Abstract
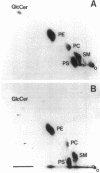
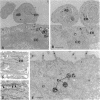
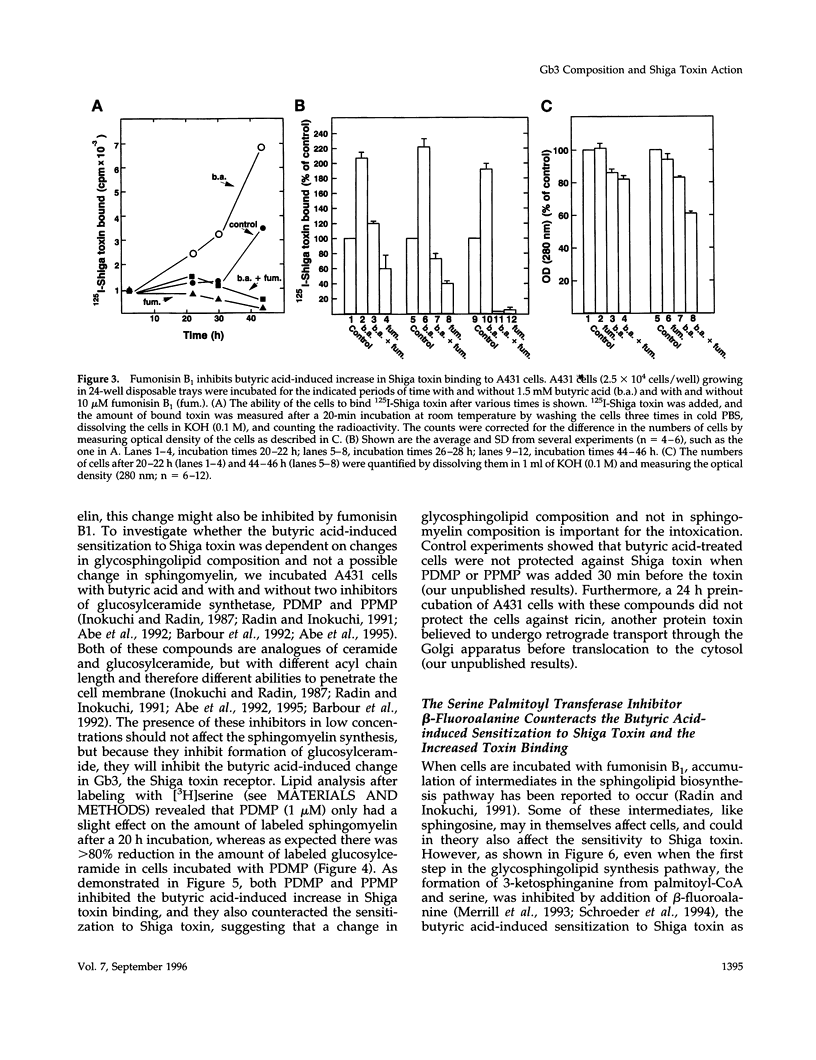
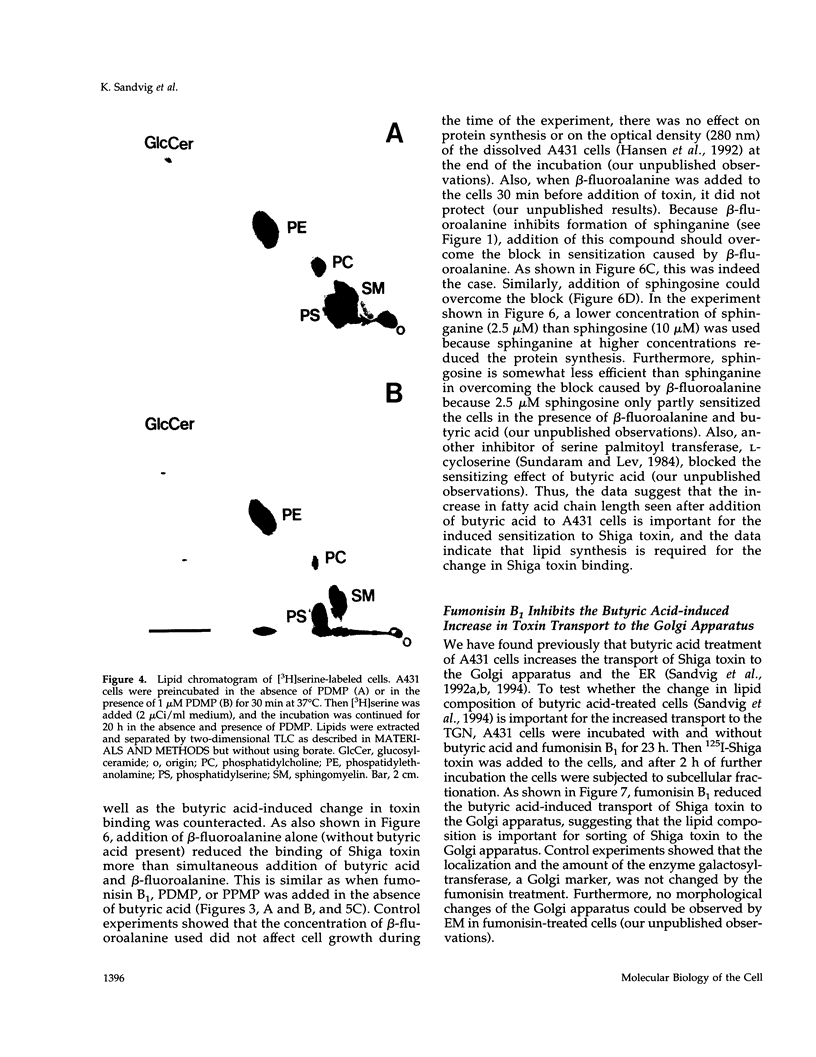
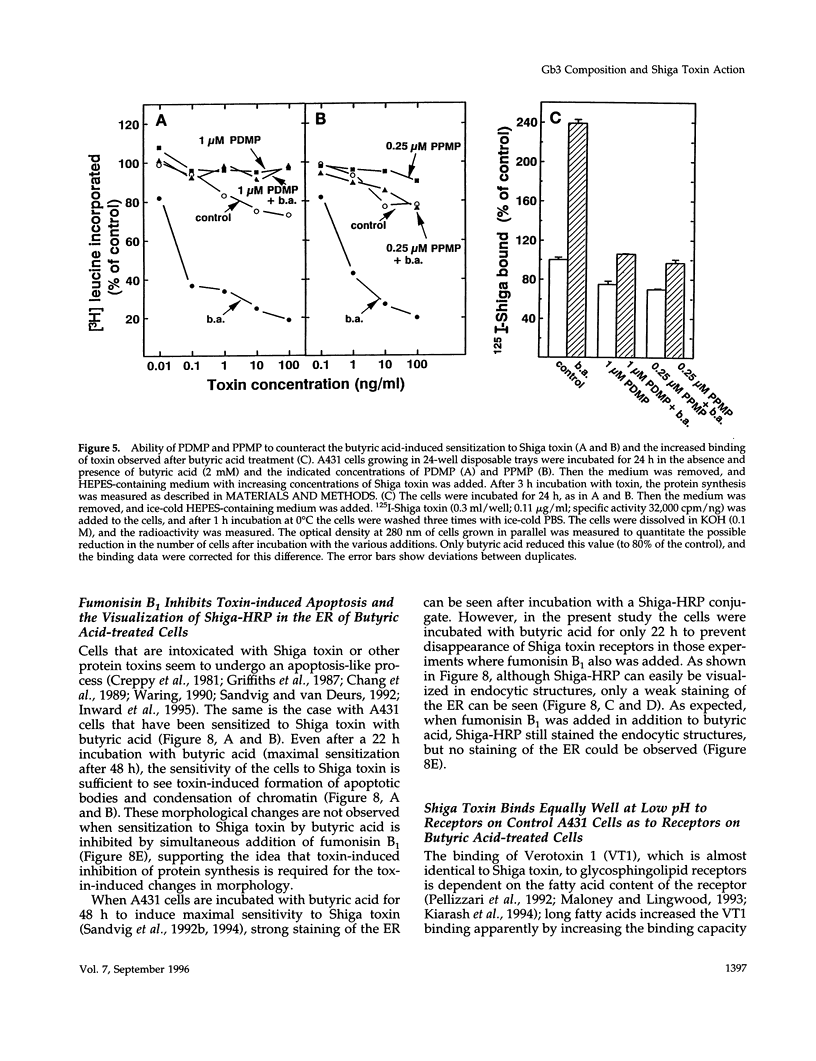
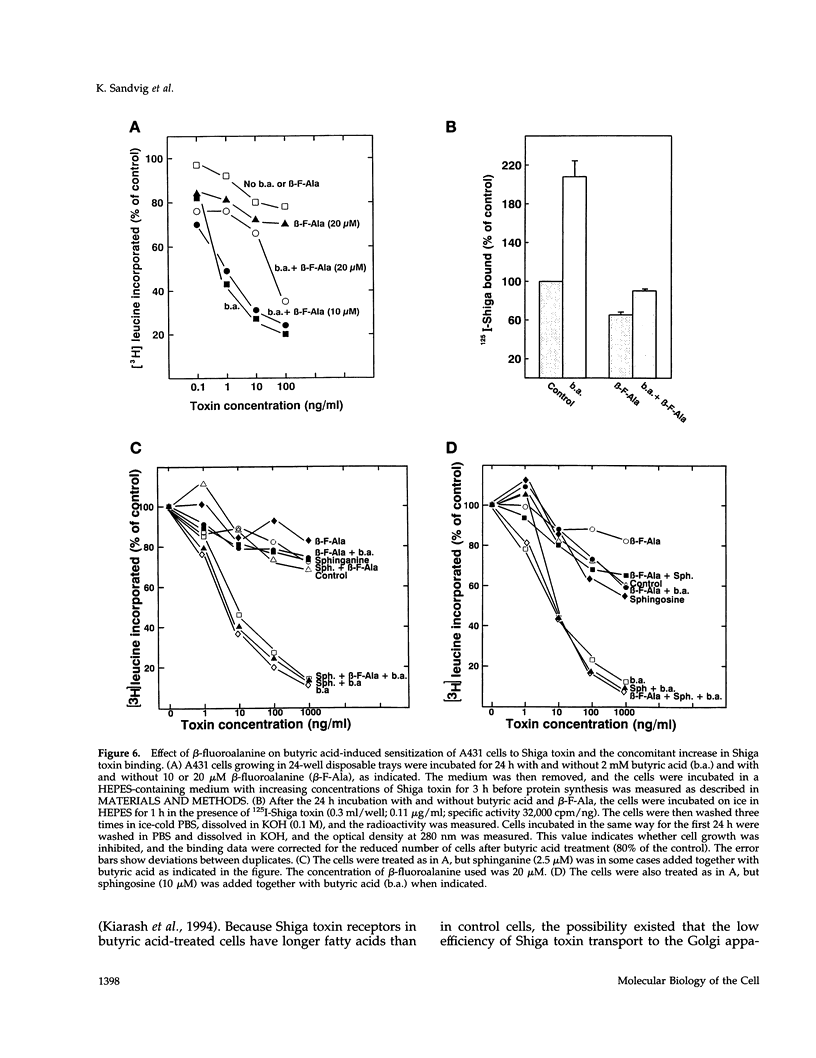
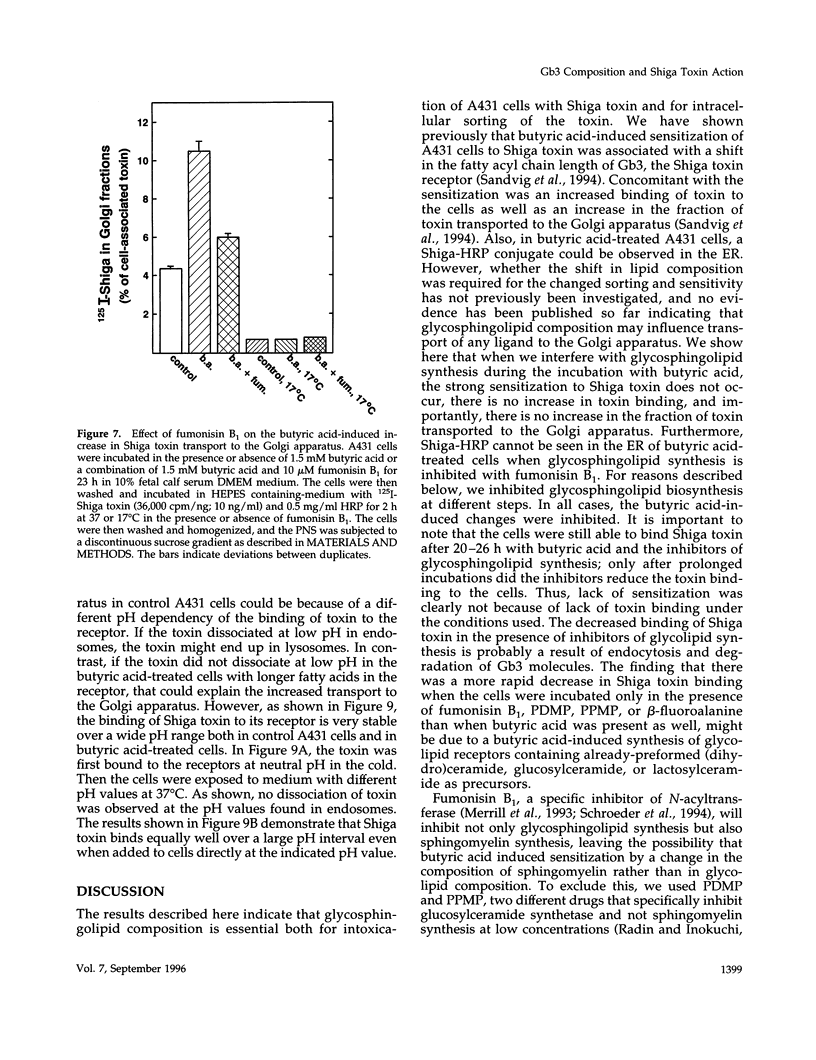
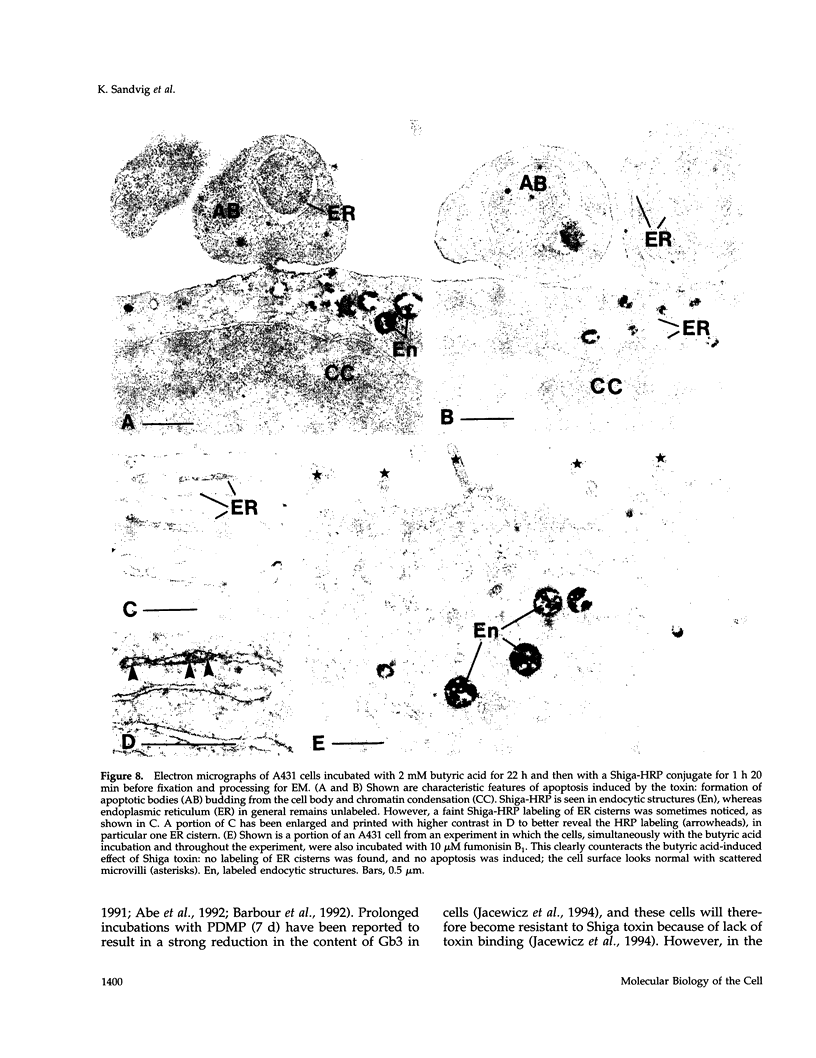
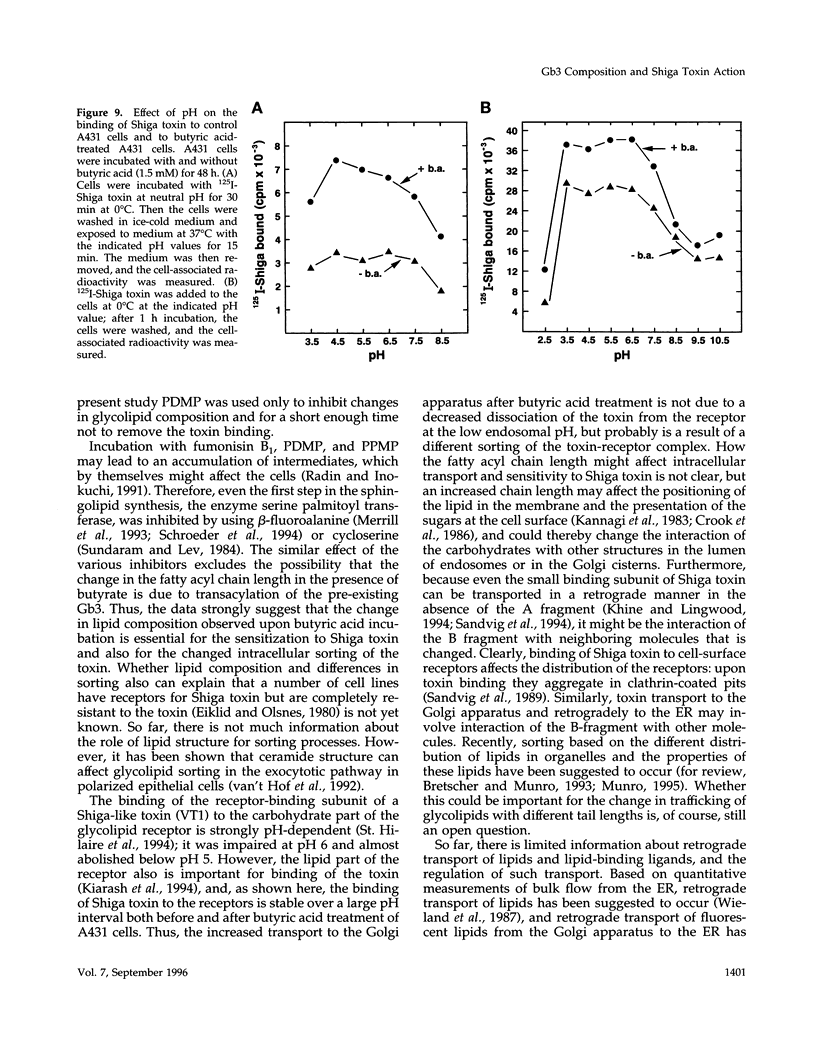
The human epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431 becomes highly sensitive to Shiga toxin upon treatment with butyric acid. This strong sensitization (> 1000-fold) is accompanied by an increase in the fraction of cell-associated toxin transported to the Golgi apparatus and to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Furthermore, our previous work showed that the length of the fatty acyl chain of Gb3, the Shiga toxin receptor, also was changed (longer fatty acids). We have not investigated the importance of this change by testing whether glycolipid synthesis is required for the changed intracellular sorting and the toxin sensitivity. We demonstrate here that inhibition of glycosphingolipid synthesis by inhibition of N-acyltransferase with fumonisin B1, by inhibition of glucosylceramide synthetase by PDMP or PPMP, or by inhibition of serine palmitoyl transferase by beta-fluoroalanine, inhibited the butyric acid-induced change in sensitivity and the increase in the fraction of cell-associated Shiga toxin transported to the Golgi apparatus and the ER. The block in butyric acid-induced sensitization caused by beta-fluoroalanine could be abolished by simultaneous addition of sphinganine or sphingosine. Thus, the data suggest that the fatty acyl chain length of glycosphingolipids is important for intracellular sorting and translocation of Shiga toxin to the cytosol.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe A., Inokuchi J., Jimbo M., Shimeno H., Nagamatsu A., Shayman J. A., Shukla G. S., Radin N. S. Improved inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthase. J Biochem. 1992 Feb;111(2):191–196. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe A., Radin N. S., Shayman J. A., Wotring L. L., Zipkin R. E., Sivakumar R., Ruggieri J. M., Carson K. G., Ganem B. Structural and stereochemical studies of potent inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthase and tumor cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1995 Mar;36(3):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour S., Edidin M., Felding-Habermann B., Taylor-Norton J., Radin N. S., Fenderson B. A. Glycolipid depletion using a ceramide analogue (PDMP) alters growth, adhesion, and membrane lipid organization in human A431 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):610–619. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Munro S. Cholesterol and the Golgi apparatus. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1280–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.8362242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändli A. W., Hansson G. C., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Simons K. A polarized epithelial cell mutant deficient in translocation of UDP-galactose into the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16283–16290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. P., Bramhall J., Graves S., Bonavida B., Wisnieski B. J. Internucleosomal DNA cleavage precedes diphtheria toxin-induced cytolysis. Evidence that cell lysis is not a simple consequence of translation inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15261–15267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Schwartz A. L., Dautry-Varsat A., Lodish H. F. Kinetics of internalization and recycling of transferrin and the transferrin receptor in a human hepatoma cell line. Effect of lysosomotropic agents. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9681–9689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R., Lingwood C. A. Roles of globotriosyl- and galabiosylceramide in verotoxin binding and high affinity interferon receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17088–17091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creppy E. E., Lugnier A. A., Beck G., Dirheimer G., Petzinger E., Frimmer M. Comparative studies by scanning electron microscopy of the effect of ricin on the cell membrane of hepatoma cells and isolated hepatocytes. Toxicol Eur Res. 1981 Jul;3(4):179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook S. J., Boggs J. M., Vistnes A. I., Koshy K. M. Factors affecting surface expression of glycolipids: influence of lipid environment and ceramide composition on antibody recognition of cerebroside sulfate in liposomes. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7488–7494. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiklid K., Olsnes S. Interaction of Shigella shigae cytotoxin with receptors on sensitive and insensitive cells. J Recept Res. 1980;1(2):199–213. doi: 10.3109/10799898009044098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garred O., Dubinina E., Holm P. K., Olsnes S., van Deurs B., Kozlov J. V., Sandvig K. Role of processing and intracellular transport for optimal toxicity of Shiga toxin and toxin mutants. Exp Cell Res. 1995 May;218(1):39–49. doi: 10.1006/excr.1995.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garred O., van Deurs B., Sandvig K. Furin-induced cleavage and activation of Shiga toxin. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10817–10821. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. D., Leek M. D., Gee D. J. The toxic plant proteins ricin and abrin induce apoptotic changes in mammalian lymphoid tissues and intestine. J Pathol. 1987 Mar;151(3):221–229. doi: 10.1002/path.1711510310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Ericsson M., Krijnse-Locker J., Nilsson T., Goud B., Söling H. D., Tang B. L., Wong S. H., Hong W. Localization of the Lys, Asp, Glu, Leu tetrapeptide receptor to the Golgi complex and the intermediate compartment in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1557–1574. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. H., Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Internalization efficiency of the transferrin receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Mar;199(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90457-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P. M., Pagano R. E. Retrograde movement of membrane lipids from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum of perforated cells: evidence for lipid recycling. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;60(2):371–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi J., Radin N. S. Preparation of the active isomer of 1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol, inhibitor of murine glucocerebroside synthetase. J Lipid Res. 1987 May;28(5):565–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inward C. D., Williams J., Chant I., Crocker J., Milford D. V., Rose P. E., Taylor C. M. Verocytotoxin-1 induces apoptosis in vero cells. J Infect. 1995 May;30(3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(95)90693-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M. S., Mobassaleh M., Gross S. K., Balasubramanian K. A., Daniel P. F., Raghavan S., McCluer R. H., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea: XVII. A mammalian cell membrane glycolipid, Gb3, is required but not sufficient to confer sensitivity to Shiga toxin. J Infect Dis. 1994 Mar;169(3):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.3.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Clausen H., Nudelman E., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Stieber A., Gonatas N. K. A hypothesis on the traffic of MG160, a medial Golgi sialoglycoprotein, from the trans-Golgi network to the Golgi cisternae. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):529–537. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph K. C., Kim S. U., Stieber A., Gonatas N. K. Endocytosis of cholera toxin into neuronal GERL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2815–2819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Stroup R., Cochran N. A., Urdal D. L., Young W. W., Jr, Hakomori S. Factors affecting expression of glycolipid tumor antigens: influence of ceramide composition and coexisting glycolipid on the antigenicity of gangliotriaosylceramide in murine lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4997–5005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khine A. A., Lingwood C. A. Capping and receptor-mediated endocytosis of cell-bound verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin). 1: Chemical identification of an amino acid in the B subunit necessary for efficient receptor glycolipid binding and cellular internalization. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Nov;161(2):319–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041610217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiarash A., Boyd B., Lingwood C. A. Glycosphingolipid receptor function is modified by fatty acid content. Verotoxin 1 and verotoxin 2c preferentially recognize different globotriaosyl ceramide fatty acid homologues. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11138–11146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Gaynor E. C., Hennecke S., Démollière C., Duden R., Emr S. D., Riezman H., Cosson P. Coatomer is essential for retrieval of dilysine-tagged proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1199–1207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Ligand-induced redistribution of a human KDEL receptor from the Golgi complex to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90476-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Brown J. E., Strömberg N., Westling-Ryd M., Schultz J. E., Karlsson K. A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez O., Schmidt A., Salaméro J., Hoflack B., Roa M., Goud B. The small GTP-binding protein rab6 functions in intra-Golgi transport. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1575–1588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. H., Jr, van Echten G., Wang E., Sandhoff K. Fumonisin B1 inhibits sphingosine (sphinganine) N-acyltransferase and de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in cultured neurons in situ. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27299–27306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesenböck G., Rothman J. E. The capacity to retrieve escaped ER proteins extends to the trans-most cisterna of the Golgi stack. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(2):309–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S. An investigation of the role of transmembrane domains in Golgi protein retention. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 2;14(19):4695–4704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Tesh V. L., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jackson M. P., Olsnes S., Sandvig K., Lindberg A. A., Keusch G. T. Shiga toxin: biochemistry, genetics, mode of action, and role in pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;180:65–94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77238-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Sandvig K. How protein toxins enter and kill cells. Cancer Treat Res. 1988;37:39–73. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-1083-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Roberts L. M., Lord J. M. Toxin entry: how reversible is the secretory pathway? Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):183–185. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90230-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellizzari A., Pang H., Lingwood C. A. Binding of verocytotoxin 1 to its receptor is influenced by differences in receptor fatty acid content. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 11;31(5):1363–1370. doi: 10.1021/bi00120a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prydz K., Hansen S. H., Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Effects of brefeldin A on endocytosis, transcytosis and transport to the Golgi complex in polarized MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):259–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg P. O., Marzella L., Glaumann H. A method for rapid isolation of rough and smooth microsomes and Golgi apparatus from rat liver in the same sucrose gradient. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Dubinina E., Garred O., Prydz K., Kozlov J. V., Hansen S. H., van Deurs B. Protein toxins: mode of action and cell entry. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Nov;20(4):724–727. doi: 10.1042/bst0200724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Garred O., Prydz K., Kozlov J. V., Hansen S. H., van Deurs B. Retrograde transport of endocytosed Shiga toxin to the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):510–512. doi: 10.1038/358510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Brown J. E., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Endocytosis from coated pits of Shiga toxin: a glycolipid-binding protein from Shigella dysenteriae 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Effect of temperature on the uptake, excretion and degradation of abrin and ricin by HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Prydz K., Hansen S. H., van Deurs B. Ricin transport in brefeldin A-treated cells: correlation between Golgi structure and toxic effect. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):971–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Prydz K., Ryd M., van Deurs B. Endocytosis and intracellular transport of the glycolipid-binding ligand Shiga toxin in polarized MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):553–562. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Ryd M., Garred O., Schweda E., Holm P. K., van Deurs B. Retrograde transport from the Golgi complex to the ER of both Shiga toxin and the nontoxic Shiga B-fragment is regulated by butyric acid and cAMP. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):53–64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Endocytosis and intracellular sorting of ricin and Shiga toxin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Endocytosis without clathrin. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;4(8):275–277. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Toxin-induced cell lysis: protection by 3-methyladenine and cycloheximide. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. J., Crane H. M., Xia J., Liotta D. C., Merrill A. H., Jr Disruption of sphingolipid metabolism and stimulation of DNA synthesis by fumonisin B1. A molecular mechanism for carcinogenesis associated with Fusarium moniliforme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3475–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharam S., Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D., Pastan I. Increased cytotoxic activity of Pseudomonas exotoxin and two chimeric toxins ending in KDEL. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17376–17381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. C., Dascher C., Roberts L. M., Lord J. M., Balch W. E. Ricin cytotoxicity is sensitive to recycling between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 25;270(34):20078–20083. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.20078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Hilaire P. M., Boyd M. K., Toone E. J. Interaction of the Shiga-like toxin type 1 B-subunit with its carbohydrate receptor. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 6;33(48):14452–14463. doi: 10.1021/bi00252a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Brodie S. E., Cohn Z. A. Membrane flow during pinocytosis. A stereologic analysis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):665–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram K. S., Lev M. Inhibition of sphingolipid synthesis by cycloserine in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 1984 Feb;42(2):577–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P. DNA fragmentation induced in macrophages by gliotoxin does not require protein synthesis and is preceded by raised inositol triphosphate levels. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14476–14480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F. T., Gleason M. L., Serafini T. A., Rothman J. E. The rate of bulk flow from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Chen C. C., Zhang M. S., Wu H. C. Disruption of the Golgi apparatus by brefeldin A inhibits the cytotoxicity of ricin, modeccin, and Pseudomonas toxin. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Feb;192(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90056-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Holm P. K., Kayser L., Sandvig K., Hansen S. H. Multivesicular bodies in HEp-2 cells are maturing endosomes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;61(2):208–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Tønnessen T. I., Petersen O. W., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Routing of internalized ricin and ricin conjugates to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):37–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bijl P., Lopes-Cardozo M., van Meer G. Sorting of newly synthesized galactosphingolipids to the two surface domains of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;132(5):813–821. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.5.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Hof W., Silvius J., Wieland F., van Meer G. Epithelial sphingolipid sorting allows for extensive variation of the fatty acyl chain and the sphingosine backbone. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):913–917. doi: 10.1042/bj2830913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]