Abstract
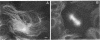
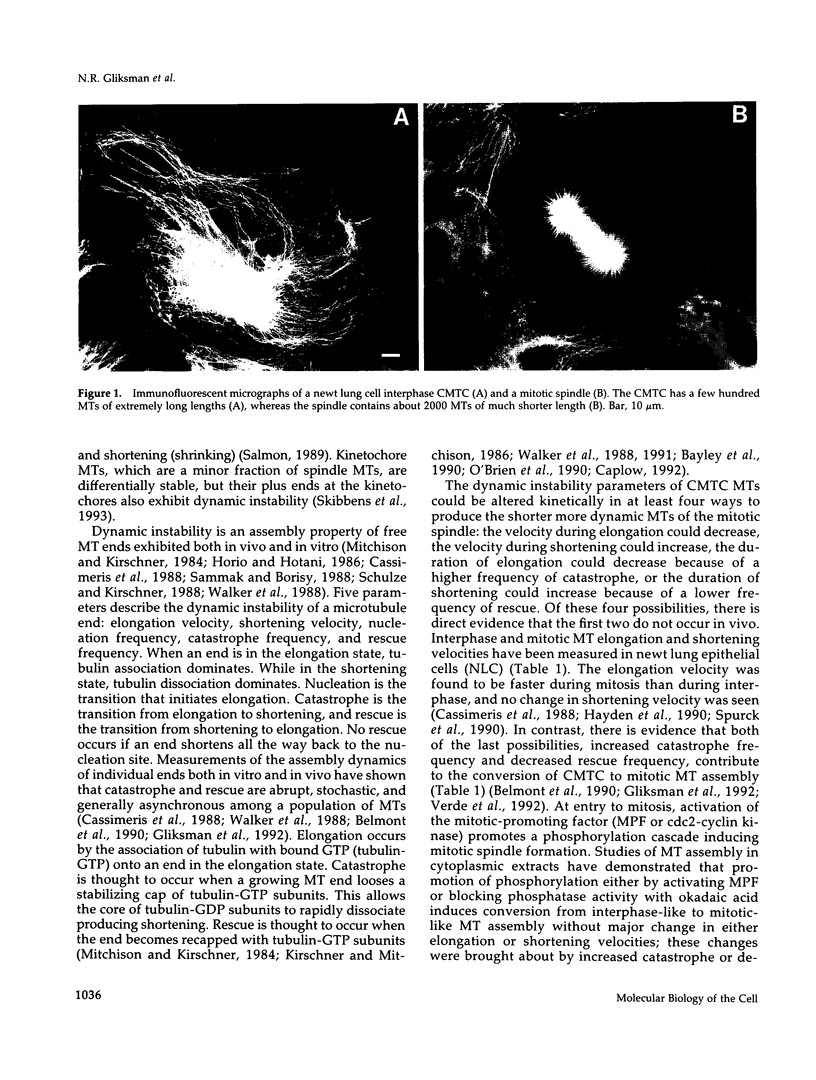
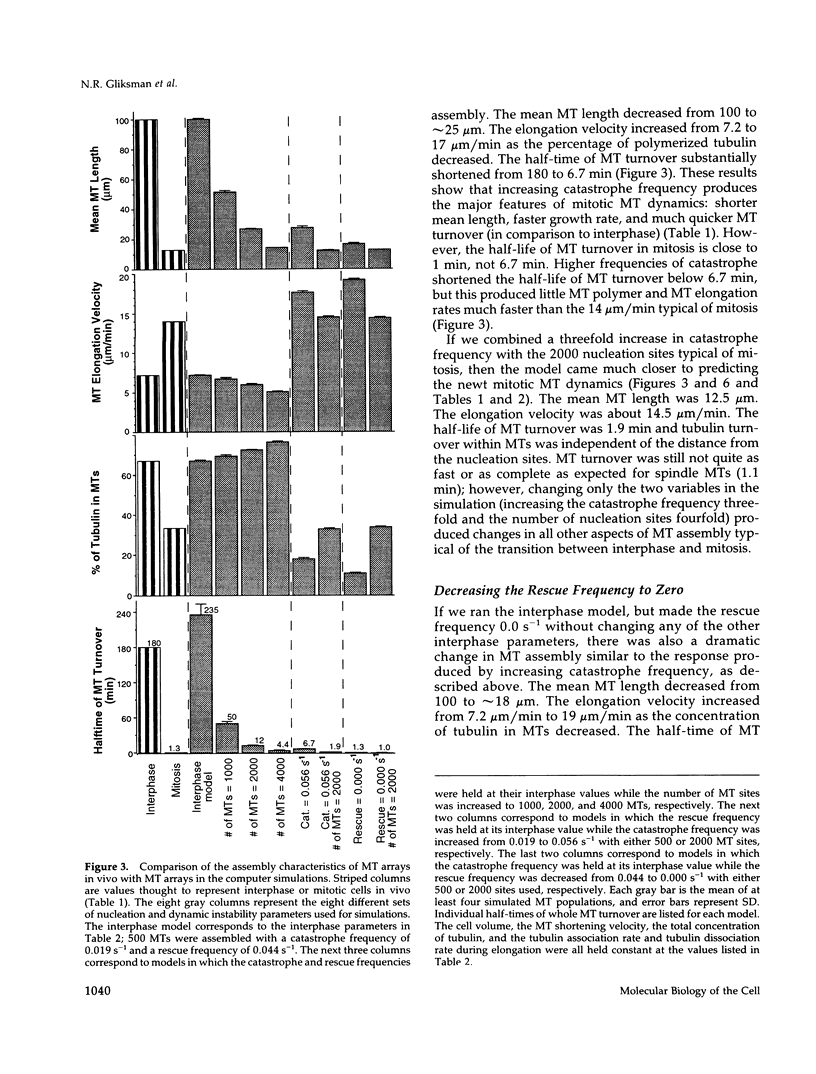
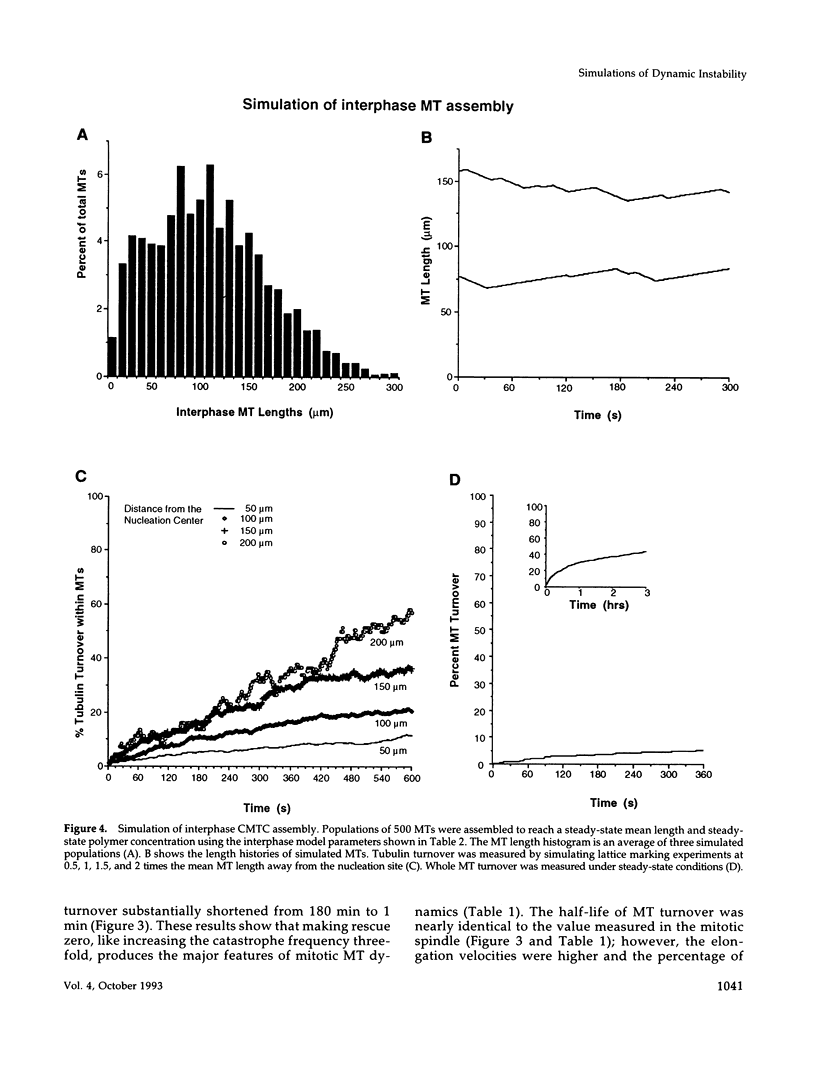
Microtubules (MTs) in newt mitotic spindles grow faster than MTs in the interphase cytoplasmic microtubule complex (CMTC), yet spindle MTs do not have the long lengths or lifetimes of the CMTC microtubules. Because MTs undergo dynamic instability, it is likely that changes in the durations of growth or shortening are responsible for this anomaly. We have used a Monte Carlo computer simulation to examine how changes in the number of MTs and changes in the catastrophe and rescue frequencies of dynamic instability may be responsible for the cell cycle dependent changes in MT characteristics. We used the computer simulations to model interphase-like or mitotic-like MT populations on the basis of the dynamic instability parameters available from newt lung epithelial cells in vivo. We started with parameters that produced MT populations similar to the interphase newt lung cell CMTC. In the simulation, increasing the number of MTs and either increasing the frequency of catastrophe or decreasing the frequency of rescue reproduced the changes in MT dynamics measured in vivo between interphase and mitosis.
Full text
PDF



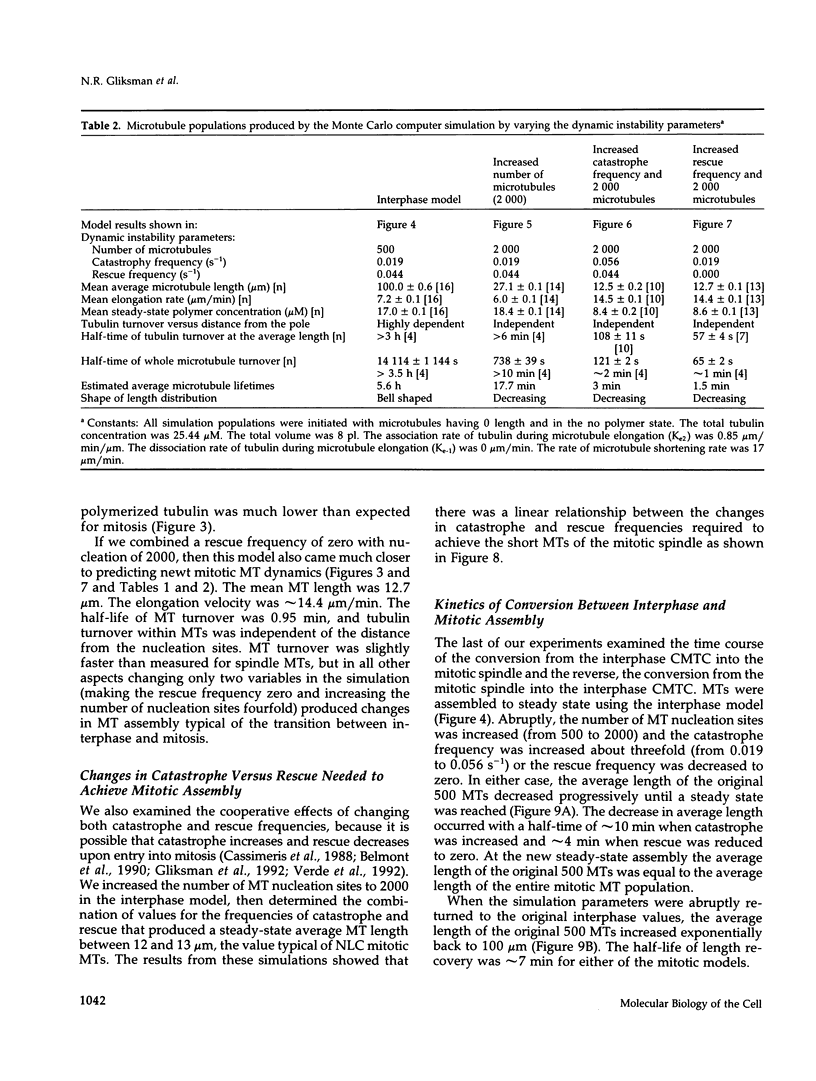
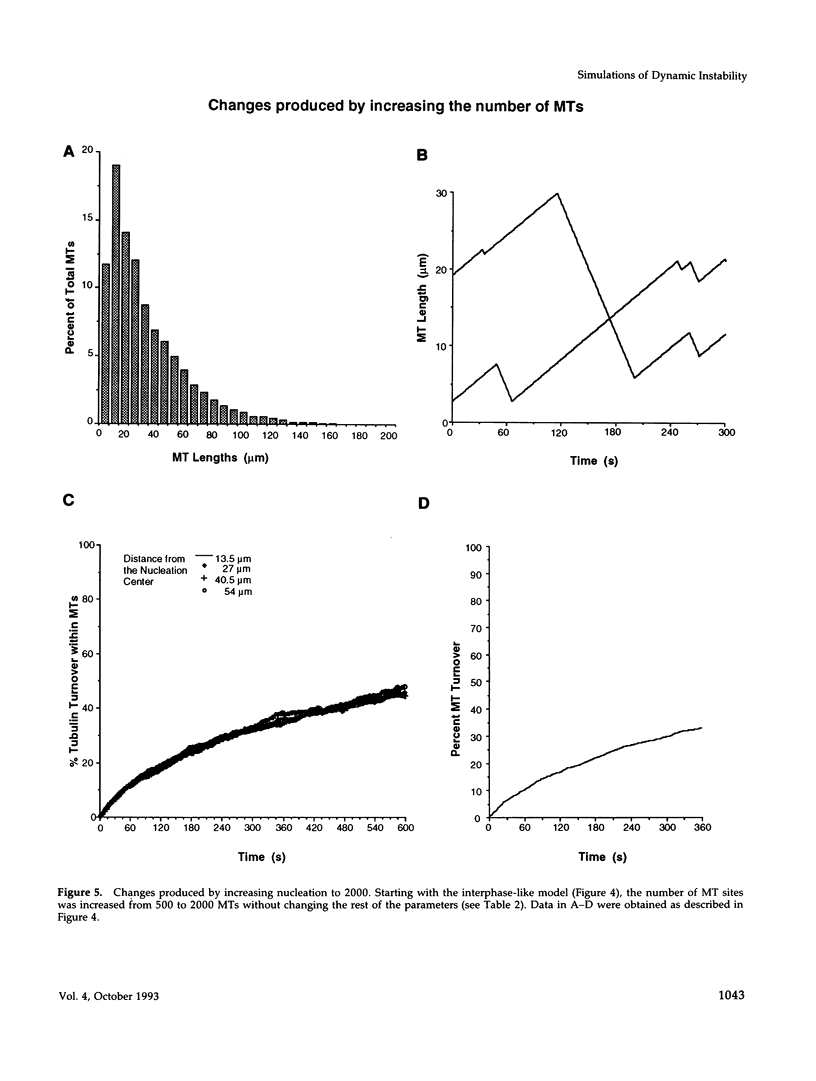
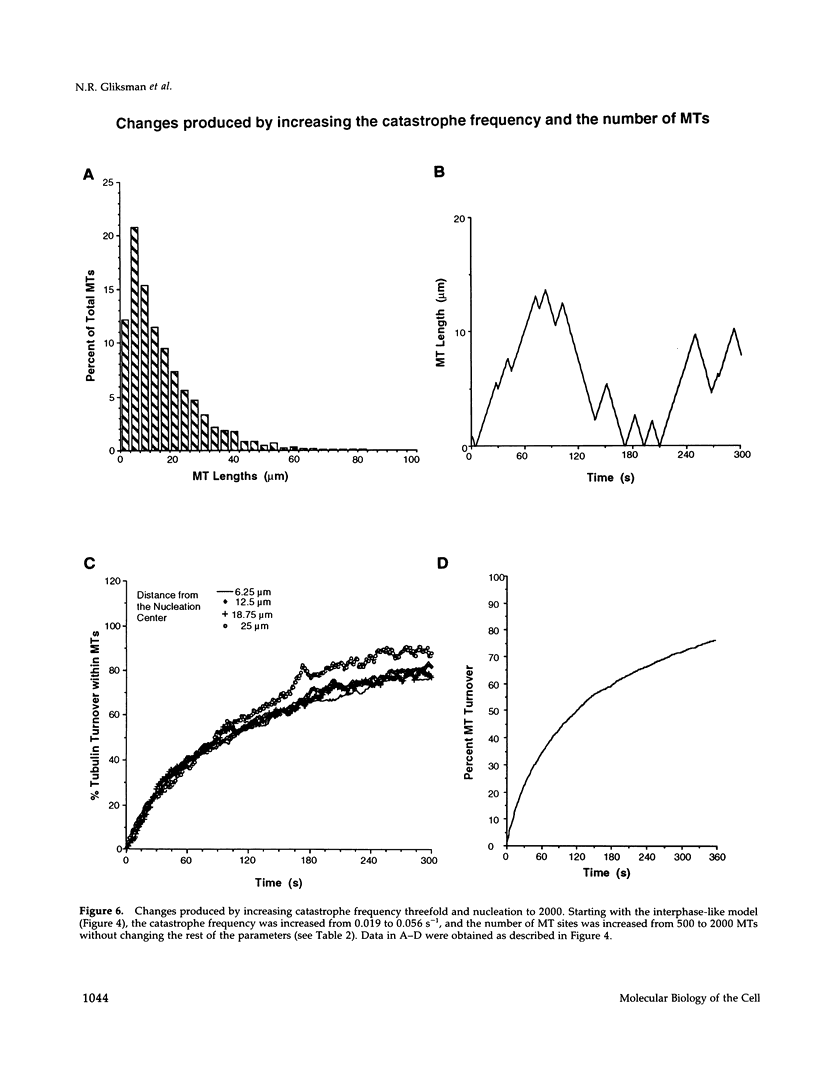
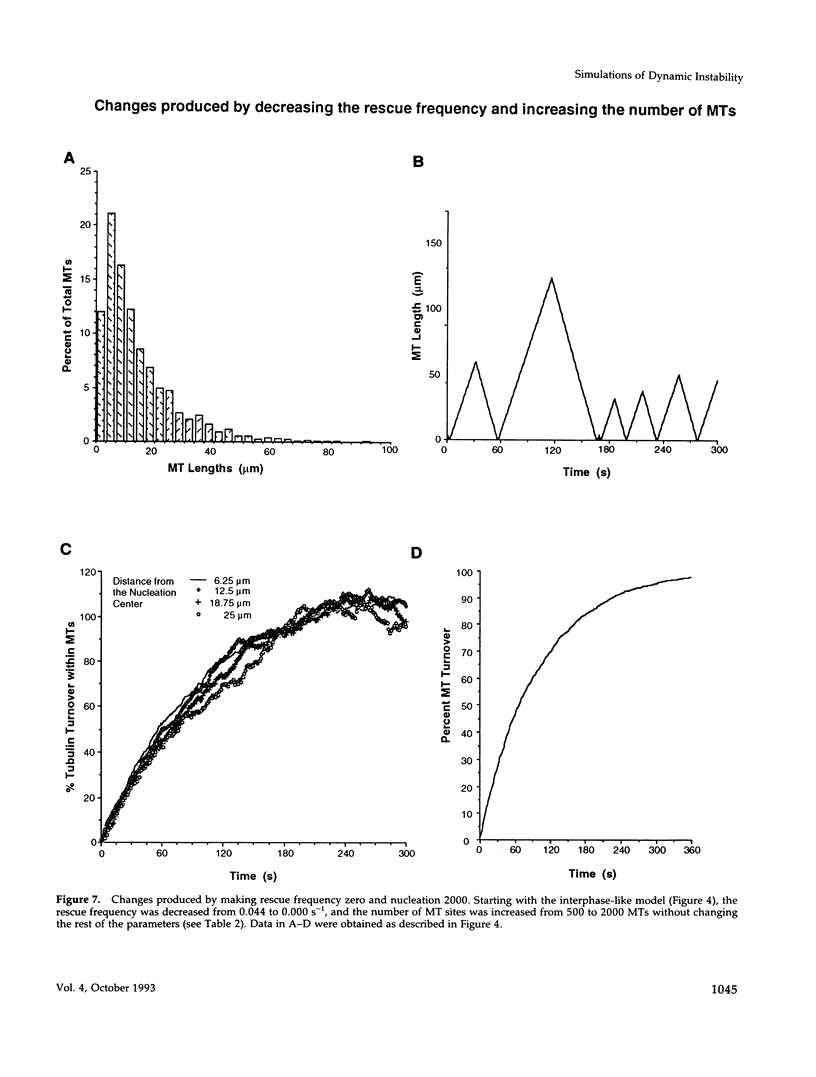




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley P. M., Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R. A simple formulation of microtubule dynamics: quantitative implications of the dynamic instability of microtubule populations in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):241–254. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. M., Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R. Microtubule dynamic instability: numerical simulation of microtubule transition properties using a Lateral Cap model. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):33–48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont L. D., Hyman A. A., Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J. Real-time visualization of cell cycle-dependent changes in microtubule dynamics in cytoplasmic extracts. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buendia B., Draetta G., Karsenti E. Regulation of the microtubule nucleating activity of centrosomes in Xenopus egg extracts: role of cyclin A-associated protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1431–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplow M. Microtubule dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L. U., Wadsworth P., Salmon E. D. Dynamics of microtubule depolymerization in monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2023–2032. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Pryer N. K., Salmon E. D. Real-time observations of microtubule dynamic instability in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2223–2231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel D. N., Hyman A. A., Cobb M. H., Kirschner M. W. Modulation of the dynamic instability of tubulin assembly by the microtubule-associated protein tau. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1141–1154. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman N. R., Parsons S. F., Salmon E. D. Okadaic acid induces interphase to mitotic-like microtubule dynamic instability by inactivating rescue. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Bowser S. S., Rieder C. L. Kinetochores capture astral microtubules during chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle: direct visualization in live newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller G., Weber K. Radioimmunoassay for tubulin: a quantitative comparison of the tubulin content of different established tissue culture cells and tissues. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):795–804. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio T., Hotani H. Visualization of the dynamic instability of individual microtubules by dark-field microscopy. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):605–607. doi: 10.1038/321605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A. A., Salser S., Drechsel D. N., Unwin N., Mitchison T. J. Role of GTP hydrolysis in microtubule dynamics: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue, GMPCPP. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1155–1167. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi H. C., Palacios M. J., McNamara L., Cleveland D. W. Gamma-tubulin is a centrosomal protein required for cell cycle-dependent microtubule nucleation. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):80–83. doi: 10.1038/356080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M., Mitchison T. Beyond self-assembly: from microtubules to morphogenesis. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama R., Borisy G. G. Microtubule-nucleating activity of centrosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells is independent of the centriole cycle but coupled to the mitotic cycle. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):822–826. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Some thoughts on the partitioning of tubulin between monomer and polymer under conditions of dynamic instability. Cell Biophys. 1987 Dec;11:35–55. doi: 10.1007/BF02797111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J. Polewards microtubule flux in the mitotic spindle: evidence from photoactivation of fluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):637–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Salmon E. D. Poleward kinetochore fiber movement occurs during both metaphase and anaphase-A in newt lung cell mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):569–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):237–242. doi: 10.1038/312237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. T., Salmon E. D., Walker R. A., Erickson H. P. Effects of magnesium on the dynamic instability of individual microtubules. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6648–6656. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Tubulin pools in differentiating neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):418–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer T. A., Asnes C. F., Wilson L. Properties of tubulin in unfertilized sea urchin eggs. Quantitation and characterization by the colchicine-binding reaction. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):599–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Kipnis D. M. Physiological regulation of total tubulin and polymerized tubulin in tissues. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):351–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Sherline P., Kipnis D. M. A sensitive method for measuring polymerized and depolymerized forms of tubulin in tissues. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):341–350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Davison E. A., Jensen L. C., Cassimeris L., Salmon E. D. Oscillatory movements of monooriented chromosomes and their position relative to the spindle pole result from the ejection properties of the aster and half-spindle. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):581–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell S. W., Grasser W. A., Murphy D. B. End-to-end annealing of microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):619–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon E. D., Leslie R. J., Saxton W. M., Karow M. L., McIntosh J. R. Spindle microtubule dynamics in sea urchin embryos: analysis using a fluorescein-labeled tubulin and measurements of fluorescence redistribution after laser photobleaching. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2165–2174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammak P. J., Borisy G. G. Direct observation of microtubule dynamics in living cells. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):724–726. doi: 10.1038/332724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammak P. J., Gorbsky G. J., Borisy G. G. Microtubule dynamics in vivo: a test of mechanisms of turnover. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):395–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J. Poleward microtubule flux mitotic spindles assembled in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):941–954. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. M., Stemple D. L., Leslie R. J., Salmon E. D., Zavortink M., McIntosh J. R. Tubulin dynamics in cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2175–2186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze E., Kirschner M. New features of microtubule behaviour observed in vivo. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):356–359. doi: 10.1038/334356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelden E., Wadsworth P. Observation and quantification of individual microtubule behavior in vivo: microtubule dynamics are cell-type specific. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):935–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Parsons S. F., Salmon E. D. Buffer conditions and non-tubulin factors critically affect the microtubule dynamic instability of sea urchin egg tubulin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;21(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/cm.970210102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibbens R. V., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Directional instability of kinetochore motility during chromosome congression and segregation in mitotic newt lung cells: a push-pull mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):859–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., McIntosh J. R. Initiation and growth of microtubules from mitotic centers in lysed mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):744–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurck T. P., Stonington O. G., Snyder J. A., Pickett-Heaps J. D., Bajer A., Mole-Bajer J. UV microbeam irradiations of the mitotic spindle. II. Spindle fiber dynamics and force production. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1505–1518. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemple D. L., Sweet S. C., Welsh M. J., McIntosh J. R. Dynamics of a fluorescent calmodulin analog in the mammalian mitotic spindle at metaphase. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;9(3):231–242. doi: 10.1002/cm.970090305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D. Severing of stable microtubules by a mitotically activated protein in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):827–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90511-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Dogterom M., Stelzer E., Karsenti E., Leibler S. Control of microtubule dynamics and length by cyclin A- and cyclin B-dependent kinases in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1097–1108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Karsenti E. Regulation of microtubule dynamics by cdc2 protein kinase in cell-free extracts of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):233–238. doi: 10.1038/343233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voter W. A., O'Brien E. T., Erickson H. P. Dilution-induced disassembly of microtubules: relation to dynamic instability and the GTP cap. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;18(1):55–62. doi: 10.1002/cm.970180106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth P., Salmon E. D. Analysis of the treadmilling model during metaphase of mitosis using fluorescence redistribution after photobleaching. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1032–1038. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth P., Salmon E. D. Microtubule dynamics in mitotic spindles of living cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:580–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., O'Brien E. T., Pryer N. K., Soboeiro M. F., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P., Salmon E. D. Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: rate constants and transition frequencies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1437–1448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Pryer N. K., Salmon E. D. Dilution of individual microtubules observed in real time in vitro: evidence that cap size is small and independent of elongation rate. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):73–81. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]