Abstract
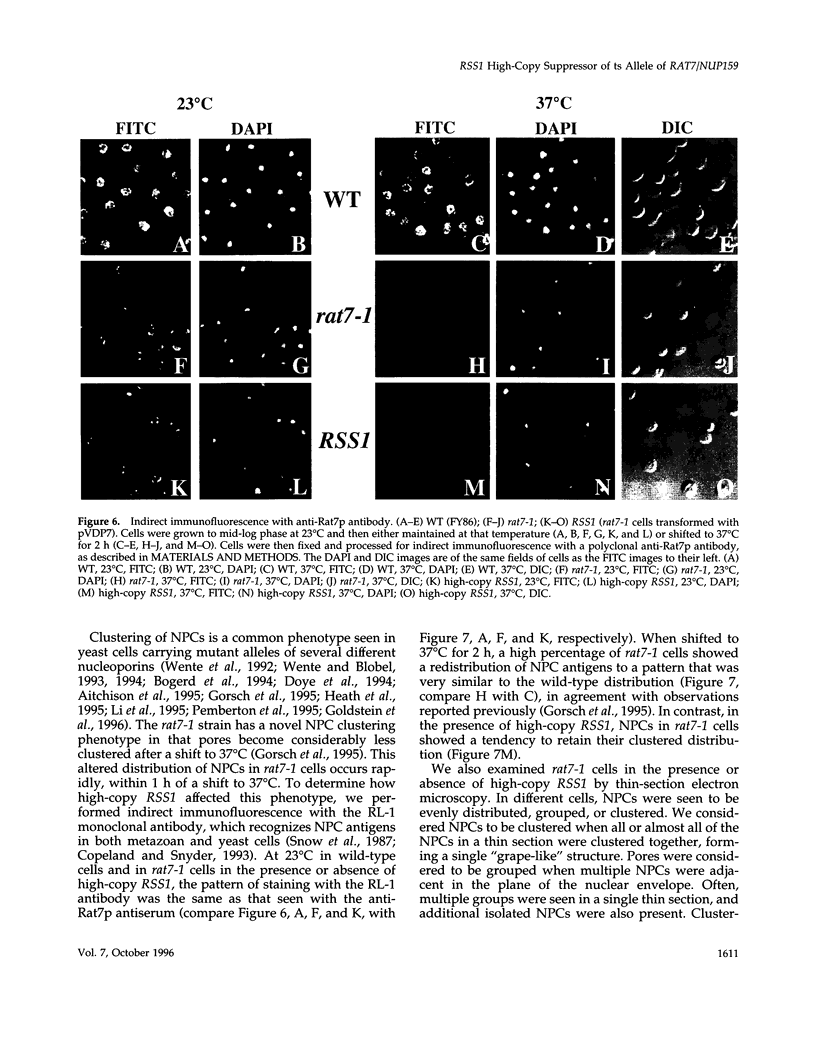
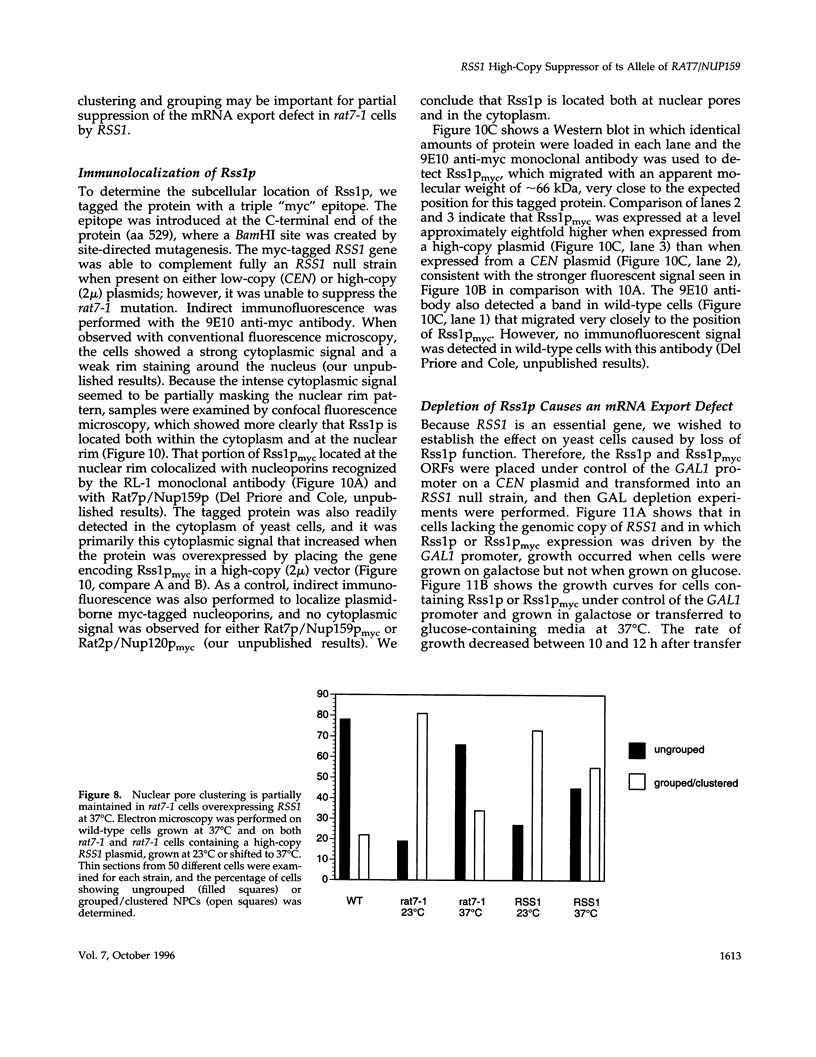
RAT7/NUP159 was identified previously in a screen for genes whose products are important for nucleocytoplasmic export of poly(A)+ RNA and encodes an essential nucleoporin. We report here the identification of RSS1 (Rat Seven Suppressor) as a high-copy extragenic suppressor of the rat7-1 temperature-sensitive allele. Rss1p encodes a novel essential protein of 538 amino acids, which contains an extended predicted coiled-coil domain and is located both at nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) and in the cytoplasm. RSS1 is the first reported high-copy extragenic suppressor of a mutant nucleoporin. Overexpression of Rss1p partially suppresses the defects in nucleocytoplasmic export of poly(A)+ RNA, rRNA synthesis and processing, and nucleolar morphology seen in rat7-1 cells shifted to the nonpermissive temperature of 37 degrees C and, thus, restores these processes to levels adequate for growth at a rate approximately one-half that of wild-type cells. After a shift to 37 degrees C, the mutant Rat7-1p/Nup159-1p is lost from the nuclear rim of rat7-1 cells and NPCs, which are clustered together in these cells grown under permissive conditions become substantially less clustered. Overexpression of Rss1p did not result in retention of the mutant Rat7-1p/Nup159-1p in NPCs, but it did result in partial maintenance of the NPC-clustering phenotype seen in mutant cells. Depletion of Rss1p by placing the RSS1 open reading frame (ORF) under control of the GAL1 promoter led to cessation of growth and nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA without affecting nuclear protein import or nuclear pore complex distribution, suggesting that RSS1 is directly involved in mRNA export. Because both rat7-1 cells and cells depleted for Rss1p are defective in mRNA export, our data are consistent with both gene products playing essential roles in the process of mRNA export and suggest that Rss1p overexpression suppresses the growth defect of rat7-1 cells at 37 degrees C by acting to maintain mRNA export.
Full text
PDF



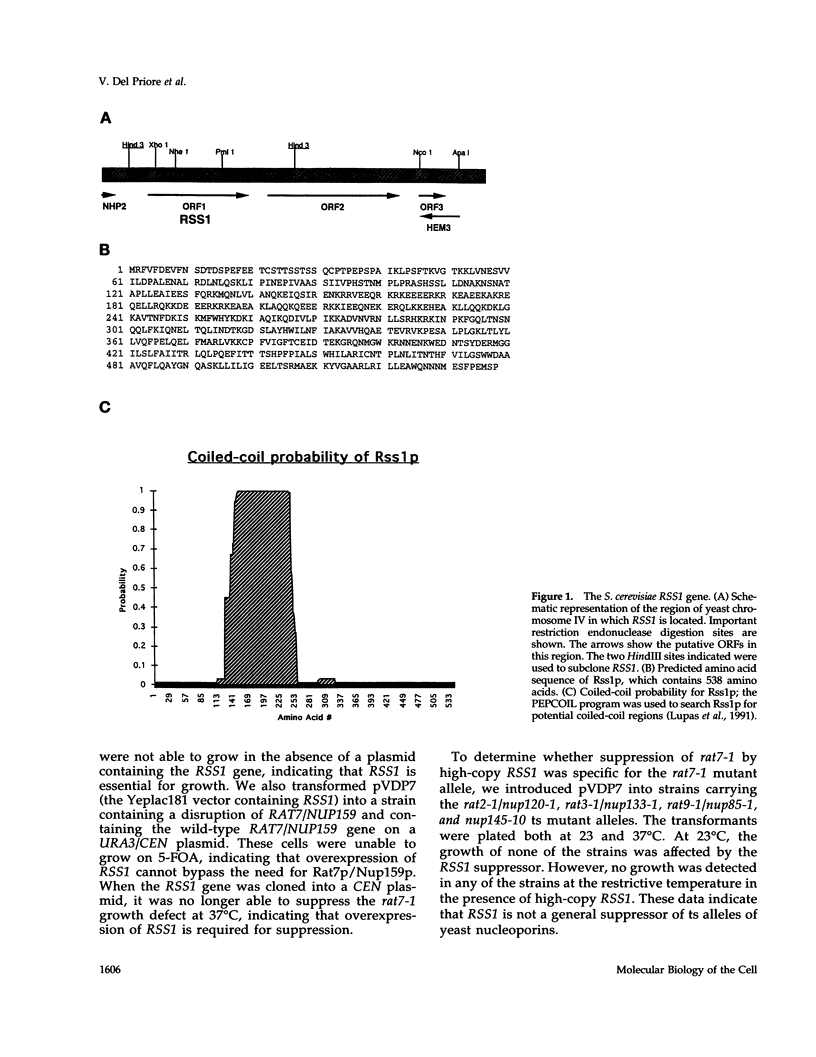

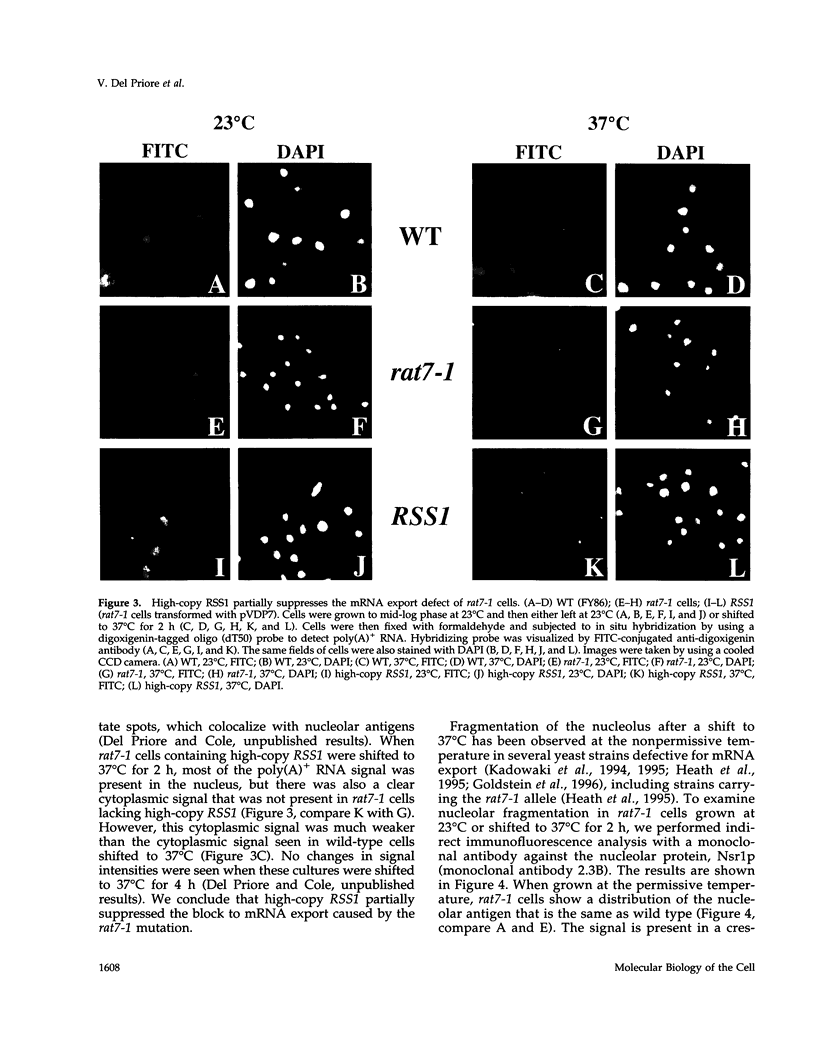











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Clark M. W., Vijayraghavan U., Abelson J. A yeast mutant, PRP20, altered in mRNA metabolism and maintenance of the nuclear structure, is defective in a gene homologous to the human gene RCC1 which is involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):72–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00259453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison J. D., Blobel G., Rout M. P. Nup120p: a yeast nucleoporin required for NPC distribution and mRNA transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1659–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Probing the structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;2(3):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W., Radermacher M. Architecture of the Xenopus nuclear pore complex revealed by three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Structural plasticity of the nuclear pore complex. J Mol Biol. 1995 Apr 28;248(2):273–293. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(95)80050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Visualization of transport-related configurations of the nuclear pore transporter. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):341–355. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82381-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. L., Douglas M. G. Organization of the nuclear pore complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1989 Aug;102(2):95–108. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(89)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudin A., Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O., Denouel A., Lacroute F., Cullin C. A simple and efficient method for direct gene deletion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3329–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerd A. M., Hoffman J. A., Amberg D. C., Fink G. R., Davis L. I. nup1 mutants exhibit pleiotropic defects in nuclear pore complex function. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):319–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Behavior of spindles and spindle plaques in the cell cycle and conjugation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):511–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.511-523.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Snyder M. Nuclear pore complex antigens delineate nuclear envelope dynamics in vegetative and conjugating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1993 Mar;9(3):235–249. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I. The nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:865–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.004245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Hurt E. C. Genetic approaches to nuclear pore structure and function. Trends Genet. 1995 Jun;11(6):235–241. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Wepf R., Hurt E. C. A novel nuclear pore protein Nup133p with distinct roles in poly(A)+ RNA transport and nuclear pore distribution. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6062–6075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Feldherr C. M. Translocation of RNA-coated gold particles through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):575–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. J., Stutz F., Lescure A., Rosbash M. mRNA nuclear export. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Apr;4(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Hurt E. C. Nuclear transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flach J., Bossie M., Vogel J., Corbett A., Jinks T., Willins D. A., Silver P. A. A yeast RNA-binding protein shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8399–8407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W. Relationship of nuclear membranes with filaments and microtubules. Protoplasma. 1971;73(2):263–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01275600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. W., Allen T. D. High resolution scanning electron microscopy of the nuclear envelope: demonstration of a new, regular, fibrous lattice attached to the baskets of the nucleoplasmic face of the nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1429–1440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Snay C. A., Heath C. V., Cole C. N. Pleiotropic nuclear defects associated with a conditional allele of the novel nucleoporin Rat9p/Nup85p. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Jun;7(6):917–934. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.6.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorsch L. C., Dockendorff T. C., Cole C. N. A conditional allele of the novel repeat-containing yeast nucleoporin RAT7/NUP159 causes both rapid cessation of mRNA export and reversible clustering of nuclear pore complexes. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(4):939–955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.4.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greber U. F., Senior A., Gerace L. A major glycoprotein of the nuclear pore complex is a membrane-spanning polypeptide with a large lumenal domain and a small cytoplasmic tail. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Vogel F., Mills A. D., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A. Distinct functions for the two importin subunits in nuclear protein import. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):246–248. doi: 10.1038/377246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. V., Copeland C. S., Amberg D. C., Del Priore V., Snyder M., Cole C. N. Nuclear pore complex clustering and nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA associated with mutation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAT2/NUP120 gene. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1677–1697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh J. E., Pryme I. F. Interaction between mRNA, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2770001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw J. E., Carragher B. O., Milligan R. A. Architecture and design of the nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90635-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Traglia H. M., Dunst R. W. The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):309–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iovine M. K., Watkins J. L., Wente S. R. The GLFG repetitive region of the nucleoporin Nup116p interacts with Kap95p, an essential yeast nuclear import factor. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1699–1713. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. RNA export. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarnik M., Aebi U. Toward a more complete 3-D structure of the nuclear pore complex. J Struct Biol. 1991 Dec;107(3):291–308. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(91)90054-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman A. E., Steinert P. M., Yuspa S., Goldman R. D. Dynamic aspects of the supramolecular organization of intermediate filament networks in cultured epidermal cells. Cell Motil. 1982;2(3):197–213. doi: 10.1002/cm.970020302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Chen S., Hitomi M., Jacobs E., Kumagai C., Liang S., Schneiter R., Singleton D., Wisniewska J., Tartakoff A. M. Isolation and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNA transport-defective (mtr) mutants. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):649–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Schneiter R., Hitomi M., Tartakoff A. M. Mutations in nucleolar proteins lead to nucleolar accumulation of polyA+ RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Sep;6(9):1103–1110. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.9.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer D. M., Strambio-de-Castillia C., Blobel G., Rout M. P. The essential yeast nucleoporin NUP159 is located on the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex and serves in karyopherin-mediated binding of transport substrate. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):19017–19021. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.19017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R., Ransom L., Kaufmann Y., Penman S. A cytoskeletal structure with associated polyribosomes obtained from HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li O., Heath C. V., Amberg D. C., Dockendorff T. C., Copeland C. S., Snyder M., Cole C. N. Mutation or deletion of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAT3/NUP133 gene causes temperature-dependent nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA and constitutive clustering of nuclear pore complexes. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Apr;6(4):401–417. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G. The nuclear and the cytoplasmic pore complex: structure, dynamics, distribution, and evolution. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1977;(6):75–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlin H., Daneholt B., Skoglund U. Translocation of a specific premessenger ribonucleoprotein particle through the nuclear pore studied with electron microscope tomography. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90224-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Blobel G., Radu A. Previously identified protein of uncertain function is karyopherin alpha and together with karyopherin beta docks import substrate at nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2008–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton L. F., Rout M. P., Blobel G. Disruption of the nucleoporin gene NUP133 results in clustering of nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1187–1191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt R., Holzenburg A., Buhle E. L., Jr, Jarnik M., Engel A., Aebi U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):883–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M., Blobel G. Protein import into nuclei: association and dissociation reactions involving transport substrate, transport factors, and nucleoporins. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ris H., Malecki M. High-resolution field emission scanning electron microscope imaging of internal cell structures after Epon extraction from sections: a new approach to correlative ultrastructural and immunocytochemical studies. J Struct Biol. 1993 Sep-Oct;111(2):148–157. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1993.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Wente S. R. Pores for thought: nuclear pore complex proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;4(10):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Wong D. H., Koepp D. M., Silver P. A. Mutants in a yeast Ran binding protein are defective in nuclear transport. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 1;14(21):5367–5378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow C. M., Senior A., Gerace L. Monoclonal antibodies identify a group of nuclear pore complex glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1143–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traglia H. M., Atkinson N. S., Hopper A. K. Structural and functional analyses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type and mutant RNA1 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2989–2999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Milligan R. A. A large particle associated with the perimeter of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):63–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Labeling of RNA and phosphoproteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:423–428. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. A temperature-sensitive NUP116 null mutant forms a nuclear envelope seal over the yeast nuclear pore complex thereby blocking nucleocytoplasmic traffic. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):275–284. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. NUP145 encodes a novel yeast glycine-leucine-phenylalanine-glycine (GLFG) nucleoporin required for nuclear envelope structure. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):955–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Rout M. P., Blobel G. A new family of yeast nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):705–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Dollard C., Ricupero-Hovasse S. L. Construction of a set of convenient Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains that are isogenic to S288C. Yeast. 1995 Jan;11(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/yea.320110107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Bartnik E., Blobel G. Primary structure analysis of an integral membrane glycoprotein of the nuclear pore. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2083–2092. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Blobel G., Rout M. P. POM152 is an integral protein of the pore membrane domain of the yeast nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):31–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Blobel G. The single transmembrane segment of gp210 is sufficient for sorting to the pore membrane domain of the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1441–1449. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R., Rine J. Transmission electron microscopy and immunocytochemical studies of yeast: analysis of HMG-CoA reductase overproduction by electron microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:473–512. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Demma M., Warren V., Dharmawardhane S., Condeelis J. Identification of an actin-binding protein from Dictyostelium as elongation factor 1a. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):494–496. doi: 10.1038/347494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G., Fey E. G., Penman S., Stein J., Stein G. Multiple types of mRNA-cytoskeleton interactions. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Nov;44(3):177–187. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240440306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G., Wilming L., Fey E. G., Penman S., Stein J., Stein G. Differential association of membrane-bound and non-membrane-bound polysomes with the cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Dec;191(2):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]