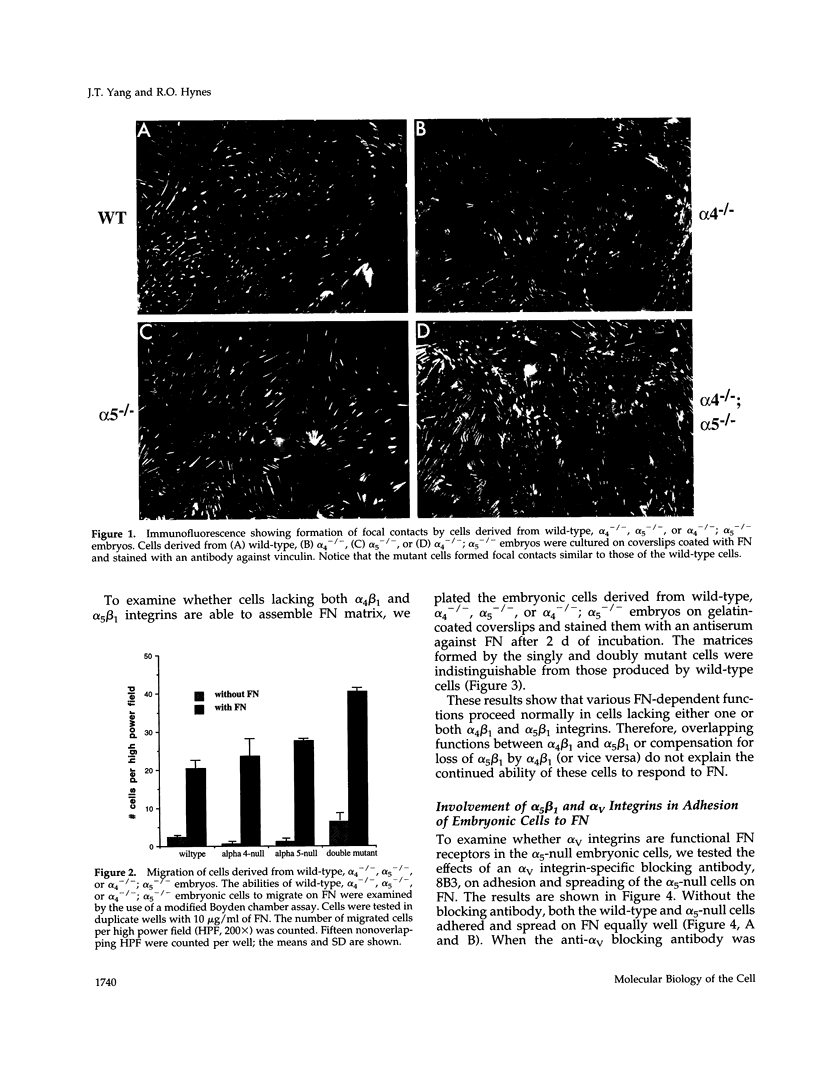
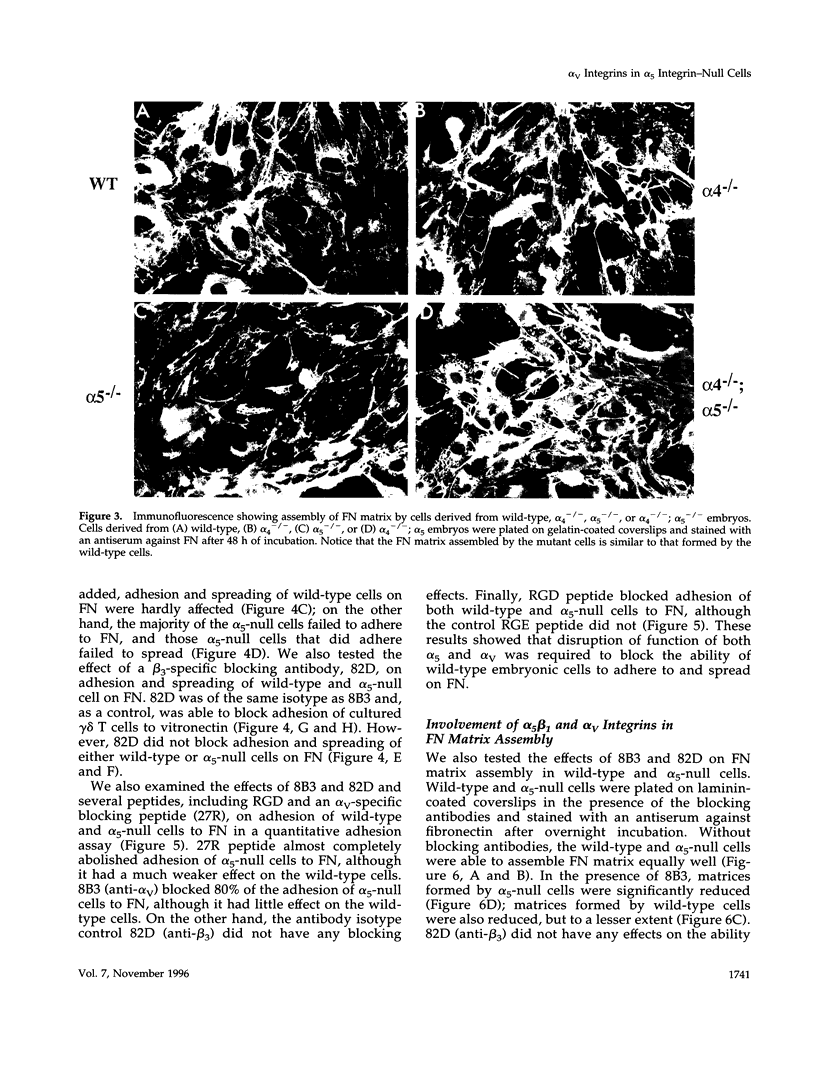
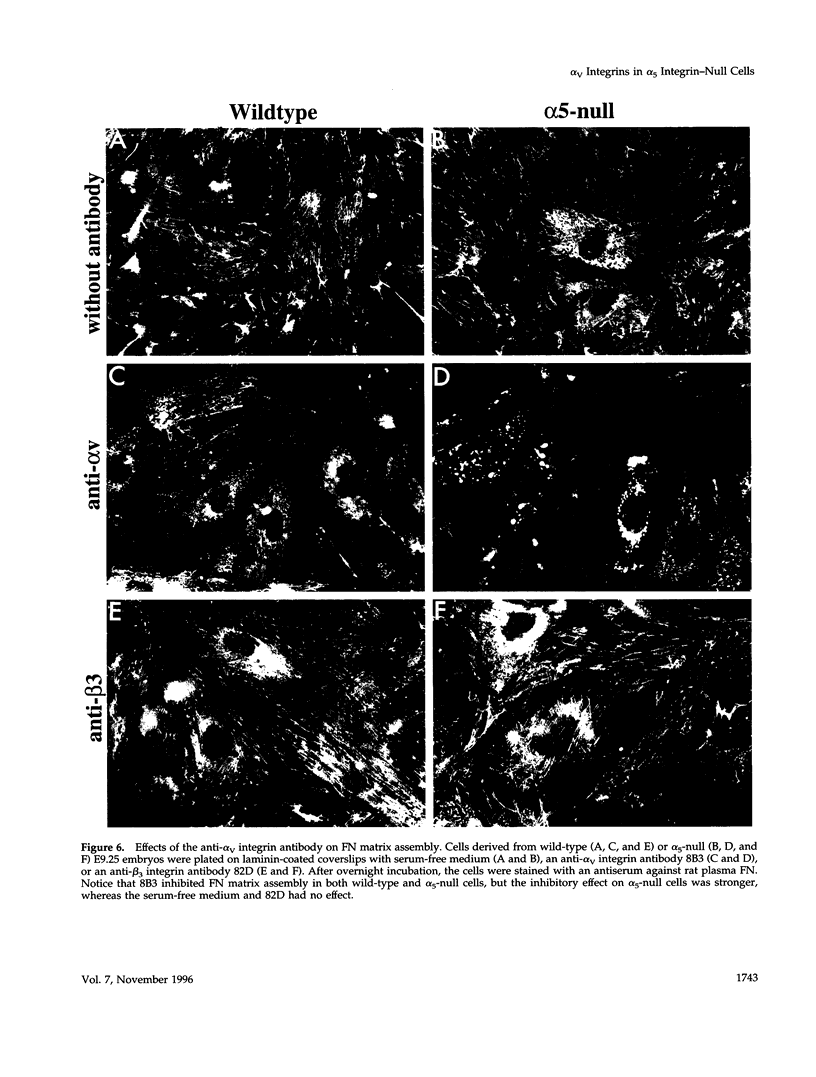
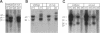Abstract
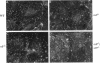
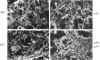
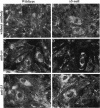
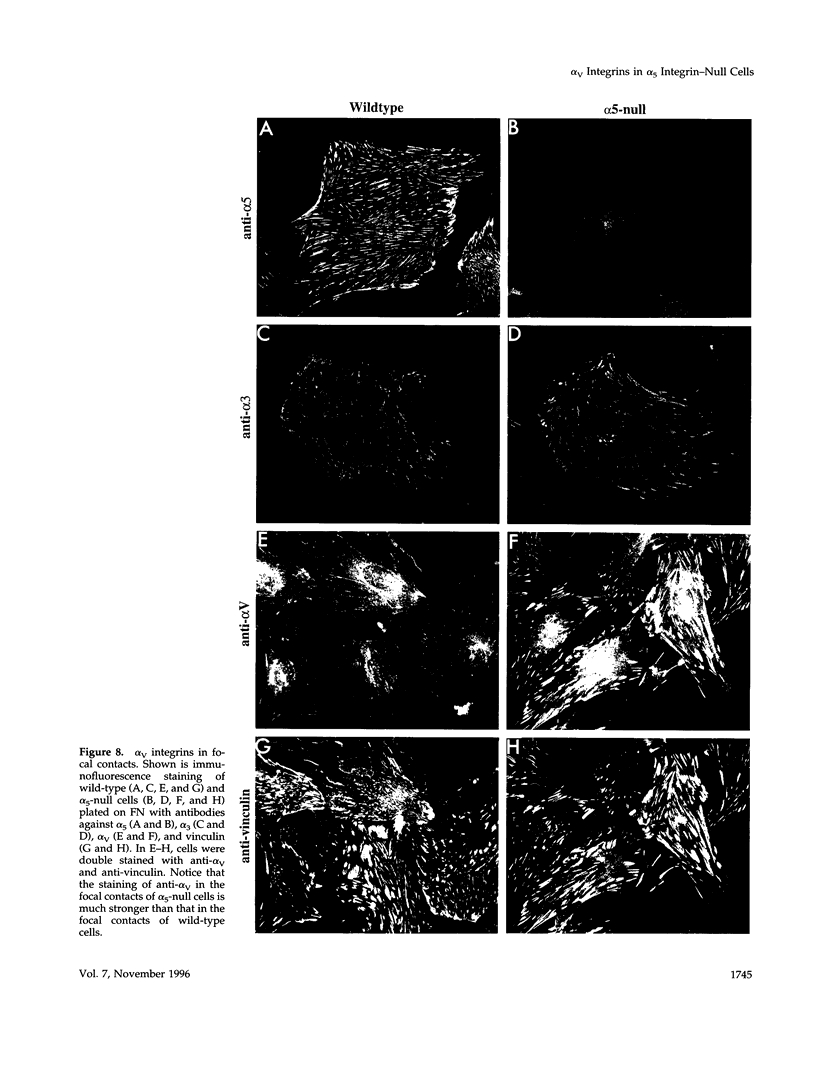
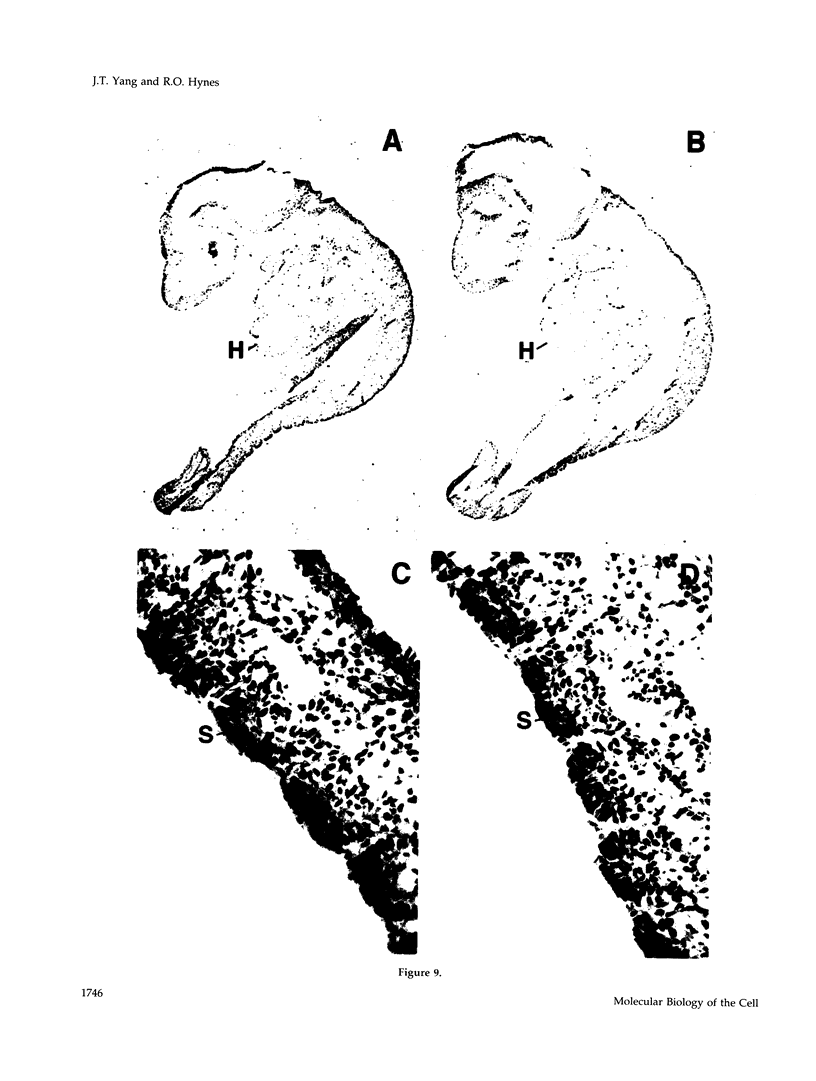
alpha 5 beta 1 integrin mediates cell adhesion to extracellular matrix by interacting with fibronectin (FN). Mouse lines carrying null mutations in genes encoding either the alpha 5 integrin subunit or FN have been generated previously. Both mutations are embryonic lethal with overlapping defects, but the defects of alpha 5-null embryos are less severe. Primary embryonic cells lacking alpha 5 beta 1 are able to adhere to FN, form focal contacts, migrate on FN, and assemble FN matrix. These results suggest the involvement of (an)other FN receptors(s). In this study, we examined functions of alpha 4 beta 1 and alpha V integrins in embryonic cells lacking alpha 5 beta 1. Our analysis of cells lacking both alpha 4 beta 1 and alpha 5 beta 1 showed that alpha 4 beta 1 is also not required for these FN-dependent functions. Using alpha V-specific blocking reagents, we showed that alpha V integrins are required for alpha 5-null cells, but not wild-type cells, to adhere and spread on FN. Our data also showed that, although the expression levels of alpha V integrins on the wild-type and alpha 5-null cells are similar, there is an increase in recruitment of alpha V integrins into focal contacts in alpha 5-null cells plated on FN, indicating that alpha V integrins can compensate functionally for the loss of alpha 5 beta 1 in focal contacts of alpha 5-null cells. Finally, our data suggested possible roles for alpha V integrins in replacing the role of alpha 5 beta 1 in FN matrix assembly in vitro and in FN-dependent embryonic functions in vivo.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Watt F. M. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1183–1198. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrez M., Chen A., Cone R. I., Pytela R., Sheppard D. The alpha v beta 6 integrin promotes proliferation of colon carcinoma cells through a unique region of the beta 6 cytoplasmic domain. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):547–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Brugge J. S. Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):233–239. doi: 10.1126/science.7716514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio C. M., Shah S., Hynes R. O. alpha 3A beta 1 integrin localizes to focal contacts in response to diverse extracellular matrix proteins. J Cell Sci. 1995 Jun;108(Pt 6):2321–2336. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.6.2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George E. L., Georges-Labouesse E. N., Patel-King R. S., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O. Defects in mesoderm, neural tube and vascular development in mouse embryos lacking fibronectin. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1079–1091. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Lander A. D. Contact and adhesive specificities in the associations, migrations, and targeting of cells and axons. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90472-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Marcantonio E. E., Stepp M. A., Urry L. A., Yee G. H. Integrin heterodimer and receptor complexity in avian and mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):409–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Donovan M. J., Goldstein S. L., Rennke H., Shepherd K., Jones R. C., Jaenisch R. Alpha 3 beta 1 integrin has a crucial role in kidney and lung organogenesis. Development. 1996 Nov;122(11):3537–3547. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.11.3537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffenburger D. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):359–369. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. F., Rutherford D. C., McCartney A. C., Mitjans F., Goodman S. L., Hart I. R. Alpha v beta 1 is a receptor for vitronectin and fibrinogen, and acts with alpha 5 beta 1 to mediate spreading on fibronectin. J Cell Sci. 1995 Mar;108(Pt 3):1227–1238. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.3.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mautner V., Hynes R. O. Surface distribution of LETS protein in relation to the cytoskeleton of normal and transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):743–768. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith J. E., Jr, Fazeli B., Schwartz M. A. The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):953–961. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira P., Gerber D., Huang S. Y., Tonegawa S. Ontogenic development and tissue distribution of V gamma 1-expressing gamma/delta T lymphocytes in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):1921–1930. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy H., Hemler M. E. Cloning, primary structure and properties of a novel human integrin beta subunit. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1561–1568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08275.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., O'Brien V., Kornberg L., Juliano R. Signal transduction by cell adhesion receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jul 28;1242(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(95)00005-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg C., Postigo A. A., Sikorski E. E., Butcher E. C., Pytela R., Erle D. J. Role of integrin alpha 4 beta 7/alpha 4 beta P in lymphocyte adherence to fibronectin and VCAM-1 and in homotypic cell clustering. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Schaller M. D., Ginsberg M. H. Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:549–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennerberg K., Lohikangas L., Gullberg D., Pfaff M., Johansson S., Fässler R. Beta 1 integrin-dependent and -independent polymerization of fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;132(1-2):227–238. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Keivens V. M., O'Toole T. E., McDonald J. A., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin activation and cytoskeletal interaction are essential for the assembly of a fibronectin matrix. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90184-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O. Cell adhesion events mediated by alpha 4 integrins are essential in placental and cardiac development. Development. 1995 Feb;121(2):549–560. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.2.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O. Embryonic mesodermal defects in alpha 5 integrin-deficient mice. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1093–1105. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Morla A. O., Vuori K., Bauer J. S., Juliano R. L., Ruoslahti E. The alpha v beta 1 integrin functions as a fibronectin receptor but does not support fibronectin matrix assembly and cell migration on fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):235–242. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]