Abstract
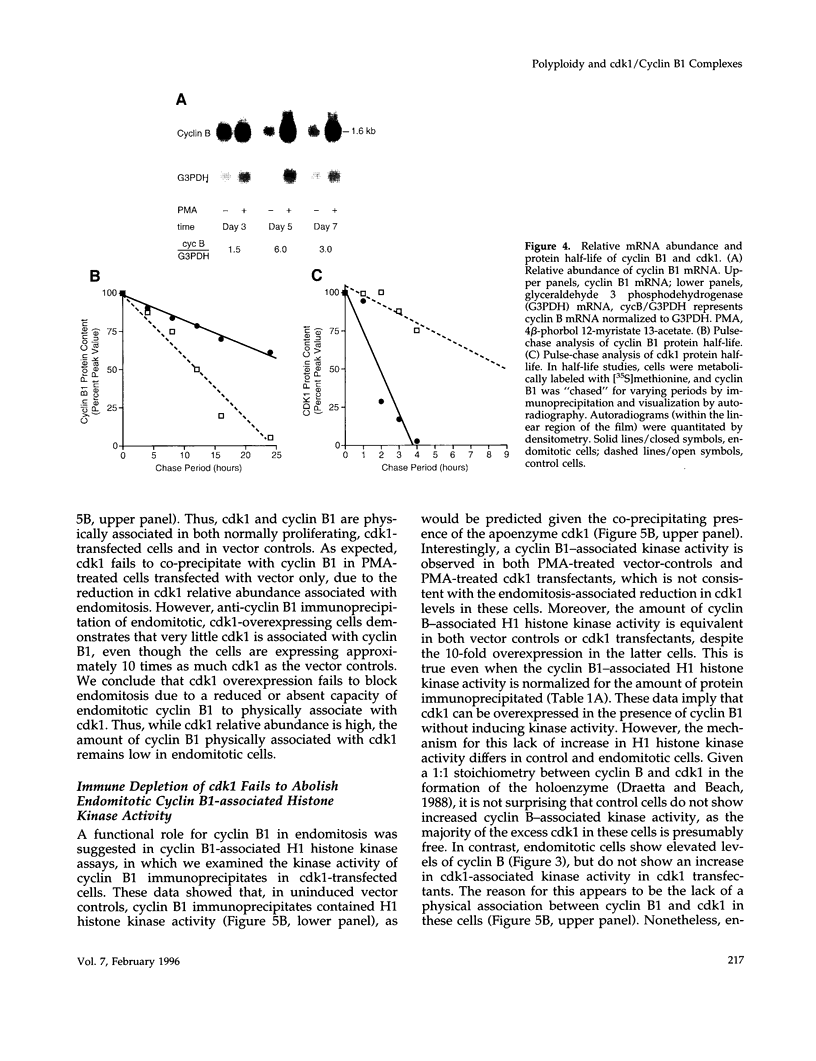
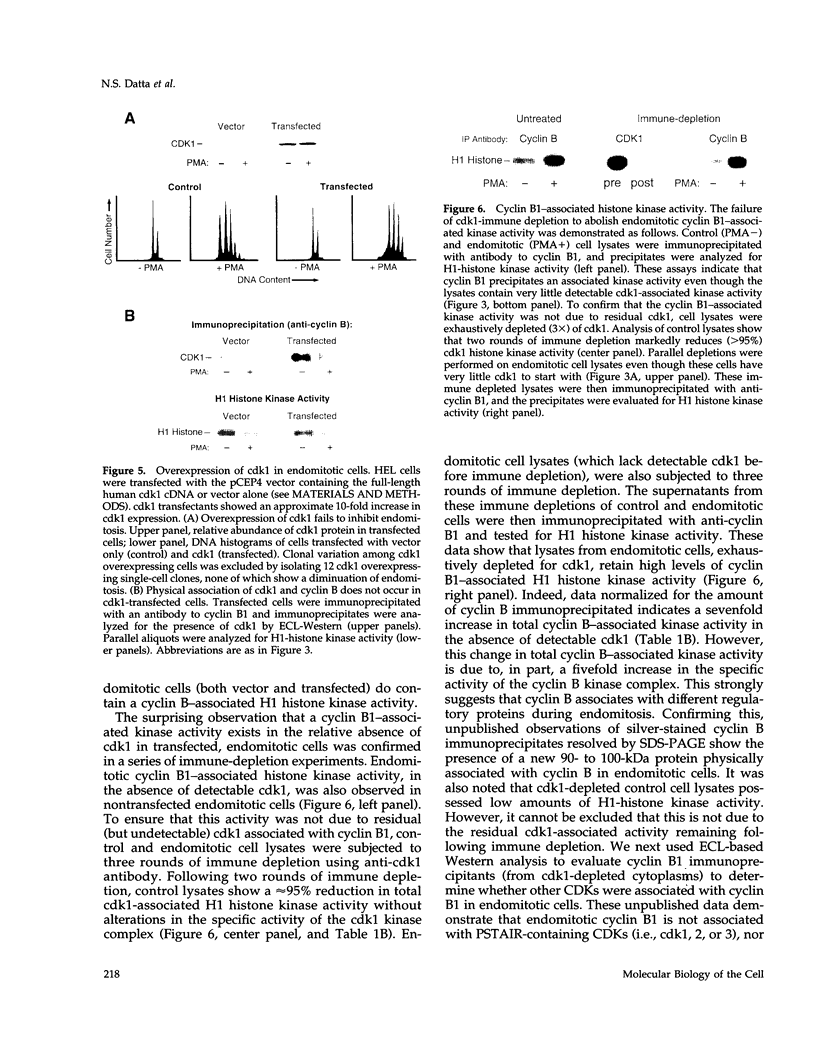
The pathways that regulate the S-phase events associated with the control of DNA replication are poorly understood. The bone marrow megakaryocytes are unique in that they leave the diploid (2C) state to differentiate, synthesizing 4 to 64 times the normal DNA content within a single nucleus, a process known as endomitosis. Human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells model this process, becoming polyploid during phorbol diester-induced megakaryocyte differentiation. The mitotic arrest occurring in these polyploid cells involves novel alterations in the cdk1/cyclin B1 complex: a marked reduction in cdk1 protein levels, and an elevated and sustained expression of cyclin B1. Endomitotic cells thus lack cdk1/cyclin B1-associated H1-histone kinase activity. Constitutive over-expression of cdk1 in endomitotic cells failed to re-initiate normal mitotic events even though cdk1 was present in a 10-fold excess. This was due to an inability of cyclin-B1 to physically associate with cdk1. Nonetheless, endomitotic cyclin B1 possesses immunoprecipitable H1-histone kinase activity, and specifically translocates to the nucleus. We conclude that mitosis is abrogated during endomitosis due to the absence of cdk1 and the failure to form M-phase promoting factor, resulting in a disassociation of mitosis from the completion of S-phase. Further studies on cyclin and its interacting proteins should be informative in understanding endomitosis and cell cycle control.
Full text
PDF
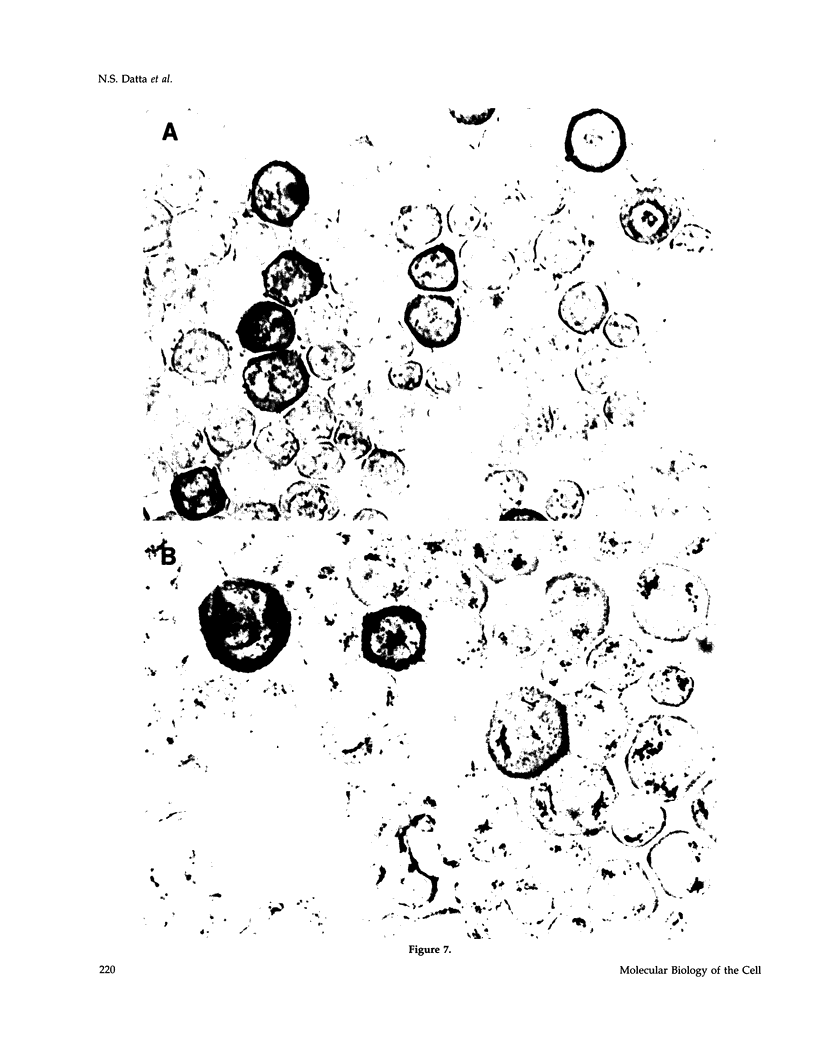









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal A. B., Kriegstein H. J., Hogness D. S. The units of DNA replication in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:205–223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Bartlett R., Crawford K., Nurse P. Involvement of p34cdc2 in establishing the dependency of S phase on mitosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):388–393. doi: 10.1038/349388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. Replication of DNA in the chromosomes of eukaryotes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Apr 18;181(1062):19–41. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBBE S., STOHLMAN F., Jr MEGAKARYOCYTOPOIESIS IN THE RAT. Blood. 1965 Jul;26:20–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbe S. Biology of megakaryocytes. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:211–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbe S., Howard D., Phalen E., Stohlman F., Jr Effects of vincristine on normal and stimulated megakaryocytopoiesis in the rat. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):593–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J., Huberman J. A. Eukaryotic chromosome replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:245–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINENDEGEN L. E., ODARTCHENKO N., COTTIER H., BOND V. P. Kinetics of megacaryocyte proliferation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Oct;111:177–182. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant P., Nigg E. A. Cyclin B2 undergoes cell cycle-dependent nuclear translocation and, when expressed as a non-destructible mutant, causes mitotic arrest in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):213–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. R., Farrell A., Deshaies R. J., Herskowitz I., Morgan D. O. Cdc37 is required for association of the protein kinase Cdc28 with G1 and mitotic cyclins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4651–4655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafi G., Larkins B. A. Endoreduplication in maize endosperm: involvement of m phase--promoting factor inhibition and induction of s phase--related kinases. Science. 1995 Sep 1;269(5228):1262–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.269.5228.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayles J., Fisher D., Woollard A., Nurse P. Temporal order of S phase and mitosis in fission yeast is determined by the state of the p34cdc2-mitotic B cyclin complex. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):813–822. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1071–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90028-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman M., Firth M., Pines J. Human cyclins B1 and B2 are localized to strikingly different structures: B1 to microtubules, B2 primarily to the Golgi apparatus. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1646–1654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. W. Cholinesterase as a possible marker for early cells of the megakaryocytic series. Blood. 1973 Sep;42(3):413–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. W. Megakaryocyte endomitosis: a review. Int J Cell Cloning. 1990 Jul;8(4):224–226. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J. Y., Matsuoka M., Strom D. K., Sherr C. J. Regulation of cyclin D-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4) by cdk4-activating kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2713–2721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E. M., Harlow E. Sequences within the conserved cyclin box of human cyclin A are sufficient for binding to and activation of cdc2 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1194–1201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. The roles of Drosophila cyclins A and B in mitotic control. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90535-m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long M. W., Heffner C. H., Williams J. L., Peters C., Prochownik E. V. Regulation of megakaryocyte phenotype in human erythroleukemia cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1072–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI114538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long M. W., Williams N., Ebbe S. Immature megakaryocytes in the mouse: physical characteristics, cell cycle status, and in vitro responsiveness to thrombopoietic stimulatory factor. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long M. W., Williams N. Immature Megakaryocytes in the Mouse: Morphology and quantitation by acetylcholinesterase staining. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):1032–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long M. W., Williams N., McDonald T. P. Immature megakaryocytes in the mouse: in vitro relationship to megakaryocyte progenitor cells and mature megakaryocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Sep;112(3):339–344. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Shibuya E. K., Dohrmann C. E., Ruderman J. V. Both cyclin A delta 60 and B delta 97 are stable and arrest cells in M-phase, but only cyclin B delta 97 turns on cyclin destruction. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4311–4320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maridor G., Gallant P., Golsteyn R., Nigg E. A. Nuclear localization of vertebrate cyclin A correlates with its ability to form complexes with cdk catalytic subunits. J Cell Sci. 1993 Oct;106(Pt 2):535–544. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Enders G. H., Wu C. L., Su L. K., Gorka C., Nelson C., Harlow E., Tsai L. H. A family of human cdc2-related protein kinases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2909–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell T. T., Jr, Jackson C. W., Friday T. J. Megakaryocytopoiesis in rats with special reference to polyploidy. Blood. 1970 Jun;35(6):775–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclins A and B1 are differentially located in the cell and undergo cell cycle-dependent nuclear transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):1–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. The differential localization of human cyclins A and B is due to a cytoplasmic retention signal in cyclin B. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3772–3781. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabellino E. M., Levene R. B., Leung L. L., Nachman R. L. Human megakaryocytes. II. Expression of platelet proteins in early marrow megakaryocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):88–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Nambi P., Peters J. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Phorbol diesters promote beta-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and adenylate cyclase desensitization in duck erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 29;121(3):973–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therman E., Sarto G. E., Stubblefield P. A. Endomitosis: a reappraisal. Hum Genet. 1983;63(1):13–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00285390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N., Jackson H. Kinetic analysis of megakaryocyte numbers and ploidy levels in developing colonies from mouse bone marrow cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1982 Sep;15(5):483–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1982.tb01571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Connolly T., Futcher B., Beach D. Human D-type cyclin. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. M., Weiss L. Megakaryocytopoiesis: incorporation of tritiated thymidine by small acetylcholinesterase-positive cells in murine bone marrow during antibody-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]