Abstract
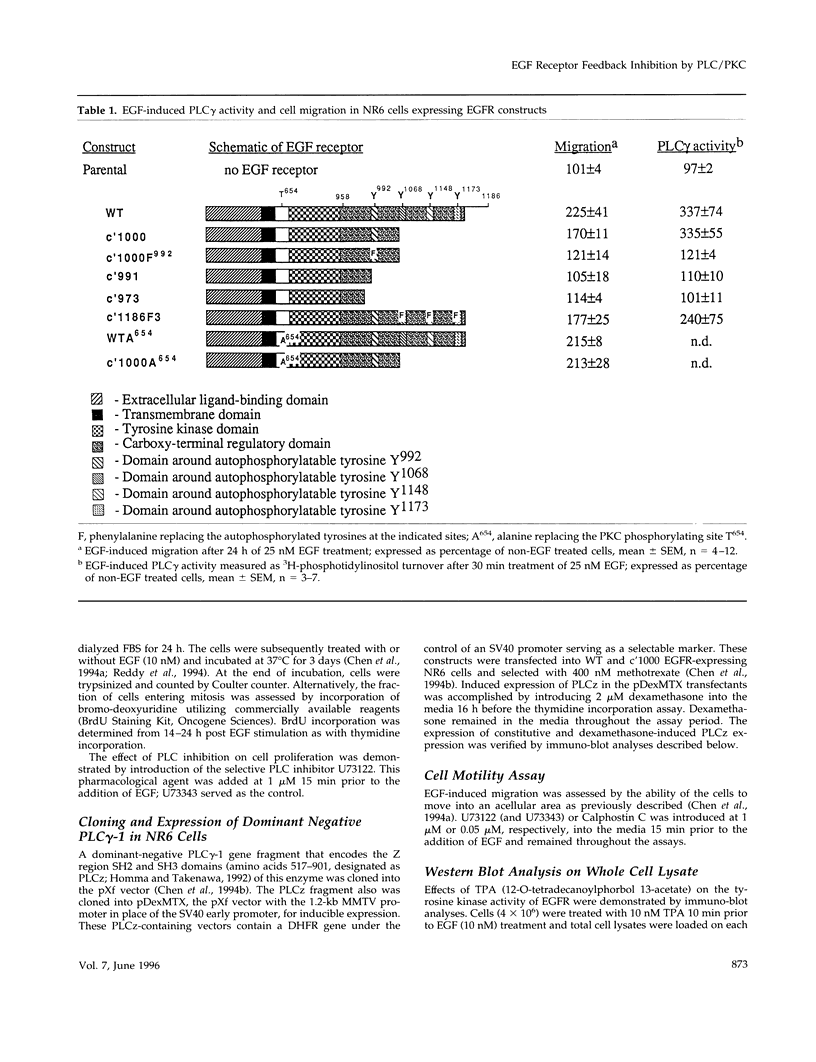
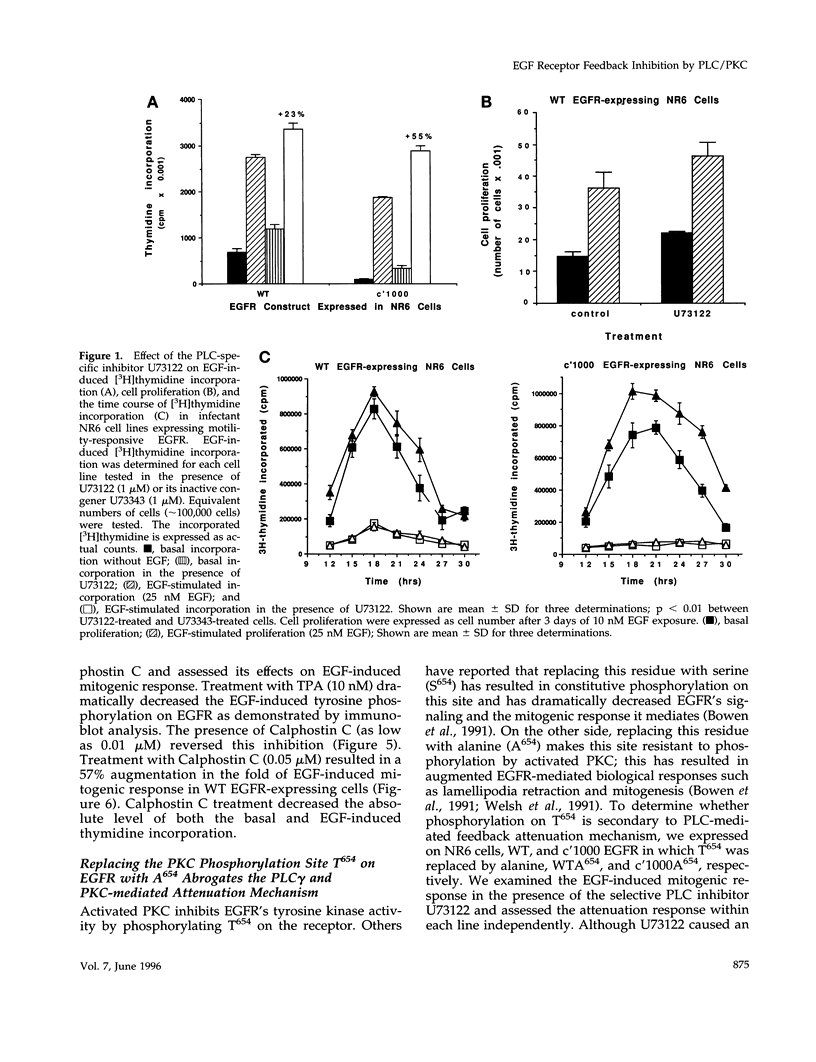
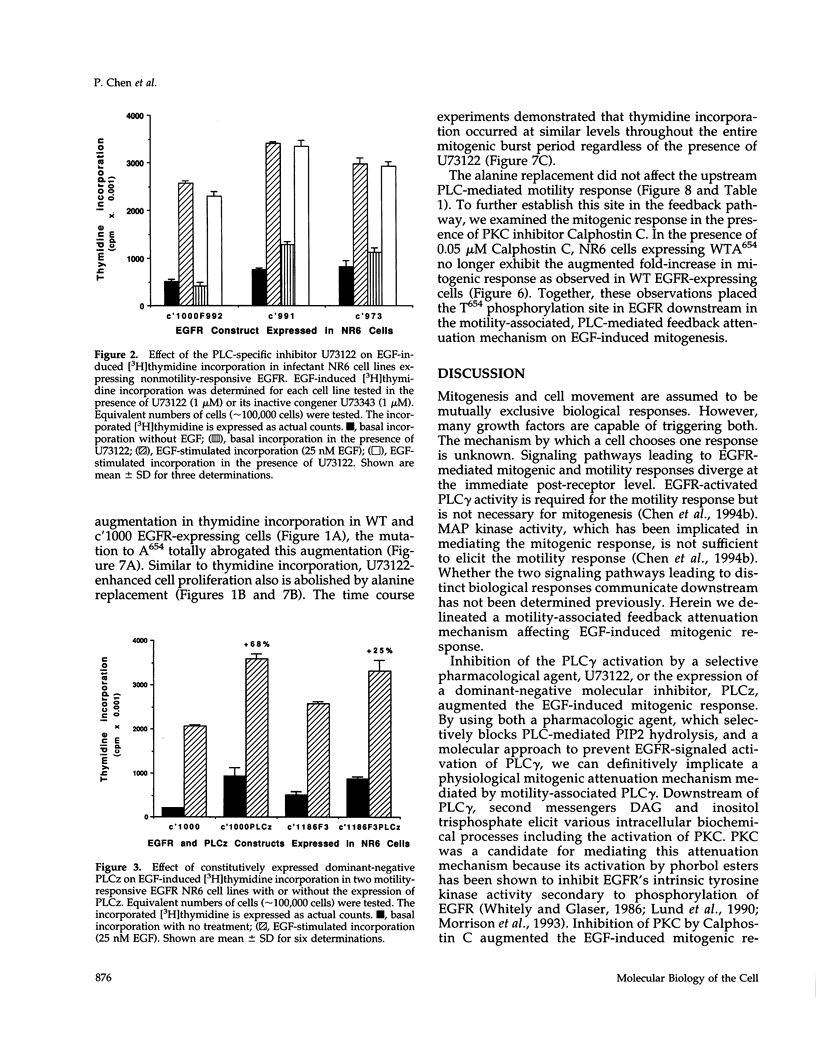
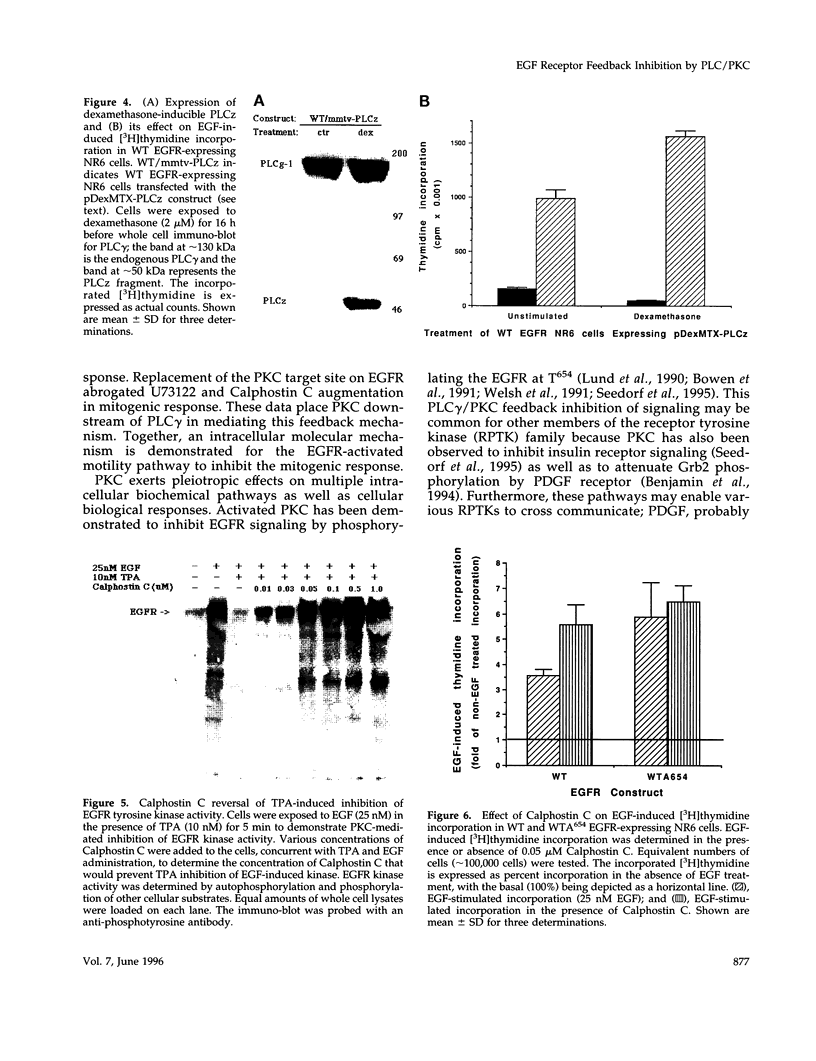
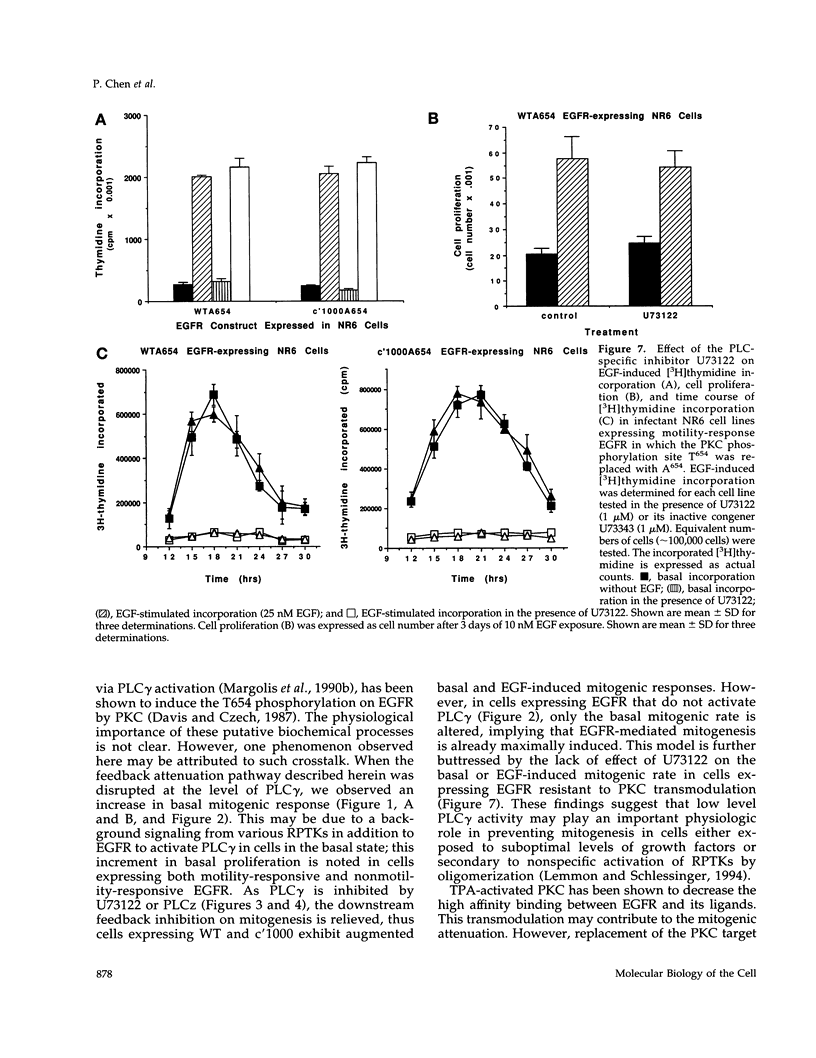
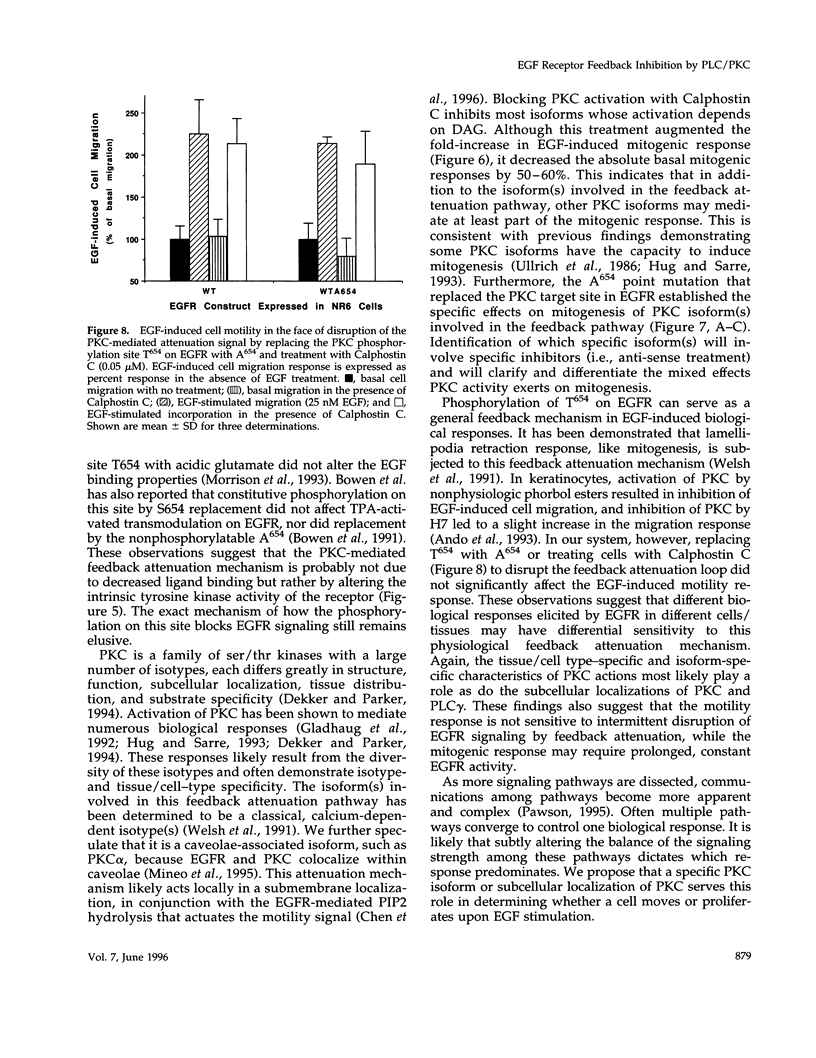
We recently demonstrated that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mediated signaling of cell motility and mitogenesis diverge at the immediate post-receptor level. How these two mutually exclusive cell responses cross-communicate is not known. We investigated a possible role for a phospholipase C (PLC)-dependent feedback mechanism that attenuates EGF-induced mitogenesis. Inhibition of PLC gamma activation by U73122 (1 microM) augmented the EGF-induced [3H]thymidine incorporation by 23-55% in two transduced NR6 fibroblast lines expressing motility-responsive EGFR; increased cell division and mitosis was observed in parallel. The time dependence of this increase revealed that it was due to an increase in maximal incorporation and not a foreshortened cell cycle. Motility-responsive cell lines expressing a dominant-negative PLC gamma fragment (PLCz) also demonstrated augmented mitogenic responses by 25-68% when compared with control cells. PLCz- or U73122-augmented mitogenesis was not observed in three non-PLC gamma activating, nonmotility-responsive EGFR-expressing cell lines. Protein kinase C (PKC), which may be activated by PLC-generated second messengers, has been proposed as mediating feedback attenuation due to its capacity to phosphorylate EGFR and inhibit the receptor's tyrosine kinase activity. Inhibition of PKC by Calphostin C (0.05 microM) resulted in a 57% augmentation in the fold of EGF-induced thymidine incorporation. To further establish PKC's role in this feedback attenuation mechanism, an EGFR point mutation, in which the PKC target threonine654 was replaced by alanine, was expressed. Cells expressing these PKC-resistant EGFR constructs demonstrated EGF-induced motility comparable to cells expressing the threonine-containing EGFR. However, when these cells were treated with U73122 or Calphostin C, the mitogenic responses are not enhanced. These findings suggest a model in which PKC activation subsequent to triggering of motility-associated PLC gamma activity attenuates the EGFR mitogenic response.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D. EGF receptor activities in mammalian development. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Sep;27(1):16–22. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080270106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderem A. Signal transduction and the actin cytoskeleton: the roles of MARCKS and profilin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Lazarus G. S., Jensen P. J. Activation of protein kinase C inhibits human keratinocyte migration. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Sep;156(3):487–496. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041560308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin C. W., Linseman D. A., Jones D. A. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates phosphorylation of growth factor receptor-binding protein-2 in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31346–31349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Thakur N. R., Gremban R. S., Bundy G. L., Fitzpatrick F. A., Smith R. J., Bunting S. Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):756–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen S., Stanley K., Selva E., Davis R. J. Constitutive phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor blocks mitogenic signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1162–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Gupta K., Wells A. Cell movement elicited by epidermal growth factor receptor requires kinase and autophosphorylation but is separable from mitogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):547–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Xie H., Sekar M. C., Gupta K., Wells A. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated cell motility: phospholipase C activity is required, but mitogen-activated protein kinase activity is not sufficient for induced cell movement. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):847–857. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Stimulation of epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 654 phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor in protein kinase C-deficient human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6832–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J. Transmembrane signaling by epidermal growth factor receptors lacking autophosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9176–9179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., Parker P. J. Protein kinase C--a question of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faletto D. L., Kaplan D. R., Halverson D. O., Rosen E. M., Vande Woude G. F. Signal transduction in c-met mediated motogenesis. EXS. 1993;65:107–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladhaug I. P., Refsnes M., Christoffersen T. Regulation of surface expression of high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor (EGF) in hepatocytes by hormones, differentiating agents, and phorbol ester. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Feb;37(2):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01308177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson A., Skoglund G., Lassing I., Lindberg U., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of profilin is specifically stimulated by phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):526–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Naldini L., Weidner K. M., Sachs M., Vigna E., Comoglio P. M., Birchmeier W. A functional domain in the heavy chain of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor binds the c-Met receptor and induces cell dissociation but not mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11574–11578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Takenawa T. Inhibitory effect of src homology (SH) 2/SH3 fragments of phospholipase C-gamma on the catalytic activity of phospholipase C isoforms. Identification of a novel phospholipase C inhibitor region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21844–21849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Sarre T. F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):329–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2910329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez de Asua L., Goin M. Prostaglandin F2 alpha decreases the affinity of epidermal growth factor receptors in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells via protein kinase C activation. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 16;299(3):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80122-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Schlessinger J. Regulation of signal transduction and signal diversity by receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K. A., Lazar C. S., Chen W. S., Walsh B. J., Welsh J. B., Herbst J. J., Walton G. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N., Wiley H. S. Phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 654 inhibits ligand-induced internalization and down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20517–20523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manske M., Bade E. G. Growth factor-induced cell migration: biology and methods of analysis. Int Rev Cytol. 1994;155:49–96. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Zilberstein A., Franks C., Felder S., Kremer S., Ullrich A., Rhee S. G., Skorecki K., Schlessinger J. Effect of phospholipase C-gamma overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.2333512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marikovsky M., Breuing K., Liu P. Y., Eriksson E., Higashiyama S., Farber P., Abraham J., Klagsbrun M. Appearance of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in wound fluid as a response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen P. J., Berger J. E., Meneses J., Phung Y., Pedersen R. A., Werb Z., Derynck R. Epithelial immaturity and multiorgan failure in mice lacking epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):337–341. doi: 10.1038/376337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison P., Takishima K., Rosner M. R. Role of threonine residues in regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15536–15543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistér M., Hammacher A., Mellström K., Siegbahn A., Rönnstrand L., Westermark B., Heldin C. H. A glioma-derived PDGF A chain homodimer has different functional activities from a PDGF AB heterodimer purified from human platelets. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):791–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis G., Seewald M. J., Gratas C., Melder D., Riebow J., Modest E. J. Selective inhibition of phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C by cytotoxic ether lipid analogues. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2835–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Variants of 3T3 cells lacking mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. C., Wells A., Lauffenburger D. A. Proliferative response of fibroblasts expressing internalization-deficient epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors is altered via differential EGF depletion effect. Biotechnol Prog. 1994 Jul-Aug;10(4):377–384. doi: 10.1021/bp00028a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds N. J., Talwar H. S., Baldassare J. J., Henderson P. A., Elder J. T., Voorhees J. J., Fisher G. J. Differential induction of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis, diacylglycerol formation and protein kinase C activation by epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha in normal human skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):535–544. doi: 10.1042/bj2940535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Shearman M., Ullrich A. Rapid and long-term effects on protein kinase C on receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18953–18960. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibilia M., Wagner E. F. Strain-dependent epithelial defects in mice lacking the EGF receptor. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):234–238. doi: 10.1126/science.7618085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Riedel H., Yarden Y., Coussens L., Gray A., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Protein kinases in cellular signal transduction: tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors and protein kinase C. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):713–724. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Welsh J. B., Lazar C. S., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Ligand-induced transformation by a noninternalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):962–964. doi: 10.1126/science.2305263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. B., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G., Wells A. A negative feedback loop attenuates EGF-induced morphological changes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):533–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley B., Glaser L. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) promotes phosphorylation at threonine-654 of the EGF receptor: possible role of protein kinase C in homologous regulation of the EGF receptor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1355–1362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




