Abstract
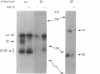
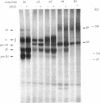
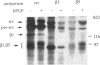
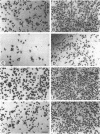
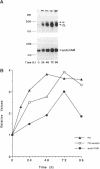
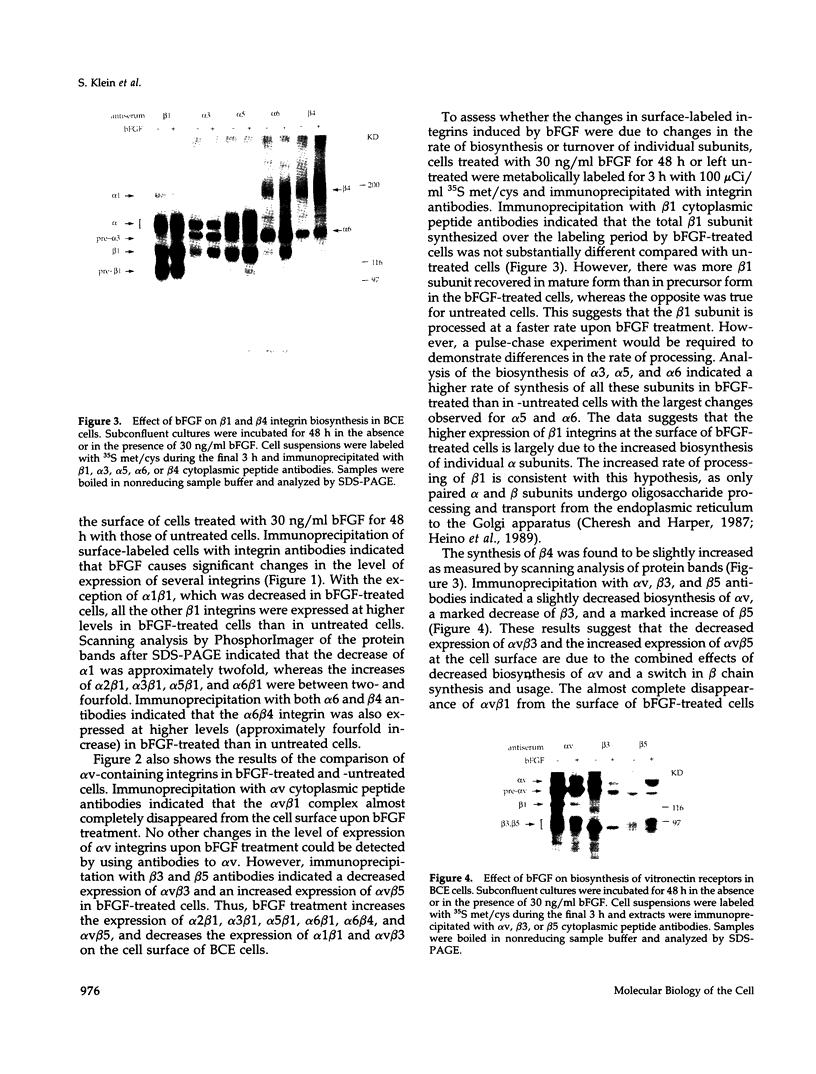
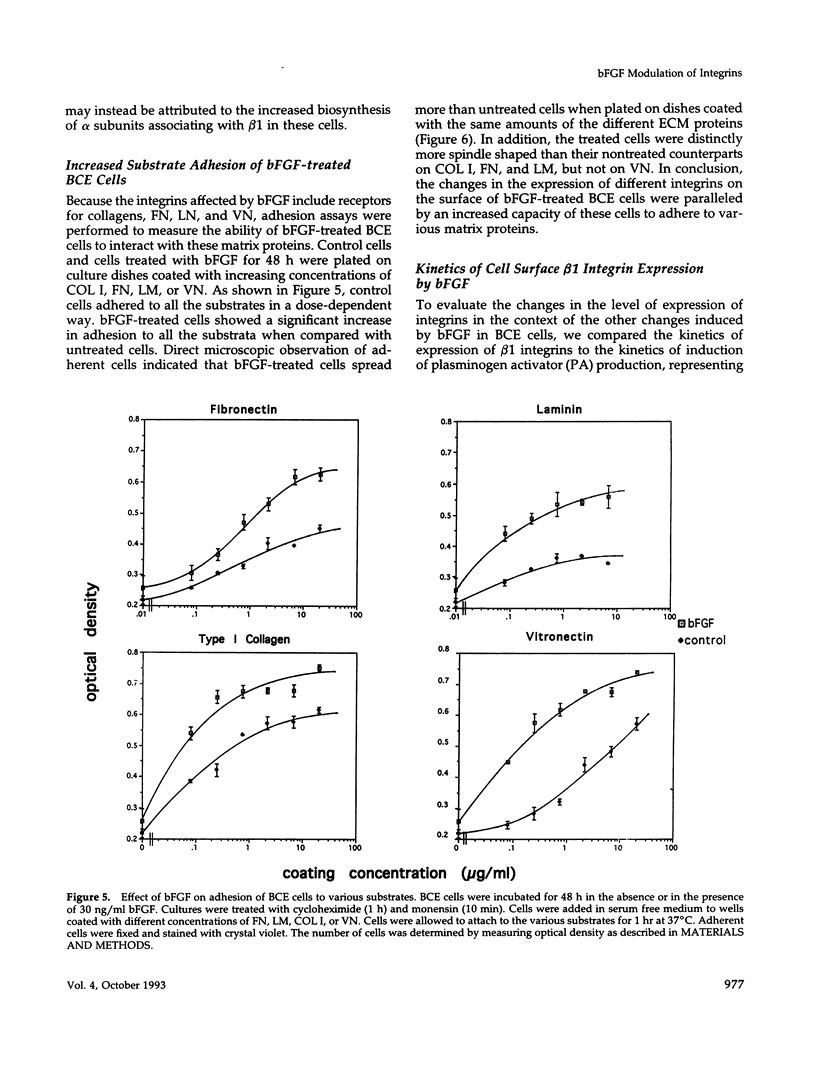
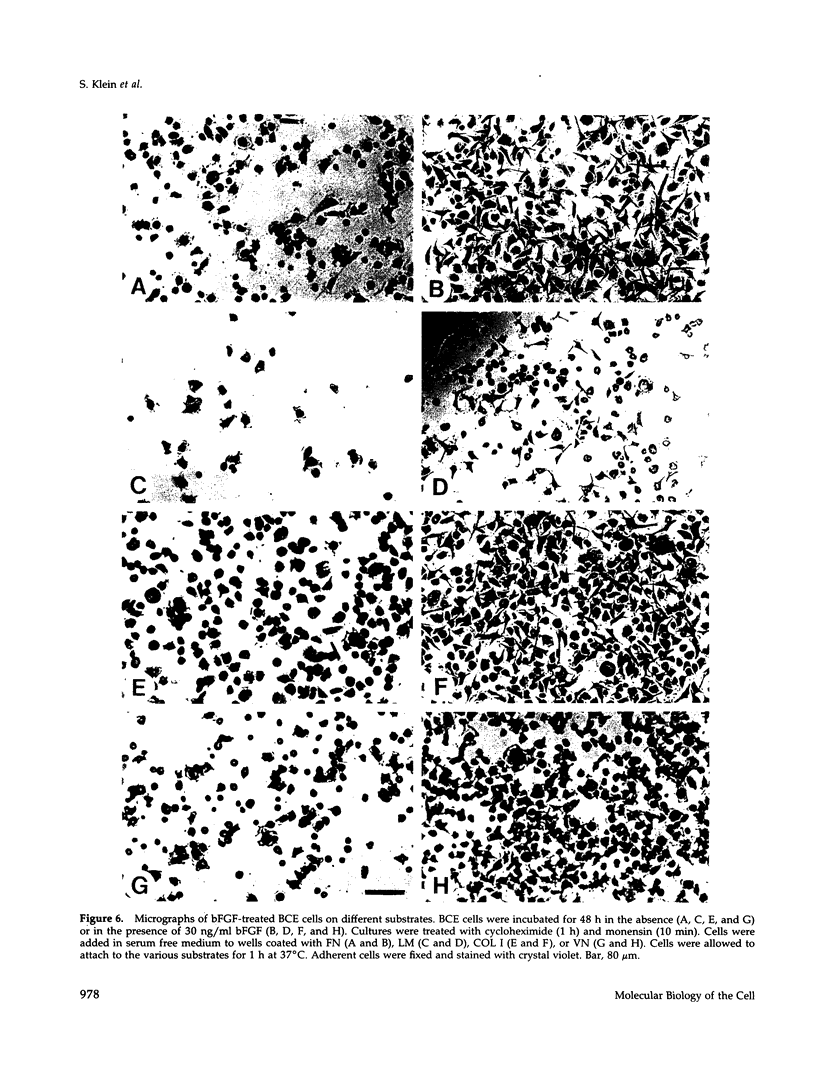
During angiogenesis capillary endothelial cells undergo a coordinated set of modifications in their interactions with extracellular matrix components. In this study we have investigated the effect of the prototypical angiogenic factor basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on the expression and function of several integrins in microvascular endothelial cells. Immunoprecipitation experiments with antibodies to individual subunits indicated that microvascular cells express at their surface several integrins. These include the alpha 1 beta 1, alpha 2 beta 1, and alpha 3 beta 1 laminin/collagen receptors; the alpha 6 beta 1 laminin receptor; the alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 1 fibronectin receptors; the alpha 6 beta 4 basement membrane receptor; and the alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 vitronectin receptors. Treatment with bFGF caused a significant increase in the surface expression of the alpha 2 beta 1, alpha 3 beta 1, alpha 5 beta 1, alpha 6 beta 1, alpha 6 beta 4, and alpha v beta 5 integrins. In contrast, the level of expression of the alpha 1 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 integrins was decreased in bFGF-treated cells. Immunoprecipitation of metabolically labeled cells indicated that bFGF increases the biosynthesis of the alpha 3, alpha 5, alpha 6, beta 4, and beta 5 subunits and decreases the production of the alpha v and beta 3 subunits. These results suggest that bFGF modulates integrin expression by altering the biosynthesis of individual alpha or beta subunits. In accordance with the upregulation of several integrins observed in bFGF-treated cells, these cells adhered better to fibronectin, laminin, vitronectin, and type I collagen than did untreated cells. The largest differences in beta 1 integrin expression occurred approximately 72 h after exposure to bFGF, at a time when the expression of the endothelial cell-to-cell adhesion molecule endoCAM was also significantly upregulated. In contrast, a shorter exposure to bFGF (24-48 h) was required for the maximal induction of plasminogen activator production in the same cells. Taken together, these results show that bFGF causes significant changes in the level of expression and function of several integrins in microvascular endothelial cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M., Buck C. A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2868–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Daise M., Levine E. M., Buck C. A. Identification and characterization of cell-substratum adhesion receptors on cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1992–2002. doi: 10.1172/JCI114109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M. Endothelial and epithelial cell adhesion molecules. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;4(3):195–203. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.3.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Oliver P. D., Romer L. H., Buck C. A. EndoCAM: a novel endothelial cell-cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1227–1237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson C. T., Knowles W. J., Bell L., Albelda S. M., Castronovo V., Liotta L. A., Madri J. A. Spatiotemporal segregation of endothelial cell integrin and nonintegrin extracellular matrix-binding proteins during adhesion events. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):789–801. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. S., Schreiner C. L., Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E., Juliano R. L. Motility of fibronectin receptor-deficient cells on fibronectin and vitronectin: collaborative interactions among integrins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):477–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Margolis M., Schreiner C., Edgell C. J., Azizkhan J., Lazarowski E., Juliano R. L. In vitro model of angiogenesis using a human endothelium-derived permanent cell line: contributions of induced gene expression, G-proteins, and integrins. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Dec;153(3):437–449. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041530302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Integrin, a transmembrane glycoprotein complex mediating cell-substratum adhesion. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;8:231–250. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_8.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Kaur P., Gil S. G., Gahr P. J., Wayner E. A. Distinct functions for integrins alpha 3 beta 1 in focal adhesions and alpha 6 beta 4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3141–3154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B. M., Kassner P. D., Schiro J. A., Byers H. R., Kupper T. S., Hemler M. E. Distinct cellular functions mediated by different VLA integrin alpha subunit cytoplasmic domains. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1051–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90077-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. F., Kramer R. H. Human microvascular endothelial cells express integrin-related complexes that mediate adhesion to the extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1989 May;139(2):275–286. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Harper J. R. Arg-Gly-Asp recognition by a cell adhesion receptor requires its 130-kDa alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1434–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defilippi P., Silengo L., Tarone G. Alpha 6.beta 1 integrin (laminin receptor) is down-regulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18303–18307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defilippi P., Truffa G., Stefanuto G., Altruda F., Silengo L., Tarone G. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma modulate the expression of the vitronectin receptor (integrin beta 3) in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7638–7645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defilippi P., van Hinsbergh V., Bertolotto A., Rossino P., Silengo L., Tarone G. Differential distribution and modulation of expression of alpha 1/beta 1 integrin on human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):855–863. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enenstein J., Waleh N. S., Kramer R. H. Basic FGF and TGF-beta differentially modulate integrin expression of human microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Dec;203(2):499–503. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaumenhaft R., Moscatelli D., Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Role of extracellular matrix in the action of basic fibroblast growth factor: matrix as a source of growth factor for long-term stimulation of plasminogen activator production and DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jul;140(1):75–81. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E. Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Stepp M. A., Suzuki S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Proteolytic processing of endogenous and recombinant beta 4 integrin subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):951–959. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Du X., Plow E. F. Inside-out integrin signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):766–771. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Birdwell C. R. Determination of cellular shape by the extracellular matrix and its correlation with the control of cellular growth. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4155–4171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Jaffe E. A., Rifkin D. B. Plasminogen activator and collagenase production by cultured capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):974–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Folkman J. How does extracellular matrix control capillary morphogenesis? Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):803–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90928-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Folkman J. Mechanochemical switching between growth and differentiation during fibroblast growth factor-stimulated angiogenesis in vitro: role of extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):317–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Madri J. A., Folkman J. A possible mechanism for inhibition of angiogenesis by angiostatic steroids: induction of capillary basement membrane dissolution. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1768–1775. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Madri J. A., Folkman J. Endothelial growth factors and extracellular matrix regulate DNA synthesis through modulation of cell and nuclear expansion. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 May;23(5):387–394. doi: 10.1007/BF02620997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D., Folkman J. Inhibition of angiogenesis through modulation of collagen metabolism. Lab Invest. 1988 Jul;59(1):44–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Godfrey V., Ch'ang L. Y., Lankford T. K., Foote L. J., Makkinje A. The beta 4 subunit of the integrin family is displayed on a restricted subset of endothelium in mice. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):145–150. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Cheng Y. F., Clyman R. Human microvascular endothelial cells use beta 1 and beta 3 integrin receptor complexes to attach to laminin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1233–1243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kueng W., Silber E., Eppenberger U. Quantification of cells cultured on 96-well plates. Anal Biochem. 1989 Oct;182(1):16–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90710-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavesley D. I., Ferguson G. D., Wayner E. A., Cheresh D. A. Requirement of the integrin beta 3 subunit for carcinoma cell spreading or migration on vitronectin and fibrinogen. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1101–1107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavesley D. I., Schwartz M. A., Rosenfeld M., Cheresh D. A. Integrin beta 1- and beta 3-mediated endothelial cell migration is triggered through distinct signaling mechanisms. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):163–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Tsuboi R., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):671–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Rapraeger A. Repression of myogenic differentiation by aFGF, bFGF, and K-FGF is dependent on cellular heparan sulfate. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):631–639. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Maier J. A., Rusnati M., Ragnotti G. Basic fibroblast growth factor is released from endothelial extracellular matrix in a biologically active form. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jul;140(1):68–74. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryynänen J., Jaakkola S., Engvall E., Peltonen J., Uitto J. Expression of beta 4 integrins in human skin: comparison of epidermal distribution with beta 1-integrin epitopes, and modulation by calcium and vitamin D3 in cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):562–567. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarone G., Russo M. A., Hirsch E., Odorisio T., Altruda F., Silengo L., Siracusa G. Expression of beta 1 integrin complexes on the surface of unfertilized mouse oocyte. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1369–1375. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel B. E., Lee S. J., Hildebrand A., Craig W., Pierschbacher M. D., Wong-Staal F., Ruoslahti E. A novel integrin specificity exemplified by binding of the alpha v beta 5 integrin to the basic domain of the HIV Tat protein and vitronectin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(2):461–468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Morla A. O., Vuori K., Bauer J. S., Juliano R. L., Ruoslahti E. The alpha v beta 1 integrin functions as a fibronectin receptor but does not support fibronectin matrix assembly and cell migration on fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):235–242. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]