Abstract
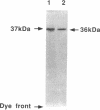
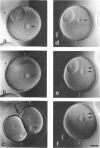
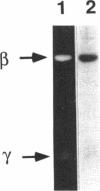
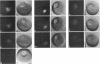
beta gamma subunits of G proteins were purified from starfish oocytes, and their role in the induction of oocyte maturation by 1-methyladenine was investigated. When injected into starfish oocytes, the purified beta gamma subunit of the starfish G protein induced germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD) faster than that of bovine brain G protein. Injection of the starfish beta gamma into cytoplasm near the germinal vesicle (GV) induced GVBD earlier than when injected into the GV or the cytoplasm near the plasma membrane. Fluorescent-labeled beta gamma was retained in the injected area even after GVBD. Injected beta gamma also induced the formation of maturation-promoting factor as well as an increase of histone H1 kinase activity. These results suggest that beta gamma dissociates from alpha-subunit by the stimulation of 1-methyladenine and interacts with a cytoplasmic effector, which results in formation of active cdc2 kinase.
Full text
PDF

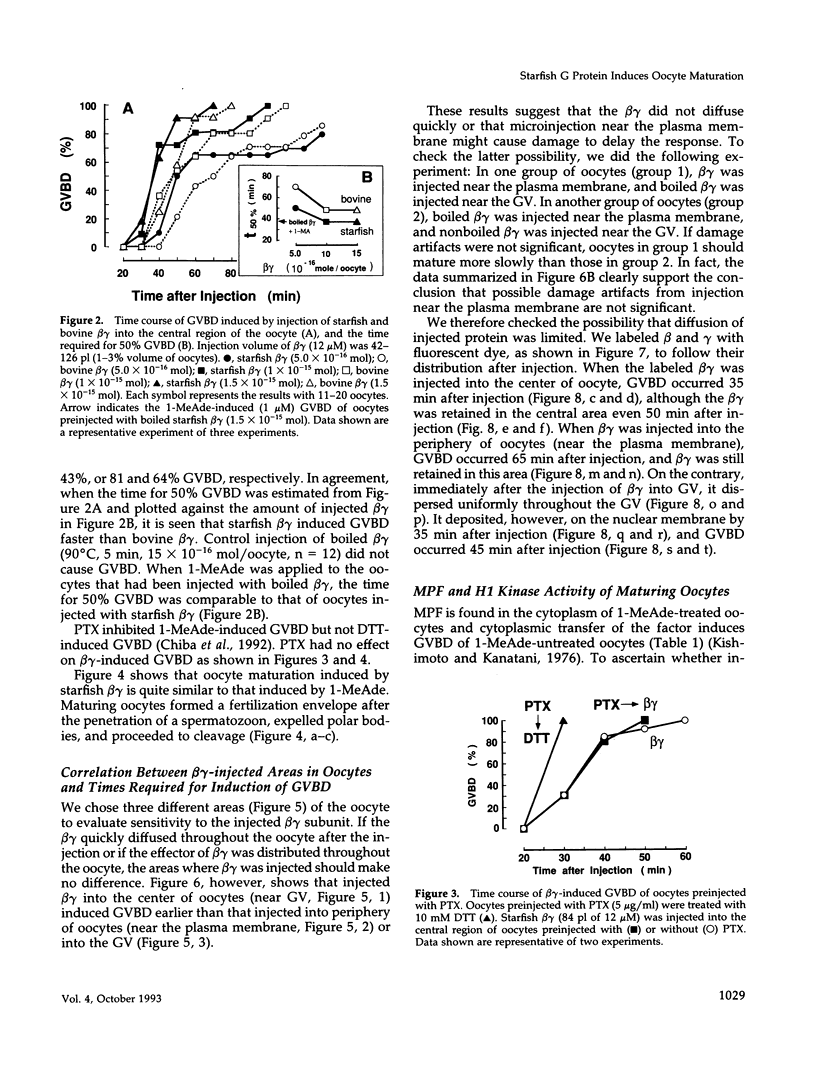
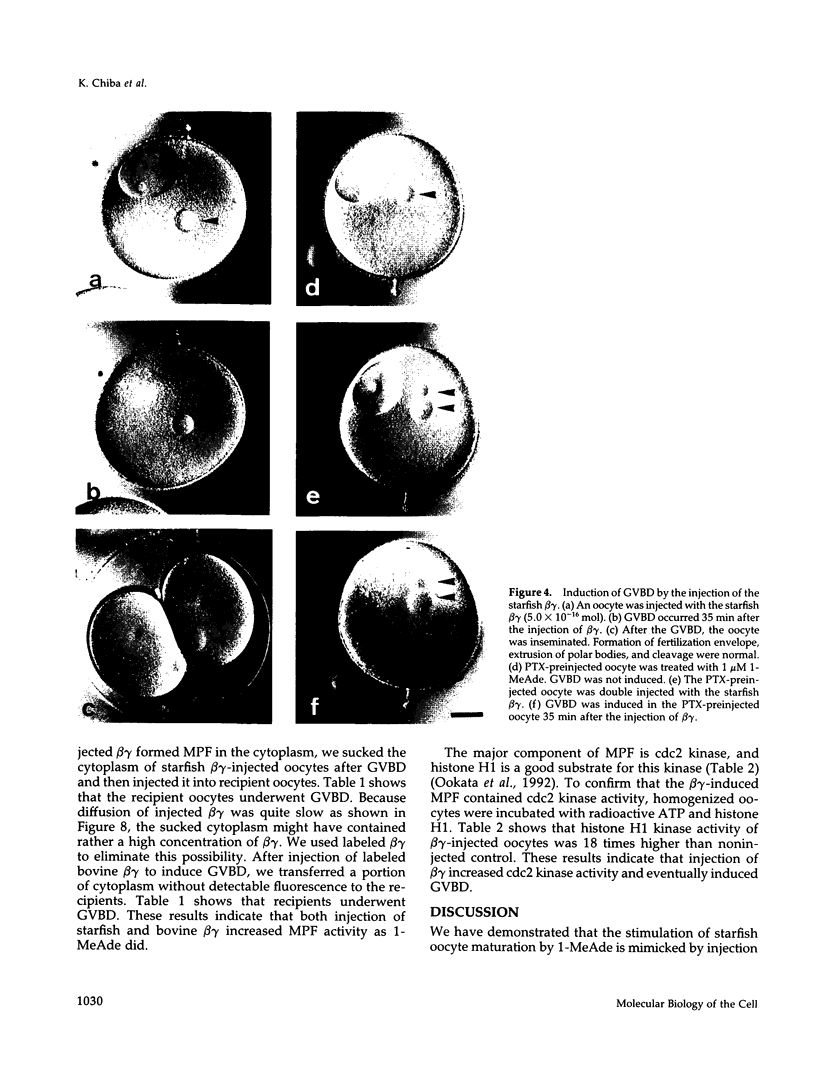
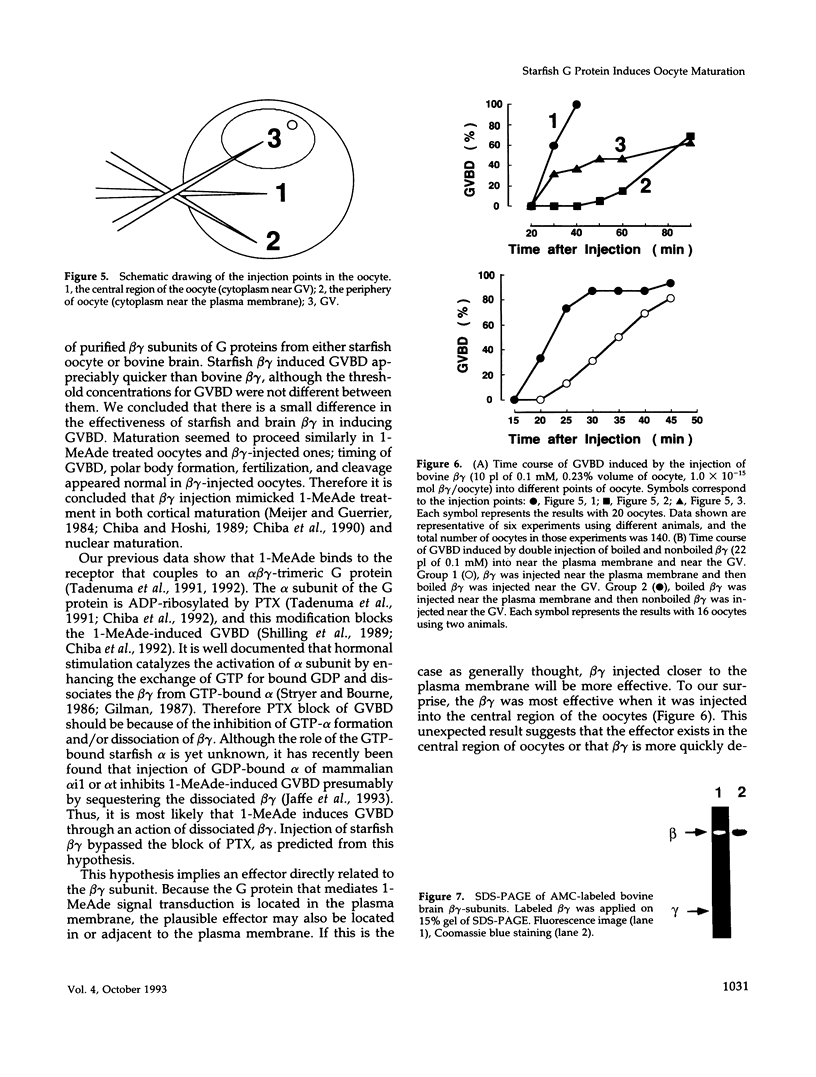
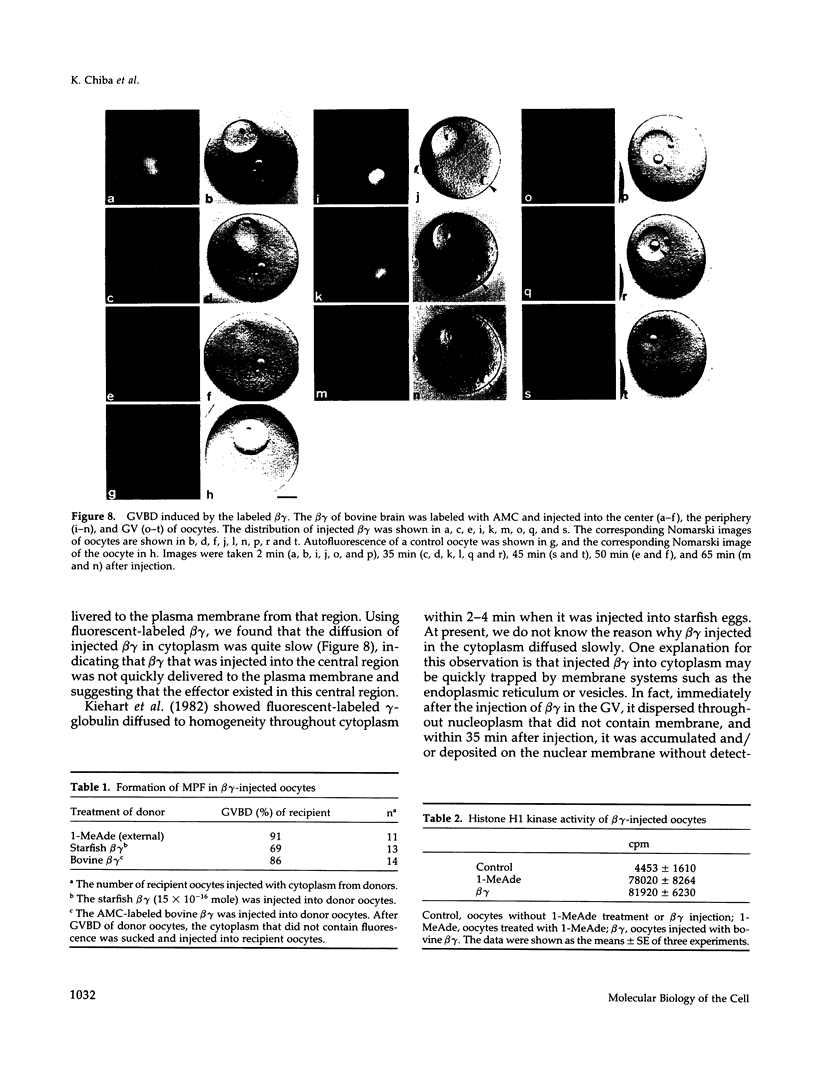


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiba K., Kado R. T., Jaffe L. A. Development of calcium release mechanisms during starfish oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 1990 Aug;140(2):300–306. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Tadenuma H., Matsumoto M., Takahashi K., Katada T., Hoshi M. The primary structure of the alpha subunit of a starfish guanosine-nucleotide-binding regulatory protein involved in 1-methyladenine-induced oocyte maturation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;207(3):833–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Simon M. I., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. G protein beta gamma subunits synthesized in Sf9 cells. Functional characterization and the significance of prenylation of gamma. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23409–23417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. A., Gallo C. J., Lee R. H., Ho Y. K., Jones T. L. Oocyte maturation in starfish is mediated by the beta gamma-subunit complex of a G-protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(4):775–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanatani H., Shirai H., Nakanishi K., Kurokawa T. Isolation and indentification on meiosis inducing substance in starfish Asterias amurensis. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):273–274. doi: 10.1038/221273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Kusakabe K., Oinuma M., Ui M. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of adenylate cyclase via inhibitory GTP-binding proteins. Calmodulin-dependent inhibition of the cyclase catalyst by the beta gamma-subunits of GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11897–11900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in rat brain serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. Interaction of the alpha-subunits with beta gamma-subunits in development of their biological activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8182–8191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P., Mabuchi I., Inoué S. Evidence that myosin does not contribute to force production in chromosome movement. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):165–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Kanatani H. Cytoplasmic factor responsible for germinal vesicle breakdown and meiotic maturation in starfish oocyte. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):321–322. doi: 10.1038/260321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Kuriyama R., Kondo H., Kanatani H. Generality of the action of various maturation-promoting factors. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Kikkawa S., Ui M., Katada T. Purification of GTP-binding proteins from bovine brain membranes. Identification of heterogeneity of the alpha-subunit of Go proteins. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81815-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Regulation of the cdc25 protein during the cell cycle in Xenopus extracts. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90540-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Lee M. G., Nurse P., Picard A., Doree M. Activation at M-phase of a protein kinase encoded by a starfish homologue of the cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):251–254. doi: 10.1038/335251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Capony J. P., Caput D., Cavadore J. C., Derancourt J., Kaghad M., Lelias J. M., Picard A., Dorée M. MPF from starfish oocytes at first meiotic metaphase is a heterodimer containing one molecule of cdc2 and one molecule of cyclin B. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3053–3058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Zarutskie P. Starfish oocyte maturation: 1-methyladenine triggers a drop of cAMP concentration related to the hormone-dependent period. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):306–315. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookata K., Hisanaga S., Okano T., Tachibana K., Kishimoto T. Relocation and distinct subcellular localization of p34cdc2-cyclin B complex at meiosis reinitiation in starfish oocytes. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1763–1772. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilling F., Chiba K., Hoshi M., Kishimoto T., Jaffe L. A. Pertussis toxin inhibits 1-methyladenine-induced maturation in starfish oocytes. Dev Biol. 1989 Jun;133(2):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana K., Yanagishima N., Kishimoto T. Preliminary characterization of maturation-promoting factor from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci. 1987 Oct;88(Pt 3):273–281. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadenuma H., Chiba K., Takahashi K., Hoshi M., Katada T. Purification and characterization of a GTP-binding protein serving as pertussis toxin substrate in starfish oocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 1;290(2):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90560-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadenuma H., Takahashi K., Chiba K., Hoshi M., Katada T. Properties of 1-methyladenine receptors in starfish oocyte membranes: involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein in the receptor-mediated signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):114–121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80782-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Krupinski J., Gilman A. G. Expression and characterization of calmodulin-activated (type I) adenylylcyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8595–8603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]