Abstract
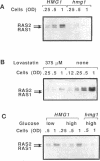
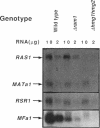
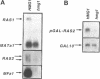
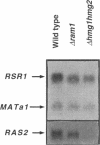
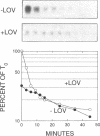
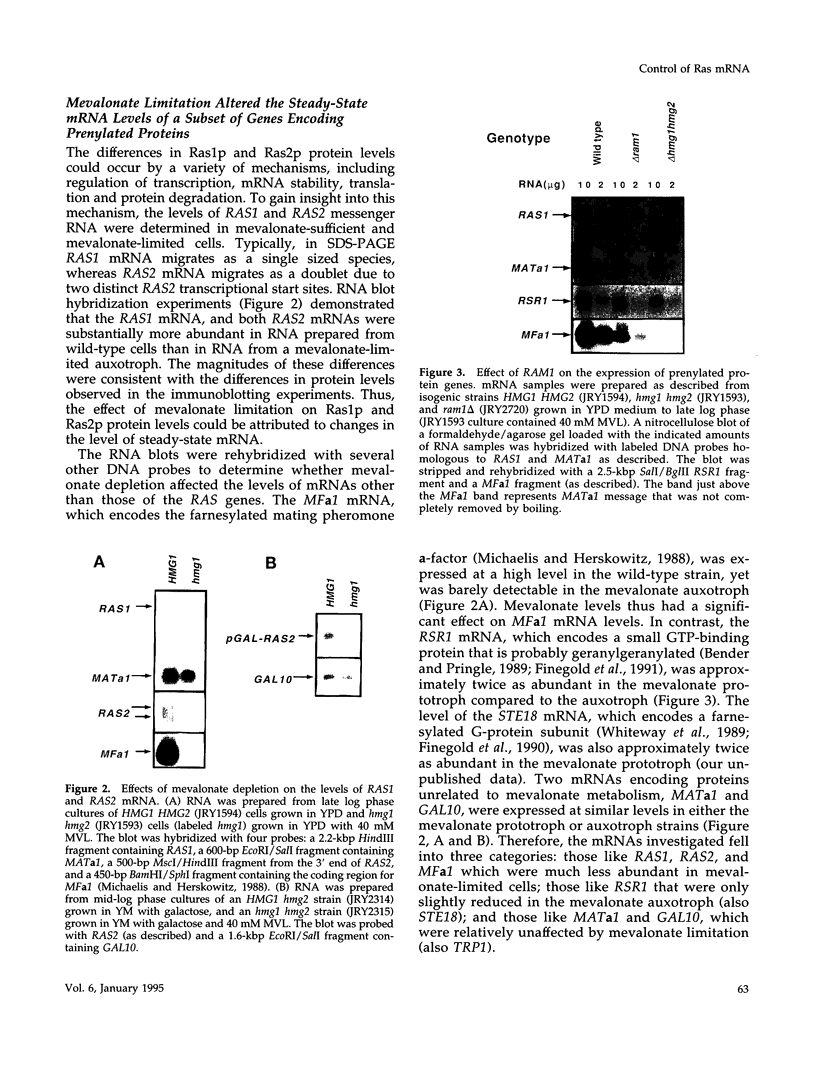
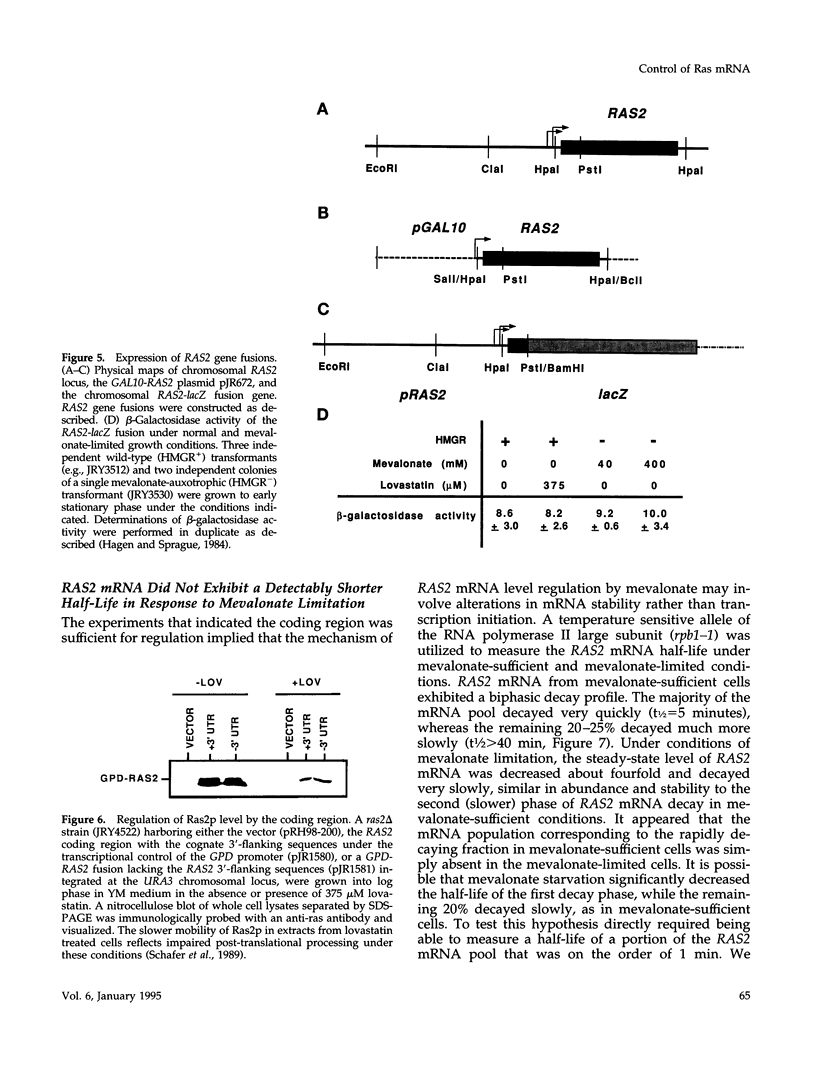
The ability of Ras proteins to initiate eukaryotic cell proliferation requires the post-translational attachment of a farnesyl group, an isoprenoid lipid moiety derived from mevalonate, to the carboxyl-terminus of the protein. This modification is essential for the subsequent processing and intracellular targeting of the Ras protein. Here we report that mevalonate is also required for the efficient synthesis of Ras proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Depletion of intracellular mevalonate resulted in decreased steady-state levels of Ras1p and Ras2p, an effect that was mediated at the level of mRNA accumulation. The sequences controlling the response of RAS2 mRNA level to mevalonate availability, mapped to the coding region of the RAS2 gene. Mevalonate starvation also had a significant effect on the expression of some, but not all, genes encoding prenylated proteins. The regulatory effect on RAS2 mRNA did not require a functional farnesyl transferase. These results uncover a novel regulatory role for mevalonate-derived products and expand the potential for inhibitors of mevalonate metabolism as anti-cancer agents.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes G., Hansen W. J., Holcomb C. L., Rine J. Asparagine-linked glycosylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: genetic analysis of an early step. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2381–2388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. E., Thorsness M., Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M., Rine J. Structural and functional conservation between yeast and human 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductases, the rate-limiting enzyme of sterol biosynthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3797–3808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck L. A., Hosick T. J., Sinensky M. Isoprenylation is required for the processing of the lamin A precursor. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1489–1499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Pringle J. R. Multicopy suppression of the cdc24 budding defect in yeast by CDC42 and three newly identified genes including the ras-related gene RSR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9976–9980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breviario D., Hinnebusch A. G., Dhar R. Multiple regulatory mechanisms control the expression of the RAS1 and RAS2 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breviario D., Hinnebusch A., Cannon J., Tatchell K., Dhar R. Carbon source regulation of RAS1 expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the phenotypes of ras2- cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4152–4156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caponigro G., Muhlrad D., Parker R. A small segment of the MAT alpha 1 transcript promotes mRNA decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a stimulatory role for rare codons. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5141–5148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Der C. J., Buss J. E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8323–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. J., Gil G., Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Luskey K. L. Sterols accelerate degradation of hamster 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase encoded by a constitutively expressed cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):634–641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker C. J., Parker R. A turnover pathway for both stable and unstable mRNAs in yeast: evidence for a requirement for deadenylation. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1632–1643. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defeo-Jones D., McAvoy E. M., Jones R. E., Vuocolo G. A., Haskell K. M., Wegrzyn R. J., Oliff A. Lovastatin selectively inhibits ras activation of the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate response element in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2307–2310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimster-Denk D., Thorsness M. K., Rine J. Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jun;5(6):655–665. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.6.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. C., Wolda S. L., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Human lamin B contains a farnesylated cysteine residue. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20422–20429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Dice J. F. Evidence for isopentenyladenine modification on a cell cycle-regulated protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9961–9970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold A. A., Johnson D. I., Farnsworth C. C., Gelb M. H., Judd S. R., Glomset J. A., Tamanoi F. Protein geranylgeranyltransferase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is specific for Cys-Xaa-Xaa-Leu motif proteins and requires the CDC43 gene product but not the DPR1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4448–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold A. A., Schafer W. R., Rine J., Whiteway M., Tamanoi F. Common modifications of trimeric G proteins and ras protein: involvement of polyisoprenylation. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):165–169. doi: 10.1126/science.1695391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada Y., Takao T., Ohguro H., Yoshizawa T., Akino T., Shimonishi Y. Farnesylated gamma-subunit of photoreceptor G protein indispensable for GTP-binding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):658–660. doi: 10.1038/346658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Schofield T. L., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Xenopus oocyte germinal-vesicle breakdown induced by [Val12]Ras is inhibited by a cytosol-localized Ras mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6630–6634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman L. E., Judd S. R., Farnsworth C. C., Powers S., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A., Tamanoi F. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective in the farnesylation of Ras proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9665–9669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Hoar E. Upstream activation sites of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are active when inverted but not when placed downstream of the "TATA box". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Regulatory proteins in yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:425–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Sprague G. F., Jr Induction of the yeast alpha-specific STE3 gene by the peptide pheromone a-factor. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):835–852. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Rine J. Regulated degradation of HMG-CoA reductase, an integral membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum, in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He B., Chen P., Chen S. Y., Vancura K. L., Michaelis S., Powers S. RAM2, an essential gene of yeast, and RAM1 encode the two polypeptide components of the farnesyltransferase that prenylates a-factor and Ras proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11373–11377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya Y., Sakurai A., Tamura S., Takahashi N. Structure of rhodotorucine A, a novel lipopeptide, inducing mating tube formation in Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91505-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Lutz R. J., Cox A. D., Conroy L., Bourne J. R., Sinensky M., Balch W. E., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid modification of rab proteins terminating in CC or CXC motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella B. T., Maltese W. A. rab GTP-binding proteins implicated in vesicular transport are isoprenylated in vitro at cysteines within a novel carboxyl-terminal motif. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8540–8544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhrer K., Domdey H. Preparation of high molecular weight RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:398–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai R. K., Perez-Sala D., Cañada F. J., Rando R. R. The gamma subunit of transducin is farnesylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7673–7677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscum L., Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M., Luskey K. L., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Domain structure of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, a glycoprotein of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):522–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Field J., Ballester R., O'Neill K., Wigler M. Mutants of H-ras that interfere with RAS effector function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Herskowitz I. The a-factor pheromone of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1309–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto B. H., Chuang C. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning of a member of a new class of low-molecular-weight GTP-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2386–2391. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Gutowski S., Sternweis P. C. G protein gamma subunits contain a 20-carbon isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5873–5877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi M., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Multivalent control of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Mevalonate-derived product inhibits translation of mRNA and accelerates degradation of enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8929–8937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu M. S., Pitts A. F., Winters T. R., Green S. H. ras isoprenylation is required for ras-induced but not for NGF-induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):795–808. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesney-Huneeus V., Wiley M. H., Siperstein M. D. Essential role for mevalonate synthesis in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling H. C., Breunger E., Epstein W. W., Crain P. F. Prenylated proteins: the structure of the isoprenoid group. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.2296720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Trueblood C. E., Yang C. C., Mayer M. P., Rosenberg S., Poulter C. D., Kim S. H., Rine J. Enzymatic coupling of cholesterol intermediates to a mating pheromone precursor and to the ras protein. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1133–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2204115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz S., Nyce J. W. Inhibition of protein isoprenylation and p21ras membrane association by dehydroepiandrosterone in human colonic adenocarcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6563–6567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Beck L. A., Leonard S., Evans R. Differential inhibitory effects of lovastatin on protein isoprenylation and sterol synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19937–19941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsness M., Schafer W., D'Ari L., Rine J. Positive and negative transcriptional control by heme of genes encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5702–5712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]