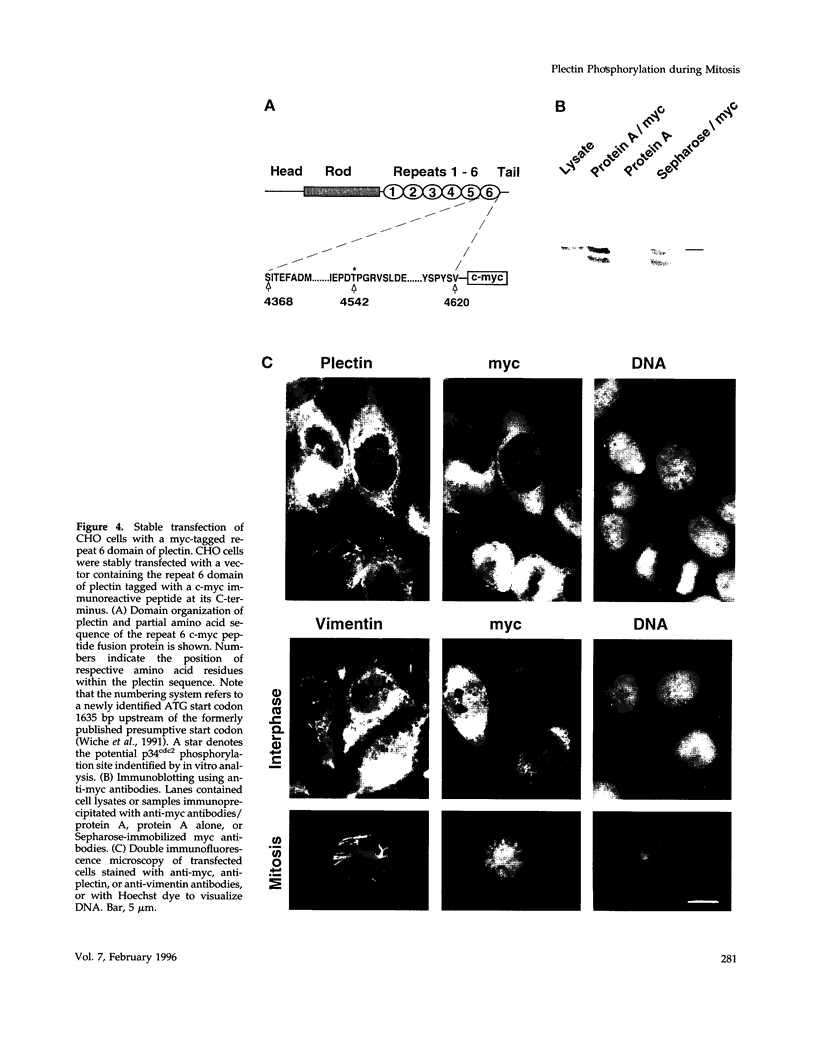
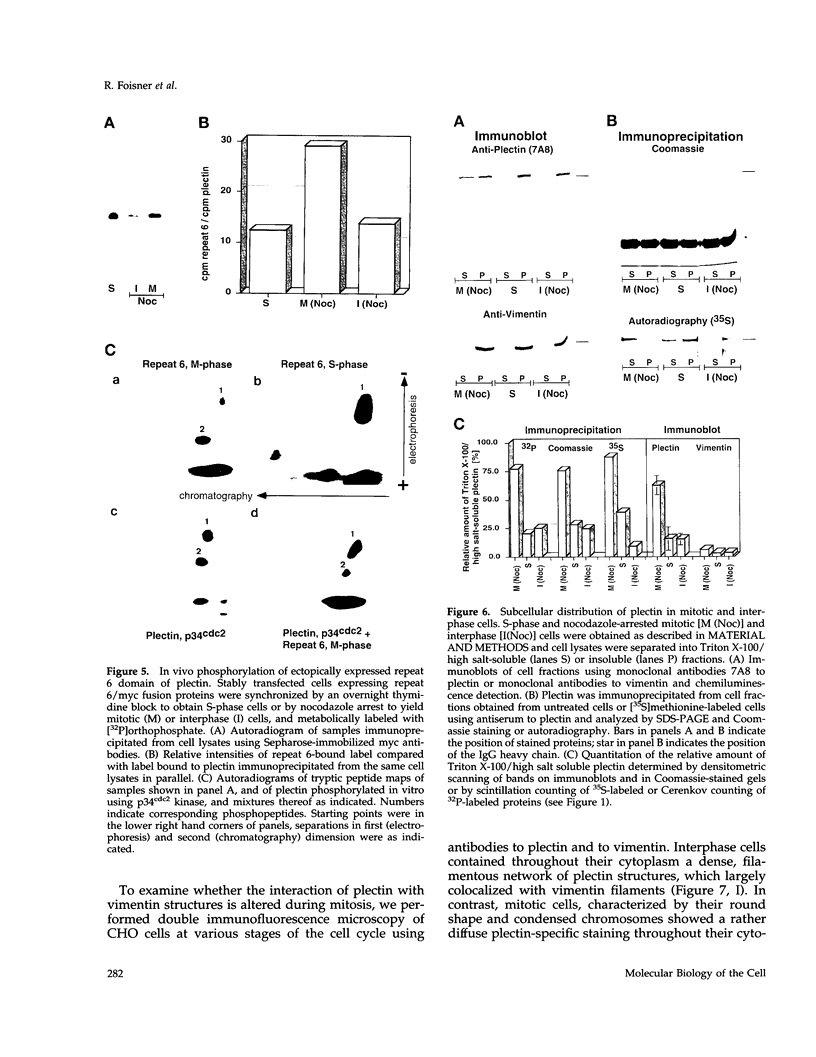
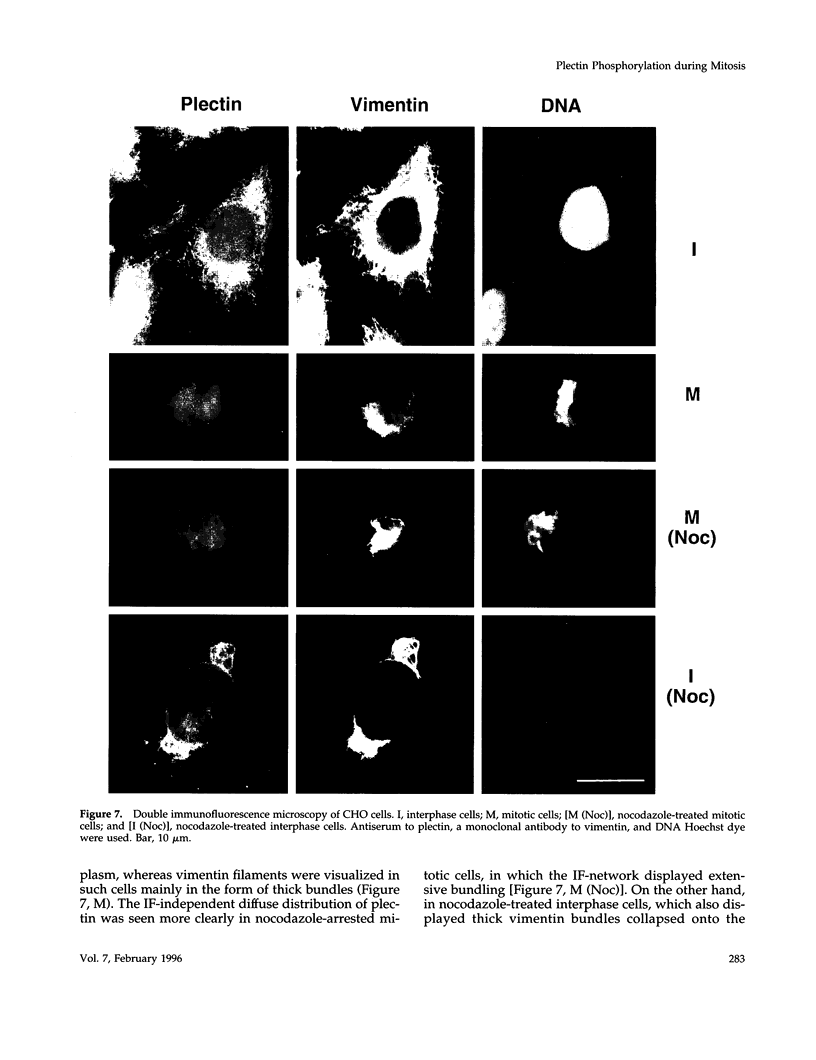
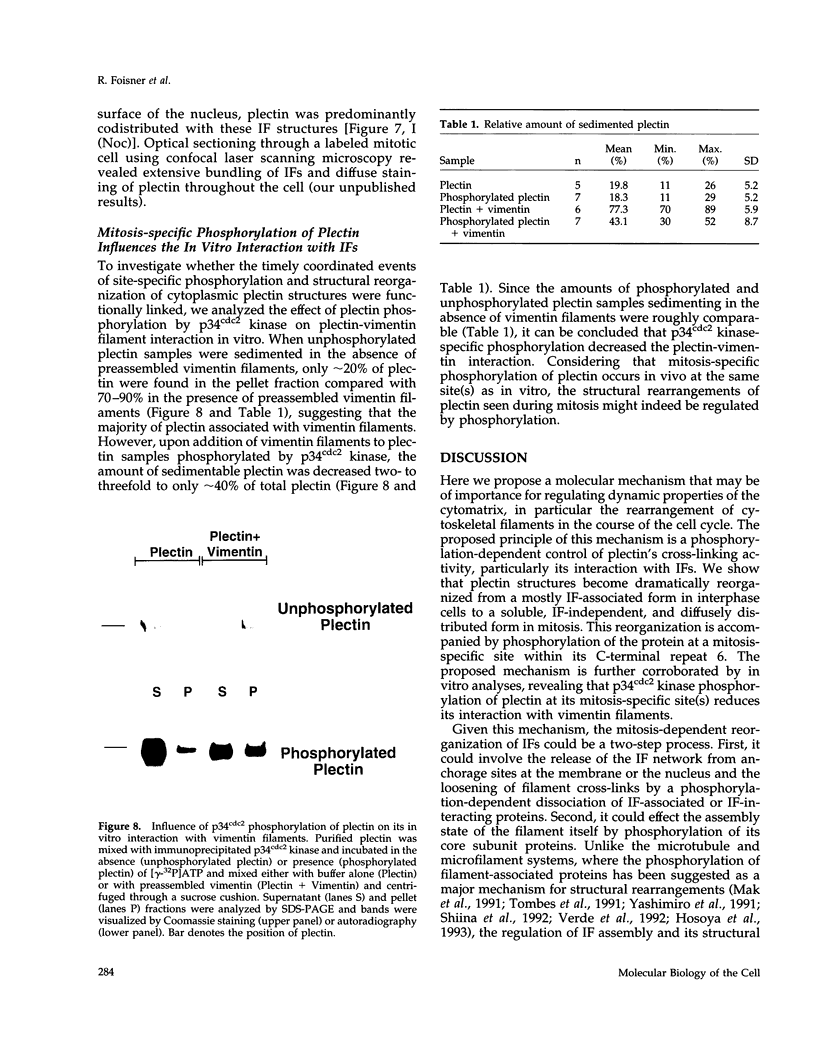
Abstract
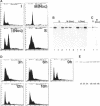
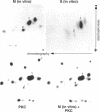
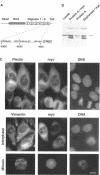
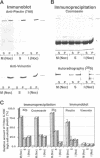
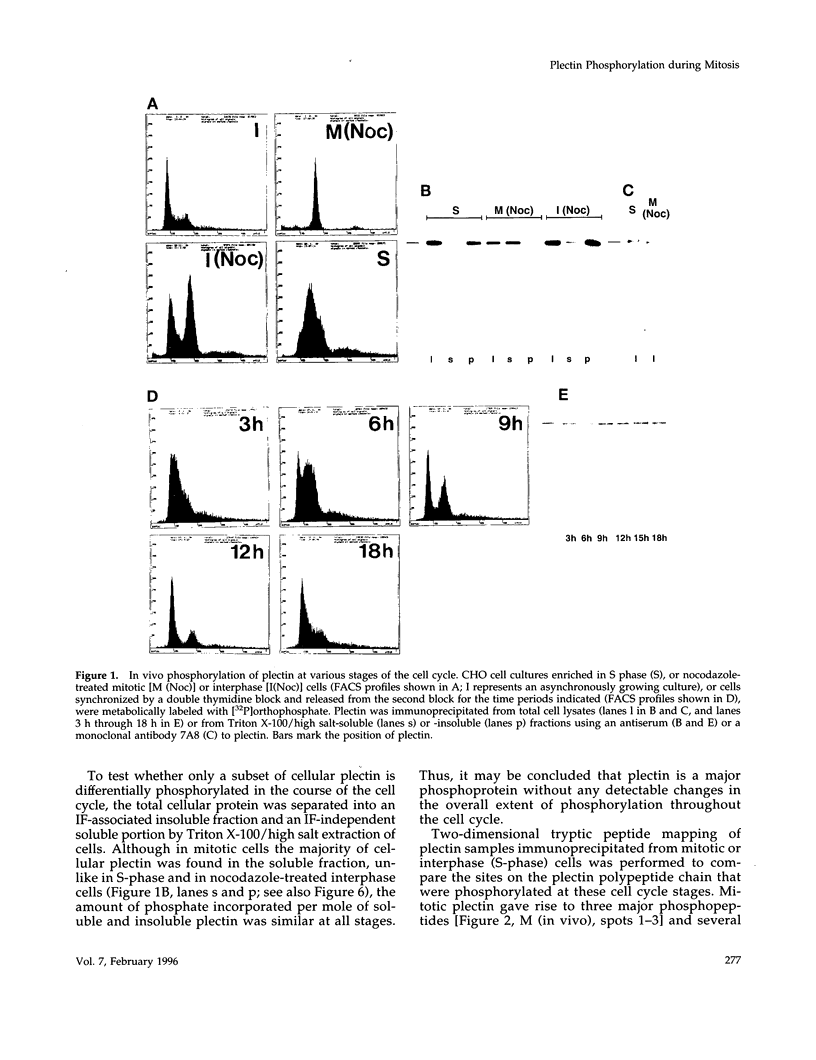
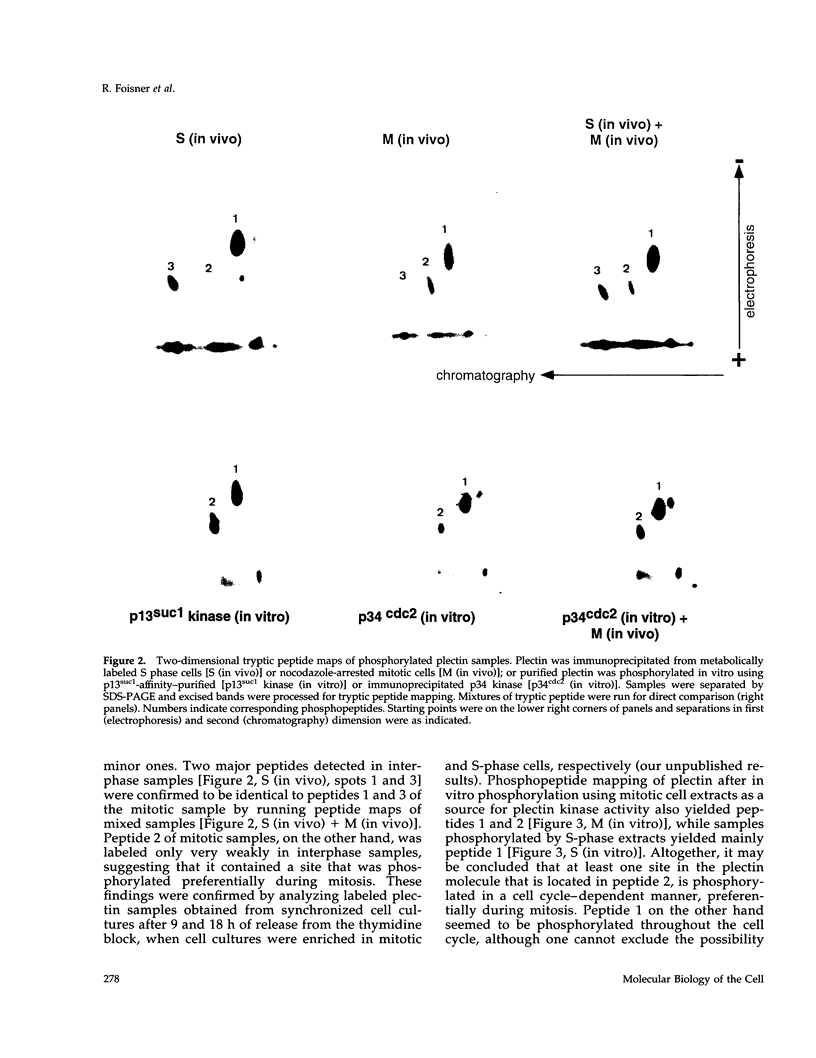
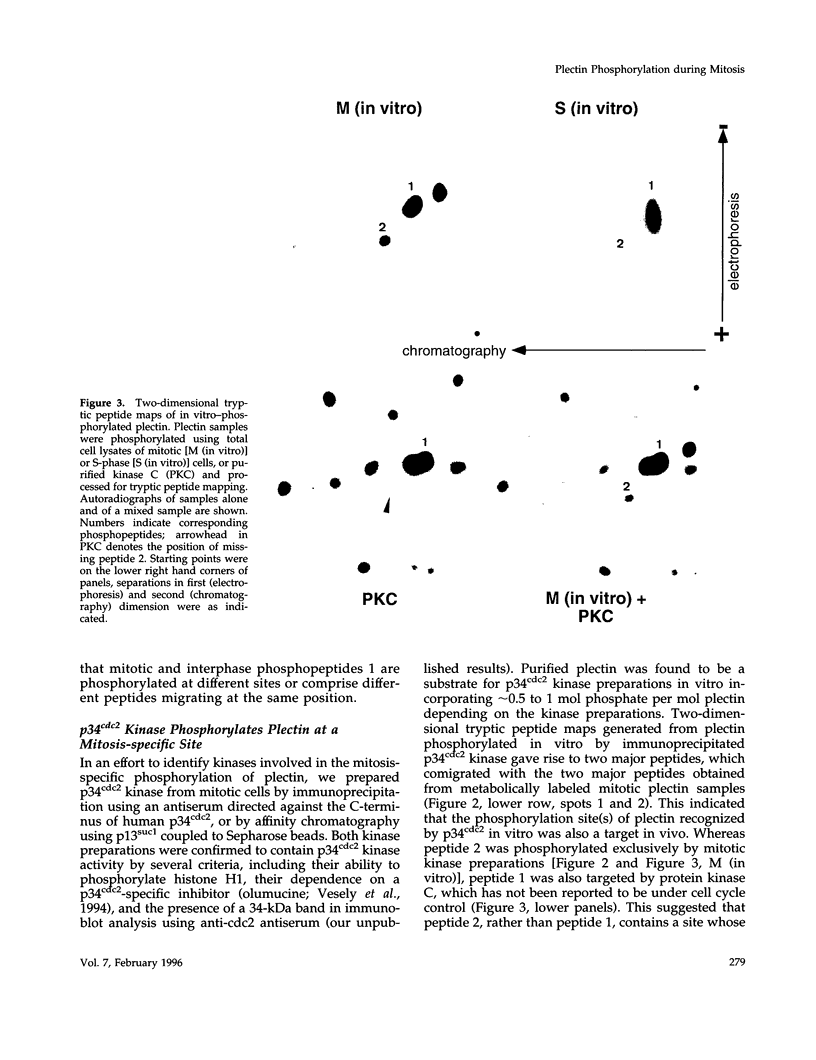
Plectin, a widespread and abundant cytoskeletal cross-linking protein, serves as a target for protein kinases throughout the cell cycle, without any significant variation in overall phosphorylation level. One of the various phosphorylation sites of the molecule was found to be phosphorylated preferentially during mitosis. By in vivo phosphorylation of ectopically expressed plectin domains in stably transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells, this site was mapped to the C-terminal repeat 6 domain of the polypeptide. The same site has been identified as an in vitro target for p34cdc2 kinase. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of plectin was accompanied by a rearrangement of plectin structures, changing from a filamentous, largely vimentin-associated state in interphase to a diffuse vimentin-independent distribution in mitosis as visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy. Subcellular fractionation studies showed that in interphase cells up to 80% of cellular plectin was found associated with an insoluble cell fraction mostly consisting of intermediate filaments, while during mitosis the majority of plectin (> 75%) became soluble. Furthermore, phosphorylation of purified plectin by p34cdc2 kinase decreased plectin's ability to interact with preassembled vimentin filaments in vitro. Together, our data suggest that a mitosis-specific phosphorylation involving p34cdc2 kinase regulates plectin's cross-linking activities and association with intermediate filaments during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailer S. M., Eppenberger H. M., Griffiths G., Nigg E. A. Characterization of A 54-kD protein of the inner nuclear membrane: evidence for cell cycle-dependent interaction with the nuclear lamina. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):389–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann K., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Piwnica-Worms H., Mandelkow E. Abnormal Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau-protein by cyclin-dependent kinases cdk2 and cdk5. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80849-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. p13suc1 acts in the fission yeast cell division cycle as a component of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3507–3514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Bischoff J. R., Beach D., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filament reorganization during mitosis is mediated by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of vimentin. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1063–1071. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90384-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Ngai K. L., Goldman R. The regulation of intermediate filament reorganization in mitosis. p34cdc2 phosphorylates vimentin at a unique N-terminal site. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7325–7328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin J. C., Segil N., Blobel G., Worman H. J. The lamin B receptor of the inner nuclear membrane undergoes mitosis-specific phosphorylation and is a substrate for p34cdc2-type protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19035–19038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessev G., Iovcheva-Dessev C., Bischoff J. R., Beach D., Goldman R. A complex containing p34cdc2 and cyclin B phosphorylates the nuclear lamin and disassembles nuclei of clam oocytes in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):523–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Peter M., Nurse P., Nigg E. A. p34cdc2 acts as a lamin kinase in fission yeast. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):797–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Feldman B., Sander L., Seifert G., Artlieb U., Wiche G. A panel of monoclonal antibodies to rat plectin: distinction by epitope mapping and immunoreactivity with different tissues and cell lines. Acta Histochem. 1994 Dec;96(4):421–438. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(11)80029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Feldman B., Sander L., Wiche G. Monoclonal antibody mapping of structural and functional plectin epitopes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):397–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Gerace L. Integral membrane proteins of the nuclear envelope interact with lamins and chromosomes, and binding is modulated by mitotic phosphorylation. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90355-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Leichtfried F. E., Herrmann H., Small J. V., Lawson D., Wiche G. Cytoskeleton-associated plectin: in situ localization, in vitro reconstitution, and binding to immobilized intermediate filament proteins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):723–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Traub P., Wiche G. Protein kinase A- and protein kinase C-regulated interaction of plectin with lamin B and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3812–3816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Wiche G. Intermediate filament-associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Wiche G. Structure and hydrodynamic properties of plectin molecules. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):515–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautel M., Leonard K., Labeit S. Phosphorylation of KSP motifs in the C-terminal region of titin in differentiating myoblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3827–3834. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D. Dynamics of intermediate filaments. Recent progress and unanswered questions. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 1;318(2):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80001-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Meier J., Simos G. Lamins and lamin-associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Burke B. Functional organization of the nuclear envelope. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:335–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Foisner R. Integral membrane proteins and dynamic organization of the nuclear envelope. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;4(4):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotow T., Tanaka T., Nakamura Y., Takeda M. Dephosphorylation of the largest neurofilament subunit protein influences the structure of crossbridges in reassembled neurofilaments. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jul;107(Pt 7):1949–1957. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.7.1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Virata M. L., Elgart G. W., Stanley J. R., Parry D. A. Comparative structural analysis of desmoplakin, bullous pemphigoid antigen and plectin: members of a new gene family involved in organization of intermediate filaments. Int J Biol Macromol. 1992 Jun;14(3):145–153. doi: 10.1016/s0141-8130(05)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald R., McKeon F. Mutations of phosphorylation sites in lamin A that prevent nuclear lamina disassembly in mitosis. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann H., Wiche G. Plectin and IFAP-300K are homologous proteins binding to microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 and to the 240-kilodalton subunit of spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1320–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann H., Wiche G. Specific in situ phosphorylation of plectin in detergent-resistant cytoskeletons from cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14610–14618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Ishiguro K., Uchida T., Okumura E., Okano T., Kishimoto T. Tau protein kinase II has a similar characteristic to cdc2 kinase for phosphorylating neurofilament proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15056–15060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Kusubata M., Okumura E., Kishimoto T. Phosphorylation of neurofilament H subunit at the tail domain by CDC2 kinase dissociates the association to microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21798–21803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya N., Hosoya H., Yamashiro S., Mohri H., Matsumura F. Localization of caldesmon and its dephosphorylation during cell division. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):1075–1082. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Ishiguro K., Omori A., Takamatsu M., Arioka M., Imahori K., Uchida T. A cdc2-related kinase PSSALRE/cdk5 is homologous with the 30 kDa subunit of tau protein kinase II, a proline-directed protein kinase associated with microtubule. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 6;335(2):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80723-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew J., Winkfein R. J., Paudel H. K., Wang J. H. Brain proline-directed protein kinase is a neurofilament kinase which displays high sequence homology to p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25922–25926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Brizuela L., Beach D., Eisenman R. N. A role for the p34cdc2 kinase and phosphatases in the regulation of phosphorylation and disassembly of lamin B2 during the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):865–875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak A. S., Carpenter M., Smillie L. B., Wang J. H. Phosphorylation of caldesmon by p34cdc2 kinase. Identification of phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19971–19975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka Y., Nishizawa K., Yano T., Shibata M., Ando S., Takahashi T., Inagaki M. Two different protein kinases act on a different time schedule as glial filament kinases during mitosis. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Koonce M. P. Mitosis. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2683078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. Cellular substrates of p34(cdc2) and its companion cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;3(9):296–301. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90011-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. Targets of cyclin-dependent protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90101-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon R. A., Paskevich P. A., Sihag R. K., Thayer C. Y. Phosphorylation on carboxyl terminus domains of neurofilament proteins in retinal ganglion cell neurons in vivo: influences on regional neurofilament accumulation, interneurofilament spacing, and axon caliber. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):1031–1046. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paudel H. K., Lew J., Ali Z., Wang J. H. Brain proline-directed protein kinase phosphorylates tau on sites that are abnormally phosphorylated in tau associated with Alzheimer's paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23512–23518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Heitlinger E., Häner M., Aebi U., Nigg E. A. Disassembly of in vitro formed lamin head-to-tail polymers by CDC2 kinase. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1535–1544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Nakagawa J., Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Nigg E. A. In vitro disassembly of the nuclear lamina and M phase-specific phosphorylation of lamins by cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90471-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: take your partners. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90185-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite L. L., Lohka M. J., Wilson K. L., Scherson T. Y., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L., Pollard T. D. Phosphorylation of myosin-II regulatory light chain by cyclin-p34cdc2: a mechanism for the timing of cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):595–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite L. L., Pollard T. D. Cytokinesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90057-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shetty K. T., Link W. T., Pant H. C. cdc2-like kinase from rat spinal cord specifically phosphorylates KSPXK motifs in neurofilament proteins: isolation and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6844–6848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina N., Moriguchi T., Ohta K., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Regulation of a major microtubule-associated protein by MPF and MAP kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3977–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Chou Y. H., Goldman R. D. Cell cycle-dependent changes in the organization of an intermediate filament-associated protein: correlation with phosphorylation by p34cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11959–11963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Chou Y. H., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments: not so tough after all. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):308–312. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Jones J. C., Gagescu R., Goldman R. D. IFAP 300 is common to desmosomes and hemidesmosomes and is a possible linker of intermediate filaments to these junctions. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):159–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Growth and nucleic acid synthesis in synchronously dividing populations of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Apr;30:344–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombes R. M., Peloquin J. G., Borisy G. G. Specific association of an M-phase kinase with isolated mitotic spindles and identification of two of its substrates as MAP4 and MAP1B. Cell Regul. 1991 Nov;2(11):861–874. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimura K., Ogawara M., Takeuchi Y., Imajoh-Ohmi S., Ha M. H., Inagaki M. Visualization and function of vimentin phosphorylation by cdc2 kinase during mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):31097–31106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Dogterom M., Stelzer E., Karsenti E., Leibler S. Control of microtubule dynamics and length by cyclin A- and cyclin B-dependent kinases in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1097–1108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Karsenti E. Regulation of microtubule dynamics by cdc2 protein kinase in cell-free extracts of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):233–238. doi: 10.1038/343233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veselý J., Havlicek L., Strnad M., Blow J. J., Donella-Deana A., Pinna L., Letham D. S., Kato J., Detivaud L., Leclerc S. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Sep 1;224(2):771–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. E., Kirschner M. W. Identification of cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation sites on nuclear lamin C. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90469-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Baker M. A. Cytoplasmic network arrays demonstrated by immunolocalization using antibodies to a high molecular weight protein present in cytoskeletal preparations from cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Becker B., Luber K., Weitzer G., Castañon M. J., Hauptmann R., Stratowa C., Stewart M. Cloning and sequencing of rat plectin indicates a 466-kD polypeptide chain with a three-domain structure based on a central alpha-helical coiled coil. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):83–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Gromov D., Donovan A., Castañn M. J., Fuchs E. Expression of plectin mutant cDNA in cultured cells indicates a role of COOH-terminal domain in intermediate filament association. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):607–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G. Plectin: general overview and appraisal of its potential role as a subunit protein of the cytomatrix. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1989;24(1):41–67. doi: 10.3109/10409238909082551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakita Y., Yamashiro S., Matsumura F. In vivo phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II during mitosis of cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):129–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro S., Yamakita Y., Hosoya H., Matsumura F. Phosphorylation of non-muscle caldesmon by p34cdc2 kinase during mitosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):169–172. doi: 10.1038/349169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro S., Yamakita Y., Ishikawa R., Matsumura F. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation causes 83K non-muscle caldesmon to dissociate from microfilaments. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):675–678. doi: 10.1038/344675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]