Abstract
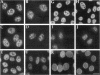
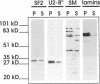
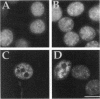
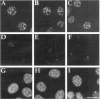
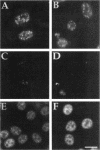
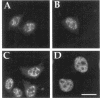
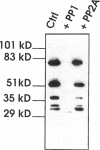
HeLa cell nuclei were permeabilized and reconstituted with nuclear extract to identify soluble nuclear factors which play a role in the organization of pre-mRNA splicing factors in the mammalian cell nucleus. Permeabilized nuclei reconstituted with nuclear extract were active in transcription and DNA replication and nuclear speckles containing pre-mRNA splicing factors were maintained over several hours independent of soluble nuclear components. The characteristic rounding up of nuclear speckles in response to inhibition of RNA polymerase II seen in vivo was reproduced in permeabilized cells and was strictly dependent on a catalytic activity present in the nuclear extract. By inhibitor titration experiments and sensitivity to inhibitor 2, this activity was identified as a member of the serine/threonine protein phosphatase 1 family (PP1). Interference with PP1 activity affected the distribution of pre-mRNA splicing factors in transcriptionally active, permeabilized cells, and excess PP1 activity caused increased dephosphorylation of SR proteins in nuclear speckles. These data show that the dynamic reorganization of the mammalian cell nucleus can be studied in permeabilized cells and that PP1 is involved in the rounding up of speckles as well as the overall organization of pre-mRNA splicing factors in the mammalian cell nucleus.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. S., Montminy M., Shenolikar S., Feramisco J. R. Expression of a peptide inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 increases phosphorylation and activity of CREB in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4398–4407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachellerie J. P., Puvion E., Zalta J. P. Ultrastructural organization and biochemical characterization of chromatin - RNA - protein complexes isolated from mammalian cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):327–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baurén G., Wieslander L. Splicing of Balbiani ring 1 gene pre-mRNA occurs simultaneously with transcription. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard W. A new staining procedure for electron microscopical cytology. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 May;27(3):250–265. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beullens M., Van Eynde A., Bollen M., Stalmans W. Inactivation of nuclear inhibitory polypeptides of protein phosphatase-1 (NIPP-1) by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13172–13177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Visualization of RNA transcription and processing. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;2(2):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birney E., Kumar S., Krainer A. R. Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisotto S., Lauriault P., Duval M., Vincent M. Colocalization of a high molecular mass phosphoprotein of the nuclear matrix (p255) with spliceosomes. J Cell Sci. 1995 May;108(Pt 5):1873–1882. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.5.1873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Sunwoo J., Labbé J. C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cell cycle oscillation of phosphatase inhibitor-2 in rat fibroblasts coincident with p34cdc2 restriction. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):74–78. doi: 10.1038/344074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1549–1554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali B., Cohen P. T., Lamond A. I. Protein phosphatase 1 can modulate alternative 5' splice site selection in a HeLa splicing extract. FEBS Lett. 1994 Oct 3;352(3):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00973-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwill K., Pawson T., Andrews B., Prasad J., Manley J. L., Bell J. C., Duncan P. I. The Clk/Sty protein kinase phosphorylates SR splicing factors and regulates their intranuclear distribution. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 15;15(2):265–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGuzman A., Lee E. Y. Preparation of low-molecular-weight forms of rabbit muscle protein phosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:356–368. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphorylation is involved in the regulation of chromatin condensation during interphase. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 2;312(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Bernhard W. Localisation of rapidly and slowly labelled nuclear RNA as visualized by high resolution autoradiography. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Immunoelectron microscope visualization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens within spread transcription complexes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Nobis P. Ultrastructural localization of transcription sites and of RNA distribution during the cell cycle of synchronized CHO cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 May;113(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S. Perichromatin fibrils are in situ forms of nascent transcripts. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;4(3):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey E. G., Krochmalnic G., Penman S. The nonchromatin substructures of the nucleus: the ribonucleoprotein (RNP)-containing and RNP-depleted matrices analyzed by sequential fractionation and resinless section electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1654–1665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D. The superfamily of arginine/serine-rich splicing factors. RNA. 1995 Sep;1(7):663–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blum A., Blobel G. Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):546–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui J. F., Lane W. S., Fu X. D. A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):678–682. doi: 10.1038/369678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui J. F., Tronchère H., Chandler S. D., Fu X. D. Purification and characterization of a kinase specific for the serine- and arginine-rich pre-mRNA splicing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10824–10828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Ward D. C. Inhibition of RNA polymerase II transcription causes chromatin decondensation, loss of nucleolar structure, and dispersion of chromosomal domains. Exp Cell Res. 1996 Apr 10;224(1):163–173. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Hoet M. H., De Jong B. A., Van der Kemp A., Van Venrooij W. J. Mapping of B cell epitopes on small nuclear ribonucleoproteins that react with human autoantibodies as well as with experimentally-induced mouse monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2560–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozák P., Hassan A. B., Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Visualization of replication factories attached to nucleoskeleton. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90235-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Spector D. L. Intron-dependent recruitment of pre-mRNA splicing factors to sites of transcription. J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(4):719–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes T. A., Pombo A., McManus J., Hozák P., Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. On the structure of replication and transcription factories. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1995;19:59–65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1995.supplement_19.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högner D., Lepper K., Seibold G., Jost E. Lamin disassembly kinetics: a cell-free system with extracts from mitotic HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jun;176(2):281–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Hassan A. B., Errington R. J., Cook P. R. Visualization of focal sites of transcription within human nuclei. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1059–1065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Yuan J., Cook P. R. A gentle method for preparing cyto- and nucleo-skeletons and associated chromatin. J Cell Sci. 1988 Jul;90(Pt 3):365–378. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagiello I., Beullens M., Stalmans W., Bollen M. Subunit structure and regulation of protein phosphatase-1 in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17257–17263. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Spector D. L. In vivo evidence that transcription and splicing are coordinated by a recruiting mechanism. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90159-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R. Pre-mRNA splicing by complementation with purified human U1, U2, U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9415–9429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Bell H., Cohen P. Identification of high levels of protein phosphatase-1 in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80741-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm G. M., Lamond A. I. Non-snRNP protein splicing factors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 25;1173(3):247–265. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90122-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Kastner B., Bach M. Structure of spliceosomal snRNPs and their role in pre-mRNA splicing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):265–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90001-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Klumpp S. Tautomycin from the bacterium Streptomyces verticillatus. Another potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S. H., Dwen P., Pederson T. Serine/threonine phosphorylation regulates binding of C hnRNP proteins to pre-mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7764–7768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P. T., Lamond A. I. Regulation of mammalian spliceosome assembly by a protein phosphorylation mechanism. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5679–5688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P., Lamond A. I. Ser/Thr-specific protein phosphatases are required for both catalytic steps of pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5263–5269. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Peebles C., Fritzler M. J., Steigerwald J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe R. T., Mayeda A., Sadowski C. L., Krainer A. R., Spector D. L. Disruption of pre-mRNA splicing in vivo results in reorganization of splicing factors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(3):249–260. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscigno R. F., Garcia-Blanco M. A. SR proteins escort the U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP to the spliceosome. RNA. 1995 Sep;1(7):692–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Murphy C., Gall J. G. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a phosphorylated epitope stains lampbrush chromosome loops and small granules in the amphibian germinal vesicle. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2217–2223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheen J. Protein phosphatase activity is required for light-inducible gene expression in maize. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3497–3505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair G. D., Brasch K. The reversible action of alpha-amanitin on nuclear structure and molecular composition. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jan;111(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3467–3481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Schrier W. H., Busch H. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of snRNPs. Biol Cell. 1983;49(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A., Mieskes G. Inhibitory effect of okadaic acid on the p-nitrophenyl phosphate phosphatase activity of protein phosphatases. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):233–239. doi: 10.1042/bj2750233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A., Sasaki K., Nagai H., Mieskes G., Isobe M., Isono K., Yasumoto T. Inhibition of specific binding of okadaic acid to protein phosphatase 2A by microcystin-LR, calyculin-A and tautomycin: method of analysis of interactions of tight-binding ligands with target protein. Biochem J. 1995 Mar 15;306(Pt 3):657–665. doi: 10.1042/bj3060657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Franchi L. Identification of protein antigens associated with the nuclear matrix and with clusters of interchromatin granules in both interphase and mitotic cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Mar;87(Pt 2):269–282. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eynde A., Wera S., Beullens M., Torrekens S., Van Leuven F., Stalmans W., Bollen M. Molecular cloning of NIPP-1, a nuclear inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1, reveals homology with polypeptides involved in RNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 24;270(47):28068–28074. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.47.28068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., Kuijpers H., Vooijs P., Van Venrooij W., Ramaekers F. Distribution of the 70K U1 RNA-associated protein during interphase and mitosis. Correlation with other U RNP particles and proteins of the nuclear matrix. J Cell Sci. 1986 Dec;86:173–190. doi: 10.1242/jcs.86.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wansink D. G., Schul W., van der Kraan I., van Steensel B., van Driel R., de Jong L. Fluorescent labeling of nascent RNA reveals transcription by RNA polymerase II in domains scattered throughout the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):283–293. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woppmann A., Will C. L., Kornstädt U., Zuo P., Manley J. L., Lührmann R. Identification of an snRNP-associated kinase activity that phosphorylates arginine/serine rich domains typical of splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2815–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y., Johnson C. V., Moen P. T., Jr, McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. Nonrandom gene organization: structural arrangements of specific pre-mRNA transcription and splicing with SC-35 domains. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1635–1647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. A simplified procedure for the purification of the protein phosphatase modulator (inhibitor-2) from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):293–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Taneja K. L., Singer R. H., Green M. R. Localization of pre-mRNA splicing in mammalian nuclei. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):809–812. doi: 10.1038/372809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]