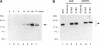Abstract
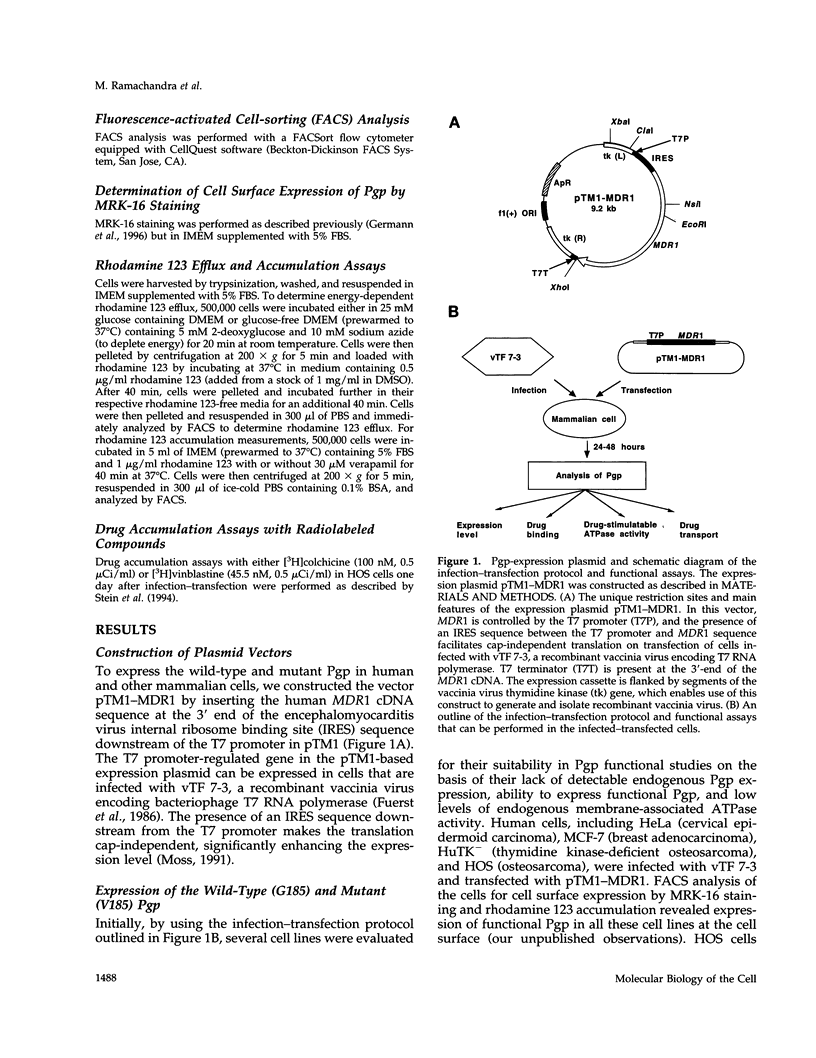
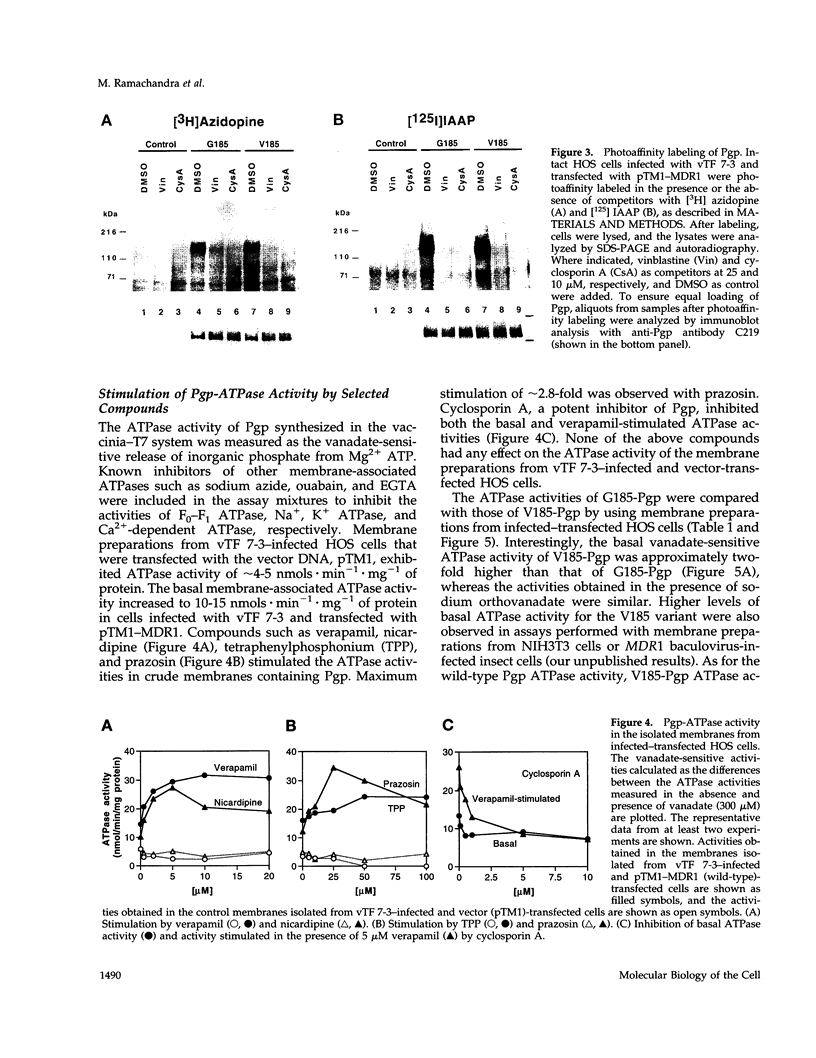
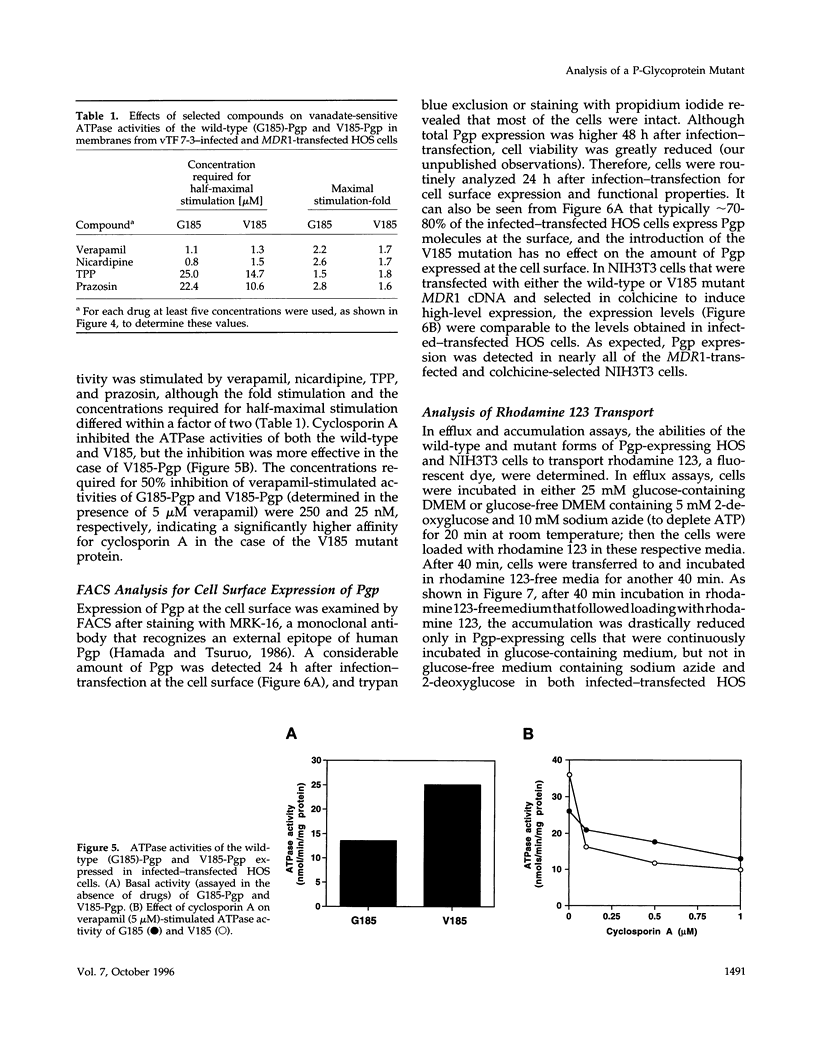
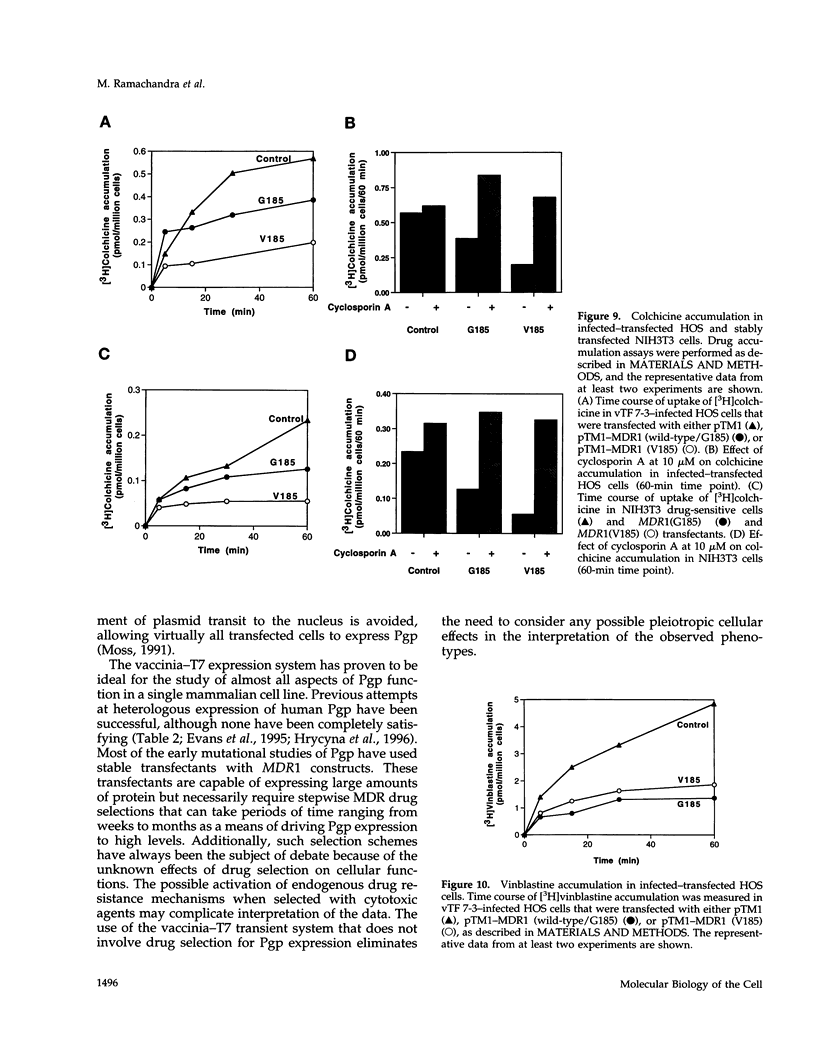
Human P-glycoprotein (Pgp) is a 170-kDa plasma membrane protein that confers multidrug resistance to otherwise sensitive cells. A mutation in Pgp, G185-->V, originally identified as a spontaneous mutation, was shown previously to alter the drug resistance profiles in cell lines that are stably transfected with the mutant MDR1 cDNA and selected with cytotoxic agents. To understand the mechanism by which the V185 mutation leads to an altered drug resistance profile, we used a transient expression system that eliminates the need for drug selection to attain high expression levels and allows for the rapid characterization of many aspects of Pgp function and biosynthesis. The mutant and wild-type proteins were expressed at similar levels after 24-48 h in human osteosarcoma (HOS) cells by infection with a recombinant vaccinia virus encoding T7 RNA polymerase and simultaneous transfection with a plasmid containing MDR1 cDNA controlled by the T7 promoter. For both mutant and wild-type proteins, photolabeling with [3H]azidopine and [125I]iodoarylazidoprazosin, drug-stimulated ATPase activity, efflux of rhodamine 123, and accumulation of radiolabeled vinblastine and colchicine were evaluated. In crude membrane preparations from HOS cells, a higher level of basal Pgp-ATPase activity was observed for the V185 variant than for the wild-type, suggesting partial uncoupling of drug-dependent ATP hydrolysis by the mutant. Several compounds, including verapamil, nicardipine, tetraphenylphosphonium, and prazosin, stimulated ATPase activities of both the wild-type and mutant similarly, whereas cyclosporin A inhibited the ATPase activity of the mutant more efficiently than that of the wild-type. This latter observation explains the enhanced potency of cyclosporin A as an inhibitor of the mutant Pgp. No differences were seen in verapamil-inhibited rhodamine 123 efflux, but the rate of accumulation was slower for colchicine and faster for vinblastine in cells expressing the mutant protein, as compared with those expressing wild-type Pgp. We conclude that the G185-->V mutation confers pleiotropic alterations on Pgp, including an altered basal ATPase activity and altered interaction with substrates and the inhibitor cyclosporin A.
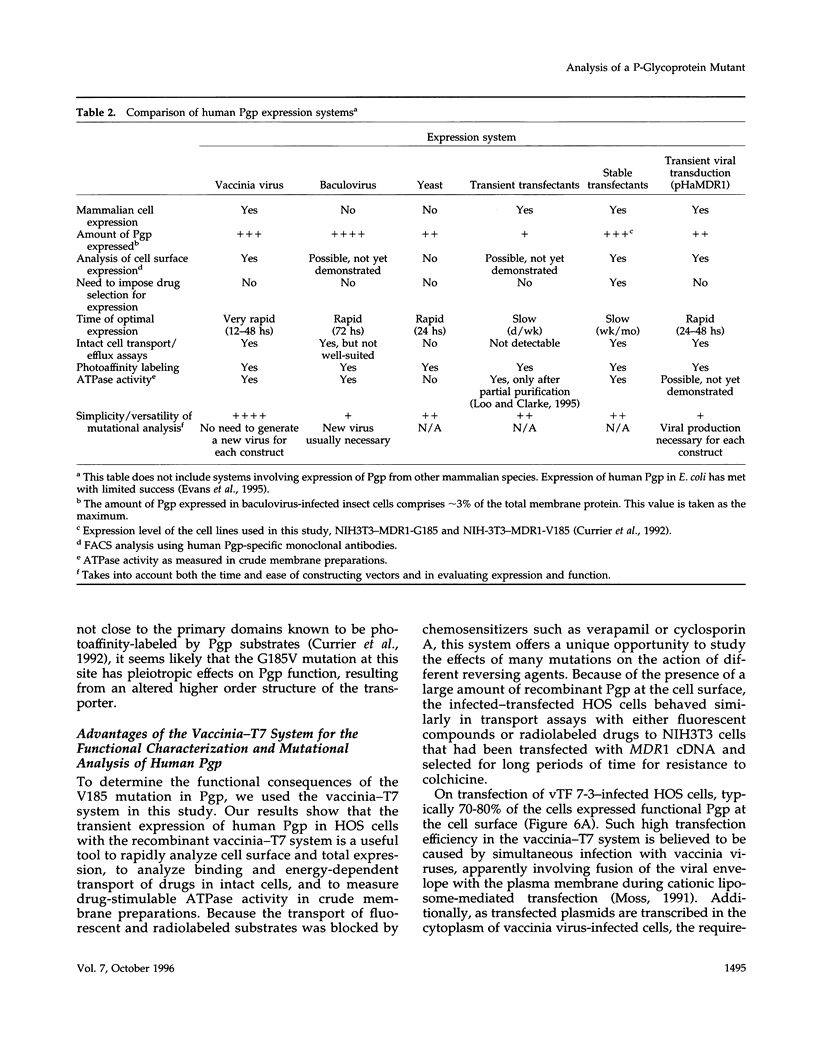
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
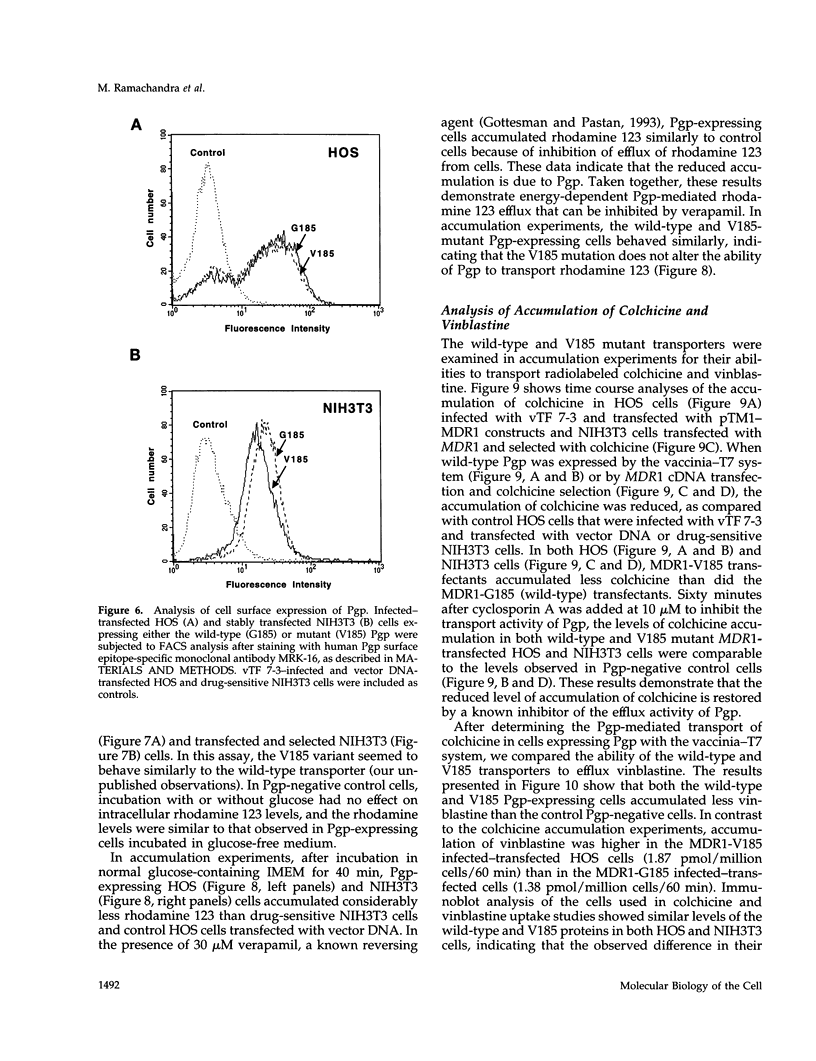
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
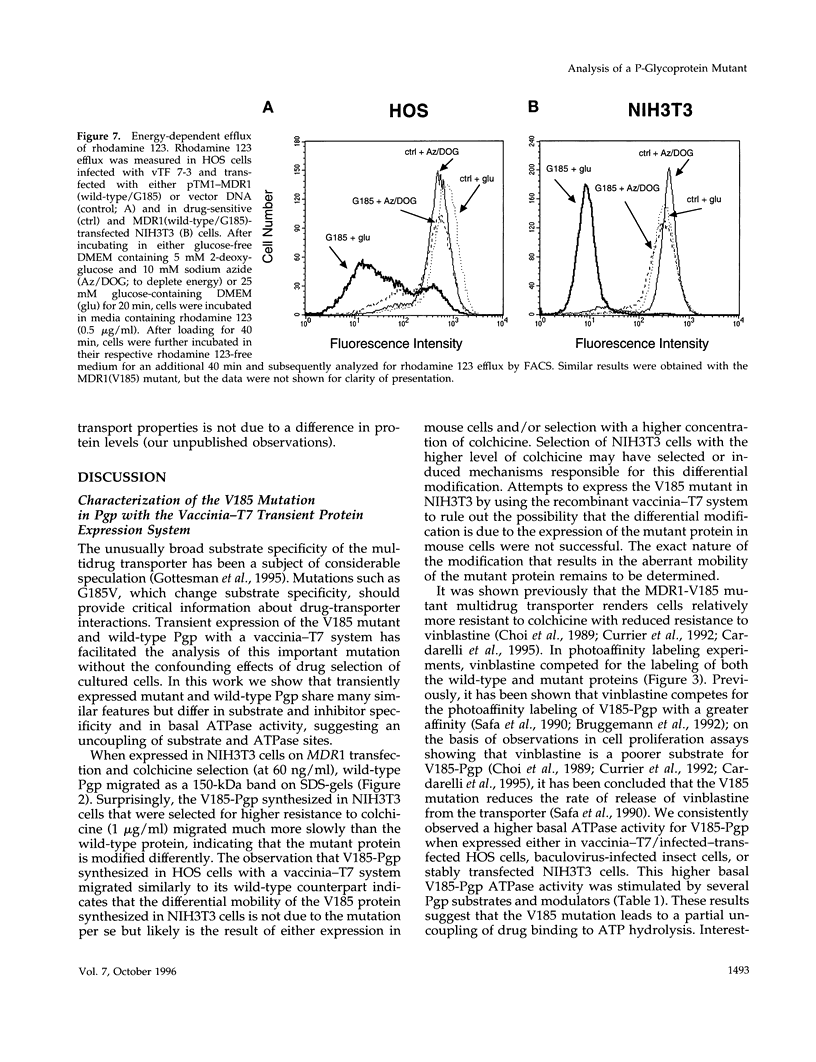
- Ambudkar S. V., Lelong I. H., Zhang J., Cardarelli C. O., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Partial purification and reconstitution of the human multidrug-resistance pump: characterization of the drug-stimulatable ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8472–8476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
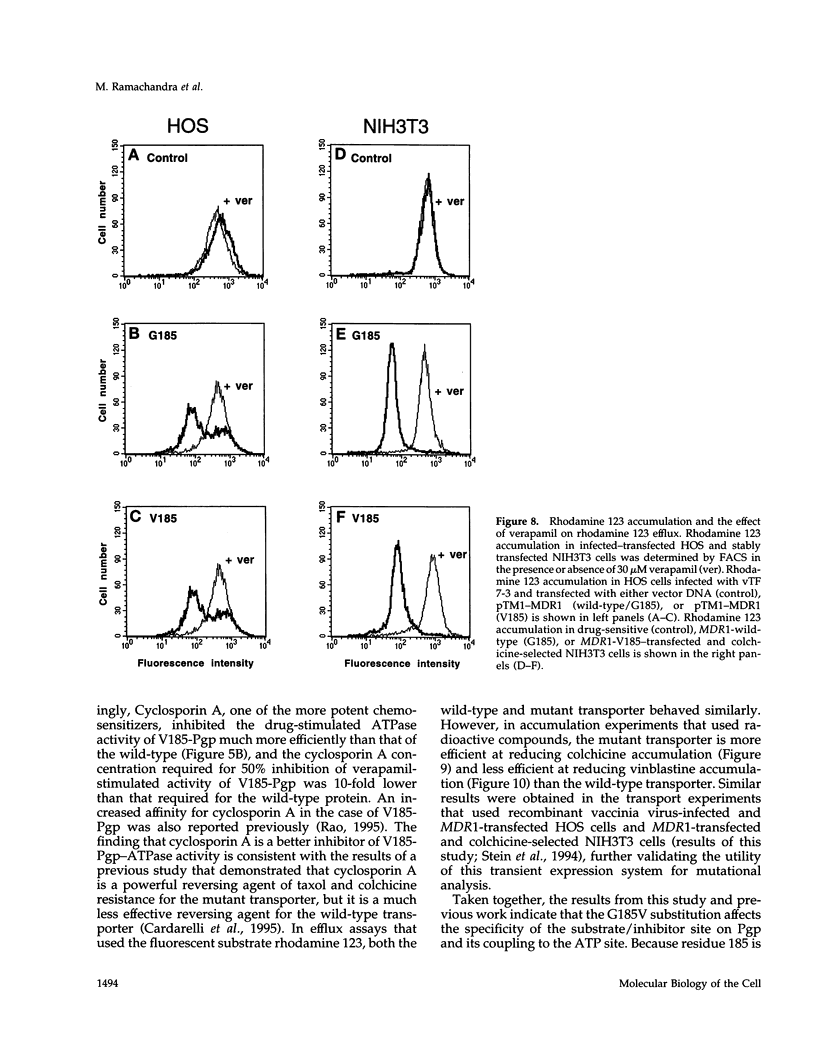
- Ambudkar S. V. Purification and reconstitution of functional human P-glycoprotein. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1995 Feb;27(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02110327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzaria M., Schurr E., Gros P. Discrete mutations introduced in the predicted nucleotide-binding sites of the mdr1 gene abolish its ability to confer multidrug resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5289–5297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T., Cirtain M. C. Continued expression of vinca alkaloid resistance by CCRF-CEM cells after treatment with tunicamycin or pronase. Cancer Res. 1982 Jan;42(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruggemann E. P., Currier S. J., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Characterization of the azidopine and vinblastine binding site of P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21020–21026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruggemann E. P., Germann U. A., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Two different regions of P-glycoprotein [corrected] are photoaffinity-labeled by azidopine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15483–15488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli C. O., Aksentijevich I., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Differential effects of P-glycoprotein inhibitors on NIH3T3 cells transfected with wild-type (G185) or mutant (V185) multidrug transporters. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 1;55(5):1086–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. J., Chin J. E., Ueda K., Clark D. P., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M., Roninson I. B. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. H., Chen C. J., Kriegler M., Roninson I. B. An altered pattern of cross-resistance in multidrug-resistant human cells results from spontaneous mutations in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90568-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell M. M., Tsuruo T., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. ATP-binding properties of P glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant KB cells. FASEB J. 1987 Jul;1(1):51–54. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.1.2886389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier S. J., Kane S. E., Willingham M. C., Cardarelli C. O., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Identification of residues in the first cytoplasmic loop of P-glycoprotein involved in the function of chimeric human MDR1-MDR2 transporters. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25153–25159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doige C. A., Yu X., Sharom F. J. ATPase activity of partially purified P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 24;1109(2):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90078-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elroy-Stein O., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. Cap-independent translation of mRNA conferred by encephalomyocarditis virus 5' sequence improves the performance of the vaccinia virus/bacteriophage T7 hybrid expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. L., Ni B., Hrycyna C. A., Chen D., Ambudkar S. V., Pastan I., Germann U. A., Gottesman M. M. Heterologous expression systems for P-glycoprotein: E. coli, yeast, and baculovirus. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1995 Feb;27(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF02110330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges E., Bradley G., Gariepy J., Ling V. Detection of P-glycoprotein isoforms by gene-specific monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germann U. A., Chambers T. C., Ambudkar S. V., Licht T., Cardarelli C. O., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Characterization of phosphorylation-defective mutants of human P-glycoprotein expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 19;271(3):1708–1716. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.3.1708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germann U. A., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Expression of the human multidrug transporter in insect cells by a recombinant baculovirus. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2295–2303. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Hrycyna C. A., Schoenlein P. V., Germann U. A., Pastan I. Genetic analysis of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:607–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.29.120195.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Tsuruo T. Functional role for the 170- to 180-kDa glycoprotein specific to drug-resistant tumor cells as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. P., Goodfellow H. R., Valverde M. A., Gill D. R., Sepúlveda V., Higgins C. F. Protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein regulates cell volume-activated chloride channels. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio M., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. ATP-dependent transport of vinblastine in vesicles from human multidrug-resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3580–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioka N., Tsubota J., Kakehi Y., Komano T., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I., Ueda K. P-glycoprotein gene (MDR1) cDNA from human adrenal: normal P-glycoprotein carries Gly185 with an altered pattern of multidrug resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91985-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Thorner J. Functional expression of human mdr1 in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2302–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V., Kartner N., Sudo T., Siminovitch L., Riordan J. R. Multidrug-resistance phenotype in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Treat Rep. 1983 Oct;67(10):869–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo T. W., Clarke D. M. Rapid purification of human P-glycoprotein mutants expressed transiently in HEK 293 cells by nickel-chelate chromatography and characterization of their drug-stimulated ATPase activities. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21449–21452. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo T. W., Clarke D. M. Reconstitution of drug-stimulated ATPase activity following co-expression of each half of human P-glycoprotein as separate polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7750–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Baculoviruses: high-level expression in insect cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Vaccinia virus: a tool for research and vaccine development. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1662–1667. doi: 10.1126/science.2047875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Gottesman M. M., Ueda K., Lovelace E., Rutherford A. V., Willingham M. C. A retrovirus carrying an MDR1 cDNA confers multidrug resistance and polarized expression of P-glycoprotein in MDCK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4486–4490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao U. S. Mutation of glycine 185 to valine alters the ATPase function of the human P-glycoprotein expressed in Sf9 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6686–6690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safa A. R., Stern R. K., Choi K., Agresti M., Tamai I., Mehta N. D., Roninson I. B. Molecular basis of preferential resistance to colchicine in multidrug-resistant human cells conferred by Gly-185----Val-185 substitution in P-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7225–7229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Müller M., Homolya L., Holló Z., Seprödi J., Germann U. A., Gottesman M. M., Price E. M., Boucher R. C. Interaction of bioactive hydrophobic peptides with the human multidrug transporter. FASEB J. 1994 Jul;8(10):766–770. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.10.7914178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Price E. M., Boucher R. C., Germann U. A., Scarborough G. A. Expression of the human multidrug resistance cDNA in insect cells generates a high activity drug-stimulated membrane ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4854–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Kemp S., Dollé M., Rudenko G., Wagenaar E. N-glycosylation and deletion mutants of the human MDR1 P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7474–7481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. B., Ling V. ATPase activity of purified and reconstituted P-glycoprotein from Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3745–3754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. B., Ling V. Reconstitution of drug transport by purified P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16167–16175. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharom F. J., Yu X., Doige C. A. Functional reconstitution of drug transport and ATPase activity in proteoliposomes containing partially purified P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24197–24202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein W. D., Cardarelli C., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Kinetic evidence suggesting that the multidrug transporter differentially handles influx and efflux of its substrates. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):763–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Cardarelli C., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Expression of a full-length cDNA for the human "MDR1" gene confers resistance to colchicine, doxorubicin, and vinblastine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde M. A., Díaz M., Sepúlveda F. V., Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F. Volume-regulated chloride channels associated with the human multidrug-resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):830–833. doi: 10.1038/355830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Sachs C. W., Fu H. W., Fine R. L., Casey P. J. Characterization of prenylcysteines that interact with P-glycoprotein and inhibit drug transport in tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 29;270(39):22859–22865. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.39.22859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Shawi M. K., Senior A. E. Characterization of the adenosine triphosphatase activity of Chinese hamster P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4197–4206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]