoC are directly phosphorylated by PKCε resulting in an increase in RhoA/RhoC activation (7). In addition to regulation of RhoA and RhoC, other groups have published that PKCε directly phosphorylates Akt and Stat3. PKCε phosphorylates Akt at serine 473 leading to a full Akt activation state (14). A recent report showed that PKCε phosphorylates Stat3 at Ser727 resulting in an increase in nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation of Stat3 (15). Elevated Akt phosphorylation (Ser473) significantly correlates with a worse outcome in HNSCC (16, 17). Nuclear Stat3 accumulation is associated with a decrease in relapse-free and overall survival in HNSCC (18). Thus, targeting PKCε is an attractive therapeutic strategy as inhibition of PKCε will result in dampening of multiple signal transduction pathways that are dysregulated in HNSCC.
Protein-protein interactions are critical events in numerous signaling pathways. However, since protein to protein interfaces are usually extensive, shallow, and hydrophobic, the disruption of protein-protein interactions has proven to be difficult targets for small-molecule drugs. So, we decided to take a different approach and rationally designed a bi-functional targeting peptide. We merged two existing and published technologies and constructed a peptide with two functional modules, HN1 and PKCε, connected by a linker module. The HN1 module is a 12-mer peptide, TSPLNIHNGQKL, reported to preferentially bind and internalize into HNSCC cell lines in vitro (19). Moreover, HN1 was demonstrated to be stable in vivo and able to localize into HNSCC xenograft tumors (19). The PKCε inhibitory module (εV1-2) is an 8-mer peptide, EAVSLKPT, taken from amino acids 14–21 located in the pseudo-C2 domain of PKCε (20). There is literature to demonstrate that the pseudo-C2 domain of PKCε is required for binding to receptors of activated protein kinase C (RACKs) (21, 22). The PKCε-RACK interaction allows for the proper trafficking and localization of active PKCε (21, 22). The RACK binding site on PKCε was reported to be a discrete region located at amino acids 14–21 (20). A peptide (εV1-2) corresponding to this sequence inhibited the translocation and function of active PKCε through blocking the PKCε-RACK interaction in cardiac myocytes (20). Moreover, εV1-2 was shown to be a specific PKCε inhibitor and not able to block the translocation and function of other PKCs, specifically PKCα, βand δ(20). Subsequent work has clearly demonstrated that εV1-2 is a specific PKCε inhibitor in other cell types, including neuronal cells and pancreatic β-cells (23, 24). The control module is a non-functional scrambled PKCε peptide, LSETKPAV (20). The linker module consists of a 6-mer sequence of 6-aminohexanoic acid to allow for proper spatial spacing to prevent steric interference between the HN1- and PKCε-targeting modules.
To determine the efficiency and selectivity of HN1-PKCε for HNSCC cells in vitro, oral epithelial cells (NOE), UMSCC1, and UMSCC36 were untreated or treated with a series of different fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled peptides (3 μM for 48 hours), followed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis (Figure 1A). NOE cells treated with FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε had minimal effect and resulted in 1.2% FITC-positive cells with a mean fluorescence intensity of 1.9. In contrast, FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε treatment of UMSCC1 and UMSCC36 cells resulted in 82.1% and 86.5% FITC-positive cells, respectively. The mean fluorescence intensity was 15.9 for UMSCC1 cells and 18.3 for UMSCC36 cells with FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε treatment. As expected, treatment with FITC-labeled scramble-PKCε, a peptide with an inactive cancer cell homing module, was not as efficient and resulted in 10.2% FITC-positive cells for UMSCC1 and 5.3% FITC-positive cells for UMSCC36. It is clear that FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε is greater than 8-fold more efficient (p<0.03) than FITC-labeled scramble-PKCε providing evidence that the addition of the functional HN1 cancer cell homing module is a critical value-added feature to enhance the uptake of the PKCε inhibitory module in HNSCC cells. Treatment with FITC-labeled HN1-control had a similar effect as FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε and resulted in 82.6% FITC-positive cells for UMSCC1 and 82.7% FITC-positive cells for UMSCC36. This is an important observation and demonstrates that modification of the amino acid sequence order of the PKCε inhibitory module to a nonfunctional scrambled control version does not alter the internalization efficiency into HNSCC cells. Interestingly, FITC-labeled PKCε is more efficient than FITC-labeled scramble-PKCε. A likely explanation is that the uptake of FITC-labeled peptides into HNSCC cells is mass/size-dependent since FITC-labeled scramble-PKCε consists of 26 amino acid residues and FITC-labeled PKCε consists of only 8 amino acid residues. Nonetheless, the internalization efficiency of FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε is superior to FITC-labeled PKCε (p<0.04). Lastly, as shown in Figures 1C and D, a dose- and time-dependent uptake of FITC-labeled HN1-PKCε was observed in UMSCC1 and UMSCC36 cells.
Figure 1.
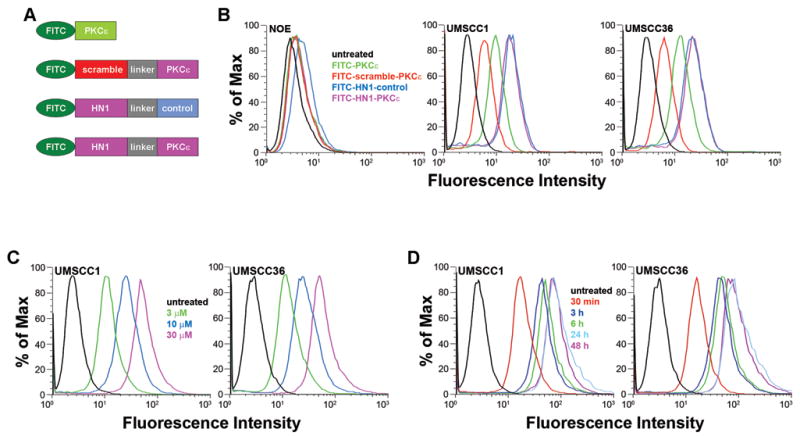
HN1-PKCε selectively penetrates HNSCC cells in vitro. A. Schematic diagram of FITC-labeled peptides. HN1 module: cancer cell homing peptide. Scrambled module: nonfunctional scrambled HN1 module. Linker module: linker peptide. PKCε module: PKCε inhibitory peptide: Control module: non-functional scrambled PKCε module. Peptides were end-capped (5′-acetylated and 3′-amidated) to enhance stability. B. HN1-PKCε preferentially internalizes into HNSCC in vitro. Normal oral epithelial cells (NOE), and HNSCC cells, UMSCC1 and UMSCC36, were untreated or incubated with FITC-labeled peptides (3μM) for 48 hours. Cells were harvested and analyzed by FACS. B. Dose-dependent internalization of HN1-PKCε into HNSCC cells. UMSCC1 and UMSCC36 cells were untreated or incubated with 3, 10, or 30 μM HN1-PKCε for 48 hours. Cells were harvested and analyzed by FACS. C. Time-dependent internalization of HN1-PKCε into HNSCC cells. UMSCC1 and UMSCC36 cells were untreated or incubated with 30 μM HN1-PKCε for 30 minutes, 3, 6, 24, or 48 hours. Cells were harvested and analyzed by FACS. These histograms are representative of several independent experiments.
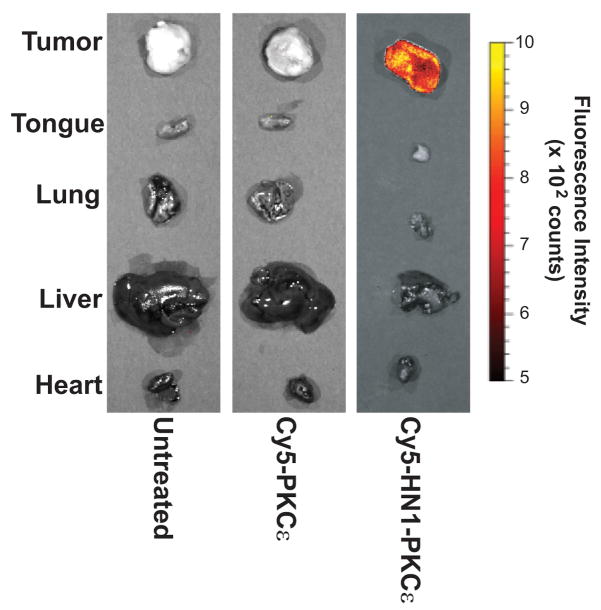
Next, we examined if HN1-PKCε specifically localizes to HNSCC tumors in vivo. We decided to use Cy5 as the fluorophore for this experiment since Cy5 exhibits longer excitation and emissions wavelengths then FITC and thus, enables deeper tissue penetration. Athymic nude mice with established UMSCC1 tumors in the flank were untreated or treated with Cy5-labeled PKCε or HN1-PKCε (10 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection). After 24 hours, mice were euthanized and tumors and various organs were resected for fluorescence intensity analysis using the Xenogen IVIS Spectrum Imaging System (Figure 2). Ex vivo analysis showed that the tumors and various organs resected from untreated or Cy5-labeled PKCε-treated mice exhibit minimal fluorescence. In contrast, Cy5-labeled HN1-PKCε was selectively delivered to the HNSCC tumor. Fluorescence intensity was greater than 8-fold higher (p<0.0001) in the tumor compared to the various organs in Cy5-labeled HN1-PKCε-treated mice. These results showed that HN1-PKCε selectively homed to and penetrated into HNSCC tumors in vivo.
Figure 2.
HN1-PKCε selectively homes to HNSCC xenografts in vivo. Nude mice with established UMSCC1 tumors in the flank were untreated or treated with Cy5-labeled HN1-control or HN1-PKCε (IP injection, 10 mg/kg). After 24 hours, mice were euthanized and tumors and various organs were resected for fluorescence intensity analysis using the Xenogen IVIS Spectrum Imaging System.
Our work corroborated the findings from Hong and Clayman (19) and demonstrated that the HN1 motif selectively homes and penetrates HNSCC cells in comparison to immortalized oral epithelial cells. Furthermore, we have evidence that HN1-PKCε does not internalize into primary keratinocytes (data not shown). Hong and Clayman reported that HN1 did not internalize into DU145 human prostate cancer cells, SW480 human colon cells, and U373 MG human astrocytoma cells suggesting that HN1 may be specific to squamous cell carcinoma (19). However, this is not the case as HN1-PKCε efficiently internalized into MDA-MB231 (70.1% FITC-positive; mean fluorescence intensity of 64.2) and SKBR3 (49.4% FITC-positive; mean fluorescence intensity of 27.3) human breast cancer cells. Interestingly, HN1-PKCε penetrated MCF10A nontumorigenic mammary epithelial cells with much lower efficiency (8.8% FITC-positive; mean fluorescence intensity of 5.9). These results provide initial evidence that HN1 may be cancer cell-specific but not organ-specific. Our observations do not detract from the significance and utility of HN1 but rather expands the potential clinical use of HN1 to other cancer types.
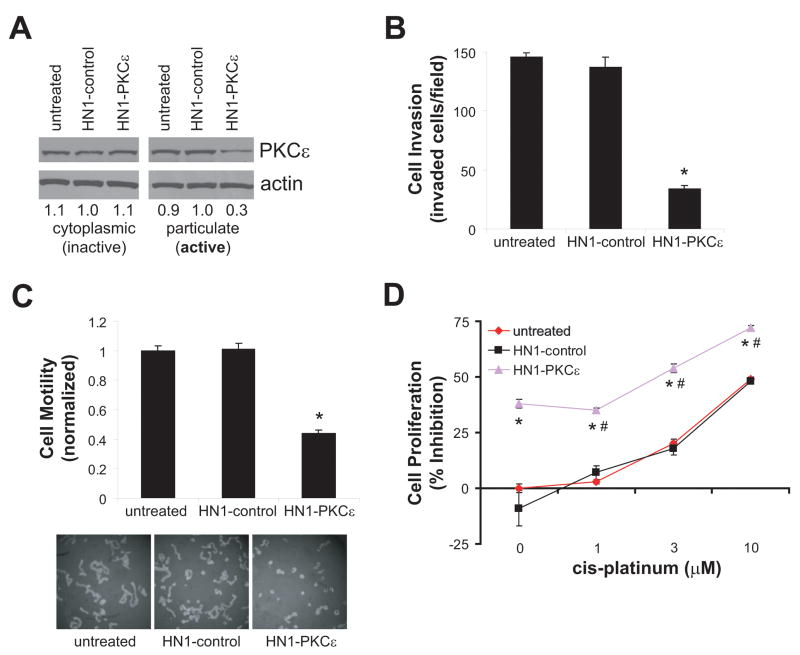
The PKCε inhibitory module was demonstrated to selectively block the translocation of active PKCε in numerous cell types, including cardiac myocytes, pancreatic β-cells, and neuronal cells (19, 23, 24). There is evidence to indicate that inactive PKCε is localized in the cytoplasmic fraction and upon activation translocates to the particulate fraction (25, 26). To determine if HN1-PKCε can block the translocation of active PKCε in HNSCC cells, UMSCC1 cells were untreated or incubated with HN1-control or HN1-PKCε for 24 hours. Subsequently, cells were activated with PMA and cell lysates were fractionated for cytoplasmic and particulate proteins. As shown in Figure 3A, active PKCε is dramatically lower in HN1-PKCε-treated cells than in untreated or HN1-control treated cells. These results provide direct evidence that HN1-PKCε disrupts the proper localization of PKCε resulting in “normalization” of active PKCε levels in HNSCC cells.
Figure 3.
HN1-PKCε blocks active PKCε translocation and inhibits cell invasion, motility, and proliferation. A. HN1-PKCε disrupts localization of active PKCε in HNSCC cells. Inactive and active PKCε levels were detected by western blot analysis with an anti-PKCε antibody. Bands were quantified by densitometry and data is presented as fraction of PKCε levels relative to the HN1-control-treated cells. B. HN1-PKCε inhibits cell invasion. Cell invasion was assessed using the Modified Boyden chamber invasion assay with Matrigel basement membrane. Invasive cells were counted and presented as invaded cells per field. * p-value < 0.001, n=12. C. HN1-PKCε inhibits cell motility. Cell motility was assessed using the 2-dimensional random cell motility assay. Cells were fixed and areas of clearing in the microbead field corresponding to phagokinetic cell tracks were quantified using NIH ScionImager. * p-value < 0.001, n=5. D. HN1-PKCε inhibits cell proliferation. Cell proliferation was determined using the MTT assay. * p-value < 0.006, n=4; HN1-PKCε compared to HN1-control or cis-platinum. # p-value < 0.001, n=4; monotherapy HN1-PKCε compared to combination regimen of HN1-PKCε and cis-platinum.
We determined the effects of HN1-PKCε on cell invasion, cell motility, and cell proliferation. UMSCC1 cells were untreated or incubated with 30 μM HN1-control and HN1-PKCε for 72 hours. Subsequently, cells were trypsinized and re-plated in appropriate experimental wells to assess for cell invasion and cell motility. UMSCC1 cells treated with HN1-PKCε were significantly less invasive and motile than untreated cells or HN1-control treated cells (Figures 3B and 3C). HN1-PKCε inhibited cell invasion by 72 ± 2% (p<0.001, n=12) and cell motility was suppressed by 56 ± 2% (p<0.001, n=5) in UMSCC1 cells. As shown in Figure 3D, the effects of HN1-PKCε on cell proliferation as monotherapy or in combination therapy with cis-platinum was assessed. As expected, cis-platinum (no peptide treatment) inhibited cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner; ranging from 3 ± 1% inhibition for 1 μM to 49 ± 2% inhibition for 10 μM. HN1-control (30 μM for 72 hours) had no effect on cell proliferation as monotherapy and no additional effect was observed in combination with cis-platinum. Single agent treatment of HN1-PKCε (30 μM for 72 hours) significantly inhibited cell proliferation by 39 ± 2% and moreover, used in a combination treatment regimen, an additive effect is observed with cis-platinum. Single agent cis-platinum (10 μM for 72 hours) inhibited cell proliferation by 49 ± 2%, whereas, the combination regimen of 30 μM HN1-PKCε and 10 μM cis-platinum for 72 hours inhibited cell proliferation by 72 ± 4%. The combination regimen resulted in a 47% increase in inhibition of cell proliferation compared to single agent cis-platinum treatment. This observation supports the notion that the combination regimen of a PKCε inhibitor and cis-platinum is more efficacious than either single agent therapy alone. It is critical to point out that the HN1 module does not have anti-cancer properties as the HN1-control peptide had no effect on cell invasion, motility, and proliferation. These observations strongly indicate that the PKCε inhibitory module is solely responsible for the anti-tumor effects as observed in these phenotypic experiments.
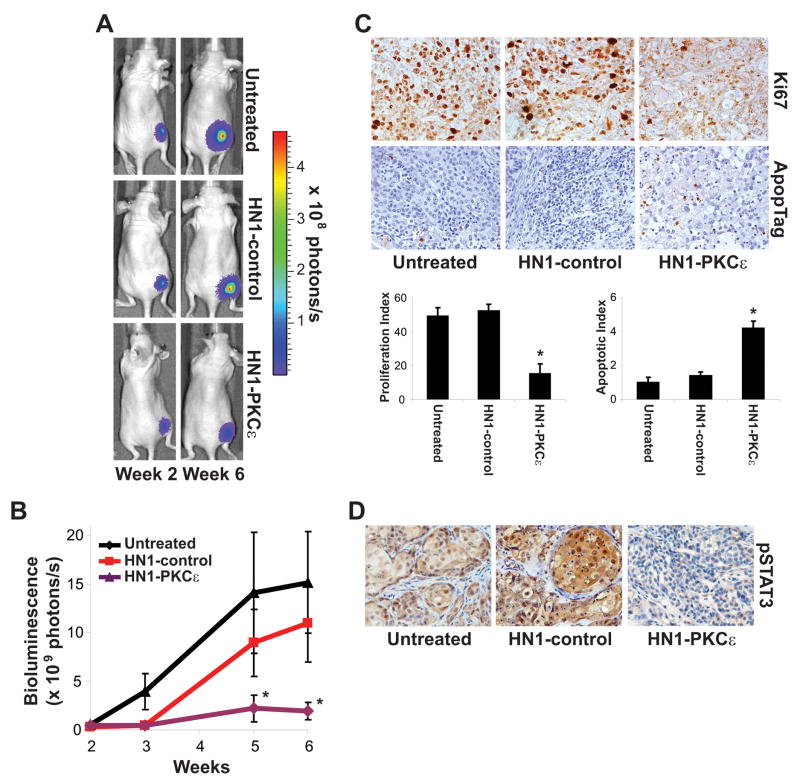
The anti-tumor efficacy of HN1-PKCε was assessed in a xenograft model of HNSCC. UMSCC1 cells were infected with a lentivirus expression vector to drive constitutive Firefly luciferase (pLentilox-Luc) to allow us to measure tumor response using a highly sensitive and dynamic in vivo bioluminescence imaging modality. UMSCC1-luciferase cells (1 × 106) were implanted into the flank of 10-week old athymic nude mice and tumors were allowed to develop without treatment. At 2-weeks post-implantation, mice with established tumors of approximately 40 mm3 in volume were imaged for bioluminescence intensity. Mice were randomly assigned to three treatment groups, untreated (n=9), HN1-control (10 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection, 3X week, n=8), or HN1-PKCε (10 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection, 3X week, n=11) based on bioluminescence intensity to achieve a statistically similar mean bioluminescence intensity at the start of the treatment protocol. At the end of the 4 week treatment protocol, mean tumor bioluminescence intensity between the untreated arm and HN1-control-treated arm was statistically similar (p>0.05); 15.2 ± 5.2 photons/s for the untreated mice and 11.0 ± 3.9 photons/s for the HN1-control-treated mice (Figure 4B). Mice from the HN1-PKCε treatment arm showed a dramatic difference and had a mean tumor bioluminescence intensity of only 1.9 ± 0.9 photons/s. Mean tumor bioluminescence intensity was about 5.8-fold higher in the HN1-control arm in comparison to the HN1-PKCε arm (p<0.02). As shown in Figure 4C, immunohistochemistry staining indicated that HN1-PKCε treatment resulted in a 71± 8% decrease in the tumor proliferation index and a 314 ± 29% increase in the tumor apoptotic index compared to HN1-control treatment (p<0.001). Additionally, pStat3 (S727) levels, a downstream target of active PKCε, were markedly lower in the tumors from the HN1-PKCε arm than from the untreated or HN1-control arm. These in vivo results demonstrate a robust anti-tumor effect with HN1-PKCε treatment in HNSCC.
Figure 4.
HN1-PKCε retards tumor growth in a pre-clinical model of HNSCC. A. Bioluminescence images from a representative mouse in the untreated arm, HN1-control treatment arm, and HN1-PKCε treatment arm. B. Bioluminescence. Tumor bioluminescence activity was measured using the Xenogen IVIS Spectrum Imaging System. * p-value < 0.02. C. Tumor proliferation and apoptotic index. Tumor sections were stained for proliferating cells using an anti-Ki67 antibody (DAKO, Denmark) and apoptotic cells using the ApopTag kit (Intergen Company, Purchase, NY). Proliferation and apoptotic index was determined by counting the number of Ki67- and TUNEL-positive cells per 500 total cells in five separate random fields at high power (400X). * p-value < 0.001. D. Tumor pSTAT (S727) levels. Tumor section were stained for S727-phosphorylated Stat3 using an anti-phospho-S727-Stat3 antibody (Cell Signaling, Beverly, MA). These are representative sections for each treatment arm.
The paradigm of molecularly-targeted anti-cancer therapies is beginning to take hold. To date, several molecularly-targeted anti-cancer therapies, such as bevacizumab and cetuximab, have proven to be effective approaches for managing cancer patients. Many of these molecularly-targeted anti-cancer agents have shown to be more selective for cancer cells and thus exhibit lower overall toxicity profiles than standard chemotherapeutics. Nevertheless, dose-limiting toxicities, most likely due to drug delivery to non-target cells and organs, remain a critical issue even with molecularly-targeted anti-cancer drugs. Development of a bi-functional anti-cancer drug consisting of a molecularly-targeted therapeutic and a tumor-targeting component will enable the specific delivery of an anti-cancer therapeutic to tumor cells resulting in increased local efficacy while limiting peripheral toxicity. HN1-PKCε was conceived with these two criteria in mind. Our results clearly demonstrate that HN1-PKCε is functioning as designed and selectively penetrates HNSCC cells to inhibit active PKCε translocation. Systemic administration of HN1-PKCε significantly retarded the growth of HNSCC xenograft as measured by a highly sensitive in vivo bioluminescence imaging modality. There was no apparent difference in the weight of untreated, HN1-control-treated, and HN1-PKCε-treated mice during the active treatment period providing initial evidence that HN1-PKCε has a favorable toxicity profile. Taken together, this study indicates that HN1-PKCε has potent anti-tumor effects and further development of HN1-PKCε as an anti-cancer therapeutic for HNSCC is warranted.
Acknowledgments
Work supported in part by from the National Cancer Institute, P50CA97248 and R01CA135096, and the Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute.
References
- 1.Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer Statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Funk GF, Karnell LH, Robinson RA, Zhen WK, Trask DK, Hoffman HT. Presentation, treatment, and outcome of oral cavity cancer: a National Cancer Data Base report. Head Neck. 2002;24:165–80. doi: 10.1002/hed.10004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pugliano FA, Piccirillo JF, Zequeria MR, Fredrickson JM, Perez CA, Simpson JR. Clinical severity staging system for oral cavity cancer: five year survival. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;120:38–45. doi: 10.1016/S0194-5998(99)70367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jansen AP, Verwiebe EG, Dreckschmidt NE, Wheeler DL, Oberley TD, Verma AK. Protein kinase C-epsilon transgenic mice: a unique model for metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001;61:808–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pan Q, Bao LW, Kleer CG, et al. Protein kinase Cε is a predictive biomarker of aggressive breast cancer and a validated target for RNA interference anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8366–71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wu D, Foreman TL, Gregory CW, et al. Protein kinase Cepsilon has the potential to advance the recurrence of human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:2423–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pan Q, Bao LW, Teknos TN, Merajver SD. Targeted disruption of PKCε reduces cell invasion and motility through inactivation of RhoA and RhoC GTPases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9379–84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Martinez-Gimeno C, Diaz-Meco MT, Dominguez I, Moscat J. Alterations in levels of different protein kinase C isotypes and their influence on behavior of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: epsilonPKC, a novel prognostic factor for relapse and survival. Head Neck. 1995;17:516–25. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880170609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schechtman D, Mochly-Rosen D. Isozyme-specific inhibitors and activators of protein kinase C. Methods Enzymol. 2002;345:470–89. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(02)45039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mackay HJ, Twelves CJ. Protein kinase C: a target for anticancer drugs? Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003;10:389–96. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0100389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Serova M, Ghoul A, Benhadji KA, et al. Preclinical and clinical development of novel agents that target the protein kinase C family. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:466–78. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nezhat F, Wadler S, Muggia F, et al. Phase II trial of the combination of bryostatin-1 and cisplatin in advance or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix: a New York Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol. 2004;93:144–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2003.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Peterson AC, Harlin H, Karrison T, et al. A randomized phase II trial of interleukin-2 in combination with four different doses of bryostatin-1 in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs. 2006;24:141–9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-006-5935-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang J, Baines CP, Zong C, et al. Functional proteomic analysis of a three-tier PKC-epsilon-Akt-eNOS signaling module in cardiac protection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;288:H954–61. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00756.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aziz MH, Manoharan HT, Verma AK. Protein kinase Cε, which sensitizes skin to sun’s UVradiation-induced cutaneous damage and development of squamous cell carcinomas, associates with Stat3. Cancer Res. 2007;63:1385–93. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lim J, Kim JH, Paeng JY, et al. Prognostic value of activated Akt expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58:1199–205. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.024786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Massarelli E, Liu DD, Lee JJ, et al. Akt activation correlates with adverse outcome in tongue cancer. Cancer. 2005;104:2430–6. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shah NG, Trivedi TI, Tankshali RA, et al. Stat3 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: association with clinical parameters and survival. Int J Biol Markers. 2006;21:175–83. doi: 10.1177/172460080602100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hong FD, Clayman GL. Isolation of a peptide for targeted drug delivery into human head and neck solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6551–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Johnson JA, Gray MO, Chen C, Mochly-Rosen D. A protein kinase C translocation inhibitor as a isozyme-selective antagonist of cardiac function. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24962–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.40.24962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Csukai M, Chen CH, De Matteis MA, Mochly-Rosen D. The coatomer proteinβ′-COP, a selective binding protein (RACK) for protein kinase Cε. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29200–06. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.46.29200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Besson A, Wilson TL, Yong VW. The anchoring protein RACK1 links protein kinase Cepsilon to integrin beta chains. Requirements for adhesion and motility. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:22073–84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111644200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yedovitzky M, Mochly-Rosen D, Johnson JA, et al. Translocation inhibitors define specificity of protein kinase C isoenzyme in pancreatic b-cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:1417–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.3.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hundle B, McMahon T, Dadgar J, Chen CH, Mochly-Rosen D, Messing RO. An inhibitory fragment derived from protein kinase Cepsilon prevents enhancement of nerve growth factor responses by ethanol and porbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:15028–35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.23.15028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xiao GQ, Qu Y, Sun ZQ, Mochly-Rosen D, Boutjdir M. Evidence for functional role of epsilonPKC isozyme in the regulation of cardiac Na(+) channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281:C1477–86. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.5.C1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brandman R, Disatnik MH, Churchill E, Mochly-Rosen D. Peptides derived from the C2 domain of protein kinase C epsilon (epsilon PKC) modulate epsilon PKC activity and identify potential protein-protein interaction surfaces. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:4113–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608521200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]