Abstract
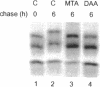
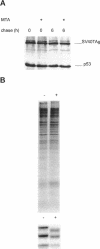
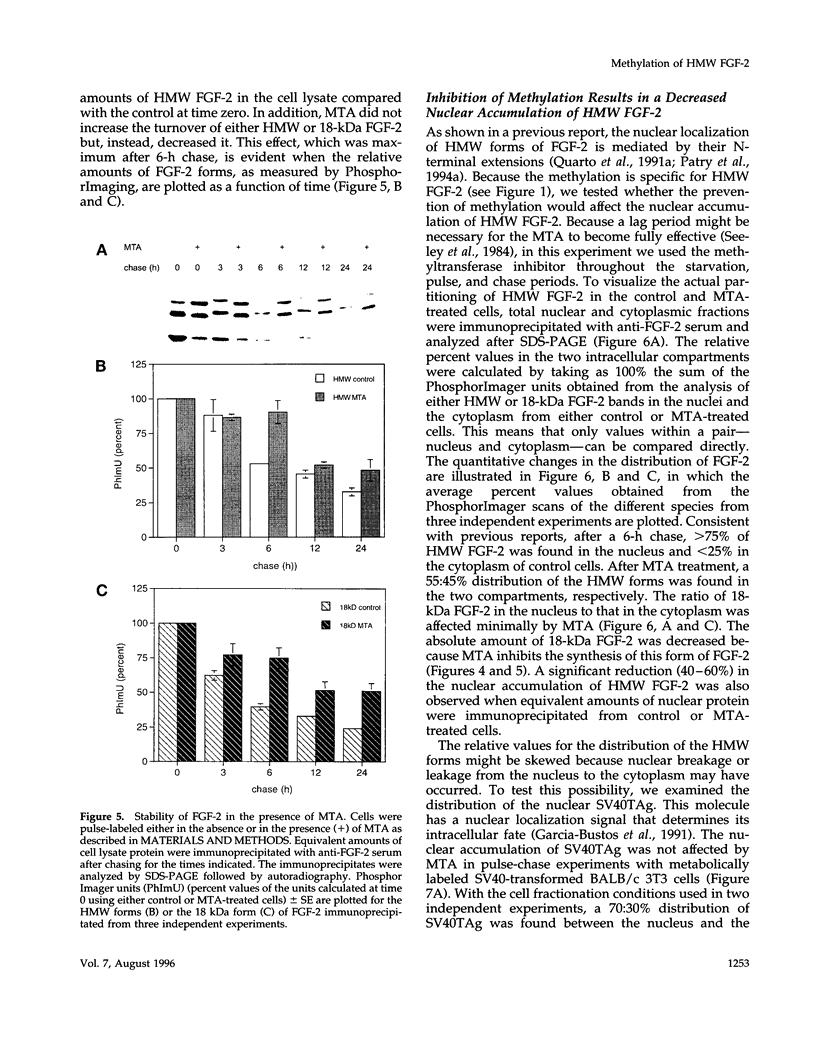
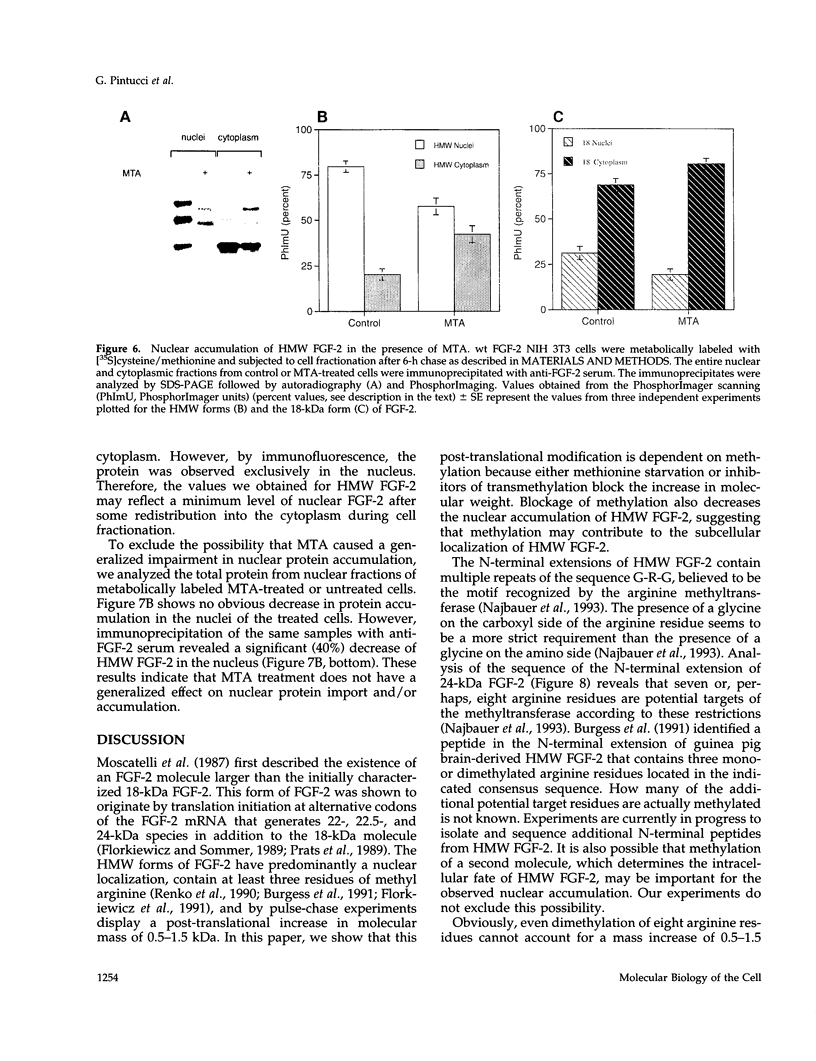
The high molecular weight (HMW) forms (24, 22.5, and 22 kDa) of basic fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) contain an N-terminal extension responsible for their predominantly nuclear localization. These forms of FGF-2 are post-translationally modified, resulting in a 1- to 2-kDa increase in apparent molecular mass. Here we show that this post-translational modification is inhibited by methionine starvation and by the methyltransferase inhibitors 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA) and 3-deaza-adenosine. Inhibition of the methylation-dependent modification results in a significant decrease in HMW FGF-2 nuclear accumulation, suggesting that methylation is relevant to the intracellular distribution of these forms of FGF-2. Treatment with MTA does not affect either the synthesis or the intracellular fate of another nuclear protein, the SV40 large T antigen, demonstrating that this drug does not have a generalized effect on nuclear protein accumulation. These results link HMW FGF-2 post-translational modification to its intracellular distribution.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):662–665. doi: 10.1038/343662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A. Potential mechanisms regulating the extracellular activities of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Mol Reprod Dev. 1994 Sep;39(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080390108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Moscatelli D. The FGF family of growth factors and oncogenes. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;59:115–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikfalvi A., Dupuy E., Inyang A. L., Fayein N., Leseche G., Courtois Y., Tobelem G. Binding, internalization, and degradation of basic fibroblast growth factor in human microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Mar;181(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikfalvi A., Klein S., Pintucci G., Quarto N., Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Differential modulation of cell phenotype by different molecular weight forms of basic fibroblast growth factor: possible intracellular signaling by the high molecular weight forms. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(1):233–243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt R. T. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent macromolecule methyltransferases: potential targets for the design of chemotherapeutic agents. J Med Chem. 1980 Apr;23(4):347–357. doi: 10.1021/jm00178a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulle N., Jones E. M., Auguste P., Baird A. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of fibroblast growth factor-2. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jun;9(6):767–775. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.6.8592522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner G., Nguyen H., Gabrilove J., Rifkin D. B., Wilson E. L. Basic fibroblast growth factor expression in human bone marrow and peripheral blood cells. Blood. 1993 Feb 1;81(3):631–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Amalric F., Prats H. Alternative initiation of translation determines cytoplasmic or nuclear localization of basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):573–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Bizik J., Mehlman T., Quarto N., Rifkin D. B. Direct evidence for methylation of arginine residues in high molecular weight forms of basic fibroblast growth factor. Cell Regul. 1991 Feb;2(2):87–93. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Gurney E. G. Time-dependent maturation of the simian virus 40 large T antigen-p53 complex studied by using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):565–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.565-573.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. Protein methylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;5(6):977–983. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90080-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Vogel J. P., Deschenes R. J., Stock J. Posttranslational modification of the Ha-ras oncogene protein: evidence for a third class of protein carboxyl methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4643–4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. D., Florkiewicz R. Z., Neumann J., Mort-Hopkins T., Dorn G. W., 2nd, Lightfoot P., German R., Howles P. N., Kier A., O'Toole B. A. Abnormal bone growth and selective translational regulation in basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) transgenic mice. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Dec;6(12):1861–1873. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.12.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danpure C. J. How can the products of a single gene be localized to more than one intracellular compartment? Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;5(6):230–238. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enenstein J., Waleh N. S., Kramer R. H. Basic FGF and TGF-beta differentially modulate integrin expression of human microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Dec;203(2):499–503. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein J. D. Methionine metabolism in mammals. J Nutr Biochem. 1990 May;1(5):228–237. doi: 10.1016/0955-2863(90)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Baird A., Gonzalez A. M. Multiple forms of bFGF: differential nuclear and cell surface localization. Growth Factors. 1991;4(4):265–275. doi: 10.3109/08977199109043912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Sommer A. Human basic fibroblast growth factor gene encodes four polypeptides: three initiate translation from non-AUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3978–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J., Heitman J., Hall M. N. Nuclear protein localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):83–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90013-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R. Regulation and function of non-AUG-initiated proto-oncogenes. Biochimie. 1994;76(9):880–886. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(94)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Sloan-Brown K., Spotts G. D. Translational activation of the non-AUG-initiated c-myc 1 protein at high cell densities due to methionine deprivation. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1229–1240. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ganoth D., Pehrson J., Palazzo R. E., Cohen L. H. Methylated ubiquitin inhibits cyclin degradation in clam embryo extracts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16376–16379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Schlessinger J., Dionne C. A. Fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases: molecular analysis and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 10;1135(2):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90136-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. A., Langmack E. L., Aswad D. W. Partial repair of deamidation-damaged calmodulin by protein carboxyl methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12283–12287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Tuck M., Kim M., Campagnoni A. T., Paik W. K. Studies on myelin basic protein-specific protein methylase I in various dysmyelinating mutant mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Giancotti F. G., Presta M., Albelda S. M., Buck C. A., Rifkin D. B. Basic fibroblast growth factor modulates integrin expression in microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Oct;4(10):973–982. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.10.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku P. T., D'Amore P. A. Regulation of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) gene and protein expression following its release from sublethally injured endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 1995 Jul;58(3):328–343. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240580307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Amalric F., Ghaffari S. H., Rao S. V., Dumbar T. S., Olson M. O. Protein and cDNA sequence of a glycine-rich, dimethylarginine-containing region located near the carboxyl-terminal end of nucleolin (C23 and 100 kDa). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9167–9173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Zhan X., Garfinkel S., Friedman S., Prudovsky I., Jackson A., Wessendorf J., Hu X., Gamble S., Shi J. Novel mechanisms of fibroblast growth factor 1 function. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1994;49:105–123. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571149-4.50009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Inhibition of the tyrosine kinase activity of the fibroblast growth factor receptor by the methyltransferase inhibitor 5'-methylthioadenosine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4244–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. J. The ins and outs of fibroblast growth factors. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Muthukrishnan L., Warder E., D'Amore P. A. Growth factors are released by mechanically wounded endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Morimoto T., Rifkin D. B. Basic fibroblast growth factor released by single, isolated cells stimulates their migration in an autocrine manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11007–11011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Morimoto T., Rifkin D. B. Basic fibroblast growth factor, a protein devoid of secretory signal sequence, is released by cells via a pathway independent of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi complex. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Apr;151(1):81–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Manejias R., Rifkin D. B. Mr 25,000 heparin-binding protein from guinea pig brain is a high molecular weight form of basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5778–5782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najbauer J., Johnson B. A., Young A. L., Aswad D. W. Peptides with sequences similar to glycine, arginine-rich motifs in proteins interacting with RNA are efficiently recognized by methyltransferase(s) modifying arginine in numerous proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10501–10509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opalenik S. R., Shin J. T., Wehby J. N., Mahesh V. K., Thompson J. A. The HIV-1 TAT protein induces the expression and extracellular appearance of acidic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17457–17467. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K. S., Frost B., Tuck M., Ho L. L., Kim S., Paik W. K. Enzymatic methylation of in vitro synthesized apocytochrome c enhances its transport into mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14702–14708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patry V., Arnaud E., Amalric F., Prats H. Involvement of basic fibroblast growth factor NH2 terminus in nuclear accumulation. Growth Factors. 1994;11(3):163–174. doi: 10.3109/08977199409046914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patry V., Bugler B., Amalric F., Promé J. C., Prats H. Purification and characterization of the 210-amino acid recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor form (FGF-2). FEBS Lett. 1994 Jul 25;349(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00633-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats H., Kaghad M., Prats A. C., Klagsbrun M., Lélias J. M., Liauzun P., Chalon P., Tauber J. P., Amalric F., Smith J. A. High molecular mass forms of basic fibroblast growth factor are initiated by alternative CUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1836–1840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarto N., Finger F. P., Rifkin D. B. The NH2-terminal extension of high molecular weight bFGF is a nuclear targeting signal. J Cell Physiol. 1991 May;147(2):311–318. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041470217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarto N., Talarico D., Florkiewicz R., Rifkin D. B. Selective expression of high molecular weight basic fibroblast growth factor confers a unique phenotype to NIH 3T3 cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Sep;2(9):699–708. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.9.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarto N., Talarico D., Sommer A., Florkiewicz R., Basilico C., Rifkin D. B. Transformation by basic fibroblast growth factor requires high levels of expression: comparison with transformation by hst/K-fgf. Oncogene Res. 1989;5(2):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattan S. I., Derventzi A., Clark B. F. Protein synthesis, posttranslational modifications, and aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Nov 21;663:48–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb38648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renko M., Quarto N., Morimoto T., Rifkin D. B. Nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of different basic fibroblast growth factor species. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):108–114. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley P. J., Rukenstein A., Connolly J. L., Greene L. A. Differential inhibition of nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor effects on the PC12 pheochromocytoma line. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):417–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. An amino-terminally extended and post-translationally modified form of a 25kD basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1267–1274. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Rifkin D. B. Interaction of heparin with human basic fibroblast growth factor: protection of the angiogenic protein from proteolytic degradation by a glycosaminoglycan. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):215–220. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilgrain I., Baird A. Phosphorylation of basic fibroblast growth factor by a protein kinase associated with the outer surface of a target cell. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1003–1012. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilgrain I., Gonzalez A. M., Baird A. Phosphorylation of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) in the nuclei of SK-Hep-1 cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 4;331(3):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80342-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]