Abstract
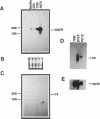
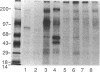
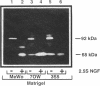
Although overexpression of the low-affinity p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) is frequently associated with advanced stages of human melanoma progression, the functional significance of this finding is unknown. We examined whether the degree of cell surface expression of p75NTR in human melanoma cell variants determines their extent of invasion stimulated by nerve growth factor (NGF). Treatment of MeWo melanoma cells or a metastatic spontaneous wheat germ agglutinin-resistant variant subline (70W) of MeWo cells with 2.5S NGF resulted in a dose-dependent enhancement of invasion through a reconstituted basement membrane. This effect was most pronounced with the 70W subline that exhibits brain-metastasizing potential in nude mice but was not found with a poorly metastatic MeWo variant subline (3S5). The expression of p75NTR as determined by Northern blotting and immunoprecipitation analysis of 125I-labeled cell surface proteins correlated with NGF-stimulated invasion. The MeWo melanoma sublines used in this study did not express p140proto-trkA mRNA or any p140proto-trkA variant transcripts including p70trkA as determined by Northern analysis and RT-PCR analysis. Thus, these melanoma cells would not be expected to form functional p75-p140 heterodimers or p140-p140 homodimers capable of transducing an NGF-generated signal to p140proto-trkA cytoplasmic substrates. These cells did express authentic p145trkC transcripts. However, NGF did not catalytically activate p145trkC receptors via increased tyrosine phosphorylation as would be expected if p145trkC participated in the signaling established by NGF. Furthermore, a NGF-stimulated purine-analogue-sensitive kinase activity was found to coimmunoprecipitate with p75NTR. This p75NTR-associated kinase may coordinate initial signaling events evoked by p75NTR ligand interaction. Addition of 2.5S NGF, at concentrations that should saturate cell surface p75NTR, to matrix-adherent cultures of human MeWo and 70W but not 3S5 melanoma cells suppressed the expression of 92-kDa type IV collagenase and stimulated the production of 72-kDa type IV collagenase in its fully active 68-kDa form. In the absence of p140proto-trkA, the matrix-dependent effects of NGF on metalloproteinase expression of brain-metastatic 70W melanoma cells suggest a signaling role for the low-affinity melanoma p75NTR receptor and its associated purine-analogue-sensitive kinase in signaling enhanced matrix penetration of NGF-rich stromal microenvironments such as the brain.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Iwamoto Y., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Aaronson S. A., Kozlowski J. M., McEwan R. N. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3239–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albino A. P., Davis B. M., Nanus D. M. Induction of growth factor RNA expression in human malignant melanoma: markers of transformation. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18):4815–4820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batistatou A., Volonté C., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor employs multiple pathways to induce primary response genes in PC12 cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):363–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battegay E. J., Raines E. W., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. TGF-beta induces bimodal proliferation of connective tissue cells via complex control of an autocrine PDGF loop. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90448-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. M., Sternberg D. W., Hempstead B. L., Chao M. V. The low-affinity p75 nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor mediates NGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7106–7110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. Keeping track of neurotrophin receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90540-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. Tissue localization of nerve growth factor and nerve growth factor receptors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;165:55–70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75747-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Bothwell M. A., Ross A. H., Koprowski H., Lanahan A. A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the human NGF receptor. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.3008331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabham P. W., Gallimore P. H., Grand R. J. Vitronectin is the major serum protein essential for NGF-mediated neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Oct;202(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90083-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. H., Rydel R. E., Connolly J. L., Greene L. A. PC12 cell mutants that possess low- but not high-affinity nerve growth factor receptors neither respond to nor internalize nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):830–843. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada J., Cavanaugh P. G., Lotan O., Nicolson G. L. Separable growth and migration factors for large-cell lymphoma cells secreted by microvascular endothelial cells derived from target organs for metastasis. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):349–354. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R., Birch M., Marshall J. F. Cell adhesion receptor expression during melanoma progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1991 Jun;10(2):115–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00049409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Kath R., Williams N., Valyi-Nagy I., Rodeck U. Growth-regulatory factors for normal, premalignant, and malignant human cells in vitro. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;54:213–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60812-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Thurin J., Balaban G., Bennicelli J. L., Herlyn D., Elder D. E., Bondi E., Guerry D., Nowell P., Clark W. H. Characteristics of cultured human melanocytes isolated from different stages of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5670–5676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuer J. G., Fatemie-Nainie S., Wheeler E. F., Bothwell M. Structure and developmental expression of the chicken NGF receptor. Dev Biol. 1990 Feb;137(2):287–304. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90255-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa M., Dennis J. W., Man S., Kerbel R. S. Isolation and characterization of spontaneous wheat germ agglutinin-resistant human melanoma mutants displaying remarkably different metastatic profiles in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 1;48(3):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Redmond S. M., Fu X. C., Saurer S. M., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Activation of the receptor kinase domain of the trk oncogene by recombination with two different cellular sequences. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):147–154. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., Li E., Huber L. J., Landis S. C., Sharpe A. H., Chao M. V., Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the gene encoding the low affinity NGF receptor p75 leads to deficits in the peripheral sensory nervous system. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):737–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90286-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C. M., Rodland K. D., Matrisian L., Magun B. E., Ciment G. NGF induction of the gene encoding the protease transin accompanies neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1587–1596. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menter D. G., Patton J. T., Updyke T. V., Kerbel R. S., Maamer M., McIntire L. V., Nicolson G. L. Transglutaminase stabilizes melanoma adhesion under laminar flow. Cell Biophys. 1991 Apr;18(2):123–143. doi: 10.1007/BF02989810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra G., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Identification and biochemical characterization of p70TRK, product of the human TRK oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6707–6711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Lotan D., Baig M. M., Carralero R. M., Wood W. R., Hendrix M. J., Lotan R. Inhibition by retinoic acid of type IV collagenolysis and invasion through reconstituted basement membrane by metastatic rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 1;49(7):1698–1706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Santos E. Induction by NGF of meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes expressing the trk proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):558–561. doi: 10.1126/science.1850550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Cancer metastasis: tumor cell and host organ properties important in metastasis to specific secondary sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 15;948(2):175–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(88)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Cancer progression and growth: relationship of paracrine and autocrine growth mechanisms to organ preference of metastasis. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Feb;204(2):171–180. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis: tumor and host properties and the role of oncogenes and suppressor genes. Curr Opin Oncol. 1991 Feb;3(1):75–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskam R., Coulier F., Ernst M., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Frequent generation of oncogenes by in vitro recombination of TRK protooncogene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J. K., Didolkar M. S., Pickren J. W., Moore R. H. Metastatic pattern of malignant melanoma. A study of 216 autopsy cases. Am J Surg. 1978 Jun;135(6):807–810. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Ayer-Le Lievre C., Söder O., Villar M. J., Metsis M., Olson L., Ritzen M., Hökfelt T. Expression of beta-nerve growth factor receptor mRNA in Sertoli cells downregulated by testosterone. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):704–707. doi: 10.1126/science.2154035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabizadeh S., Oh J., Zhong L. T., Yang J., Bitler C. M., Butcher L. L., Bredesen D. E. Induction of apoptosis by the low-affinity NGF receptor. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):345–348. doi: 10.1126/science.8332899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke M. J., Misko T. P., Hsu C., Herzenberg L. A., Shooter E. M. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the rat nerve growth factor receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):593–597. doi: 10.1038/325593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. H., Grob P., Bothwell M., Elder D. E., Ernst C. S., Marano N., Ghrist B. F., Slemp C. C., Herlyn M., Atkinson B. Characterization of nerve growth factor receptor in neural crest tumors using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6681–6685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariola H., Saarma M., Sainio K., Arumäe U., Palgi J., Vaahtokari A., Thesleff I., Karavanov A. Dependence of kidney morphogenesis on the expression of nerve growth factor receptor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.1658930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulfas P., Soppet D., Escandon E., Tessarollo L., Mendoza-Ramirez J. L., Rosenthal A., Nikolics K., Parada L. F. The rat trkC locus encodes multiple neurogenic receptors that exhibit differential response to neurotrophin-3 in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):975–990. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90212-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela D. M., Maisonpierre P. C., Glass D. J., Rojas E., Nuñez L., Kong Y., Gies D. R., Stitt T. N., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. Alternative forms of rat TrkC with different functional capabilities. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volonté C., Greene L. A. 6-Methylmercaptopurine riboside is a potent and selective inhibitor of nerve growth factor-activated protein kinase N. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):700–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volonté C., Greene L. A. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells: dissection by purine analogues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11050–11055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volonté C., Ross A. H., Greene L. A. Association of a purine-analogue-sensitive protein kinase activity with p75 nerve growth factor receptors. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):71–78. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt S., Shooter E. M., Davies A. M. Expression of the NGF receptor gene in sensory neurons and their cutaneous targets prior to and during innervation. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90054-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Schlessinger J., Chao M. V. Chimeric NGF-EGF receptors define domains responsible for neuronal differentiation. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1850551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zupan A. A., Osborne P. A., Smith C. E., Siegel N. R., Leimgruber R. M., Johnson E. M., Jr Identification, purification, and characterization of truncated forms of the human nerve growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11714–11720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]