Abstract
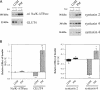
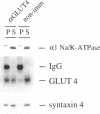
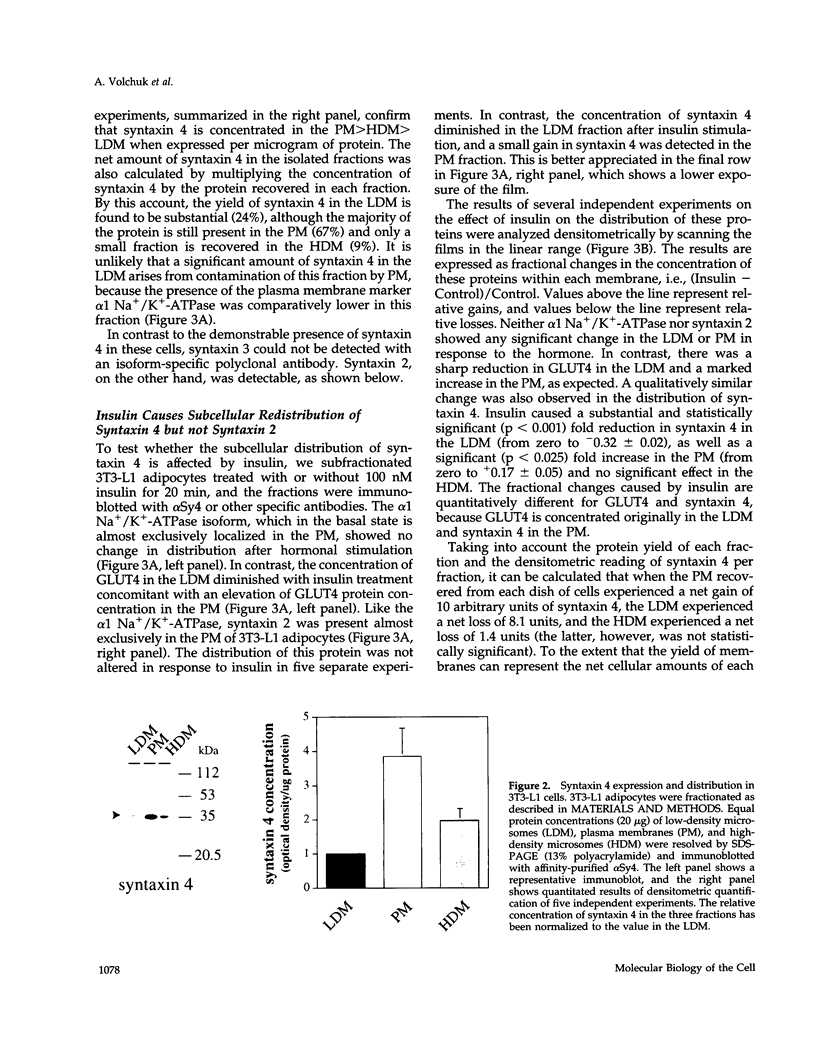
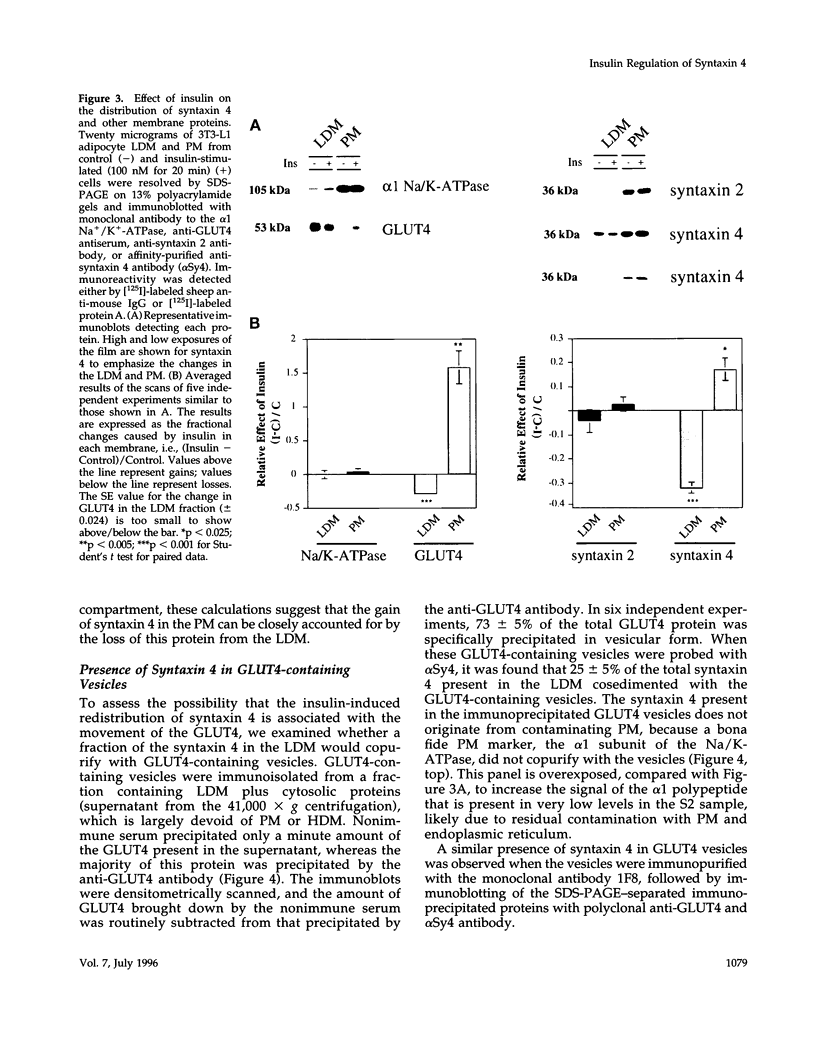
Syntaxins are thought to be membrane receptors that bind proteins of the synaptobrevin/vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) family found on transport vesicles. Recently, we detected synaptobrevin II and cellubrevin on immunopurified vesicles containing the glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) in insulin-responsive cells. In an effort to identify the plasma membrane receptors for these vesicles, we now examine the expression of syntaxins in the 3T3-L1 adipocyte cell line. Neither syntaxin 1A nor 1B was found, in keeping with the neuronal restriction of these isoforms. In contrast, syntaxins 2 and 4 were readily detectable. By subcellular fractionation and estimation of protein yields, 67% of syntaxin 4 was localized to the plasma membrane, 24% to the low-density microsomes, and 9% to the high-density microsomes. Interestingly, acute insulin treatment decreased the content of syntaxin 4 in low-density microsomes and caused a corresponding gain in the plasma membrane fraction, reminiscent of the recruitment of GLUT4 glucose transporters. In contrast, there was no change in the distribution of syntaxin 2, which was mostly associated in the plasma membrane. A fraction of the intracellular syntaxin 4 was recovered with immunopurified GLUT4-containing vesicles. Moreover, anti-syntaxin 4 antibodies introduced in permeabilized 3T3-L1 adipocytes significantly reduced the insulin-dependent stimulation of glucose transport, in contrast to the introduction of irrelevant immunoglobulin G, which was without consequence. We propose that either the plasma membrane and/or the vesicular syntaxin 4 are involved in docking and/or fusion of GLUT4 vesicles at the cell surface of 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akagawa K., Barnstable C. J. Identification and characterization of cell types in monolayer cultures of rat retina using monoclonal antibodies. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 24;383(1-2):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. C., Trimble W. S., Lienhard G. E. Members of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins are components of glucose transporter-containing vesicles from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11681–11684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Bennett M. K., Peterson K. E., Scheller R. H. Protein-protein interactions contributing to the specificity of intracellular vesicular trafficking. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. F., Young P. W., Yonezawa K., Kasuga M., Holman G. D. Inhibition of the translocation of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 cells by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 15;300(Pt 3):631–635. doi: 10.1042/bj3000631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli T., Chilcote T., Mundigl O., Binz T., Niemann H., De Camilli P. Tetanus toxin-mediated cleavage of cellubrevin impairs exocytosis of transferrin receptor-containing vesicles in CHO cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1015–1024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez L. M., Quintanar J. L., Viniegra S., Salinas E., Moya F., Reig J. A. Anti-syntaxin antibodies inhibit calcium-dependent catecholamine secretion from permeabilized chromaffin cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 5;206(1):1–7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst J. J., Andrews G. C., Contillo L. G., Singleton D. H., Genereux P. E., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E. Effect of the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by a thiophosphotyrosine peptide on glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):26000–26005. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.26000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa H. P., Saisu H., Ishizuka T., Sekine Y., Tsugita A., Odani S., Abe T. A complex of rab3A, SNAP-25, VAMP/synaptobrevin-2 and syntaxins in brain presynaptic terminals. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 13;330(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson G., Bean A. J., Scheller R. H., Juntti-Berggren L., Deeney J. T., Berggren P. O., Meister B. Identification of synaptic proteins and their isoform mRNAs in compartments of pancreatic endocrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12487–12491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Piper R. C., Slot J. W. Insulin stimulation of GLUT-4 translocation: a model for regulated recycling. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;4(4):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S., Yamamoto A., Inoue A., Inoue Y., Akagawa K., Kawamura Y., Kawamoto K., Tashiro Y. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of the HPC-1 antigen in rat cerebellum. J Neurocytol. 1993 Nov;22(11):995–1005. doi: 10.1007/BF01218356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu S., Kornhauser J. M., Burant C. F., Seino S., Mayo K. E., Bell G. I. Glucose transporter expression in brain. cDNA sequence of mouse GLUT3, the brain facilitative glucose transporter isoform, and identification of sites of expression by in situ hybridization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Blasi J., Jahn R. Clostridial neurotoxins: new tools for dissecting exocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Hess L. J., James D. E. Differential sorting of two glucose transporters expressed in insulin-sensitive cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C570–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Pang S., Harris D. S., Heuser J., James D. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter (GLUT4) to the cell surface in permeabilized 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effects of ATP insulin, and GTP gamma S and localization of GLUT4 to clathrin lattices. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1181–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Nishimura H., Clark A. E., Kozka I. J., Vannucci S. J., Simpson I. A., Quon M. J., Cushman S. W., Holman G. D. Use of bismannose photolabel to elucidate insulin-regulated GLUT4 subcellular trafficking kinetics in rat adipose cells. Evidence that exocytosis is a critical site of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17820–17829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Shone C. C., Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H., Montecucco C. Botulinum neurotoxin type C cleaves a single Lys-Ala bond within the carboxyl-terminal region of syntaxins. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10566–10570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze K. L., Broadie K., Perin M. S., Bellen H. J. Genetic and electrophysiological studies of Drosophila syntaxin-1A demonstrate its role in nonneuronal secretion and neurotransmission. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90414-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Student A. K., Hsu R. Y., Lane M. D. Induction of fatty acid synthetase synthesis in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4745–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumitani S., Ramlal T., Liu Z., Klip A. Expression of syntaxin 4 in rat skeletal muscle and rat skeletal muscle cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Aug 15;213(2):462–468. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., De Camilli P., Niemann H., Jahn R. Membrane fusion machinery: insights from synaptic proteins. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya M., Toyonaga S., Takahashi M., Yamamoto A., Fujiwara T., Akagawa K., Moriyama Y., Mizushima S. Syntaxin 1 (HPC-1) is associated with chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):15930–15933. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.15930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volchuk A., Mitsumoto Y., He L., Liu Z., Habermann E., Trimble W., Klip A. Expression of vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP-2)/synaptobrevin II and cellubrevin in rat skeletal muscle and in a muscle cell line. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 15;304(Pt 1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj3040139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volchuk A., Sargeant R., Sumitani S., Liu Z., He L., Klip A. Cellubrevin is a resident protein of insulin-sensitive GLUT4 glucose transporter vesicles in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):8233–8240. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.8233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walch-Solimena C., Blasi J., Edelmann L., Chapman E. R., von Mollard G. F., Jahn R. The t-SNAREs syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 are present on organelles that participate in synaptic vesicle recycling. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]