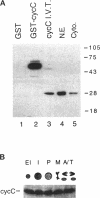
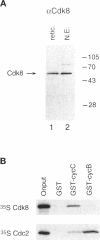
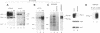Abstract
A number of cyclins have been described, most of which act together with their catalytic partners, the cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), to regulate events in the eukaryotic cell cycle. Cyclin C was originally identified by a genetic screen for human and Drosophila cDNAs that complement a triple knock-out of the CLN genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Unlike other cyclins identified in this complementation screen, there has been no evidence that cyclin C has a cell-cycle role in the cognate organism. Here we report that cyclin C is a nuclear protein present in a multiprotein complex. It interacts both in vitro and in vivo with Cdk8, a novel protein-kinase of the Cdk family, structurally related to the yeast Srb10 kinase. We also show that Cdk8 can interact in vivo with the large subunit of RNA polymerase II and that a kinase activity that phosphorylates the RNA polymerase II large subunit is present in Cdk8 immunoprecipitates. Based on these observations and sequence similarity to the kinase/cyclin pair Srb10/Srb11 in S. cerevisiae, we suggest that cyclin C and Cdk8 control RNA polymerase II function.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besse S., Vigneron M., Pichard E., Puvion-Dutilleul F. Synthesis and maturation of viral transcripts in herpes simplex virus type 1 infected HeLa cells: the role of interchromatin granules. Gene Expr. 1995;4(3):143–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R. Cyclin-dependent kinases. CAK-handed kinase activation. Curr Biol. 1995 Jan 1;5(1):40–42. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor has an associated DNA-dependent ATPase (dATPase) activity strongly stimulated by the TATA region of promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessen P., Fondrat C., Valencien C., Mugnier C. BISANCE: a French service for access to biomolecular sequence databases. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Oct;6(4):355–356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Draetta G. Mutations at sites involved in Suc1 binding inactivate Cdc2. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6177–6184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., Sprenger F., Duronio R. J., Leopold P., O'Farrell P. H. Distinct molecular mechanism regulate cell cycle timing at successive stages of Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 15;8(4):440–452. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Nurse P., Johnson L. N. Mutational analysis supports a structural model for the cell cycle protein kinase p34. Protein Eng. 1994 Feb;7(2):243–253. doi: 10.1093/protein/7.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Gileadi O., Li Y., Kornberg R. D. CTD kinase associated with yeast RNA polymerase II initiation factor b. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90298-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Svejstrup J. Q., Henry N. L., Kornberg R. D. Relationship of CDK-activating kinase and RNA polymerase II CTD kinase TFIIH/TFIIK. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1103–1109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Derancourt J., Capony J. P., Galas S., Girard F., Lorca T., Shuttleworth J., Dorée M., Cavadore J. C. The MO15 gene encodes the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that activates cdc2 and other cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) through phosphorylation of Thr161 and its homologues. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3111–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Morgan D. O. A novel cyclin associates with MO15/CDK7 to form the CDK-activating kinase. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90535-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner C. J., Thompson C. M., Zhang J., Chao D. M., Liao S. M., Koleske A. J., Okamura S., Young R. A. Association of an activator with an RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 15;9(8):897–910. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.8.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst K., Fisher F., McAndrew P. C., Goding C. R. The transcription factor, the Cdk, its cyclin and their regulator: directing the transcriptional response to a nutritional signal. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5410–5420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06876.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D., Russo A. A., Polyak K., Gibbs E., Hurwitz J., Massagué J., Pavletich N. P. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):313–320. doi: 10.1038/376313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaffman A., Herskowitz I., Tjian R., O'Shea E. K. Phosphorylation of the transcription factor PHO4 by a cyclin-CDK complex, PHO80-PHO85. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1153–1156. doi: 10.1126/science.8108735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Björklund S., Li Y., Sayre M. H., Kornberg R. D. A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. W., Jackson P. K., Kirschner M. W. Mitosis in transition. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Buratowski S., Nonet M., Young R. A. A novel transcription factor reveals a functional link between the RNA polymerase II CTD and TFIID. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90298-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Young R. A. An RNA polymerase II holoenzyme responsive to activators. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):466–469. doi: 10.1038/368466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Young R. A. The RNA polymerase II holoenzyme and its implications for gene regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Mar;20(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88977-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Haars R., Kabisch R., Will H., Bautz F. A., Bautz E. K. Monoclonal antibody directed against RNA polymerase II of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):193–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00267369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchin S., Yeghiayan P., Carlson M. Cyclin-dependent protein kinase and cyclin homologs SSN3 and SSN8 contribute to transcriptional control in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahue E. E., Smith A. V., Orr-Weaver T. L. A novel cyclin gene from Drosophila complements CLN function in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2166–2175. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. A protein kinase that phosphorylates the C-terminal repeat domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Drosophila cdc2 homologs: a functional homolog is coexpressed with a cognate variant. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3573–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. M., Zhang J., Jeffery D. A., Koleske A. J., Thompson C. M., Chao D. M., Viljoen M., van Vuuren H. J., Young R. A. A kinase-cyclin pair in the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):193–196. doi: 10.1038/374193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léopold P., O'Farrell P. H. An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90043-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):131–134. doi: 10.1038/374131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Tassan J. P., Nigg E. A., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Weinberg R. A. A cyclin associated with the CDK-activating kinase MO15. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):254–257. doi: 10.1038/371254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. Cyclin-dependent protein kinases: key regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Bioessays. 1995 Jun;17(6):471–480. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Ordering S phase and M phase in the cell cycle. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Shuttleworth J. The cdc2-related protein p40MO15 is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that can activate p33cdk2 and p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3123–3132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R., Adamczewski J. P., Seroz T., Vermeulen W., Tassan J. P., Schaeffer L., Nigg E. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M. The MO15 cell cycle kinase is associated with the TFIIH transcription-DNA repair factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1093–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K. R., Smith R. L., O'Shea E. K. Phosphate-regulated inactivation of the kinase PHO80-PHO85 by the CDK inhibitor PHO81. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):122–126. doi: 10.1126/science.7939631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. J., Nigg E. A. Identification of 21 novel human protein kinases, including 3 members of a family related to the cell cycle regulator nimA of Aspergillus nidulans. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Oct;4(10):821–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Mäkelä T. P., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C., Weinberg R. A., Young R. A. Association of Cdk-activating kinase subunits with transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):280–282. doi: 10.1038/374280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiekhattar R., Mermelstein F., Fisher R. P., Drapkin R., Dynlacht B., Wessling H. C., Morgan D. O., Reinberg D. Cdk-activating kinase complex is a component of human transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):283–287. doi: 10.1038/374283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger F., Trosclair M. M., Morrison D. K. Biochemical analysis of torso and D-raf during Drosophila embryogenesis: implications for terminal signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1163–1172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surosky R. T., Strich R., Esposito R. E. The yeast UME5 gene regulates the stability of meiotic mRNAs in response to glucose. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3446–3458. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassan J. P., Jaquenoud M., Léopold P., Schultz S. J., Nigg E. A. Identification of human cyclin-dependent kinase 8, a putative protein kinase partner for cyclin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8871–8875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassan J. P., Schultz S. J., Bartek J., Nigg E. A. Cell cycle analysis of the activity, subcellular localization, and subunit composition of human CAK (CDK-activating kinase). J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):467–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. M., Koleske A. J., Chao D. M., Young R. A. A multisubunit complex associated with the RNA polymerase II CTD and TATA-binding protein in yeast. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1361–1375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90362-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahi M., Johnson A. D. Identification of genes required for alpha 2 repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1995 May;140(1):79–90. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Signaling and regulation by a mammalian glucocorticoid receptor in Drosophila cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;5(6):844–853. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-6-844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]