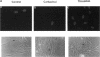
Abstract
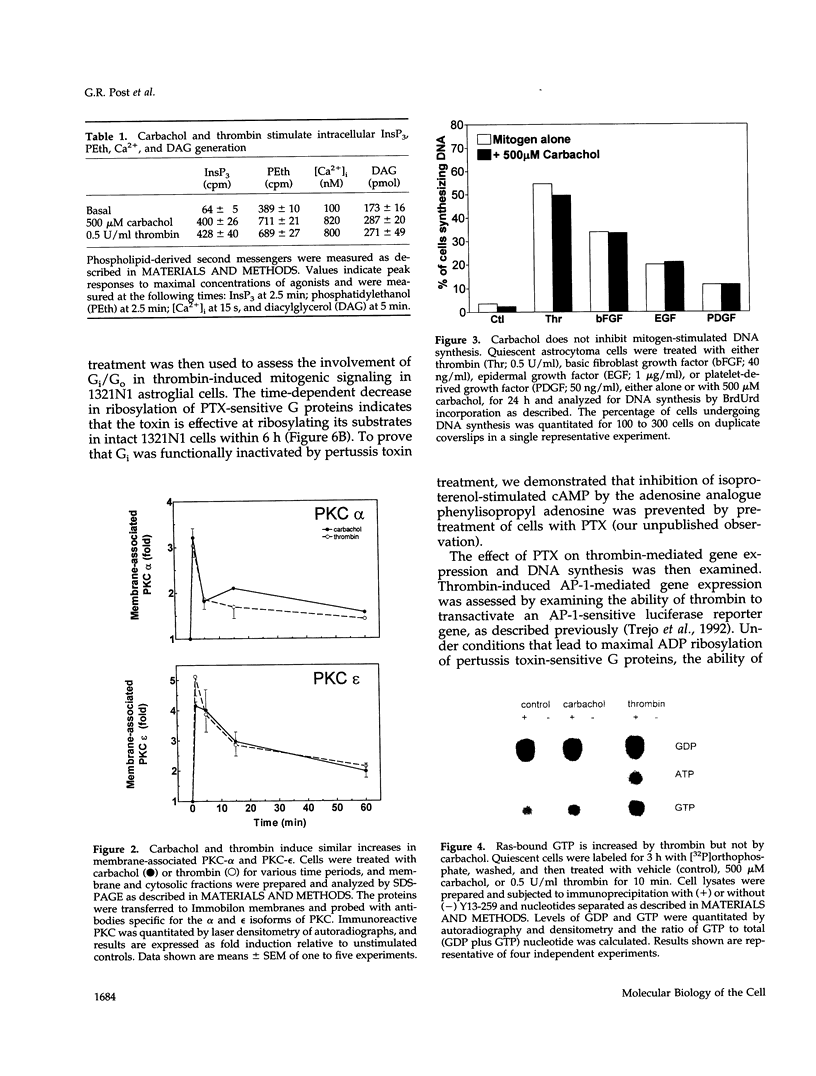
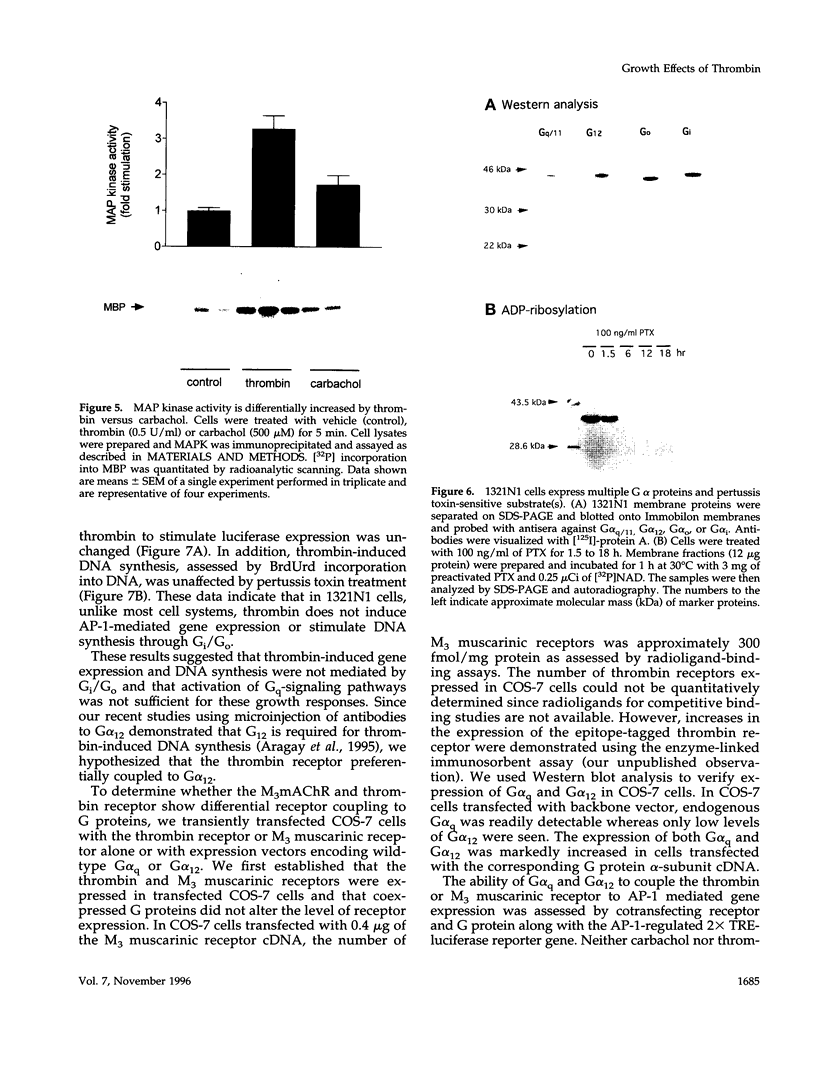
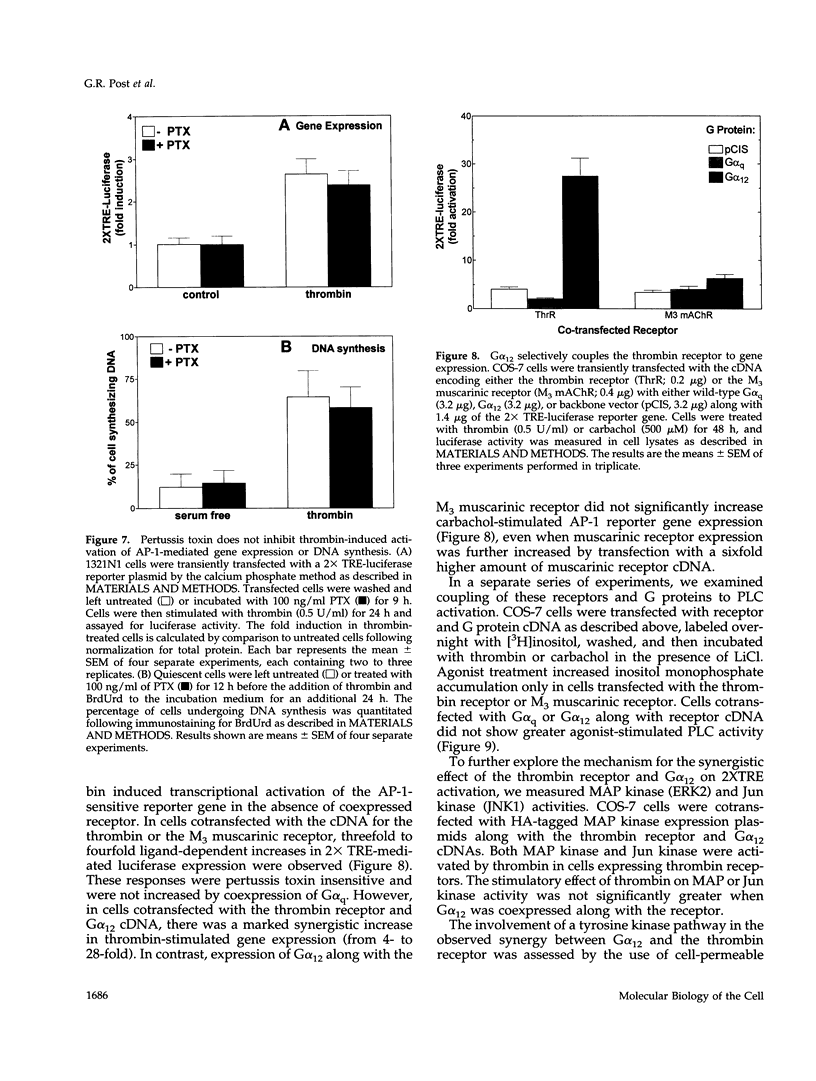
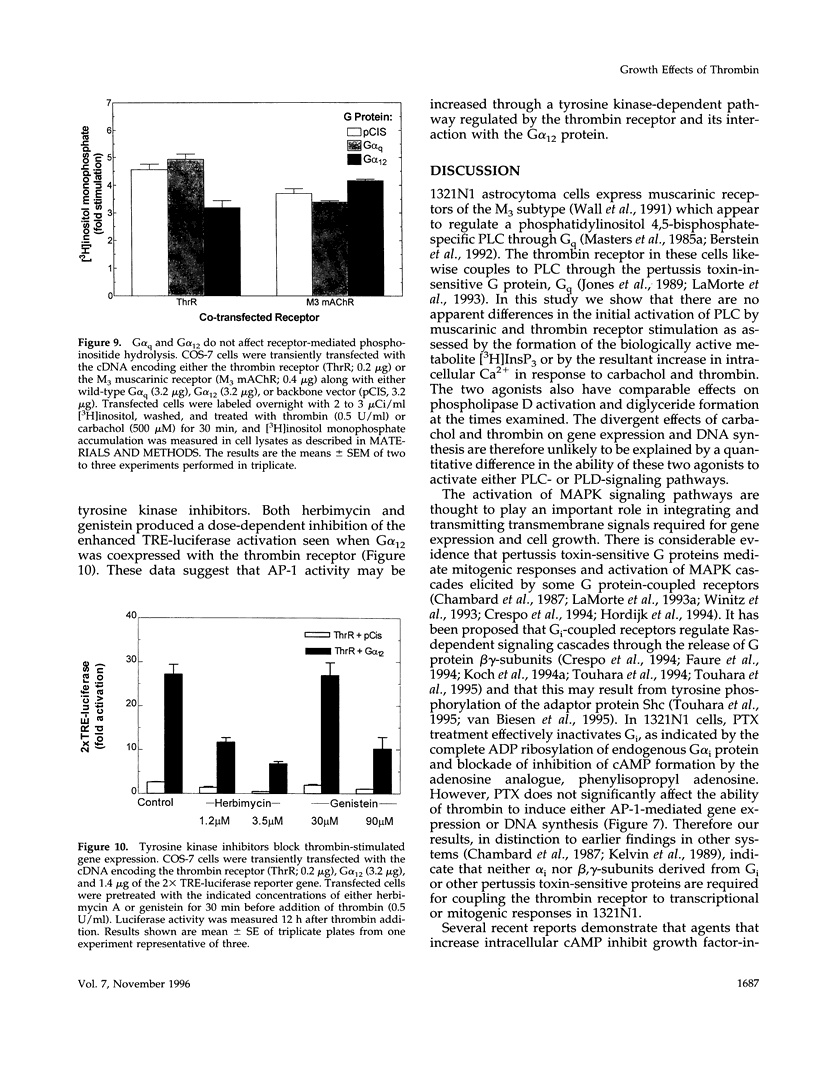
In 1321N1 astrocytoma cells, thrombin, but not carbachol, induces AP-1-mediated gene expression and DNA synthesis. To understand the divergent effects of these G protein-coupled receptor agonists on cellular responses, we examined Gq-dependent signaling events induced by thrombin receptor and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor stimulation. Thrombin and carbachol induce comparable changes in phosphoinositide and phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis, mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, diglyceride generation, and redistribution of protein kinase C; thus, activation of these Gq-signaling pathways appears to be insufficient for gene expression and mitogenesis. Thrombin increases Ras and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation to a greater extent than carbachol in 1321N1 cells. The effects of thrombin are not mediated through Gi, since ribosylation of Gi/Go proteins by pertussis toxin does not prevent thrombin-induced gene expression or thrombin-stimulated DNA synthesis. We recently reported that the pertussis toxin-insensitive G12 protein is required for thrombin-induced DNA synthesis. We demonstrate here, using transfection of receptors and G proteins in COS-7 cells, that G alpha 12 selectively couples the thrombin receptor to AP-1-mediated gene expression. This does not appear to result from increased mitogen-activated protein kinase activity but may reflect activation of a tyrosine kinase pathway. We suggest that preferential coupling of the thrombin receptor to G12 accounts for the selective ability of thrombin to stimulate Ras, mitogen-activated protein kinase, gene expression, and mitogenesis in 1321N1 cells.
Full text
PDF



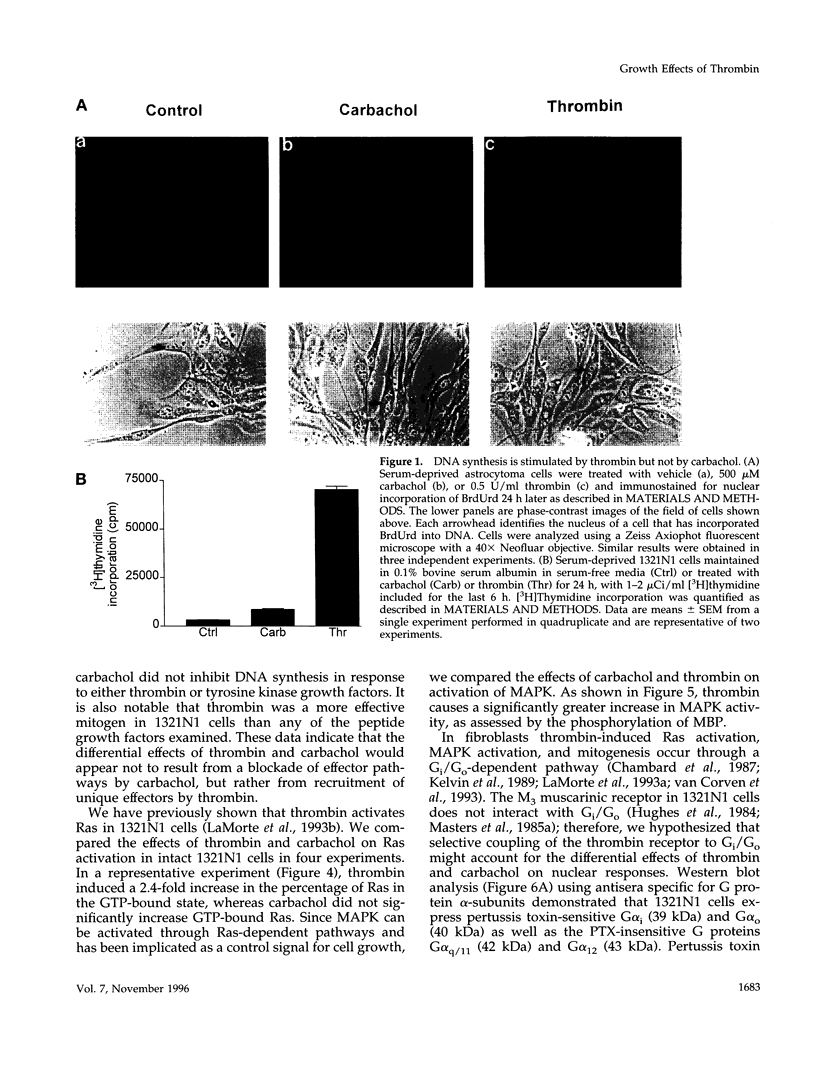



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aragay A. M., Collins L. R., Post G. R., Watson A. J., Feramisco J. R., Brown J. H., Simon M. I. G12 requirement for thrombin-stimulated gene expression and DNA synthesis in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 25;270(34):20073–20077. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.20073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Acetylcholine analogue stimulates DNA synthesis in brain-derived cells via specific muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):146–150. doi: 10.1038/340146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga H. S., Walker R. K., Winberry L. K., Rittenhouse S. E. Platelet adenylate cyclase and phospholipase C are affected differentially by ADP-ribosylation. Effects on thrombin-mediated responses. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):297–300. doi: 10.1042/bj2520297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Yun J., Wess J. Mapping of single amino acid residues required for selective activation of Gq/11 by the m3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17741–17748. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.17741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl A. M., Johnson N. L., Dhanasekaran N., Johnson G. L. G alpha 12 and G alpha 13 stimulate Rho-dependent stress fiber formation and focal adhesion assembly. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):24631–24634. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.24631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Pronk G. J., van Weeren P. C., Chardin P., Bos J. L. cAMP antagonizes p21ras-directed activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 and phosphorylation of mSos nucleotide exchange factor. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4211–4220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh K. P., Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D., Bradshaw R. A. Reciprocal modulation of astrocyte stellation by thrombin and protease nexin-1. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1735–1743. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Paris S., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. Two growth factor signalling pathways in fibroblasts distinguished by pertussis toxin. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):800–803. doi: 10.1038/326800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. M., Fleming T. P., McGovern E. S., Chedid M., Miki T., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of a transforming gene encoding the wild-type G alpha 12 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):762–768. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. R., Minden A., Karin M., Brown J. H. Galpha12 stimulates c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase through the small G proteins Ras and Rac. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 19;271(29):17349–17353. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.29.17349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., McCormick F. Inhibition by cAMP of Ras-dependent activation of Raf. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1069–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7694367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespo P., Xu N., Simonds W. F., Gutkind J. S. Ras-dependent activation of MAP kinase pathway mediated by G-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):418–420. doi: 10.1038/369418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhanasekaran N., Prasad M. V., Wadsworth S. J., Dermott J. M., van Rossum G. Protein kinase C-dependent and -independent activation of Na+/H+ exchanger by G alpha 12 class of G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11802–11806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure M., Voyno-Yasenetskaya T. A., Bourne H. R. cAMP and beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins stimulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in COS-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):7851–7854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Turnell A. S., Grabham P. W. Cellular consequences of thrombin-receptor activation. Biochem J. 1996 Jan 15;313(Pt 2):353–368. doi: 10.1042/bj3130353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandt R., Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Evidence for two GTPases activated by thrombin in membranes of human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2370669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guizzetti M., Costa P., Peters J., Costa L. G. Acetylcholine as a mitogen: muscarinic receptor-mediated proliferation of rat astrocytes and human astrocytoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996 Feb 22;297(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00746-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Gallego C., Lowndes J. M., Pleiman C. M., Sable C., Eisfelder B. J., Johnson G. L. Analysis of the fibroblast transformation potential of GTPase-deficient gip2 oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermouet S., Merendino J. J., Jr, Gutkind J. S., Spiegel A. M. Activating and inactivating mutations of the alpha subunit of Gi2 protein have opposite effects on proliferation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10455–10459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooley R., Yu C. Y., Symons M., Barber D. L. G alpha 13 stimulates Na+-H+ exchange through distinct Cdc42-dependent and RhoA-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 15;271(11):6152–6158. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.11.6152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordijk P. L., Verlaan I., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced by lysophosphatidic acid in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Evidence that phosphorylation of map kinase is mediated by the Gi-p21ras pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Marshall C. J. Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase activation via a G-protein-coupled pathway requiring p21ras and p74raf-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20717–20720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Pertussis toxin differentiates between two mechanisms of attenuation of cyclic AMP accumulation by muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. H., Nelken N. A., Coughlin S. R. Thrombin-induced events in non-platelet cells are mediated by the unique proteolytic mechanism established for the cloned platelet thrombin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):827–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Wong Y. H., Vu T. K., Coughlin S. R. The cloned platelet thrombin receptor couples to at least two distinct effectors to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and inhibit adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20831–20834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Gerszten R., Zheng Y. W., Welsh J. B., Turck C. W., Coughlin S. R. Determinants of thrombin receptor cleavage. Receptor domains involved, specificity, and role of the P3 aspartate. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16435–16440. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Satoh T., Kaziro Y., Itoh H. G protein beta gamma subunit activates Ras, Raf, and MAP kinase in HEK 293 cells. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 10;368(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00643-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Blair L. A., Marshall J., Goedert M., Hanley M. R. The mas oncogene encodes an angiotensin receptor. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):437–440. doi: 10.1038/335437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. G., McDonough P. M., Brown J. H. Thrombin and trypsin act at the same site to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium mobilization. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):142–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan C., Seuwen K., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Coordinate, biphasic activation of p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase and S6 kinase by growth factors in hamster fibroblasts. Evidence for thrombin-induced signals different from phosphoinositide turnover and adenylylcyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13369–13375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelvin D. J., Simard G., Sue-A-Quan A., Connolly J. A. Growth factors, signaling pathways, and the regulation of proliferation and differentiation in BC3H1 muscle cells. II. Two signaling pathways distinguished by pertussis toxin and a potential role for the ras oncogene. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):169–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Hawes B. E., Allen L. F., Lefkowitz R. J. Direct evidence that Gi-coupled receptor stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase is mediated by G beta gamma activation of p21ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12706–12710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Hawes B. E., Inglese J., Luttrell L. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Cellular expression of the carboxyl terminus of a G protein-coupled receptor kinase attenuates G beta gamma-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6193–6197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Pouyssegur J., Weber M. J. p42/mitogen-activated protein kinase as a converging target for different growth factor signaling pathways: use of pertussis toxin as a discrimination factor. Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):675–684. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMorte V. J., Harootunian A. T., Spiegel A. M., Tsien R. Y., Feramisco J. R. Mediation of growth factor induced DNA synthesis and calcium mobilization by Gq and Gi2. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):91–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMorte V. J., Kennedy E. D., Collins L. R., Goldstein D., Harootunian A. T., Brown J. H., Feramisco J. R. A requirement for Ras protein function in thrombin-stimulated mitogenesis in astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19411–19415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letterio J. J., Coughlin S. R., Williams L. T. Pertussis toxin-sensitive pathway in the stimulation of c-myc expression and DNA synthesis by bombesin. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1117–1119. doi: 10.1126/science.3465038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malarkey K., Belham C. M., Paul A., Graham A., McLees A., Scott P. H., Plevin R. The regulation of tyrosine kinase signalling pathways by growth factor and G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem J. 1995 Jul 15;309(Pt 2):361–375. doi: 10.1042/bj3090361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Harden T. K., Brown J. H. Relationships between phosphoinositide and calcium responses to muscarinic agonists in astrocytoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Martin M. W., Harden T. K., Brown J. H. Pertussis toxin does not inhibit muscarinic-receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis or calcium mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):933–937. doi: 10.1042/bj2270933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Quinn M. T., Brown J. H. Agonist-induced desensitization of muscarinic receptor-mediated calcium efflux without concomitant desensitization of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;27(3):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough P. M., Eubanks J. H., Brown J. H. Desensitization and recovery of muscarinic and histaminergic Ca2+ mobilization in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):135–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2490135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Pouysségur J. cAMP-mediated growth inhibition in fibroblasts is not mediated via mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (ERK) inhibition. cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces a temporal shift in growth factor-stimulated MAP kinases. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 7;271(23):13476–13483. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.23.13476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto M., Kennedy E., Goldstein D., Brown J. H. Rapid heterologous desensitization of muscarinic and thrombin receptor-mediated phospholipase D activation. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):406–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Laugwitz K. L., Spicher K., Schultz G. G proteins of the G12 family are activated via thromboxane A2 and thrombin receptors in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace A. M., Wong Y. H., Bourne H. R. A mutant alpha subunit of Gi2 induces neoplastic transformation of Rat-1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7031–7035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post G. R., Brown J. H. G protein-coupled receptors and signaling pathways regulating growth responses. FASEB J. 1996 May;10(7):741–749. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.10.7.8635691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad M. V., Dermott J. M., Heasley L. E., Johnson G. L., Dhanasekaran N. Activation of Jun kinase/stress-activated protein kinase by GTPase-deficient mutants of G alpha 12 and G alpha 13. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 4;270(31):18655–18659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M., Winitz S., Johnson G. L. Acetylcholine muscarinic m1 receptor regulation of cyclic AMP synthesis controls growth factor stimulation of Raf activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2343–2351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Kahan C., Hartmann T., Pouyssegur J. Strong and persistent activation of inositol lipid breakdown induces early mitogenic events but not Go to S phase progression in hamster fibroblasts. Comparison of thrombin and carbachol action in cells expressing M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22292–22299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S., Herman W. H. Protein kinase C and protein tyrosine kinase activity contribute to mitogenic signaling by endothelin-1. Cross-talk between G protein-coupled receptors and pp60c-src. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9347–9357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M. P., Simon M. I. G alpha 12 and G alpha 13 subunits define a fourth class of G protein alpha subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5582–5586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touhara K., Hawes B. E., van Biesen T., Lefkowitz R. J. G protein beta gamma subunits stimulate phosphorylation of Shc adapter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9284–9287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touhara K., Inglese J., Pitcher J. A., Shaw G., Lefkowitz R. J. Binding of G protein beta gamma-subunits to pleckstrin homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10217–10220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejo J., Chambard J. C., Karin M., Brown J. H. Biphasic increase in c-jun mRNA is required for induction of AP-1-mediated gene transcription: differential effects of muscarinic and thrombin receptor activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4742–4750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trilivas I., Brown J. H. Increases in intracellular Ca2+ regulate the binding of [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate to intact 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3102–3107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trilivas I., McDonough P. M., Brown J. H. Dissociation of protein kinase C redistribution from the phosphorylation of its substrates. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8431–8438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Chambard J. C., Paris S., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. alpha-Thrombin-induced early mitogenic signalling events and G0 to S-phase transition of fibroblasts require continual external stimulation. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2927–2932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara Prasad M. V., Shore S. K., Dhanasekaran N. Activated mutant of G alpha 13 induces Egr-1, c-fos, and transformation in NIH 3T3 cells. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2425–2429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyno-Yasenetskaya T. A., Pace A. M., Bourne H. R. Mutant alpha subunits of G12 and G13 proteins induce neoplastic transformation of Rat-1 fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2559–2565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyno-Yasenetskaya T., Conklin B. R., Gilbert R. L., Hooley R., Bourne H. R., Barber D. L. G alpha 13 stimulates Na-H exchange. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):4721–4724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall S. J., Yasuda R. P., Li M., Wolfe B. B. Development of an antiserum against m3 muscarinic receptors: distribution of m3 receptors in rat tissues and clonal cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):783–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. H., Nuccitelli R. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents thrombin-induced mitogenesis, but not intracellular free calcium release, in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5608–5613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winitz S., Russell M., Qian N. X., Gardner A., Dwyer L., Johnson G. L. Involvement of Ras and Raf in the Gi-coupled acetylcholine muscarinic m2 receptor activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19196–19199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Dent P., Jelinek T., Wolfman A., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Inhibition of the EGF-activated MAP kinase signaling pathway by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1065–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.7694366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu N., Bradley L., Ambdukar I., Gutkind J. S. A mutant alpha subunit of G12 potentiates the eicosanoid pathway and is highly oncogenic in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6741–6745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Biesen T., Hawes B. E., Luttrell D. K., Krueger K. M., Touhara K., Porfiri E., Sakaue M., Luttrell L. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Receptor-tyrosine-kinase- and G beta gamma-mediated MAP kinase activation by a common signalling pathway. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):781–784. doi: 10.1038/376781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Hordijk P. L., Medema R. H., Bos J. L., Moolenaar W. H. Pertussis toxin-sensitive activation of p21ras by G protein-coupled receptor agonists in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1257–1261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]