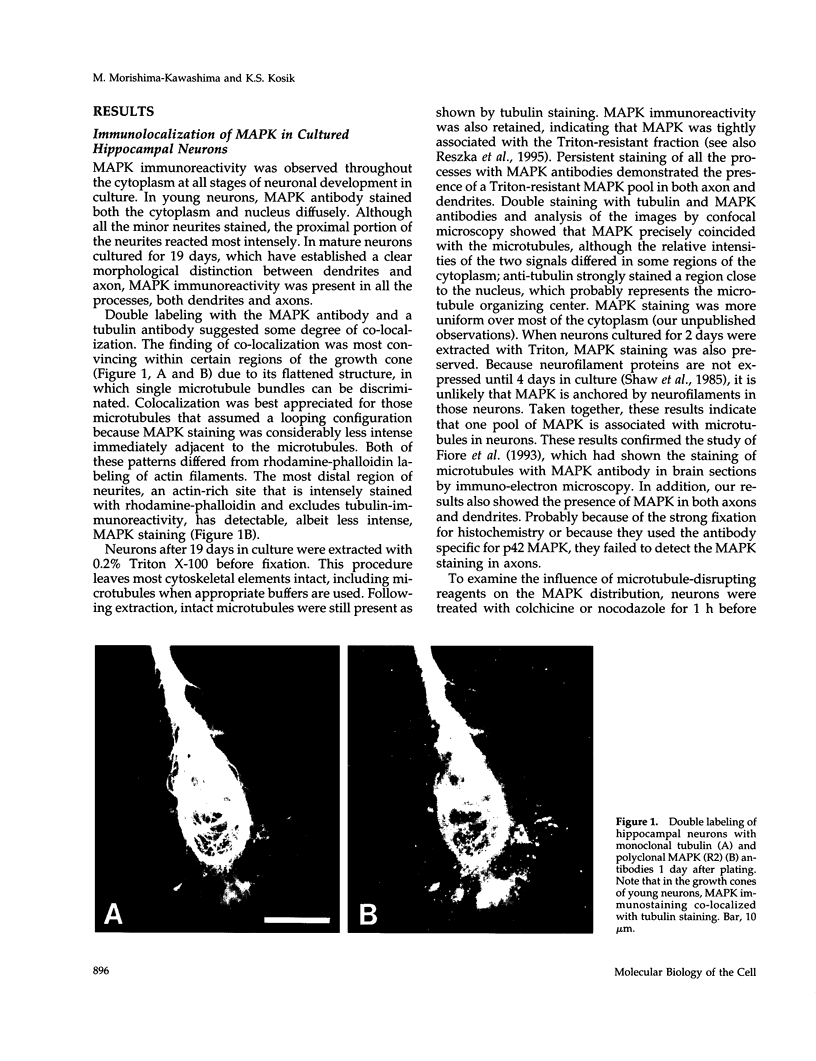
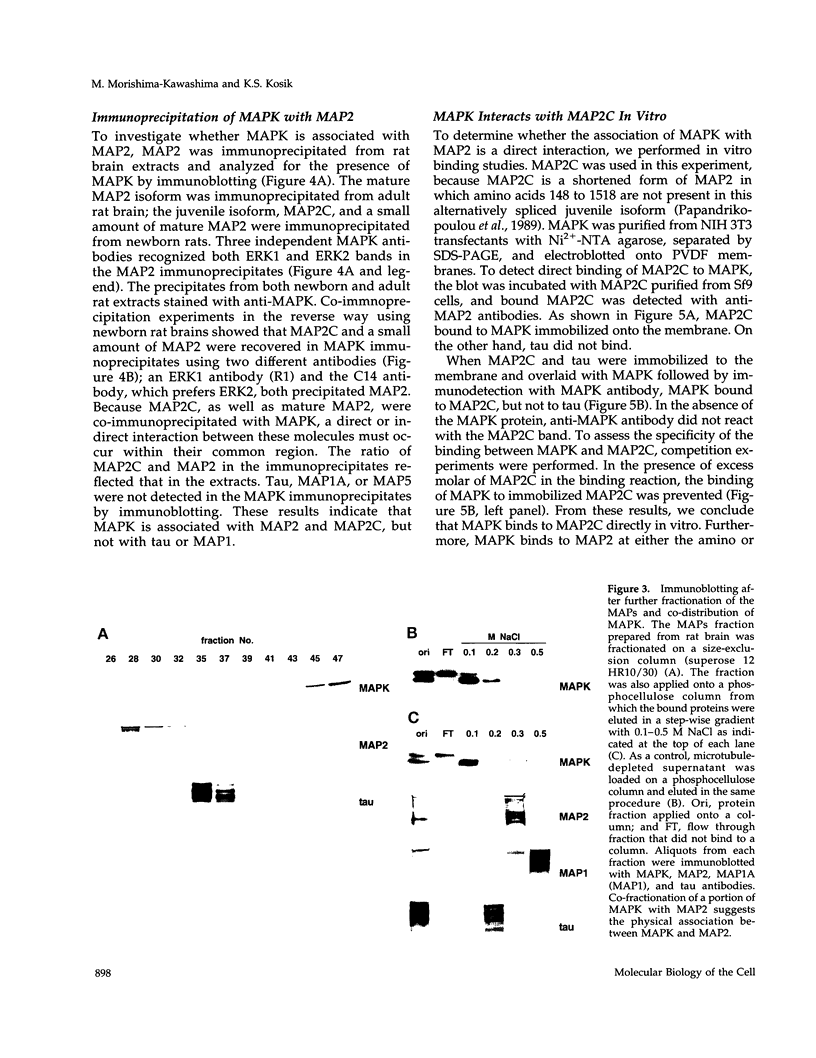
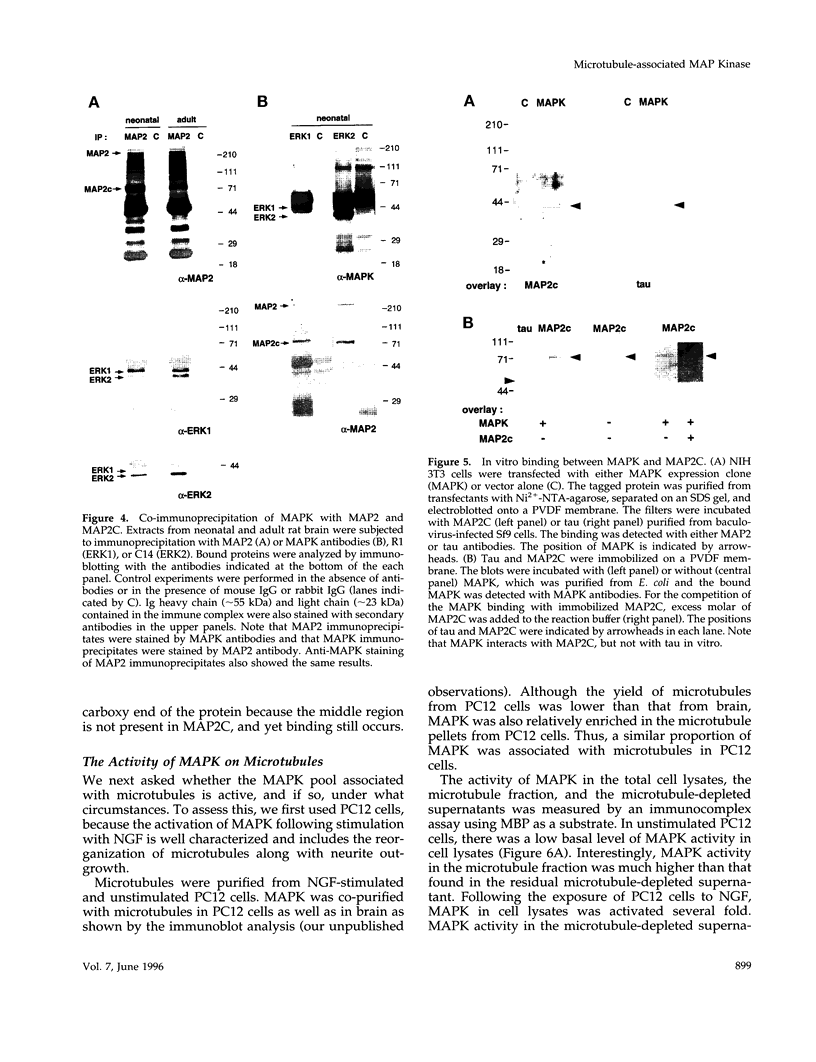
Abstract
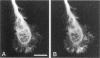
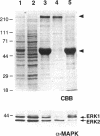
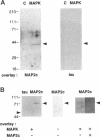
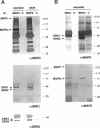
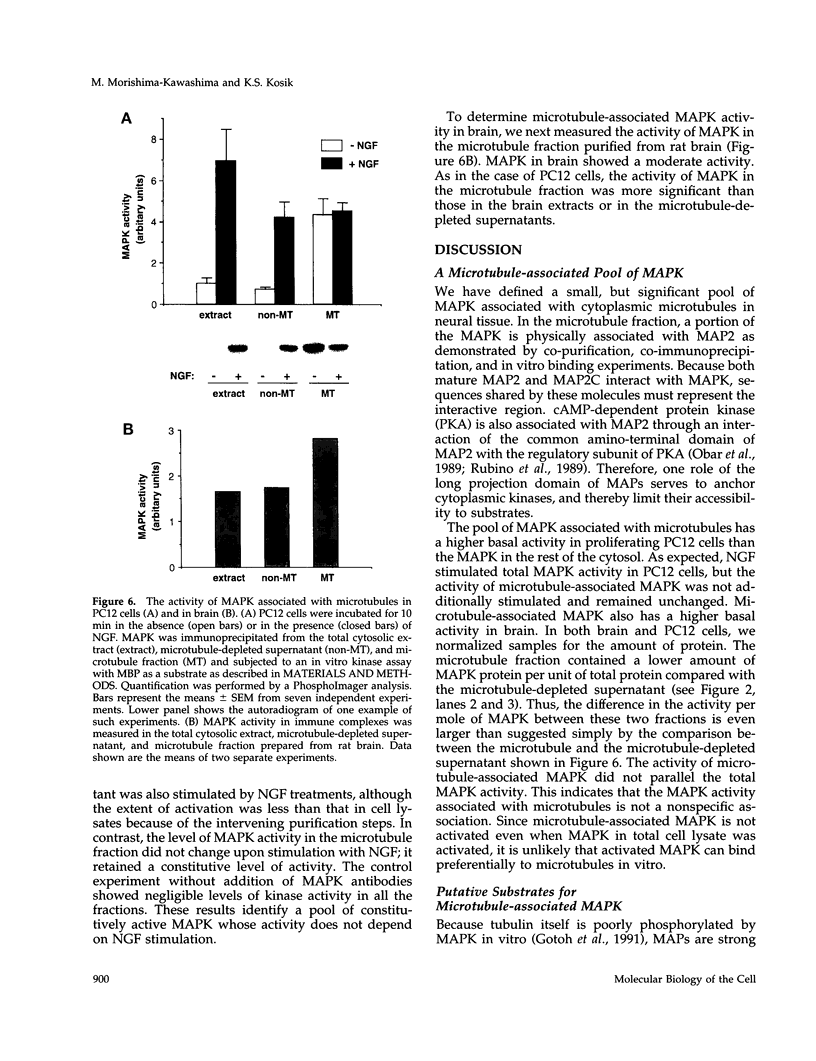
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is activated by many kinds of stimuli and plays an important role in integrating signal transduction cascades. MAPK is present abundantly in brain, where we have studied its association with microtubules. Immunofluorescence of primary hippocampal neurons revealed that MAPK staining co-localized with microtubules and biochemical analyses showed that MAPK co-purified with microtubules. Approximately 4% of MAPK in cytosolic extracts was associated with microtubules, where it was associated with both tubulin and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) fractions. Further fractionation of MAPs suggested that a portion of MAPK is associated with MAP2. An association with MAP2 was also demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation and in vitro binding experiments. A similar association was shown for the juvenile MAP2 isoform, MAP2C. The pool of MAPK associated with microtubules had a higher activity relative to the nonassociated pool in both brain and proliferating PC12 cells. Although MAPK was activated by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells, the activity of microtubule-associated MAPK did not further increase. These results raise the possibility that microtubule-associated MAPK operates through constitutive phosphorylation activity to regulate microtubule function in neurons.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Krebs E. G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Li P., Marsden L. A., Williams N., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Raf-1 is a potential substrate for mitogen-activated protein kinase in vivo. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):573–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2770573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Sato G. H. Growth of a rat neuroblastoma cell line in serum-free supplemented medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):514–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. Identification of multiple extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) with antipeptide antibodies. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):357–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Slaughter T., Black M. M. Newly assembled microtubules are concentrated in the proximal and distal regions of growing axons. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):867–882. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner D., Oellers N., Szabad J., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Zipursky S. L., Hafen E. A gain-of-function mutation in Drosophila MAP kinase activates multiple receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathways. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):875–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. T., Cobb M. H., Baer R. Phosphorylation of the TAL1 oncoprotein by the extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinase ERK1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):801–808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Pelech S. L., Blenis J. Mitogen-activated Swiss mouse 3T3 RSK kinases I and II are related to pp44mpk from sea star oocytes and participate in the regulation of pp90rsk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley S., Paterson H., Kemp P., Marshall C. J. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):841–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel D. N., Hyman A. A., Cobb M. H., Kirschner M. W. Modulation of the dynamic instability of tubulin assembly by the microtubule-associated protein tau. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1141–1154. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes G., Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Döring F., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Goris J., Dorée M., Mandelkow E. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase transforms tau protein into an Alzheimer-like state. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Nguyen V. T., Dahmus M. E., Pagès G., Pouysségur J., Bensaude O. Enhanced phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II upon serum stimulation of quiescent cells: possible involvement of MAP kinases. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4787–4797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldar-Finkelman H., Seger R., Vandenheede J. R., Krebs E. G. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by epidermal growth factor is mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase/p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway in NIH/3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):987–990. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiore R. S., Bayer V. E., Pelech S. L., Posada J., Cooper J. A., Baraban J. M. p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in brain: prominent localization in neuronal cell bodies and dendrites. Neuroscience. 1993 Jul;55(2):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90516-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Cohen E. S., Jakes R., Cohen P. p42 MAP kinase phosphorylation sites in microtubule-associated protein tau are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A1. Implications for Alzheimer's disease [corrected]. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 2;312(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81418-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Seth A., Raden D. L., Bowman D. S., Fay F. S., Davis R. J. Serum-induced translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase to the cell surface ruffling membrane and the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1089–1101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. M., Koo E. H., Selkoe D. J., Qiu W. Q., Kosik K. S. Secreted beta-amyloid precursor protein stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase and enhances tau phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustke N., Steiner B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Meyer H. E., Goedert M., Mandelkow E. The Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau protein reduces microtubule binding and involves Ser-Pro and Thr-Pro motifs. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80767-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm-Alvarez S. F., Kim P. Y., Sheetz M. P. Regulation of vesicle transport in CV-1 cells and extracts. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):955–966. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi M., Ohta K., Gotoh Y., Mori A., Murofushi H., Sakai H., Nishida E. Mitogen-activated-protein-kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins, microtubule-associated protein 2 and microtubule-associated protein 4, induces an alteration in their function. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):43–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y., Fujii T., Arai T., Tanaka R., Kaziro Y. The presence of an adenosine-5'-triphosphatase dependent on 6S tubulin and calcium ions in rat brain microtubules. J Biochem. 1979 Aug;86(2):587–590. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Shiratsuchi A., Sato S., Omori A., Arioka M., Kobayashi S., Uchida T., Imahori K. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta is identical to tau protein kinase I generating several epitopes of paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 5;325(3):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Takamatsu M., Tomizawa K., Omori A., Takahashi M., Arioka M., Uchida T., Imahori K. Tau protein kinase I converts normal tau protein into A68-like component of paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10897–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Vaillancourt R. R. Sequential protein kinase reactions controlling cell growth and differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;6(2):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Microtubules, membrane traffic, and cell organization. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90206-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knops J., Kosik K. S., Lee G., Pardee J. D., Cohen-Gould L., McConlogue L. Overexpression of tau in a nonneuronal cell induces long cellular processes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):725–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Ishiguro K., Omori A., Takamatsu M., Arioka M., Imahori K., Uchida T. A cdc2-related kinase PSSALRE/cdk5 is homologous with the 30 kDa subunit of tau protein kinase II, a proline-directed protein kinase associated with microtubule. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 6;335(2):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80723-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Binder L., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Lee G. Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoinne A., Erikson E., Maller J. L., Price D. J., Avruch J., Cohen P. Purification and characterisation of the insulin-stimulated protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle; close similarity to S6 kinase II. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):723–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc N., Kosik K. S., Cowan N., Pienkowski T. P., Baas P. W. Process formation in Sf9 cells induced by the expression of a microtubule-associated protein 2C-like construct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6223–6227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. M., Cobb M. H., Blackshear P. J. Evidence that extracellular signal-regulated kinases are the insulin-activated Raf-1 kinase kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1088–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton I. A., Curmi P., Campbell D. G., Cohen P., Sobel A. The phosphorylation of stathmin by MAP kinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 Nov;127-128:151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF01076766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Sardet C., Pagès G., L'Allemain G., Brunet A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce nuclear translocation of MAP kinases (p42mapk and p44mapk) but not of their activator MAP kinase kinase (p45mapkk) in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1079–1088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindwall G., Cole R. D. Phosphorylation affects the ability of tau protein to promote microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5301–5305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Scherer P. E., Vidugiriene J., Tang Z., Hermanowski-Vosatka A., Tu Y. H., Cook R. F., Sargiacomo M. Characterization of caveolin-rich membrane domains isolated from an endothelial-rich source: implications for human disease. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):111–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Tsao H., Cobb M. H., Greene L. A. NGF and other growth factors induce an association between ERK1 and the NGF receptor, gp140prototrk. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1053–1065. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90065-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q., Soria J. P., Wood J. G. p44mpk MAP kinase induces Alzheimer type alterations in tau function and in primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Jul 1;35(4):439–444. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Drewes G., Biernat J., Gustke N., Van Lint J., Vandenheede J. R., Mandelkow E. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and the Alzheimer-like state of microtubule-associated protein tau. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. J., Matten W. T., Hermann A. S., Candia J. M., Rong S., Fukasawa K., Vande Woude G. F., Ahn N. G. Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP kinase kinase. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):966–970. doi: 10.1126/science.8052857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Phosphorylation of Xenopus mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase by MAP kinase kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3277–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo E. S., Shin R. W., Billingsley M. L., Van deVoorde A., O'Connor M., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. Biopsy-derived adult human brain tau is phosphorylated at many of the same sites as Alzheimer's disease paired helical filament tau. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):989–1002. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlvain J. M., Jr, Burkhardt J. K., Hamm-Alvarez S., Argon Y., Sheetz M. P. Regulation of kinesin activity by phosphorylation of kinesin-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19176–19182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D. Localization of protein kinases by anchoring proteins: a theme in signal transduction. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):247–251. doi: 10.1126/science.7716516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima-Kawashima M., Hasegawa M., Takio K., Suzuki M., Yoshida H., Titani K., Ihara Y. Proline-directed and non-proline-directed phosphorylation of PHF-tau. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):823–829. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Kinoshita S., Sasagawa T., Sasaki K., Naruto M., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Phosphorylation at threonine-235 by a ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is essential for transcription factor NF-IL6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2207–2211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R. Inactivation of MAP kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Wartmann M., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Isolation and characterization of two growth factor-stimulated protein kinases that phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 669. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15266–15276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Dingus J., Bayley H., Vallee R. B. The RII subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase binds to a common amino-terminal domain in microtubule-associated proteins 2A, 2B, and 2C. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookata K., Hisanaga S., Bulinski J. C., Murofushi H., Aizawa H., Itoh T. J., Hotani H., Okumura E., Tachibana K., Kishimoto T. Cyclin B interaction with microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4) targets p34cdc2 kinase to microtubules and is a potential regulator of M-phase microtubule dynamics. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):849–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papandrikopoulou A., Doll T., Tucker R. P., Garner C. C., Matus A. Embryonic MAP2 lacks the cross-linking sidearm sequences and dendritic targeting signal of adult MAP2. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):650–652. doi: 10.1038/340650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattner J. B., Lew J., Wang J. H. p34cdc2 kinase is localized to distinct domains within the mitotic apparatus. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;17(3):227–235. doi: 10.1002/cm.970170309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reszka A. A., Seger R., Diltz C. D., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Association of mitogen-activated protein kinase with the microtubule cytoskeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8881–8885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Zhen E., Owaki H., Vanderbilt C. A., Ebert D., Geppert T. D., Cobb M. H. Regulation and properties of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5097–5106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino H. M., Dammerman M., Shafit-Zagardo B., Erlichman J. Localization and characterization of the binding site for the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase on MAP2. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Peter M., Nigg E. A., Pelech S. L. Immunological characterization of avian MAP kinases: evidence for nuclear localization. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):775–787. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato-Yoshitake R., Yorifuji H., Inagaki M., Hirokawa N. The phosphorylation of kinesin regulates its binding to synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23930–23936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Krebs E. G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Banker G. A., Weber K. An immunofluorescence study of neurofilament protein expression by developing hippocampal neurons in tissue culture. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;39(1):205–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Rudolph S. A., Rosenbaum J. L., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP-dependent endogenous phosphorylation of a microtubule-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag E., Fedorov S., Kamibayashi C., Robbins D., Cobb M., Mumby M. The interaction of SV40 small tumor antigen with protein phosphatase 2A stimulates the map kinase pathway and induces cell proliferation. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90533-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag E., Nunbhakdi-Craig V., Bloom G. S., Mumby M. C. A novel pool of protein phosphatase 2A is associated with microtubules and is regulated during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1131–1144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland C., Leighton I. A., Cohen P. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by phosphorylation: new kinase connections in insulin and growth-factor signalling. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):15–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2960015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez C., Díaz-Nido J., Avila J. Variations in in vivo phosphorylation at the proline-rich domain of the microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) during rat brain development. Biochem J. 1995 Mar 1;306(Pt 2):481–487. doi: 10.1042/bj3060481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takishima K., Griswold-Prenner I., Ingebritsen T., Rosner M. R. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor T669 peptide kinase from 3T3-L1 cells is an EGF-stimulated "MAP" kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2520–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B. Molecular characterization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase bound to microtubule-associated protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3284–3290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombes R. M., Peloquin J. G., Borisy G. G. Specific association of an M-phase kinase with isolated mitotic spindles and identification of two of its substrates as MAP4 and MAP1B. Cell Regul. 1991 Nov;2(11):861–874. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse S., Gomez N., Paterson H., Marshall C., Cohen P. Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade may be required for differentiation of PC12 cells. Comparison of the effects of nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):351–355. doi: 10.1042/bj2880351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao H., Aletta J. M., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor selectively activate a protein kinase that phosphorylates high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins. Detection, partial purification, and characterization in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15471–15480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyama S., Terayama Y., Matsuyama S. Numerous phosphates of microtubule-associated protein 2 in living rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10886–10892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B. A taxol-dependent procedure for the isolation of microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):435–442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., DiBartolomeis M. J., Theurkauf W. E. A protein kinase bound to the projection portion of MAP 2 (microtubule-associated protein 2). J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):568–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe A., Hasegawa M., Suzuki M., Takio K., Morishima-Kawashima M., Titani K., Arai T., Kosik K. S., Ihara Y. In vivo phosphorylation sites in fetal and adult rat tau. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25712–25717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Mundy D. I., Cohen P., Warren G. Cell-free fusion of endocytic vesicles is regulated by phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):331–338. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]