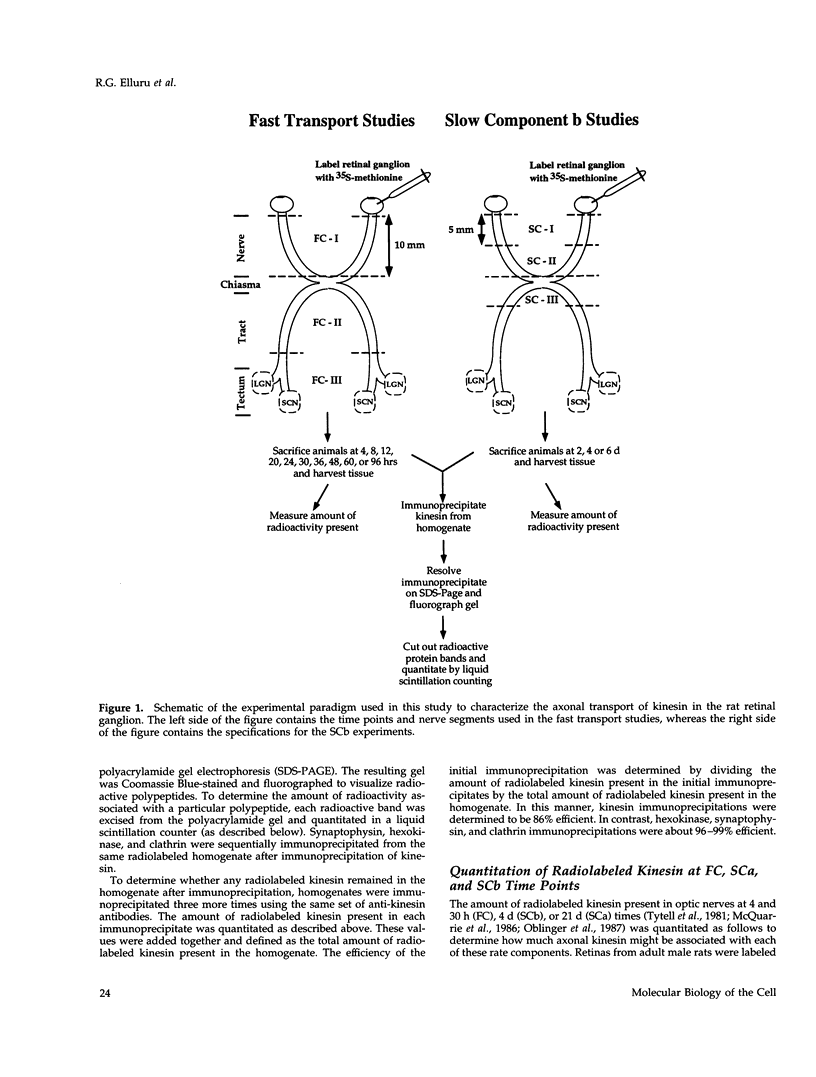
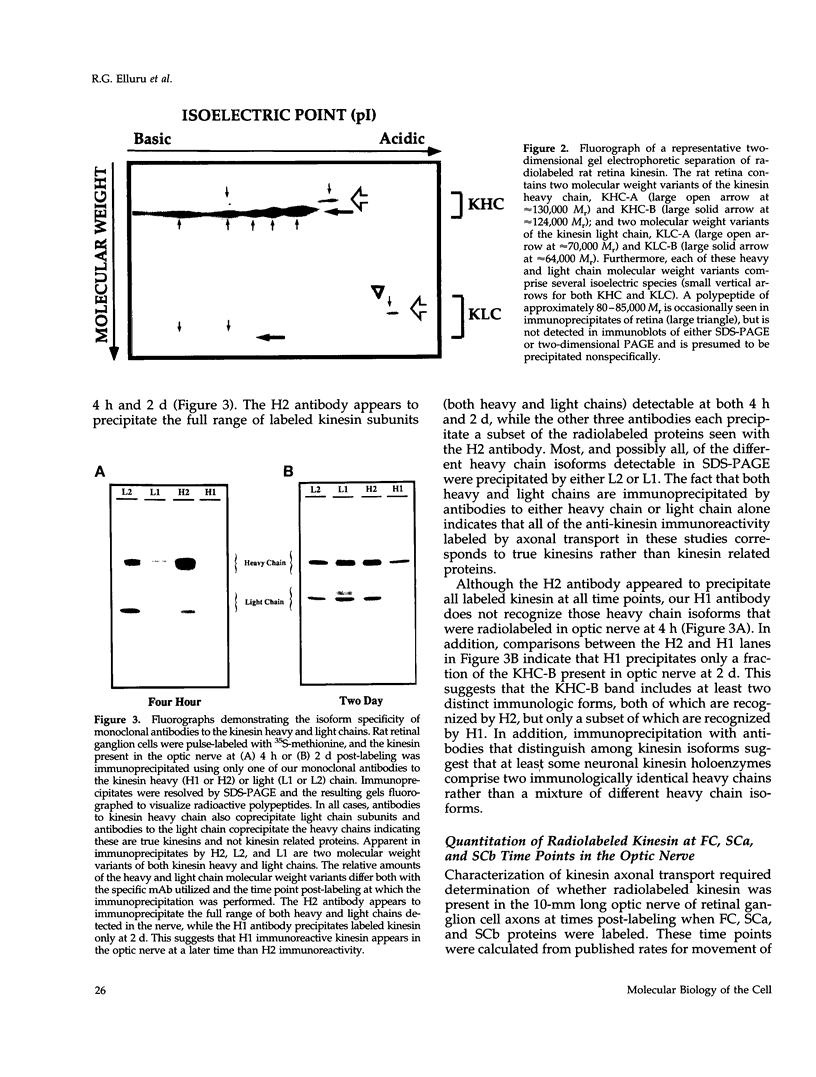
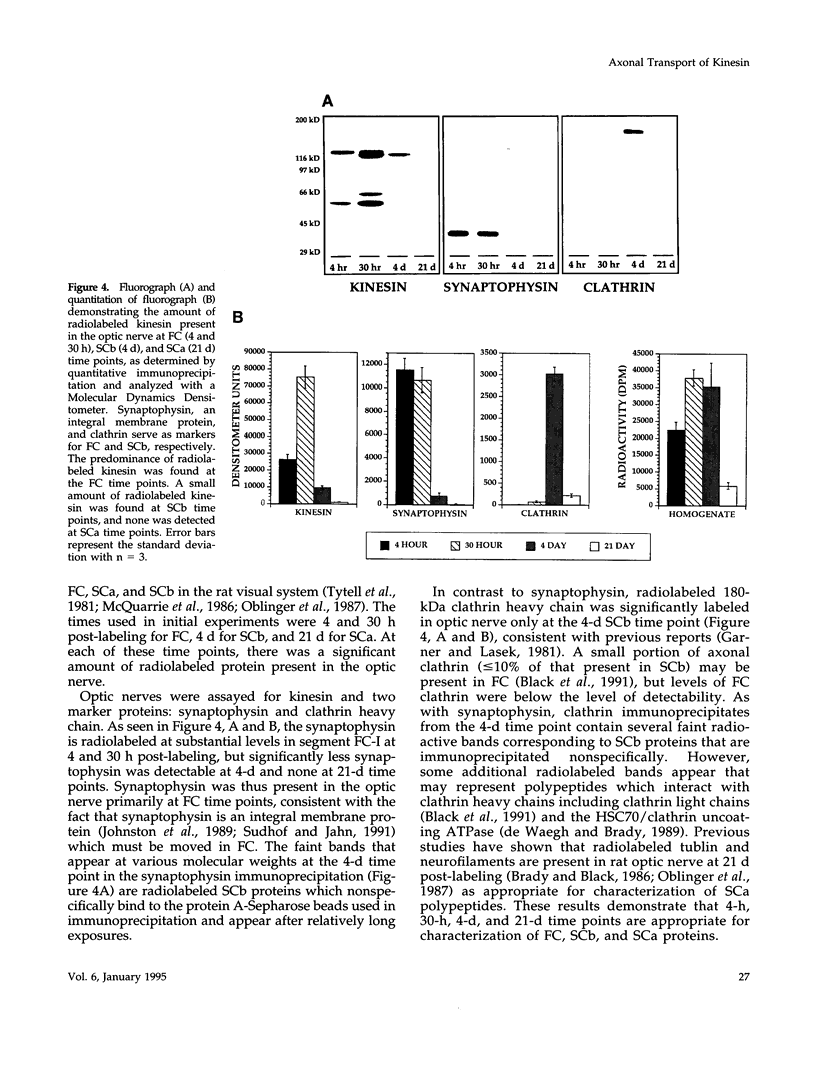
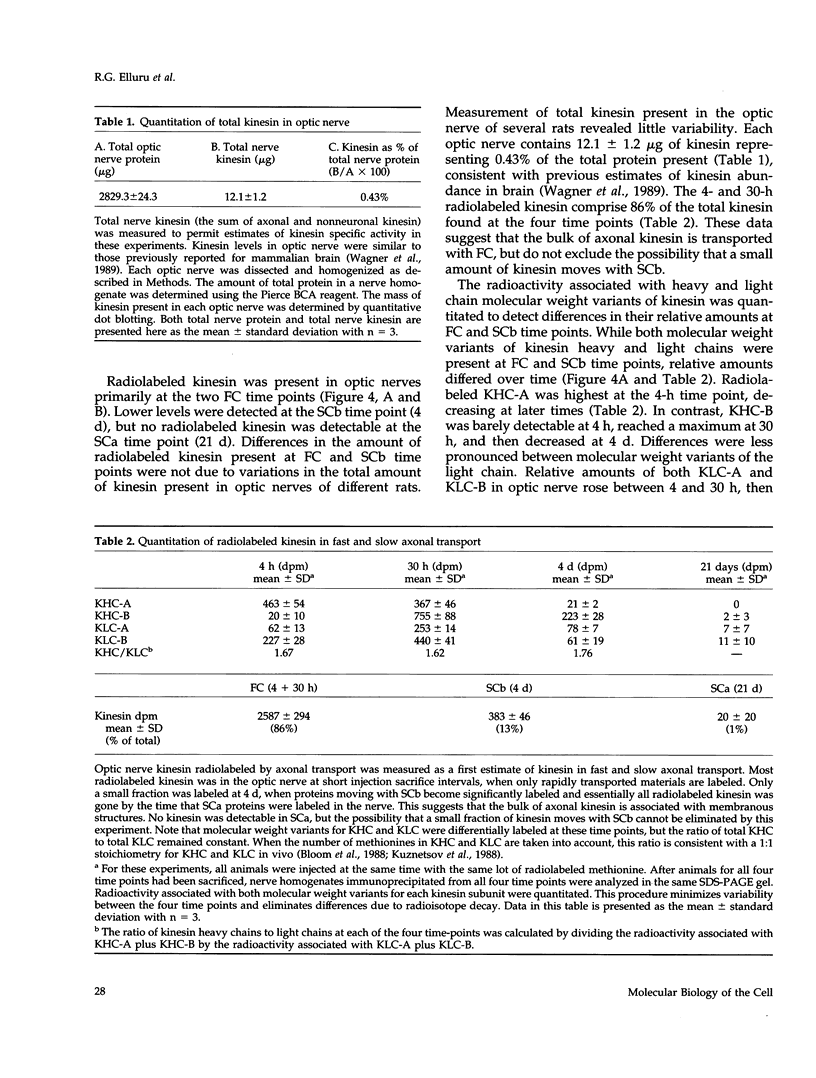
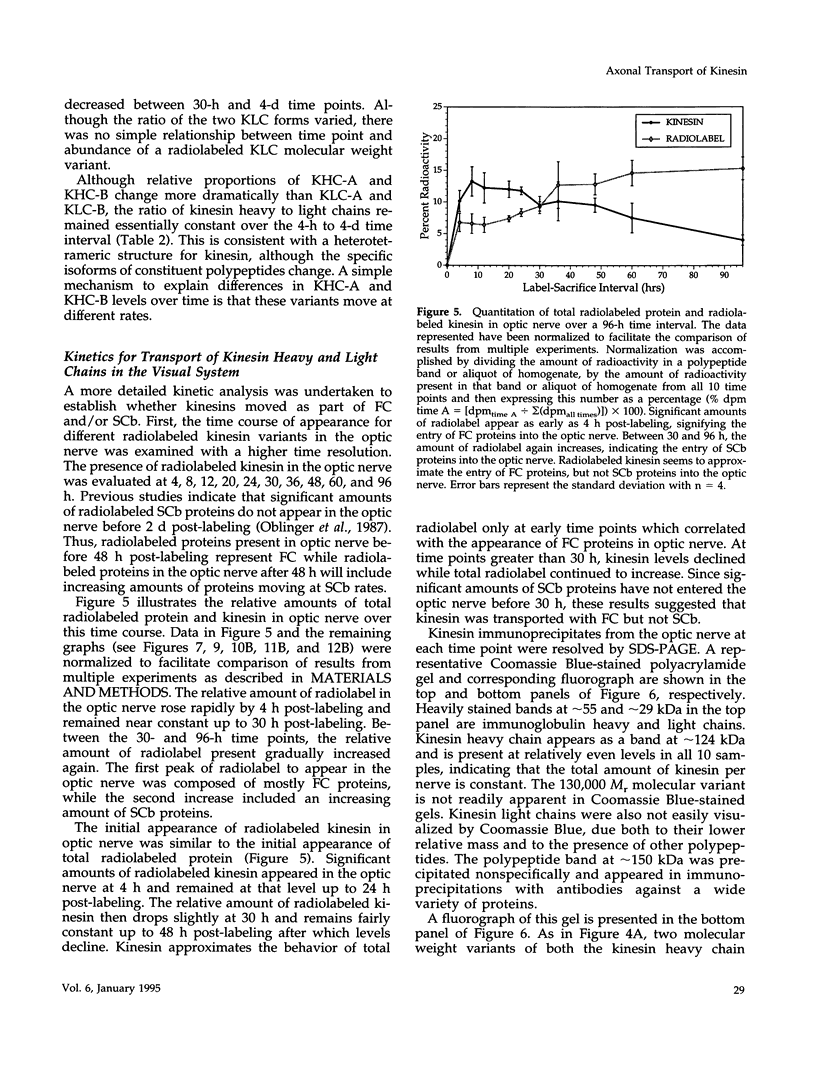
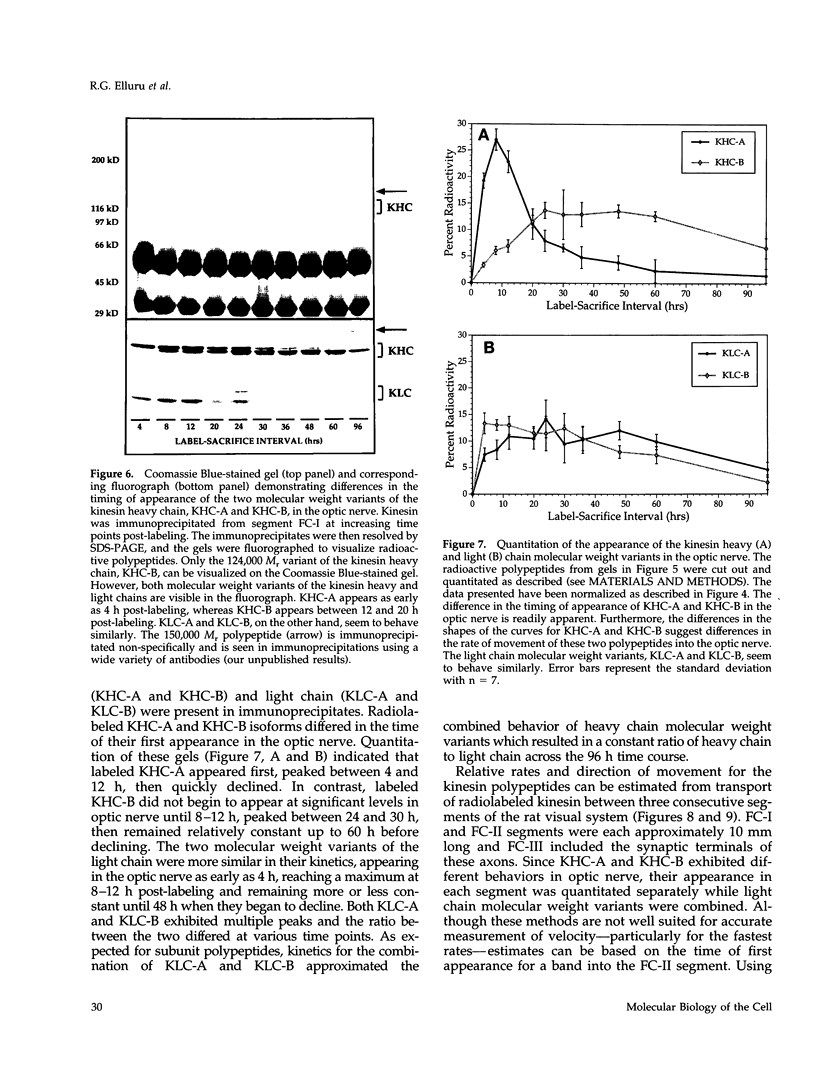
Abstract
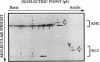
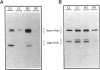
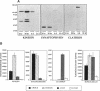
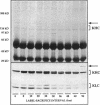
The mechanochemical ATPase kinesin is thought to move membrane-bounded organelles along microtubules in fast axonal transport. However, fast transport includes several classes of organelles moving at rates that differ by an order of magnitude. Further, the fact that cytoplasmic forms of kinesin exist suggests that kinesins might move cytoplasmic structures such as the cytoskeleton. To define cellular roles for kinesin, the axonal transport of kinesin was characterized. Retinal proteins were pulse-labeled, and movement of radiolabeled kinesin through optic nerve and tract into the terminals was monitored by immunoprecipitation. Heavy and light chains of kinesin appeared in nerve and tract at times consistent with fast transport. Little or no kinesin moved with slow axonal transport indicating that effectively all axonal kinesin is associated with membranous organelles. Both kinesin heavy chain molecular weight variants of 130,000 and 124,000 M(r) (KHC-A and KHC-B) moved in fast anterograde transport, but KHC-A moved at 5-6 times the rate of KHC-B. KHC-A cotransported with the synaptic vesicle marker synaptophysin, while a portion of KHC-B cotransported with the mitochondrial marker hexokinase. These results suggest that KHC-A is enriched on small tubulovesicular structures like synaptic vesicles and that at least one form of KHC-B is predominantly on mitochondria. Biochemical specialization may target kinesins to appropriate organelles and facilitate differential regulation of transport.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Metuzals J., Tasaki I., Brady S. T., Gilbert S. P. Fast axonal transport in squid giant axon. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6183744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D., Weiss D. G., Hayden J. H., Brown D. T., Fujiwake H., Simpson M. Gliding movement of and bidirectional transport along single native microtubules from squid axoplasm: evidence for an active role of microtubules in cytoplasmic transport. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1736–1752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaratunga A., Morin P. J., Kosik K. S., Fine R. E. Inhibition of kinesin synthesis and rapid anterograde axonal transport in vivo by an antisense oligonucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17427–17430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balczon R., Overstreet K. A., Zinkowski R. P., Haynes A., Appel M. The identification, purification, and characterization of a pancreatic beta-cell form of the microtubule adenosine triphosphatase kinesin. Endocrinology. 1992 Jul;131(1):331–336. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.1.1612013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M. M., Chestnut M. H., Pleasure I. T., Keen J. H. Stable clathrin: uncoating protein (hsc70) complexes in intact neurons and their axonal transport. J Neurosci. 1991 May;11(5):1163–1172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-05-01163.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T. Native structure and physical properties of bovine brain kinesin and identification of the ATP-binding subunit polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3409–3416. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T. A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):73–75. doi: 10.1038/317073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Black M. M. Axonal transport of microtubule proteins: cytotypic variation of tubulin and MAPs in neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:199–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Lasek R. J., Allen R. D. Fast axonal transport in extruded axoplasm from squid giant axon. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1129–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.6183745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Lasek R. J., Allen R. D. Video microscopy of fast axonal transport in extruded axoplasm: a new model for study of molecular mechanisms. Cell Motil. 1985;5(2):81–101. doi: 10.1002/cm.970050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Lasek R. J. Axonal transport: a cell-biological method for studying proteins that associate with the cytoskeleton. Methods Cell Biol. 1982;25(Pt B):365–398. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Lasek R. J. Nerve-specific enolase and creatine phosphokinase in axonal transport: soluble proteins and the axoplasmic matrix. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S. A monoclonal antibody against kinesin inhibits both anterograde and retrograde fast axonal transport in squid axoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1061–1065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Tytell M., Heriot K., Lasek R. J. Axonal transport of calmodulin: a physiologic approach to identification of long-term associations between proteins. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):607–614. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Tytell M., Lasek R. J. Axonal tubulin and axonal microtubules: biochemical evidence for cold stability. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1716–1724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr J. L., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Slaughter C. A., Brady S. T. Molecular genetics of kinesin light chains: generation of isoforms by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10114–10118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström A. B., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T. The axonal transport motor 'kinesin' is bound to anterogradely transported organelles: quantitative cytofluorimetric studies of fast axonal transport in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991 Apr;141(4):469–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath K. R., Trimbur G. M., Burgess D. R. Molecular motors are differentially distributed on Golgi membranes from polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):661–675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Niclas J., Vale R. D., Banker G., Kosik K. S. Suppression of kinesin expression in cultured hippocampal neurons using antisense oligonucleotides. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):595–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner J. A., Lasek R. J. Clathrin is axonally transported as part of slow component b: the microfilament complex. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):172–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner J. A., Lasek R. J. Cohesive axonal transport of the slow component b complex of polypeptides. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1824–1835. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01824.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. With apologies to scheherazade: tails of 1001 kinesin motors. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:319–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Levitt J. D., Wagner D. D. Characterization of alpha 2 beta 2 and alpha 2 forms of kinesin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):810–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Pfister K. K., Yorifuji H., Wagner M. C., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Submolecular domains of bovine brain kinesin identified by electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody decoration. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):867–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Sato-Yoshitake R., Kobayashi N., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Kinesin associates with anterogradely transported membranous organelles in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):295–302. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J. Phosphorylation of neuronal kinesin heavy and light chains in vivo. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):2265–2275. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J., Swanson J. A. Radial extension of macrophage tubular lysosomes supported by kinesin. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):864–866. doi: 10.1038/346864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J. The distribution, abundance and subcellular localization of kinesin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2335–2342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. M., Brady S. T., van der Kooy D., Connolly J. A. A unique tubulin antibody which disrupts particle movement in squid axoplasm. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;7(2):110–115. doi: 10.1002/cm.970070203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Transmembrane topography and evolutionary conservation of synaptophysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Gelfand V. I. Bovine brain kinesin is a microtubule-activated ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8530–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Vaisberg E. A., Shanina N. A., Magretova N. N., Chernyak V. Y., Gelfand V. I. The quaternary structure of bovine brain kinesin. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):353–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02820.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leopold P. L., McDowall A. W., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Association of kinesin with characterized membrane-bounded organelles. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;23(1):19–33. doi: 10.1002/cm.970230104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz T., Willard M. Subcellular fractionation of intra-axonally transport polypeptides in the rabbit visual system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthies H. J., Miller R. J., Palfrey H. C. Calmodulin binding to and cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of kinesin light chains modulate kinesin ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11176–11187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuarrie I. G., Brady S. T., Lasek R. J. Diversity in the axonal transport of structural proteins: major differences between optic and spinal axons in the rat. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1593–1605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01593.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin P. J., Johnson R. J., Fine R. E. Kinesin is rapidly transported in the optic nerve as a membrane associated protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 14;1146(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90366-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbors B. W., Williams R. C., Jr, McIntosh J. R. Localization of kinesin in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1193–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niclas J., Navone F., Hom-Booher N., Vale R. D. Cloning and localization of a conventional kinesin motor expressed exclusively in neurons. Neuron. 1994 May;12(5):1059–1072. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblinger M. M., Brady S. T., McQuarrie I. G., Lasek R. J. Cytotypic differences in the protein composition of the axonally transported cytoskeleton in mammalian neurons. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):453–462. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblinger M. M., Foe L. G., Kwiatkowska D., Kemp R. G. Phosphofructokinase in the rat nervous system: regional differences in activity and characteristics of axonal transport. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Sep;21(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490210105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papasozomenos S. C., Binder L. I. Phosphorylation determines two distinct species of Tau in the central nervous system. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(3):210–226. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister K. K., Wagner M. C., Stenoien D. L., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Monoclonal antibodies to kinesin heavy and light chains stain vesicle-like structures, but not microtubules, in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1453–1463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato-Yoshitake R., Yorifuji H., Inagaki M., Hirokawa N. The phosphorylation of kinesin regulates its binding to synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23930–23936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Bechtold R. Kinesin is bound with high affinity to squid axon organelles that move to the plus-end of microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):389–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Porter M. E., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Identification of kinesin in sea urchin eggs, and evidence for its localization in the mitotic spindle. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):483–486. doi: 10.1038/318483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytell M., Black M. M., Garner J. A., Lasek R. J. Axonal transport: each major rate component reflects the movement of distinct macromolecular complexes. Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):179–181. doi: 10.1126/science.6169148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urrutia R., McNiven M. A., Albanesi J. P., Murphy D. B., Kachar B. Purified kinesin promotes vesicle motility and induces active sliding between microtubules in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6701–6705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Copurification of kinesin polypeptides with microtubule-stimulated Mg-ATPase activity and kinetic analysis of enzymatic properties. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(4):195–215. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Purification of kinesin from bovine brain and assay of microtubule-stimulated ATPase activity. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:157–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96016-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Cowan W. M., Vagelos P. R. The polypeptide composition of intra-axonally transported proteins: evidence for four transport velocities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2183–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. D., Henson J. H., Wedaman K. P., Willy P. J., Morand J. N., Scholey J. M. Subcellular localization and sequence of sea urchin kinesin heavy chain: evidence for its association with membranes in the mitotic apparatus and interphase cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):817–833. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waegh S., Brady S. T. Axonal transport of a clathrin uncoating ATPase (HSC70): a role for HSC70 in the modulation of coated vesicle assembly in vivo. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Aug;23(4):433–440. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490230409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]