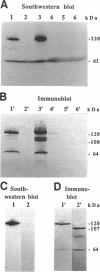
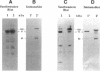
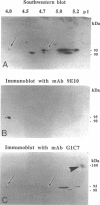
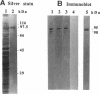
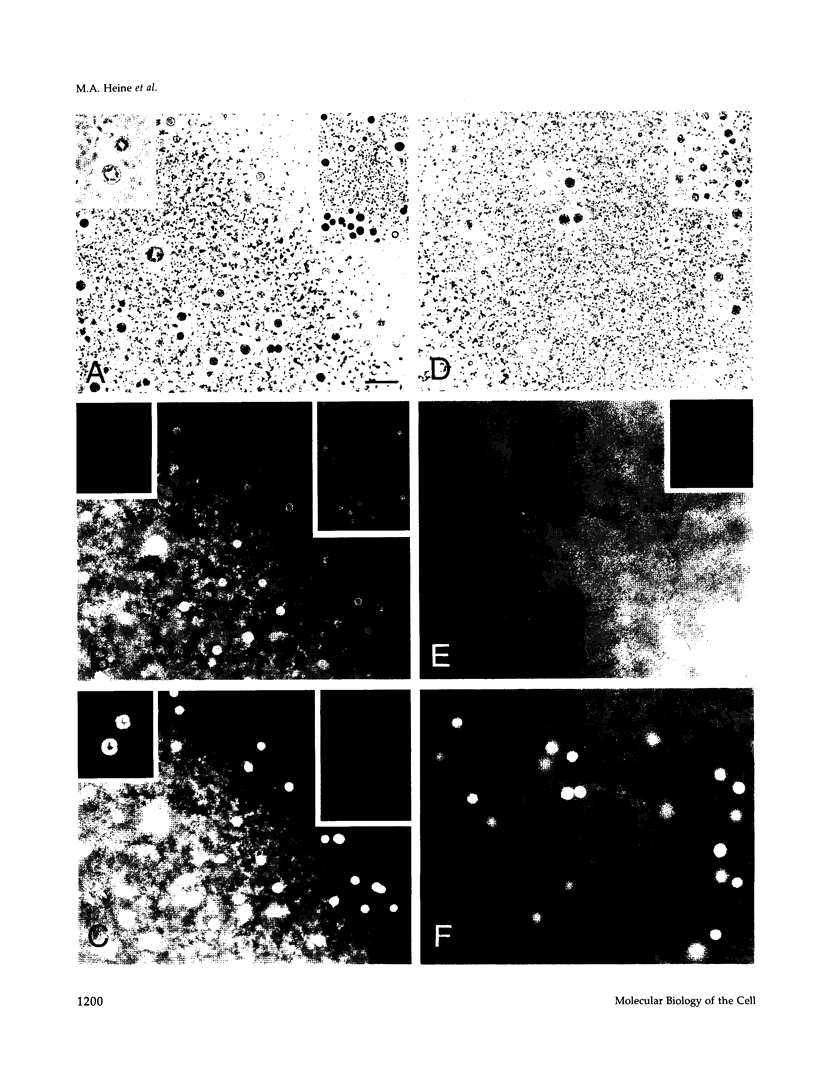
Abstract
Epitope-tagged Xenopus nucleolin was expressed in Escherichia coli cells and in Xenopus oocytes either as a full-length wild-type protein or as a truncation that lacked the distinctive carboxy glycine/arginine-rich (GAR) domain. Both full-length and truncated versions of nucleolin were tagged at their amino termini with five tandem human c-myc epitopes. Whether produced in E. coli or in Xenopus, epitope-tagged full-length nucleolin bound nucleic acid probes in in vitro filter binding assays. Conversely, the E. coli-expressed GAR truncation failed to bind the nucleic acid probes, whereas the Xenopus-expressed truncation maintained slight binding activity. Indirect immunofluorescence staining showed that myc-tagged full-length nucleolin properly localized to the dense fibrillar regions within the multiple nucleoli of Xenopus oocyte nuclei. The epitope-tagged GAR truncation also translocated to the oocyte nuclei, but it failed to efficiently localize to the nucleoli. Our results show that the carboxy GAR domain must be present for nucleolin to efficiently bind nucleic acids in vitro and to associate with nucleoli in vivo.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballal N. R., Kang Y. J., Olson M. O., Busch H. Changes in nucleolar proteins and their phosphorylation patterns during liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5921–5925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrijal S., Perros M., Gu Z., Avalosse B. L., Belenguer P., Amalric F., Rommelaere J. Nucleolin forms a specific complex with a fragment of the viral (minus) strand of minute virus of mice DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5053–5060. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belenguer P., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Amalric F. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of nucleolin by p34cdc2 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3607–3618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggiogera M., Kaufmann S. H., Shaper J. H., Gas N., Amalric F., Fakan S. Distribution of nucleolar proteins B23 and nucleolin during mouse spermatogenesis. Chromosoma. 1991 Mar;100(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00337245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H. M., Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Zalta J. P. Maturation of a 100 kDa protein associated with preribosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00777472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H., Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F. Role of phosphorylation on the maturation pathways of a 100 kDa nucleolar protein. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Mattes R. E., Buckel P. High-level expression of recombinant genes in Escherichia coli is dependent on the availability of the dnaY gene product. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90470-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Dawid I. B. Specific gene amplification in oocytes. Oocyte nuclei contain extrachromosomal replicas of the genes for ribosomal RNA. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):272–280. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Bourbon H., Lapeyre B., Wallace M. O., Chang J. H., Amalric F., Olson M. O. RNA binding fragments from nucleolin contain the ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):10922–10925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bouche G., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Detection and localization of a class of proteins immunologically related to a 100-kDa nucleolar protein. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):475–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caizergues-Ferrer M., Mariottini P., Curie C., Lapeyre B., Gas N., Amalric F., Amaldi F. Nucleolin from Xenopus laevis: cDNA cloning and expression during development. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G., Gall J. G., Berg C. A. The lampbrush chromosomes of Xenopus laevis: preparation, identification, and distribution of 5S DNA sequences. Chromosoma. 1987;95(4):236–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00294780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. M., Chiang S. Y., Yeh N. H. Increased stability of nucleolin in proliferating cells by inhibition of its self-cleaving activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7754–7758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario P. J., Bromley S. E., Gall J. G. DNA-binding proteins on lampbrush chromosome loops. Chromosoma. 1989 May;97(6):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00295024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario P. J., Gall J. G. Nucleolin from the multiple nucleoli of amphibian oocyte nuclei. Chromosoma. 1990 Apr;99(2):87–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01735323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Dilworth S. M., Black S. J., Kearsey S. E., Cox L. S., Laskey R. A. Nucleoplasmin cDNA sequence reveals polyglutamic acid tracts and a cluster of sequences homologous to putative nuclear localization signals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. M., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcription of a satellite DNA in the newt. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1137–1144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard M. S., Belenguer P., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Pantaloni A., Amalric F. A major nucleolar protein, nucleolin, induces chromatin decondensation by binding to histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard M., Lakhdar-Ghazal F., Amalric F. Repeat peptide motifs which contain beta-turns and modulate DNA condensation in chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 20;191(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande M. L., Gas N., Stevens B. J. Immunolocalization of the 100 K nucleolar protein in CHO cells. Biol Cell. 1985;53(2):99–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G. Differential synthesis of the genes for ribosomal RNA during amphibian oögenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):553–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Wu Z. A. Lampbrush chromosomes. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:149–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Harrison M. L. Induction of a substrate for casein kinase II during lymphocyte mitogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 19;804(2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisolfi L., Joseph G., Amalric F., Erard M. The glycine-rich domain of nucleolin has an unusual supersecondary structure responsible for its RNA-helix-destabilizing properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2955–2959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P., Lehtonen H., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Tollervey D., Lapeyre B. GAR1 is an essential small nucleolar RNP protein required for pre-rRNA processing in yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):673–682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera A. H., Olson M. O. Association of protein C23 with rapidly labeled nucleolar RNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6258–6264. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong A. Y., Clark M. W., Gilbert M., Oehm A., Campbell J. L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SSB1 protein and its relationship to nucleolar RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2947–2955. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Tyc K., Steitz J. A., Sollner-Webb B. The U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein functions in the first step of preribosomal RNA processing. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):897–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90338-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Inouye M. Yeast NSR1 protein that has structural similarity to mammalian nucleolin is involved in pre-rRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16252–16258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Kowalski L. R., Inouye M. Cold shock induction of yeast NSR1 protein and its role in pre-rRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16259–16265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Amalric F., Ghaffari S. H., Rao S. V., Dumbar T. S., Olson M. O. Protein and cDNA sequence of a glycine-rich, dimethylarginine-containing region located near the carboxyl-terminal end of nucleolin (C23 and 100 kDa). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9167–9173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Nucleolin, the major nucleolar protein of growing eukaryotic cells: an unusual protein structure revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Cook R. G., Ahn Y. S., Yeoman L. C., Busch H. Clustering of glycine and NG,NG-dimethylarginine in nucleolar protein C23. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6025–6028. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. An RNA polymerase I termination site can stimulate the adjacent ribosomal gene promoter by two distinct mechanisms in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1240–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noaillac-Depeyre J., Dupont M. A., Tichadou J. L., Gas N. The effect of adenosine analogue (DRB) on a major nucleolar phosphoprotein nucleolin. Biol Cell. 1989;67(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1989.tb03007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Spohn W. H., Busch H. Fibrillarin: a new protein of the nucleolus identified by autoimmune sera. Biol Cell. 1985;54(2):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Kirstein M. N., Wallace M. O. Limited proteolysis as a probe of the conformation and nucleic acid binding regions of nucleolin. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5682–5686. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Rivers Z. M., Thompson B. A., Kao W. Y., Case S. T. Interaction of nucleolar phosphoprotein C23 with cloned segments of rat ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3345–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrick L. R., Olson M. O., Busch H. Comparison of nucleolar proteins of normal rat liver and Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1316–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peculis B. A., Gall J. G. Localization of the nucleolar protein NO38 in amphibian oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Hardwick K. G., Lewis M. J. Sorting of soluble ER proteins in yeast. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1757–1762. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Nakagawa J., Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Nigg E. A. Identification of major nucleolar proteins as candidate mitotic substrates of cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90093-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Pollard K. M., Penning C. A., Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Busch H., Tan E. M. Monoclonal autoantibody from a (New Zealand black x New Zealand white)F1 mouse and some human scleroderma sera target an Mr 34,000 nucleolar protein of the U3 RNP particle. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):793–800. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Gall J. G. Monoclonal antibodies that recognize transcription unit proteins on newt lampbrush chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1047–1054. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapp M., Richter A., Weisshart K., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Wallace M. O., Kirstein M. N., Olson M. O. Characterization of a 48-kDa nucleic-acid-binding fragment of nucleolin. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;179(3):541–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U. Nuclear pore flow rate of ribosomal RNA and chain growth rate of its precursor during oogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1973 Jan;30(1):13–28. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Dargemont C., Kühn L. C., Nigg E. A. Nuclear export of proteins: the role of nuclear retention. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80051-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Nigg E. A. Protein localization to the nucleolus: a search for targeting domains in nucleolin. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jul;105(Pt 3):799–806. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Siomi M. C., Nussbaum R. L., Dreyfuss G. The protein product of the fragile X gene, FMR1, has characteristics of an RNA-binding protein. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90420-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Nakagawa T. Y., LeVan K., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure of human nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle C proteins: conservation of sequence and domain structures in heterogeneous nuclear RNA, mRNA, and pre-rRNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]