Abstract
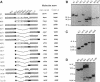
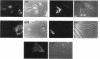
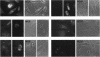
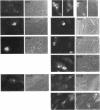
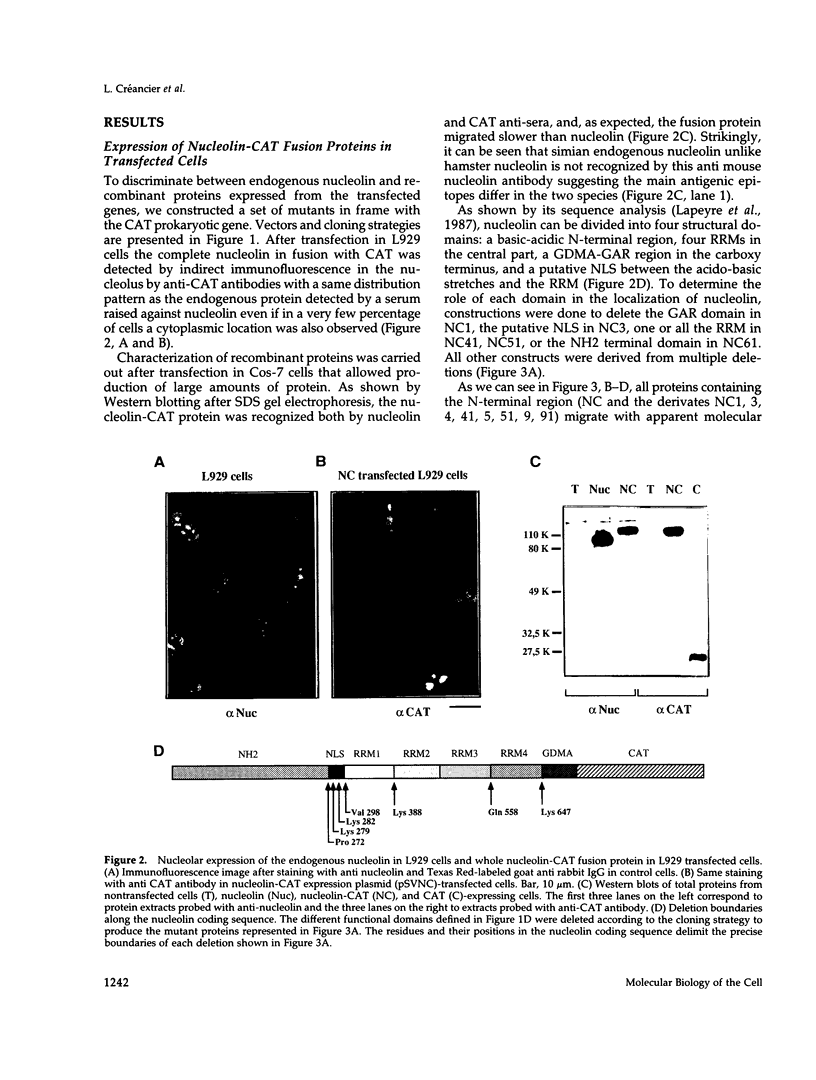
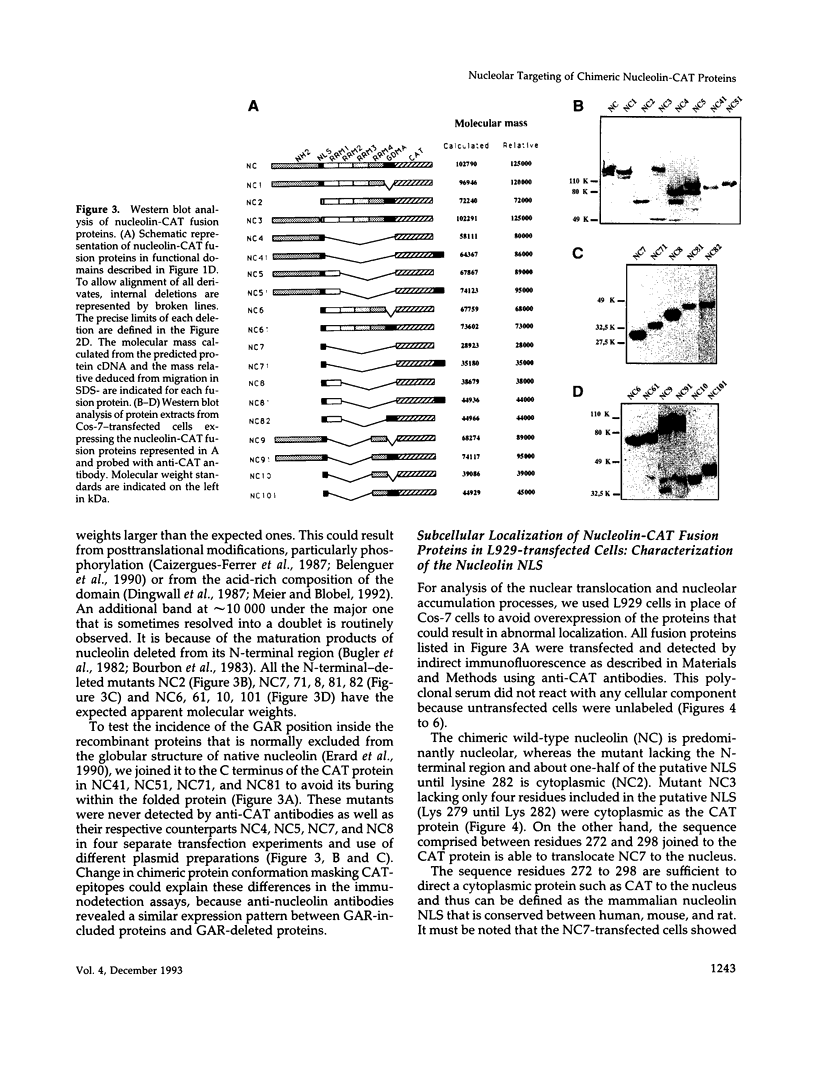
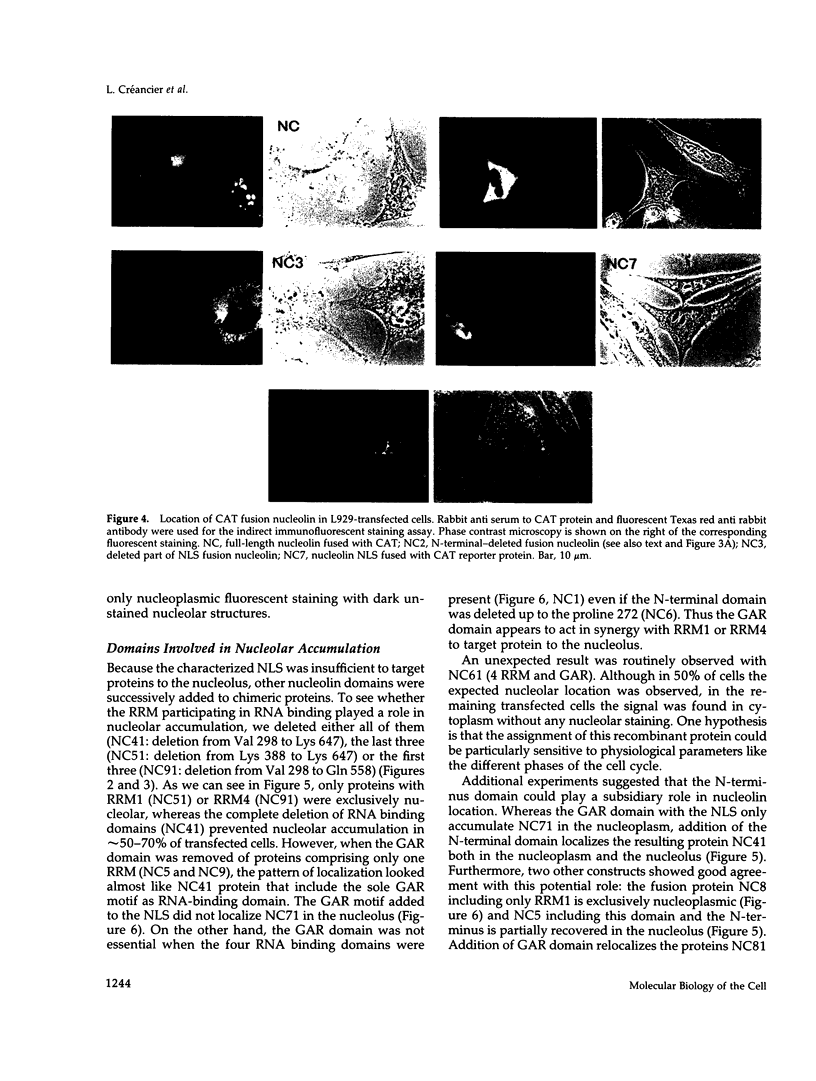
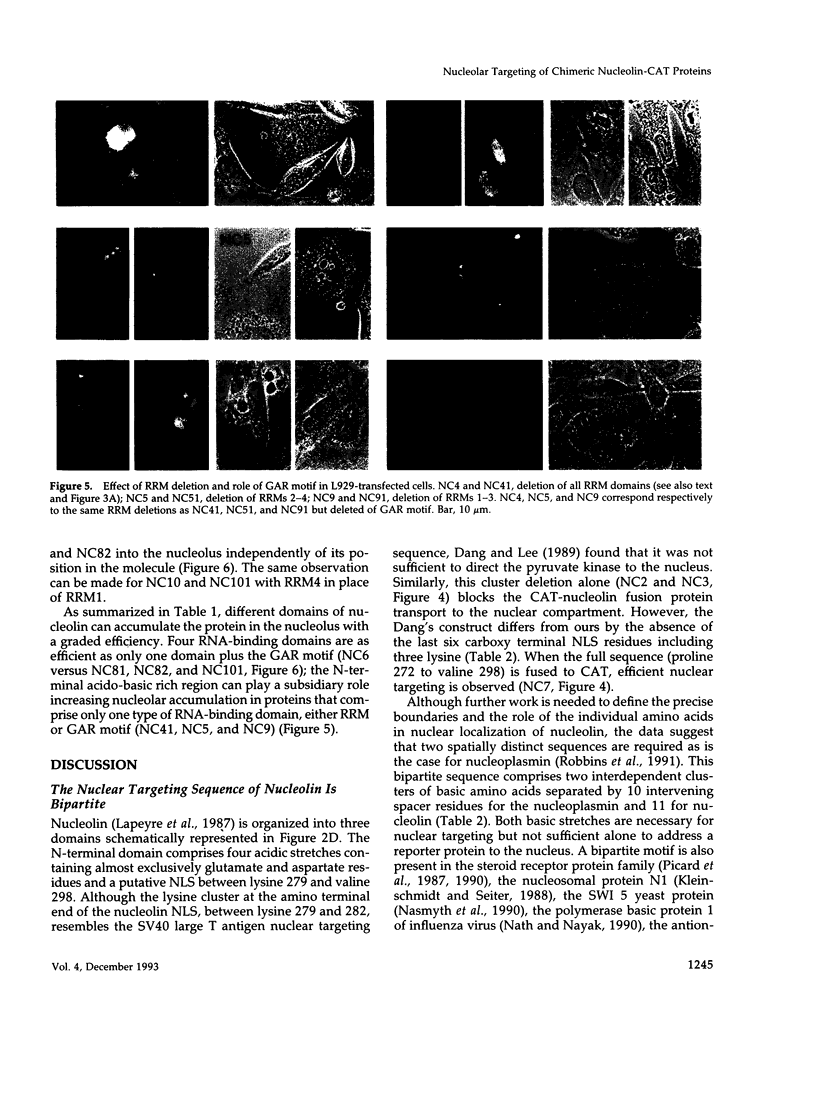
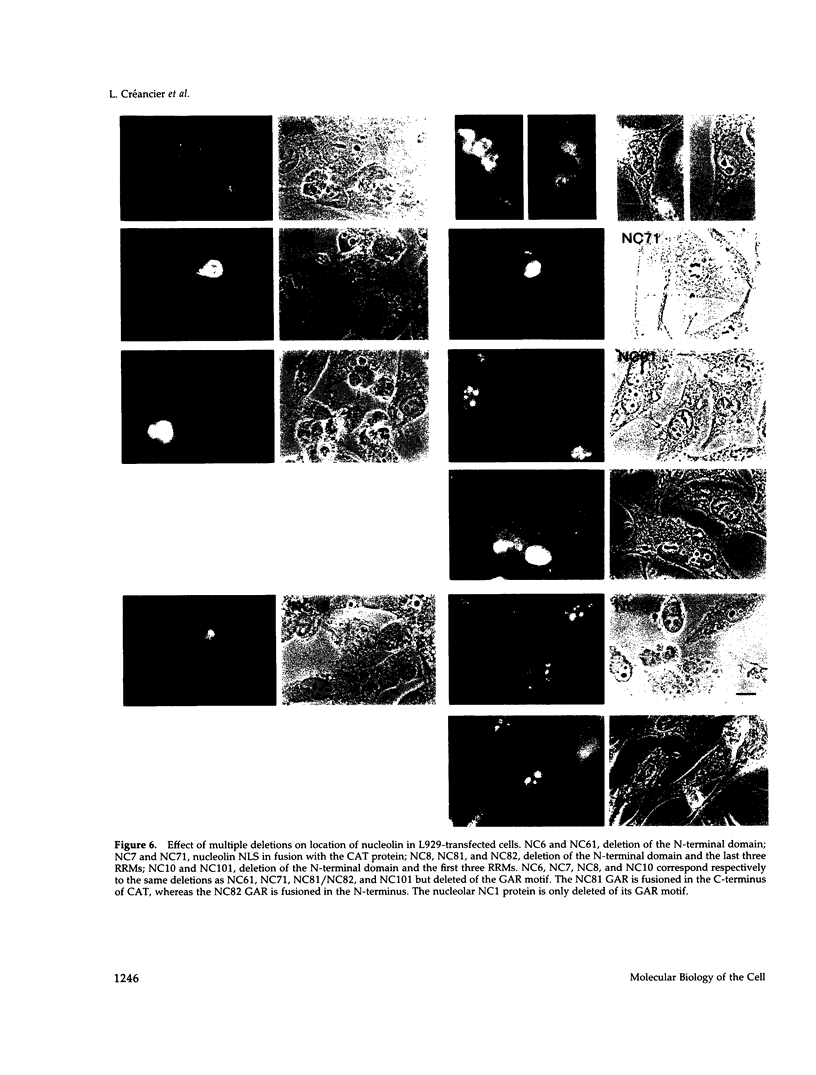
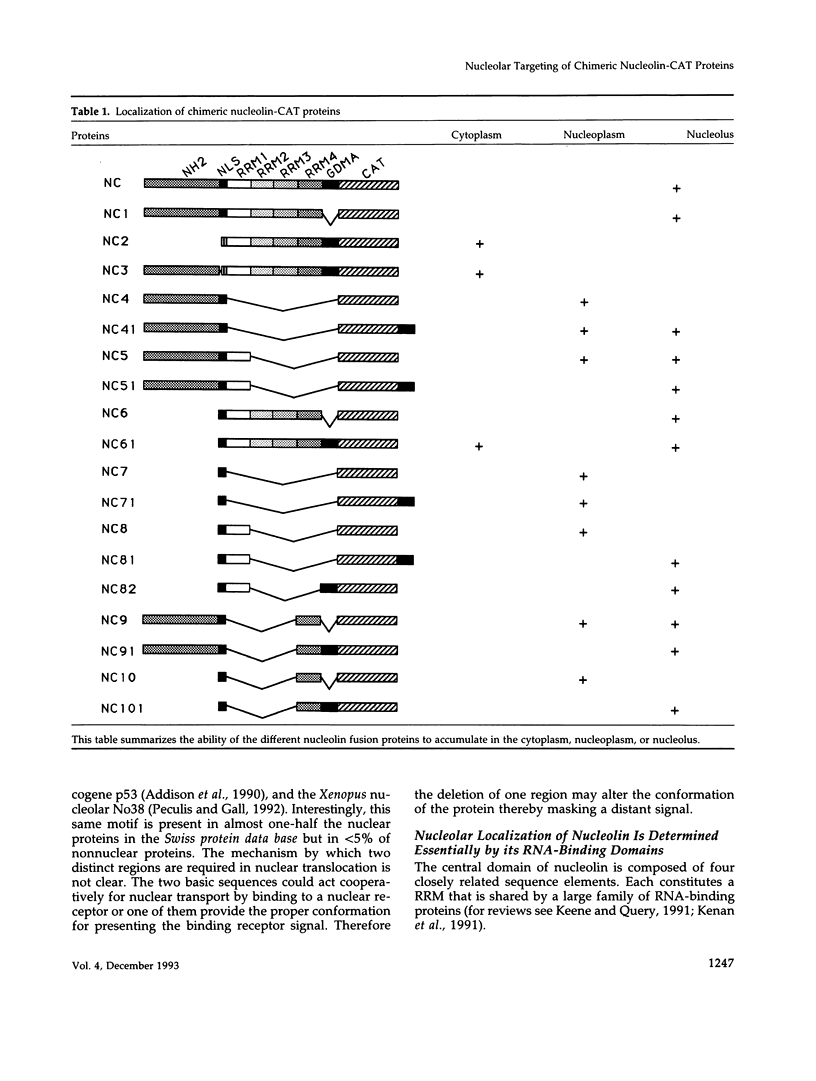
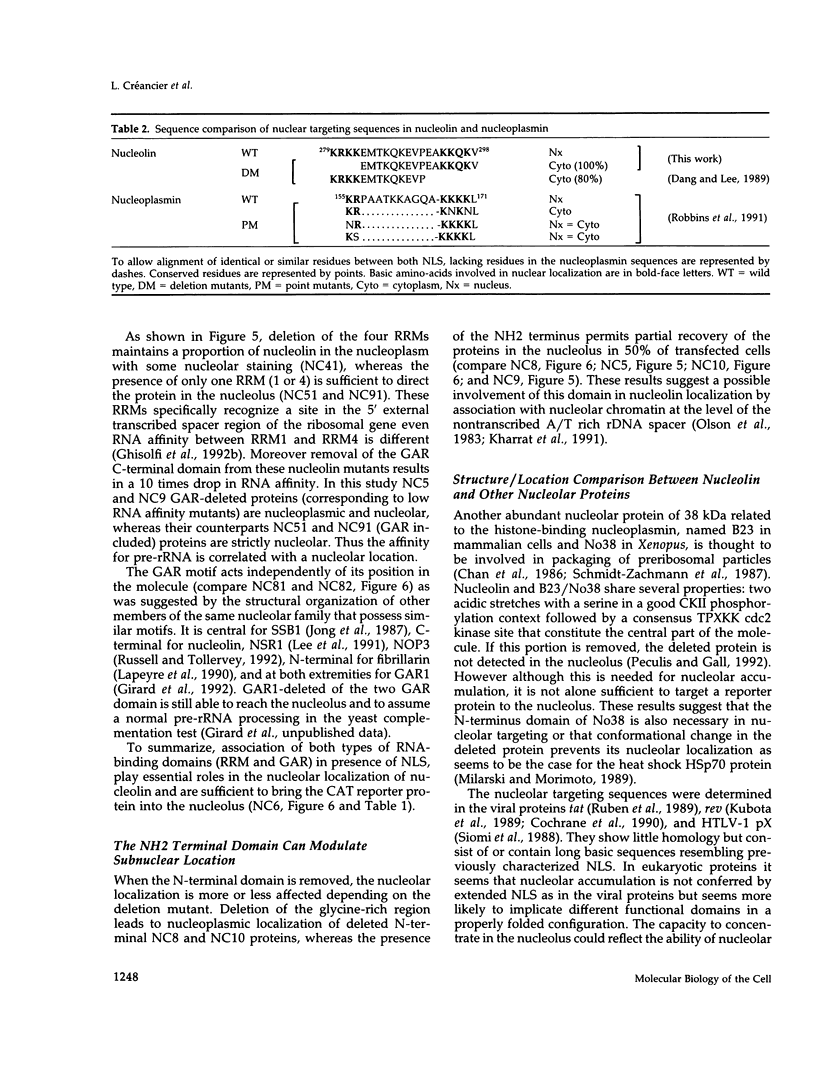
Nucleolin (713 aa), a major nucleolar protein, presents two structural domains: a N-terminus implicated in interaction with chromatin and a C-terminus containing four RNA-binding domains (RRMs) and a glycine/arginine-rich domain mainly involved in pre-rRNA packaging. Furthermore, nucleolin was shown to shuttle between cytoplasm and nucleolus. To get an insight on the nature of nuclear and nucleolar localization signals, a set of nucleolin deletion mutants in fusion with the prokaryotic chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) were constructed, and the resulting chimeric proteins were recognized by anti-CAT antibodies. First, a nuclear location signal bipartite and composed of two short basic stretches separated by eleven residues was characterized. Deletion of either motifs renders the protein cytoplasmic. Second, by deleting one or more domains implicated in nucleolin association either with DNA, RNA, or proteins, we demonstrated that nucleolar accumulation requires, in addition to the nuclear localization sequence, at least two of the five RRMs in presence or absence of N-terminus. However, in presence of only one RRM the N-terminus allowed a partial targeting of the chimeric protein to the nucleolus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison C., Jenkins J. R., Stürzbecher H. W. The p53 nuclear localisation signal is structurally linked to a p34cdc2 kinase motif. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belenguer P., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Amalric F. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of nucleolin by p34cdc2 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3607–3618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bugler B., Amalric F. Interrelations between the maturation of a 100 kDa nucleolar protein and pre rRNA synthesis in CHO cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3025–3035. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H. M., Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Zalta J. P. Maturation of a 100 kDa protein associated with preribosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00777472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Amalric F., Prats H. Alternative initiation of translation determines cytoplasmic or nuclear localization of basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):573–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Bourbon H., Lapeyre B., Wallace M. O., Chang J. H., Amalric F., Olson M. O. RNA binding fragments from nucleolin contain the ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):10922–10925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bouche G., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Detection and localization of a class of proteins immunologically related to a 100-kDa nucleolar protein. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):475–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caizergues-Ferrer M., Belenguer P., Lapeyre B., Amalric F., Wallace M. O., Olson M. O. Phosphorylation of nucleolin by a nucleolar type NII protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7876–7883. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. K., Chan W. Y., Yung B. Y., Cook R. G., Aldrich M. B., Ku D., Goldknopf I. L., Busch H. Amino acid sequence of a specific antigenic peptide of protein B23. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14335–14341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Identification of sequences important in the nucleolar localization of human immunodeficiency virus Rev: relevance of nucleolar localization to function. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):881–885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.881-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV tat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18019–18023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Dilworth S. M., Black S. J., Kearsey S. E., Cox L. S., Laskey R. A. Nucleoplasmin cDNA sequence reveals polyglutamic acid tracts and a cluster of sequences homologous to putative nuclear localization signals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard M. S., Belenguer P., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Pantaloni A., Amalric F. A major nucleolar protein, nucleolin, induces chromatin decondensation by binding to histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard M., Lakhdar-Ghazal F., Amalric F. Repeat peptide motifs which contain beta-turns and modulate DNA condensation in chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 20;191(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gas N., Escande M. L., Stevens B. J. Immunolocalization of the 100 kDa nucleolar protein during the mitotic cycle in CHO cells. Biol Cell. 1985;53(3):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisolfi L., Joseph G., Amalric F., Erard M. The glycine-rich domain of nucleolin has an unusual supersecondary structure responsible for its RNA-helix-destabilizing properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2955–2959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisolfi L., Kharrat A., Joseph G., Amalric F., Erard M. Concerted activities of the RNA recognition and the glycine-rich C-terminal domains of nucleolin are required for efficient complex formation with pre-ribosomal RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):541–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P., Lehtonen H., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Tollervey D., Lapeyre B. GAR1 is an essential small nucleolar RNP protein required for pre-rRNA processing in yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):673–682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera A. H., Olson M. O. Association of protein C23 with rapidly labeled nucleolar RNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6258–6264. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügle B., Scheer U., Franke W. W. Ribocharin: a nuclear Mr 40,000 protein specific to precursor particles of the large ribosomal subunit. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):615–627. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong A. Y., Clark M. W., Gilbert M., Oehm A., Campbell J. L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SSB1 protein and its relationship to nucleolar RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2947–2955. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan G. At the heart of the nucleolus. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):489–490. doi: 10.1038/329489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Query C. C. Nuclear RNA-binding proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:179–202. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharrat A., Derancourt J., Dorée M., Amalric F., Erard M. Synergistic effect of histone H1 and nucleolin on chromatin condensation in mitosis: role of a phosphorylated heteromer. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10329–10336. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Seiter A. Identification of domains involved in nuclear uptake and histone binding of protein N1 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1605–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota S., Siomi H., Satoh T., Endo S., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Functional similarity of HIV-I rev and HTLV-I rex proteins: identification of a new nucleolar-targeting signal in rev protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90767-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Nucleolin, the major nucleolar protein of growing eukaryotic cells: an unusual protein structure revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Mariottini P., Mathieu C., Ferrer P., Amaldi F., Amalric F., Caizergues-Ferrer M. Molecular cloning of Xenopus fibrillarin, a conserved U3 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein recognized by antisera from humans with autoimmune disease. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):430–434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Mélèse T. Identification and characterization of a nuclear localization sequence-binding protein in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8808–8812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Xue Z. X., Mélèse T. The NSR1 gene encodes a protein that specifically binds nuclear localization sequences and has two RNA recognition motifs. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Cook R. G., Ahn Y. S., Yeoman L. C., Busch H. Clustering of glycine and NG,NG-dimethylarginine in nucleolar protein C23. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6025–6028. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Hisatake K., Kondo T., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Nishimura T., Muramatsu M. Mouse rRNA gene transcription factor mUBF requires both HMG-box1 and an acidic tail for nucleolar accumulation: molecular analysis of the nucleolar targeting mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3695–3704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier U. T., Blobel G. Nopp140 shuttles on tracks between nucleolus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90539-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Morimoto R. I. Mutational analysis of the human HSP70 protein: distinct domains for nucleolar localization and adenosine triphosphate binding. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1947–1962. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Adolf G., Lydall D., Seddon A. The identification of a second cell cycle control on the HO promoter in yeast: cell cycle regulation of SW15 nuclear entry. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):631–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90110-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath S. T., Nayak D. P. Function of two discrete regions is required for nuclear localization of polymerase basic protein 1 of A/WSN/33 influenza virus (H1 N1). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4139–4145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Spohn W. H., Busch H. Fibrillarin: a new protein of the nucleolus identified by autoimmune sera. Biol Cell. 1985;54(2):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Rivers Z. M., Thompson B. A., Kao W. Y., Case S. T. Interaction of nucleolar phosphoprotein C23 with cloned segments of rat ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3345–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peculis B. A., Gall J. G. Localization of the nucleolar protein NO38 in amphibian oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Kumar V., Chambon P., Yamamoto K. R. Signal transduction by steroid hormones: nuclear localization is differentially regulated in estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. Cell Regul. 1990 Feb;1(3):291–299. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Perkins A., Purcell R., Joung K., Sia R., Burghoff R., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.1-8.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell I. D., Tollervey D. NOP3 is an essential yeast protein which is required for pre-rRNA processing. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):737–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Hügle-Dörr B., Franke W. W. A constitutive nucleolar protein identified as a member of the nucleoplasmin family. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1881–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Nam S. H., Nosaka T., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Ochs R. L., Busch H. Silver staining, immunofluorescence, and immunoelectron microscopic localization of nucleolar phosphoproteins B23 and C23. Chromosoma. 1984;90(2):139–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00292451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]