Abstract
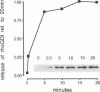
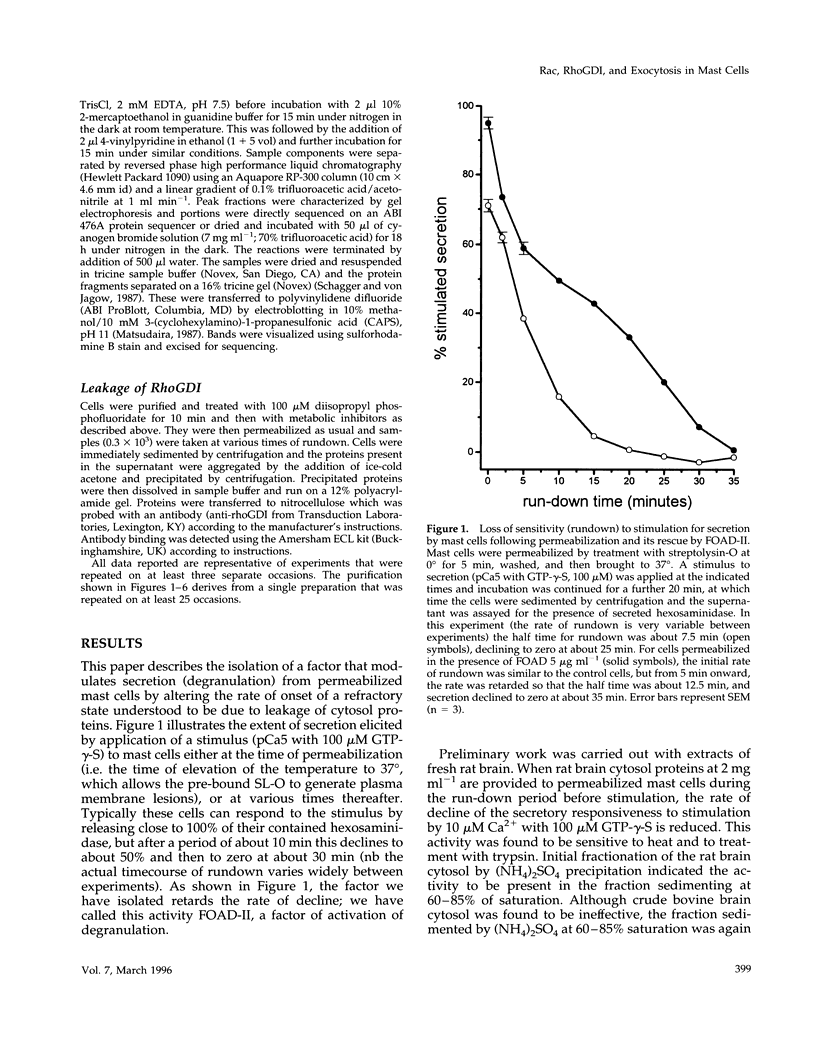
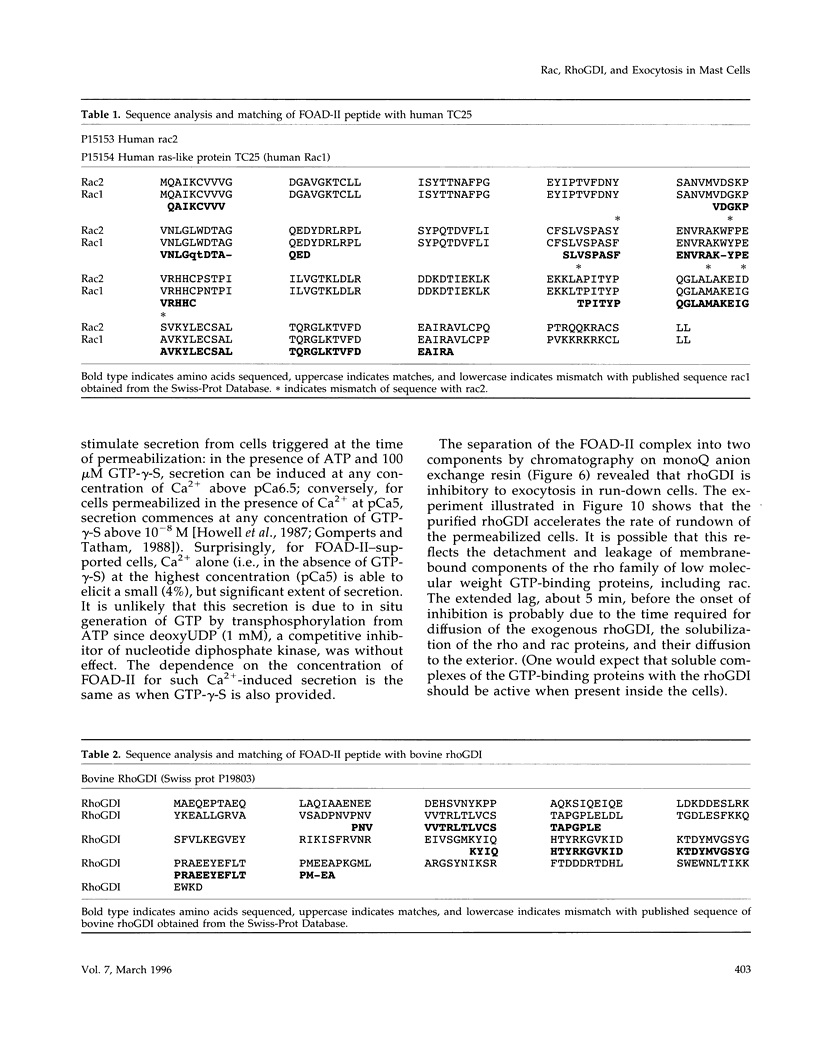
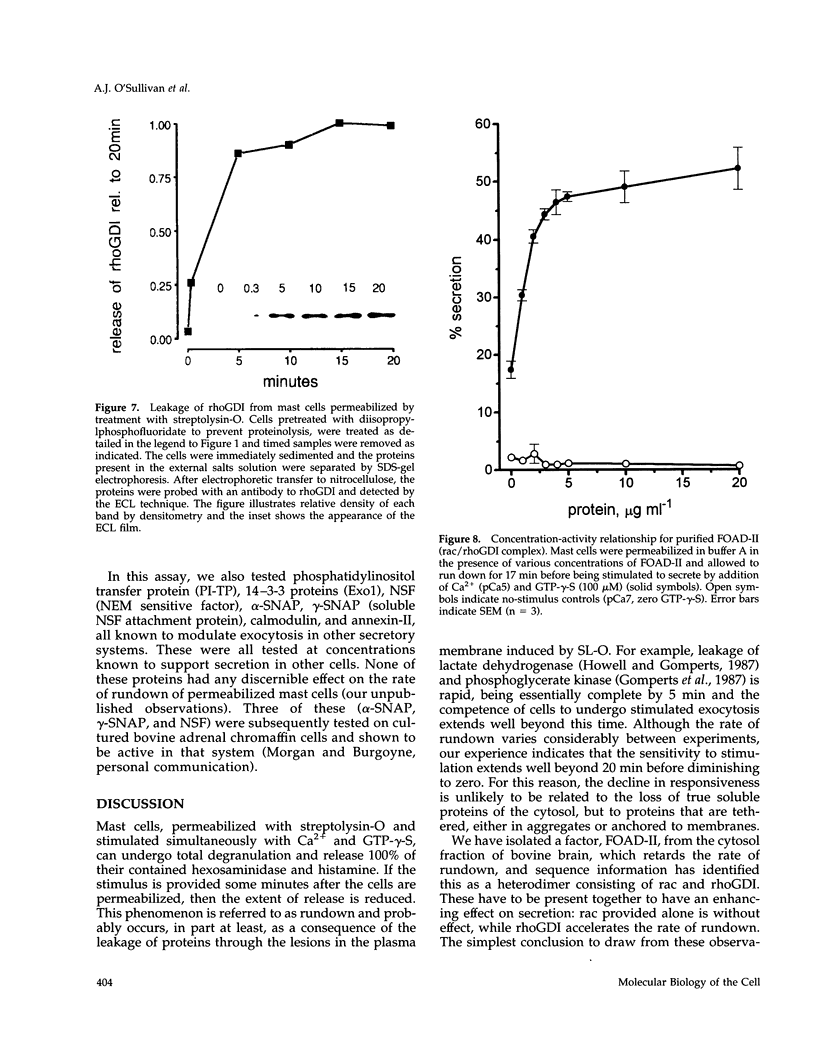
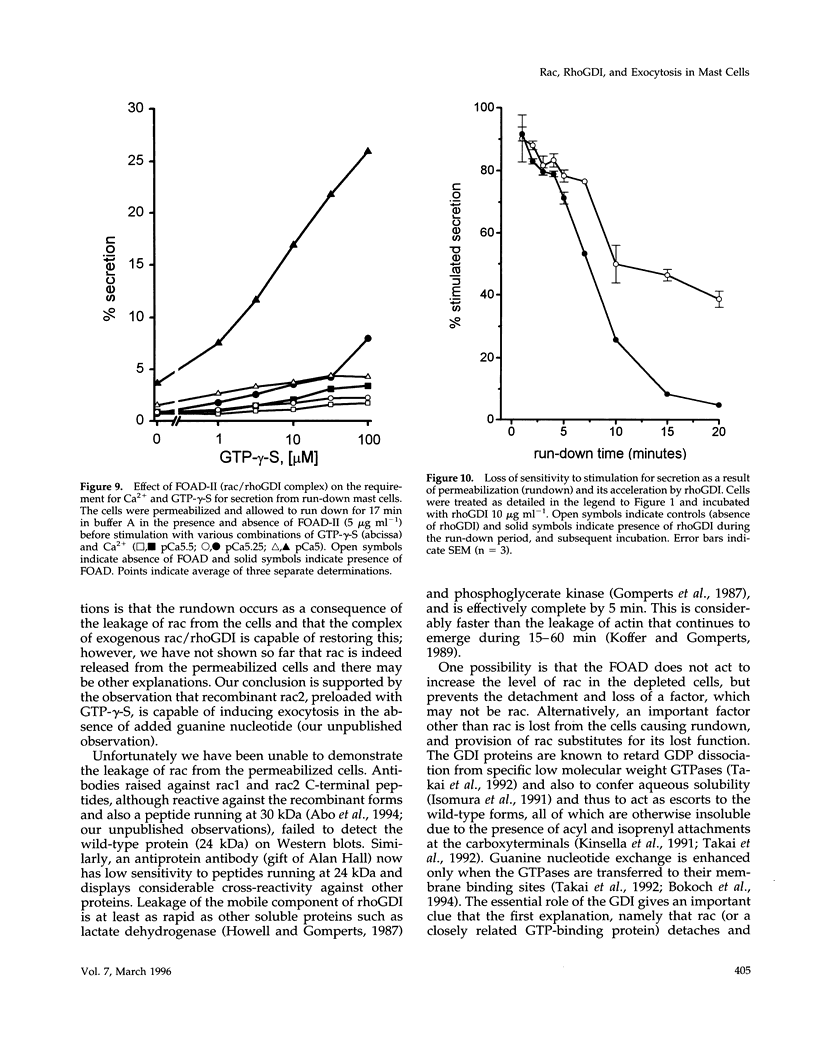
Mast cells permeabilized by treatment with streptolysin-O in the presence of Ca2+ and GTP-gamma-S can secrete almost 100% of their contained N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase. If these stimuli are provided to the permeabilized cells after a delay, the response is diminished and the ability of the cells to undergo secretion runs down progressively over a period of about 30 min. This is thought to be due to the loss of key proteins involved in the exocytotic mechanism. Using this effect as the basis of a biological assay, we have isolated a protein from bovine brain cytosol that retards the loss of responsiveness to stimulation by Ca2+ and GTP-gamma-S. Purification of this protein and peptide sequencing have enabled us to identify it as the small GTP-binding protein rac complexed to the guanine nucleotide exchange inhibitor rhoGDI. Both proteins are required to retard the loss of the secretory response, while purified rhoGDI applied alone accelerates the rundown.
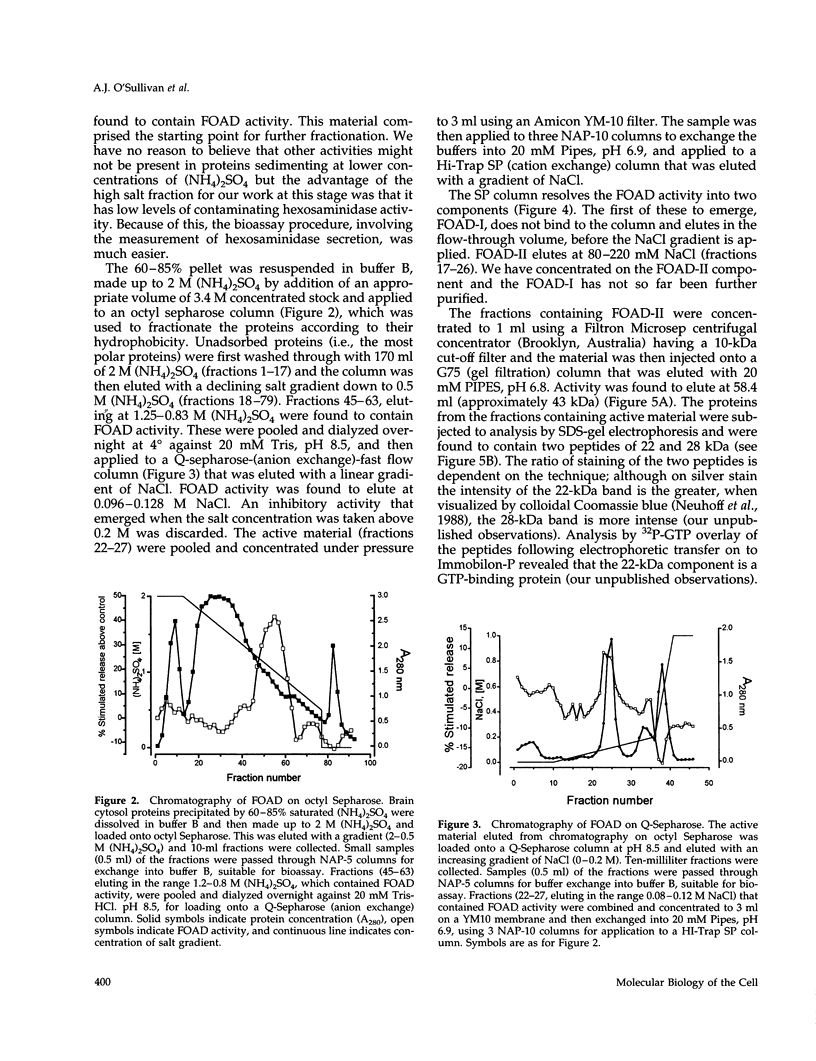
Full text
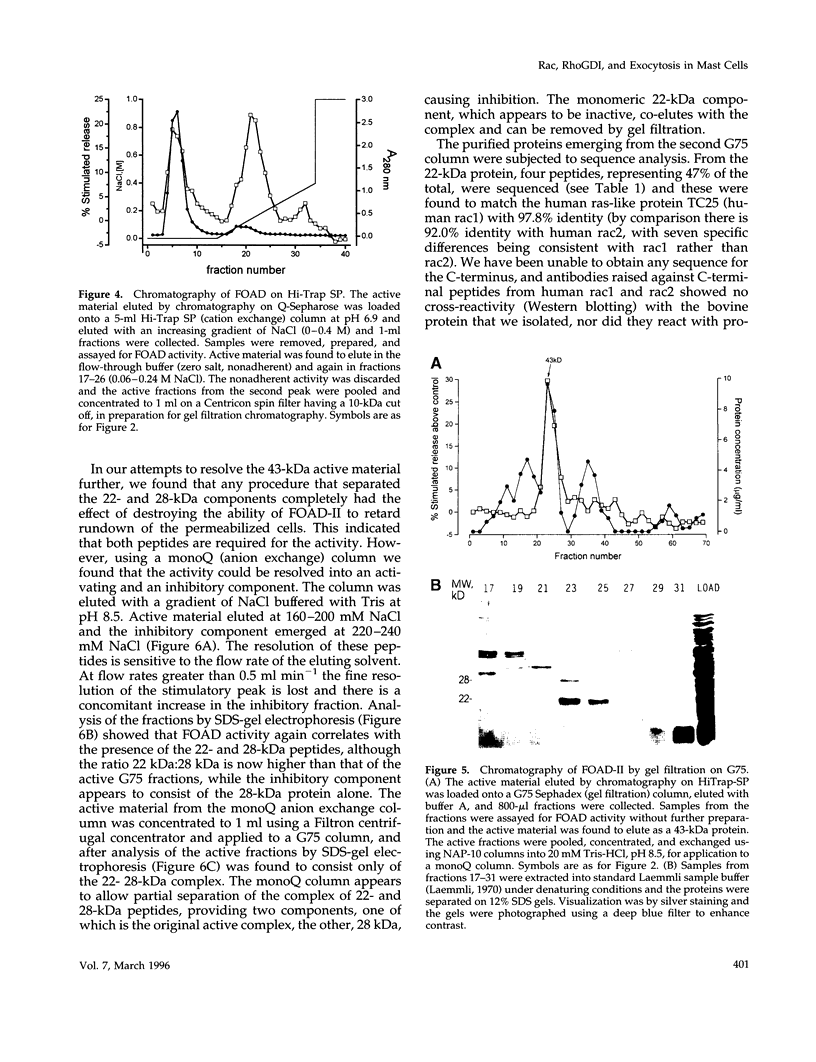
PDF

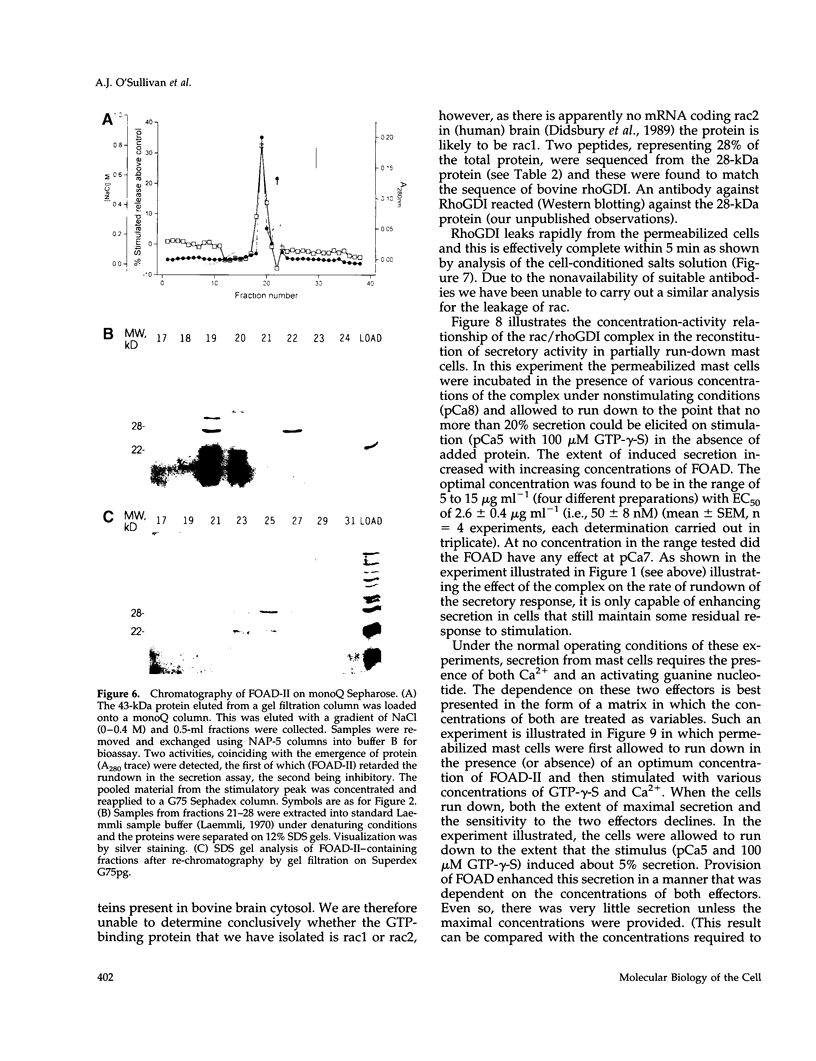



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Webb M. R., Grogan A., Segal A. W. Activation of NADPH oxidase involves the dissociation of p21rac from its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rhoGDI) followed by its translocation to the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj2980585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. M., Burgoyne R. D. The stimulatory effect of calpactin (annexin II) on calcium-dependent exocytosis in chromaffin cells: requirement for both the N-terminal and core domains of p36 and ATP. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90054-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aridor M., Rajmilevich G., Beaven M. A., Sagi-Eisenberg R. Activation of exocytosis by the heterotrimeric G protein Gi3. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1569–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.7504324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aridor M., Traub L. M., Sagi-Eisenberg R. Exocytosis in mast cells by basic secretagogues: evidence for direct activation of GTP-binding proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):909–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Bohl B. P., Chuang T. H. Guanine nucleotide exchange regulates membrane translocation of Rac/Rho GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31674–31679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Leff P., Johnson T. D., Milano C. A., Rockman H. A., McMinn T. R., Apparsundaram S., Hyek M. F., Kenakin T. P., Allen L. F. Physiological effects of inverse agonists in transgenic mice with myocardial overexpression of the beta 2-adrenoceptor. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):272–276. doi: 10.1038/374272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. P., Uhlinger D. J., Lambeth J. D. Neutrophil phospholipase D is activated by a membrane-associated Rho family small molecular weight GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21509–21512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Shani E., Joseph G., Gorzalczany Y., Sperling O., Pick E. The GDP-bound form of the small G protein Rac1 p21 is a potent activator of the superoxide-forming NADPH oxidase of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7055–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. Relationship between arachidonate release and exocytosis in permeabilized human neutrophils stimulated with formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMetLeuPhe), guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) and Ca2+. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):127–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2750127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Bennett J. P., Hide I., Kay A. B., Gomperts B. D. Mechanisms of granule enzyme secretion from permeabilized guinea pig eosinophils. Dependence on Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1905–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J., Weber R. F., Bokoch G. M., Evans T., Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16378–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dormer R. L., Ashcroft S. J. Studies on the role of calcium ions in the stimulation by adrenaline of amylase release from rat parotid. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;144(3):543–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1440543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Cockcroft S., Howell T. W., Nüsse O., Tatham P. E. The dual effector system for exocytosis in mast cells: obligatory requirement for both Ca2+ and GTP. Biosci Rep. 1987 May;7(5):369–381. doi: 10.1007/BF01362501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Tatham P. E. GTP-binding proteins in the control of exocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):983–992. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Tatham P. E. Regulated exocytotic secretion from permeabilized cells. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:178–189. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Small GTP-binding proteins and the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:31–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Fisette P. L., Jenkins G. H., Fukami K., Takenawa T., Anderson R. A., Martin T. F. ATP-dependent inositide phosphorylation required for Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):173–177. doi: 10.1038/374173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Martin T. F. Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein required for ATP-dependent priming of Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):572–575. doi: 10.1038/366572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Essential synergy between Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides in exocytotic secretion from permeabilized rat mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):191–197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Rat mast cells permeabilised with streptolysin O secrete histamine in response to Ca2+ at concentrations buffered in the micromolar range. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 18;927(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomura M., Kikuchi A., Ohga N., Takai Y. Regulation of binding of rhoB p20 to membranes by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella B. T., Erdman R. A., Maltese W. A. Carboxyl-terminal isoprenylation of ras-related GTP-binding proteins encoded by rac1, rac2, and ralA. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9786–9794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Calcium-dependence of catecholamine release from bovine adrenal medullary cells after exposure to intense electric fields. J Membr Biol. 1982;68(2):107–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01872259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffer A., Gomperts B. D. Soluble proteins as modulators of the exocytotic reaction of permeabilised rat mast cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94(Pt 3):585–591. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie T. H., Gomperts B. D. Guanine nucleotide is essential and Ca2+ is a modulator in the exocytotic reaction of permeabilized rat mast cells. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):181–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2880181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie T. H., Gomperts B. D. Nucleotides and divalent cations as effectors and modulators of exocytosis in permeabilized rat mast cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Apr 29;336(1276):25–34. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindau M., Gomperts B. D. Techniques and concepts in exocytosis: focus on mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):429–471. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90006-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Zhao Z. S., Lim L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):40–46. doi: 10.1038/367040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Gruber H. E., Walker L. L. Ribavirin inhibits mast cell mediator release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jan;240(1):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Okabe T., Sugimoto N., Senda T., Fujita H. Tetanus toxin and Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin as tools for the study of exocytosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Mar 9;710:94–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb26617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
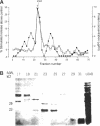
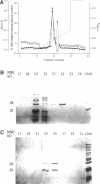
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Talamo B. R. Mediation of norepinephrine effects on free cytosolic calcium in rat parotid acinar cells by alpha 1 adrenergic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 1;37(19):3790–3793. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Interaction between protein kinase C and Exo1 (14-3-3 protein) and its relevance to exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):807–811. doi: 10.1042/bj2860807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Wilkinson M., Burgoyne R. D. Identification of Exo2 as the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A reveals a role for cyclic AMP in Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis in chromaffin cells. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3747–3752. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff V., Arold N., Taube D., Ehrhardt W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jun;9(6):255–262. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizaki T., Walent J. H., Kowalchyk J. A., Martin T. F. A key role for a 145-kDa cytosolic protein in the stimulation of Ca(2+)-dependent secretion by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23972–23981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobes C. D., Hall A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J. C., Price L. S., Ridley A. J., Hall A., Koffer A. Actin filament organization in activated mast cells is regulated by heterotrimeric and small GTP-binding proteins. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):1005–1015. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsse O., Lindau M., Cromwell O., Kay A. B., Gomperts B. D. Intracellular application of guanosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) induces exocytotic granule fusion in guinea pig eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):775–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price L. S., Norman J. C., Ridley A. J., Koffer A. The small GTPases Rac and Rho as regulators of secretion in mast cells. Curr Biol. 1995 Jan 1;5(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D., Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Identification of a key domain in annexin and 14-3-3 proteins that stimulate calcium-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 12;320(3):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80587-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Okajima F., Molski T. F., Sha'afi R. I., Ui M., Ishizaka T. Effects of ADP-ribosylation of GTP-binding protein by pertussis toxin on immunoglobulin E-dependent and -independent histamine release from mast cells and basophils. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3927–3934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian T., Aunis D., Bader M. F. Loss of proteins from digitonin-permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells essential for exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16671–16676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Correlation between secretion and phospholipase D activation in differentiated HL60 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):649–655. doi: 10.1042/bj2930649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Kikuchi A., Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61861-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Rodríguez del Castillo A., Vitale M. L. Dynamic changes in chromaffin cell cytoskeleton as prelude to exocytosis. Mol Neurobiol. 1992 Winter;6(4):339–358. doi: 10.1007/BF02757940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Deanin G. G., Standefer J. C., Vanderjagt D., Oliver J. M. Depletion of guanine nucleotides with mycophenolic acid suppresses IgE receptor-mediated degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]