Abstract
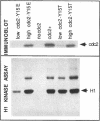
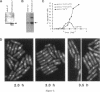
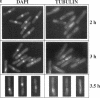
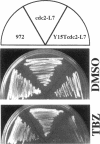
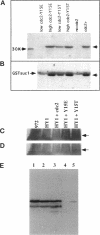
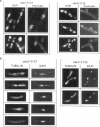
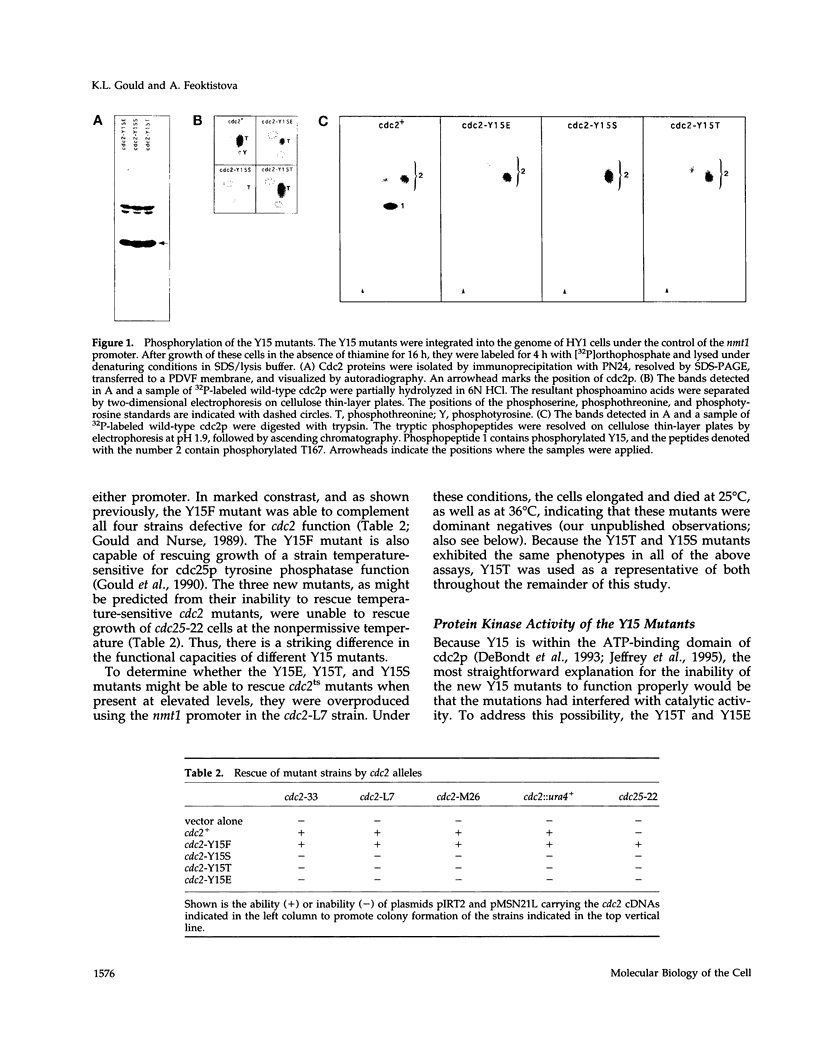
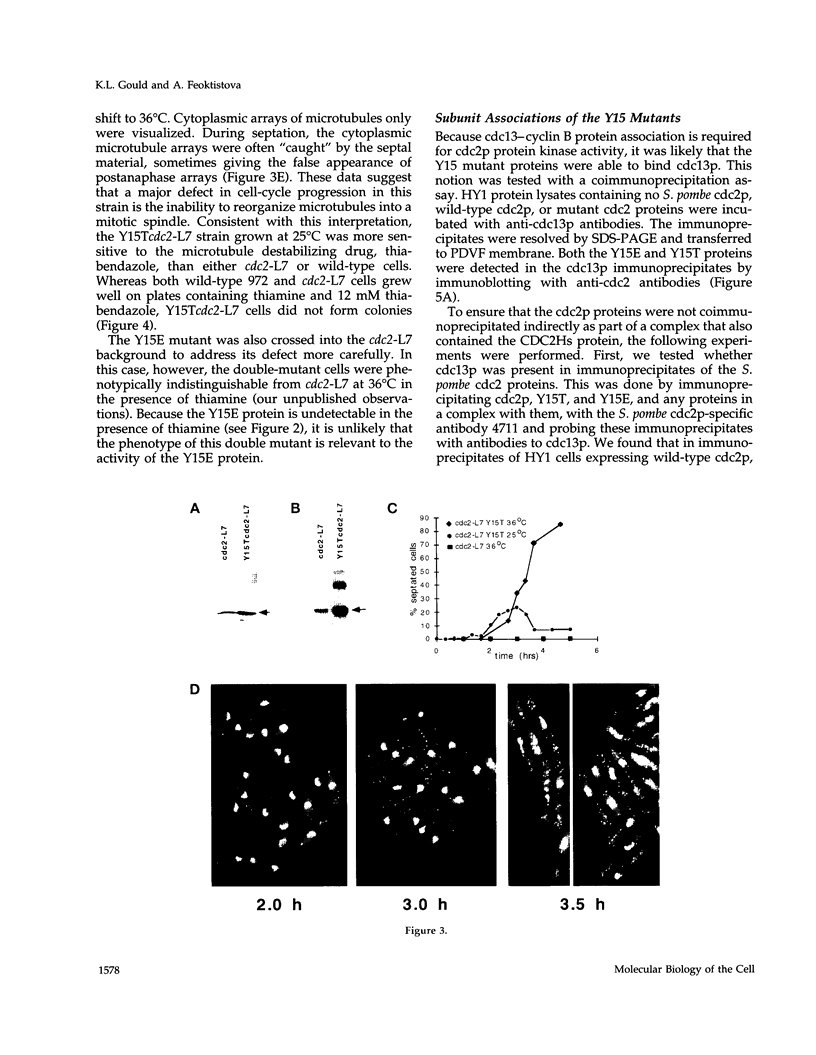
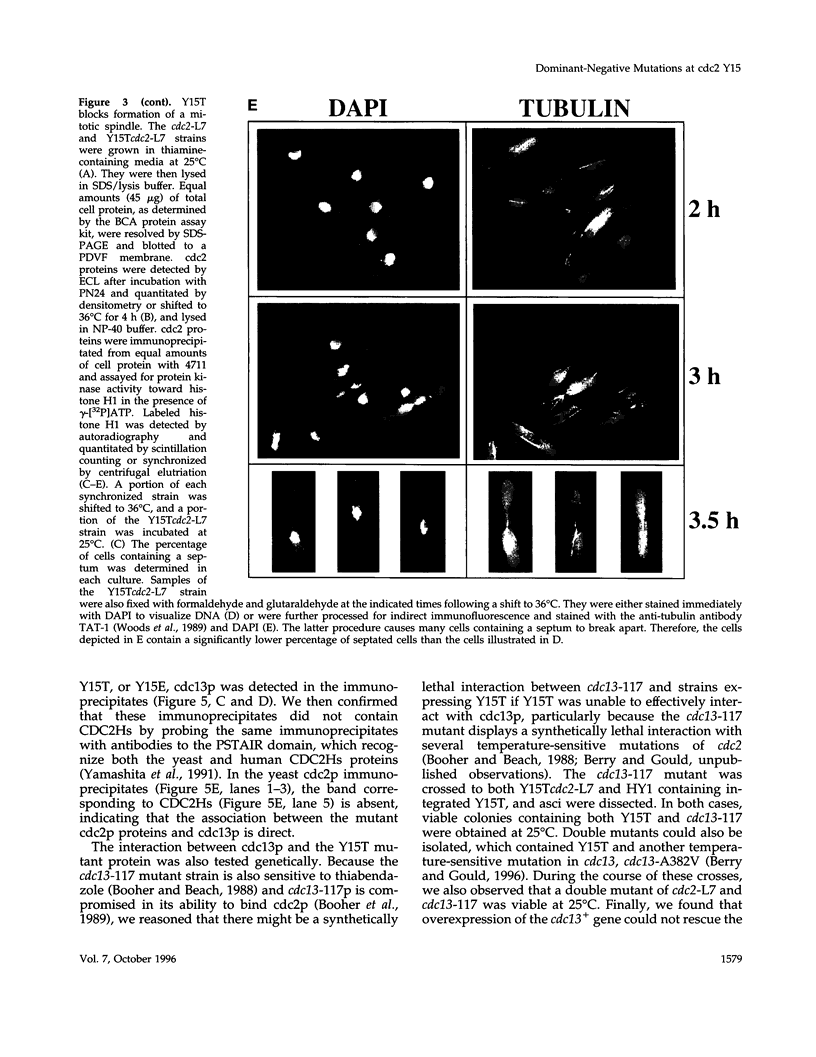
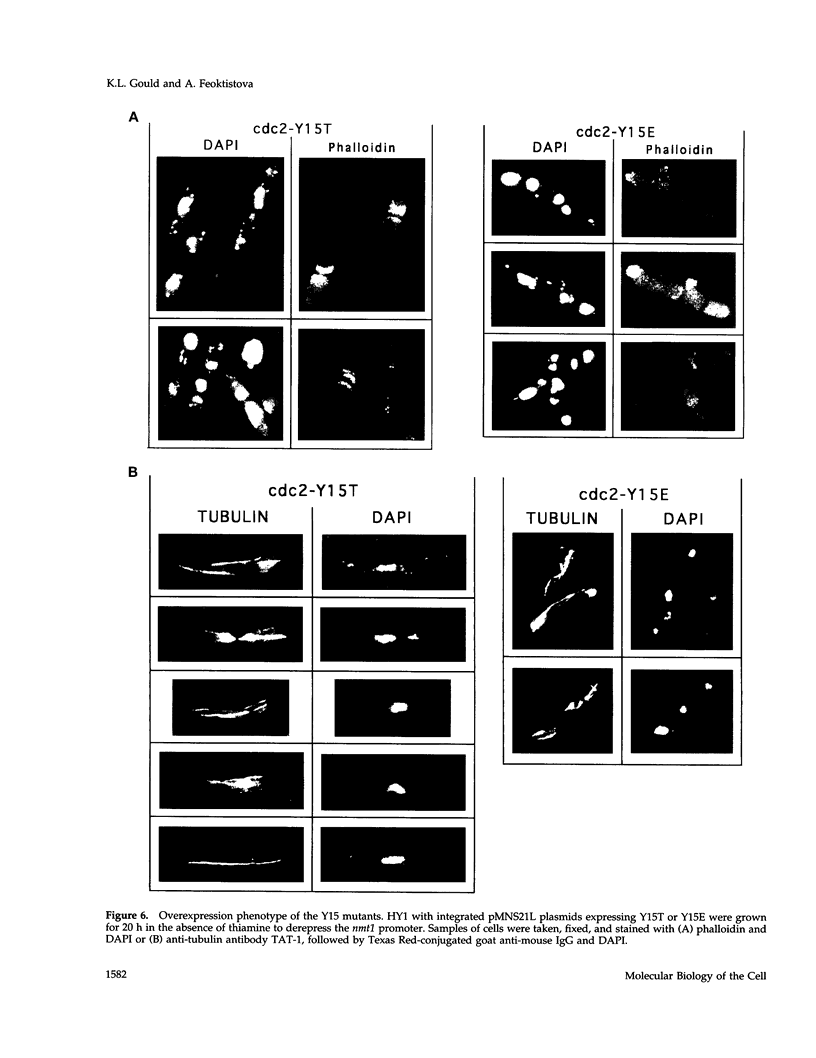
The cdc2 protein kinase family is regulated negatively by phosphorylation in the glycine ATP-binding loop at a conserved tyrosine residue, Y15, alone or in combination with T14 phosphorylation. In Schizosaccharomyces pombe and other systems, substitution of these residues with structurally similar but nonphosphorylatable amino acids has generated proteins (Y15F or T14AY15F) that behave as constitutively tyrosine-dephosphorylated proteins or threonine and tyrosine-dephosphorylated proteins. Here we report the characteristics of three additional mutants at Y15--Y15E, Y15S, and Y15T--in S. pombe cdc2p. All three mutant proteins are active in in vitro kinase assays, but are unable to functionally complement cdc2 loss-of-function mutations in vivo. Additionally, all three mutants are dominant negatives. A more detailed analysis of the Y15T mutant indicates that it can initiate chromosome condensation and F-actin contractile ring formation, but is unable to drive the reorganization of microtubules into a mitotic spindle.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton-Fessler S., Liu F., Gabrielli B., Lee M. S., Peng C. Y., Piwnica-Worms H. Cell cycle regulation of the p34cdc2 inhibitory kinases. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Sep;5(9):989–1001. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.9.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet N., Muriel W. J., Carr A. M. Versatile shuttle vectors and genomic libraries for use with Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Gene. 1992 May 1;114(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90707-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G., Schmid E., Maundrell K. TATA box mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe nmt1 promoter affect transcription efficiency but not the transcription start point or thiamine repressibility. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90552-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry L. D., Gould K. L. Novel alleles of cdc13 and cdc2 isolated as suppressors of mitotic catastrophe in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1996 Jul 26;251(6):635–646. doi: 10.1007/BF02174112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of cdc13+ in mitotic control in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: possible interaction of the gene product with microtubules. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2321–2327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne Y., Watson M. H., Hickey M. J., Holmes W., Rocque W., Reed S. I., Tainer J. A. Crystal structure and mutational analysis of the human CDK2 kinase complex with cell cycle-regulatory protein CksHs1. Cell. 1996 Mar 22;84(6):863–874. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. R., Dunphy W. G. Cdc2 regulatory factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;6(6):877–882. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Haese G. J., Walworth N., Carr A. M., Gould K. L. The Wee1 protein kinase regulates T14 phosphorylation of fission yeast Cdc2. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Apr;6(4):371–385. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.4.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleig U. N., Gould K. L., Nurse P. A dominant negative allele of p34cdc2 shows altered phosphoamino acid content and sequesters p56cdc13 cyclin. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2295–2301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleig U. N., Nurse P. Expression of a dominant negative allele of cdc2 prevents activation of the endogenous p34cdc2 kinase. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;226(3):432–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00260656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Tonks N. K., Nurse P. Complementation of the mitotic activator, p80cdc25, by a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1703321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I., Hayles J., Nurse P. Cloning and sequencing of the cyclin-related cdc13+ gene and a cytological study of its role in fission yeast mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1988 Dec;91(Pt 4):587–595. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemerly A., Engler J. de A., Bergounioux C., Van Montagu M., Engler G., Inzé D., Ferreira P. Dominant negative mutants of the Cdc2 kinase uncouple cell division from iterative plant development. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 15;14(16):3925–3936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G. A. Sequence of the cell division gene CDC2 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe; patterns of splicing and homology to protein kinases. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D., Russo A. A., Polyak K., Gibbs E., Hurwitz J., Massagué J., Pavletich N. P. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):313–320. doi: 10.1038/376313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Marks J., Schmitz N., Nigg E. A., Simanis V. Vertebrate p34cdc2 phosphorylation site mutants: effects upon cell cycle progression in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 1992 May;102(Pt 1):43–53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labib K., Craven R. A., Crawford K., Nurse P. Dominant mutants identify new roles for p34cdc2 in mitosis. EMBO J. 1995 May 15;14(10):2155–2165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Enoch T., Piwnica-Worms H. mik1+ encodes a tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30530–30537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E. Cyclin dependent kinase regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;7(6):773–780. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Reed S. I. A cell cycle checkpoint monitors cell morphogenesis in budding yeast. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):739–749. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeill S. A., Nurse P. Genetic analysis of human p34CDC2 function in fission yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Sep;240(3):315–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00280381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeill S. A., Nurse P. Mutational analysis of the fission yeast p34cdc2 protein kinase gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):415–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00277142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. Thiamine-repressible expression vectors pREP and pRIP for fission yeast. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90551-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Richardson H. E., Reed S. I. Dominant negative protein kinase mutations that confer a G1 arrest phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4426–4430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Klar A., Nurse P. Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:795–823. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):131–134. doi: 10.1038/374131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Lee M. S., Ogg S., Falk J. L., Swenson K. I., Piwnica-Worms H. Cyclin promotes the tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 in a wee1+ dependent manner. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1255–1263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Piwnica-Worms H. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickham K. M., Meyer A. N., Li J., Donoghue D. J. Requirement of mosXe protein kinase for meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes induced by a cdc2 mutant lacking regulatory phosphorylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3192–3203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: a biochemical view. Biochem J. 1995 Jun 15;308(Pt 3):697–711. doi: 10.1042/bj3080697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. L. High efficiency transformation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):621–621. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J. The function(s) of CAK, the p34cdc2-activating kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):496–500. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueland C. S., Lew D. J., Cismowski M. J., Reed S. I. Full activation of p34CDC28 histone H1 kinase activity is unable to promote entry into mitosis in checkpoint-arrested cells of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3744–3755. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Sherwin T., Sasse R., MacRae T. H., Baines A. J., Gull K. Definition of individual components within the cytoskeleton of Trypanosoma brucei by a library of monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jul;93(Pt 3):491–500. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]