Abstract
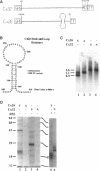
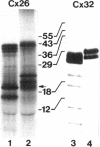
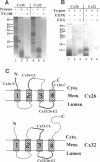
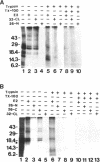
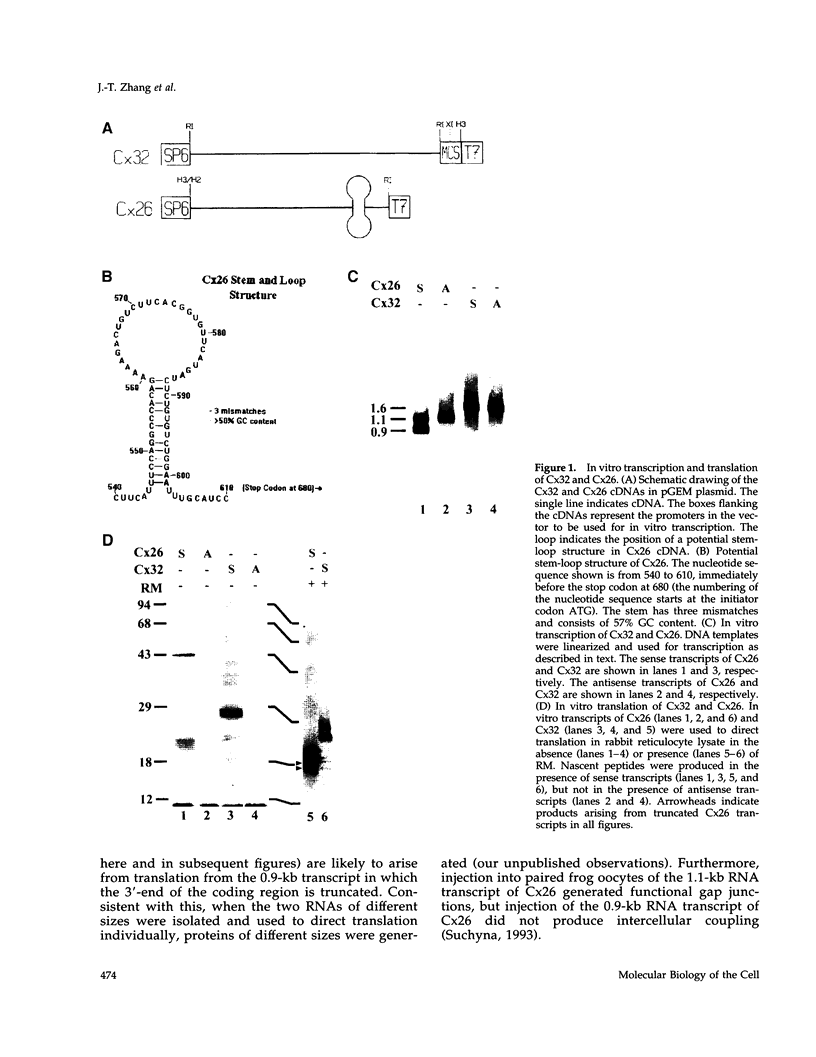
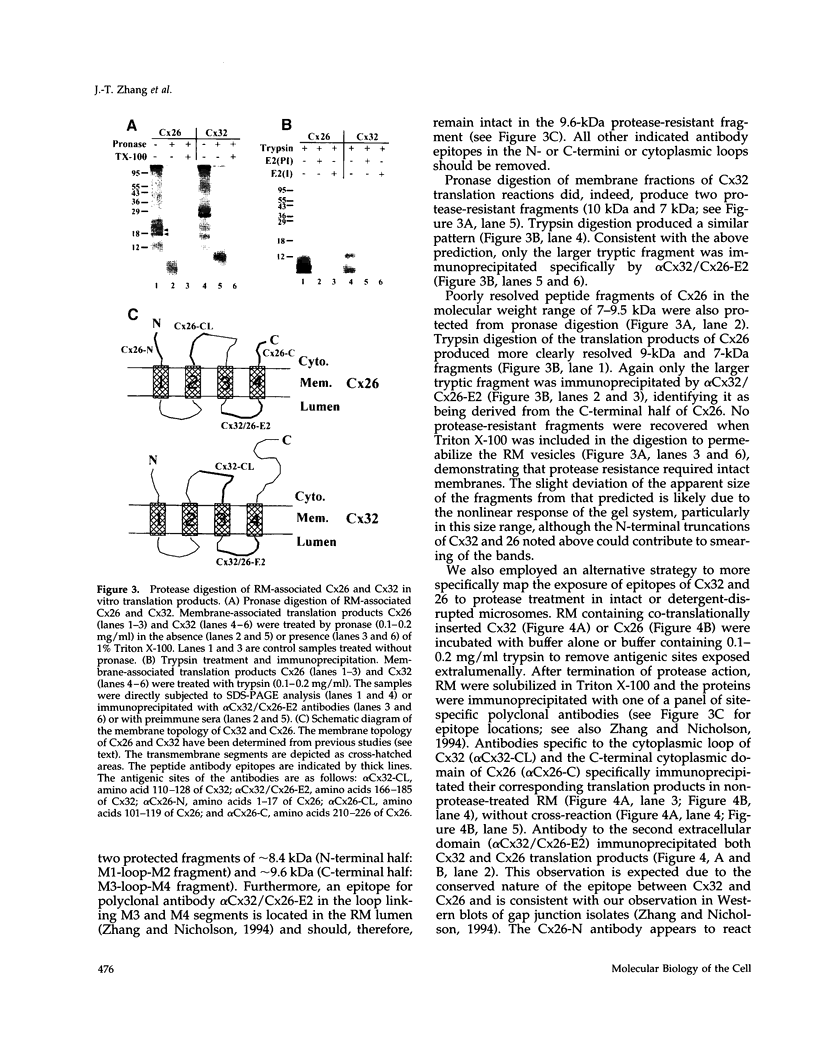
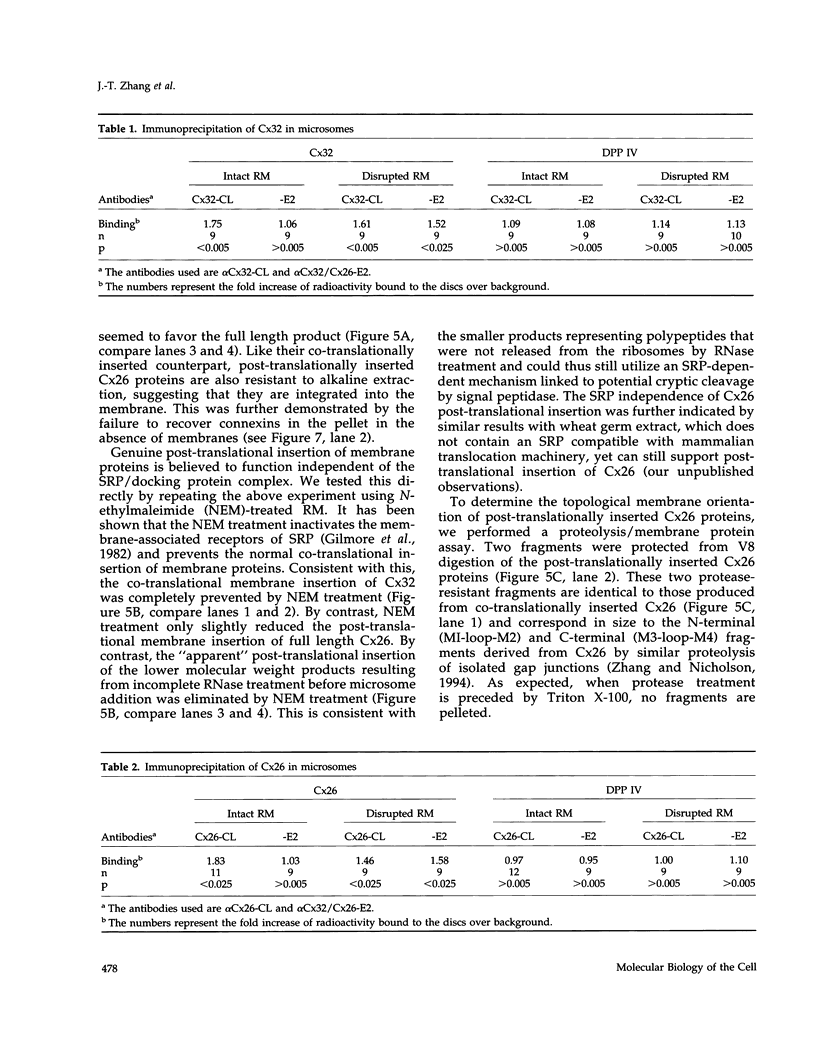
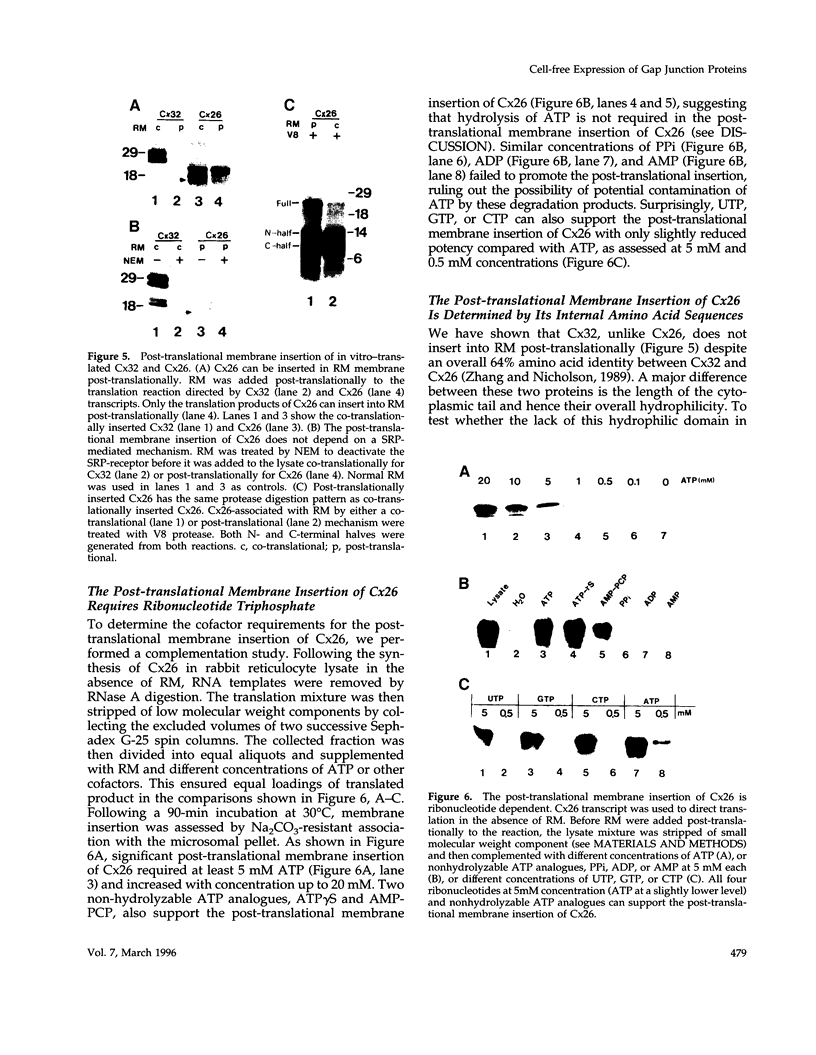
Connexins (Cx) are protein components of gap junction channels that permit the passage of small molecules between neighboring cells. cDNAs of a large family of connexins have been isolated and sequenced. A gap junction channel consists of two connexons, one from each cell in contact, composed of six connexin subunits. It has been suggested by Musil and coworkers that the oligomerization of formation of a connexon occurs at the level of the trans-Golgi network. In the present study, we initiated an analysis of the early stages of protein synthesis and membrane insertion of Cx32 and Cx26, two connexins that we have demonstrated are co-expressed in the same junctions in hepatocytes. Using an in vitro transcription and a coupled cell-free translation and translocation system, we observed that both Cx32 and Cx26 could insert into microsome membranes co-translationally, producing a topological structure indistinguishable from that in isolated gap junctions. To our surprise, Cx26 could also insert into membranes post-translationally with a native orientation. This post-translational membrane insertion process is dependent on nucleotides but not their hydrolysis. Cx32, on the other hand, could not insert into membranes post-translationally. These disparate properties of Cx32 and Cx26 are not due to the significant difference in the lengths of their C-terminal domains, but rather to their internal amino acid sequences. These observations raise the possibility that there may be another pathway for Cx26 to insert into membranes in cells and this feature may be important for the regulation of its functions. These findings may also lead us to a new approach to reconstitution without detergent extraction.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews D. Examining protein translocation in cell-free systems and microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):960-2, 964-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Goodenough D. A. Gap junctions, electrotonic coupling, and intercellular communication. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1978 Sep;16(3):1–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Gilmore R. Formation of a functional ribosome-membrane junction during translocation requires the participation of a GTP-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2253–2261. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Purification of microsomal signal peptidase as a complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M. M., Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Membrane insertion of gap junction connexins: polytopic channel forming membrane proteins. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):343–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Chappell T. G., Rothman J. E. Peptide binding and release by proteins implicated as catalysts of protein assembly. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):385–390. doi: 10.1126/science.2756425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman J., Nimmesgern E., Ohtsuka K., Hartl F. U. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):111–117. doi: 10.1038/370111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie S. C., Gilula N. B. Gap junctional communication and development. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Jan;12(1):12–16. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Disher R. M., Tiller A. A., Zhou Y., Cook R. G. Topology of the Mr 27,000 liver gap junction protein. Cytoplasmic localization of amino- and carboxyl termini and a hydrophilic domain which is protease-hypersensitive. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19105–19111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong W. J., Doyle D. Membrane orientation of rat gp110 as studied by in vitro translation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16892–16898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R. Translation in cell-free systems. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:267–276. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaunig J. E., Ruch R. J. Role of inhibition of intercellular communication in carcinogenesis. Lab Invest. 1990 Feb;62(2):135–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Molecular biology and genetics of gap junction channels. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;3(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication and the control of growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 4;560(1):1–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Prevention of protein denaturation under heat stress by the chaperonin Hsp60. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):995–998. doi: 10.1126/science.1359644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milks L. C., Kumar N. M., Houghten R., Unwin N., Gilula N. B. Topology of the 32-kd liver gap junction protein determined by site-directed antibody localizations. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):2967–2975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Lodish H. F. Post-translational insertion of a fragment of the glucose transporter into microsomes requires phosphoanhydride bond cleavage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):549–552. doi: 10.1038/322549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Lodish H. F. The human glucose transporter can insert posttranslationally into microsomes. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Goodenough D. A. Multisubunit assembly of an integral plasma membrane channel protein, gap junction connexin43, occurs after exit from the ER. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1065–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90728-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B. J., Hunkapiller M. W., Grim L. B., Hood L. E., Revel J. P. Rat liver gap junction protein: properties and partial sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7594–7598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B., Dermietzel R., Teplow D., Traub O., Willecke K., Revel J. P. Two homologous protein components of hepatic gap junctions. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):732–734. doi: 10.1038/329732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Rothman R. E., Lingappa V. R. Uncoupling translocation from translation: implications for transport of proteins across membranes. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):348–352. doi: 10.1126/science.3961485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman S., Evans W. H. Topography of connexin32 in rat liver gap junctions. Evidence for an intramolecular disulphide linkage connecting the two extracellular peptide loops. J Cell Sci. 1991 Nov;100(Pt 3):567–578. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Meyer D. I. Secretion in yeast: translocation and glycosylation of prepro-alpha-factor in vitro can occur via an ATP-dependent post-translational mechanism. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1031–1036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. E., Andrews D. W., Calayag M. C., Lingappa V. R. Construction of defined polytopic integral transmembrane proteins. The role of signal and stop transfer sequence permutations. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10470–10480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. D., Atkinson M. M. Physiological roles of permeable junctions: some possibilities. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:337–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Burt J. M. Structure-activity relations of the cardiac gap junction channel. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):C195–C205. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.2.C195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Chirico W. J., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the yeast microsomal membrane is stimulated by a soluble factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2629–2636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey S. B., John S. A., Lal R., Austin B. J., Revel J. P. The 43-kD polypeptide of heart gap junctions: immunolocalization, topology, and functional domains. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2241–2254. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. D., Korn H., Faber D. S. Long-term potentiation of electrotonic coupling at mixed synapses. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):542–545. doi: 10.1038/348542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Lee C. H., Duthie M., Ling V. Topological determinants of internal transmembrane segments in P-glycoprotein sequences. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 27;270(4):1742–1746. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.4.1742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Ling V. Membrane orientation of transmembrane segments 11 and 12 of MDR- and non-MDR-associated P-glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 12;1153(2):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90405-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Ling V. Study of membrane orientation and glycosylated extracellular loops of mouse P-glycoprotein by in vitro translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18224–18232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Nicholson B. J. Sequence and tissue distribution of a second protein of hepatic gap junctions, Cx26, as deduced from its cDNA. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3391–3401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Nicholson B. J. The topological structure of connexin 26 and its distribution compared to connexin 32 in hepatic gap junctions. J Membr Biol. 1994 Apr;139(1):15–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00232671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Gavel Y. Topogenic signals in integral membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):671–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]