Abstract
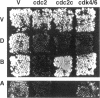
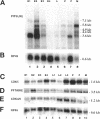
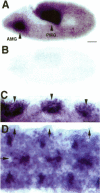
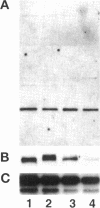
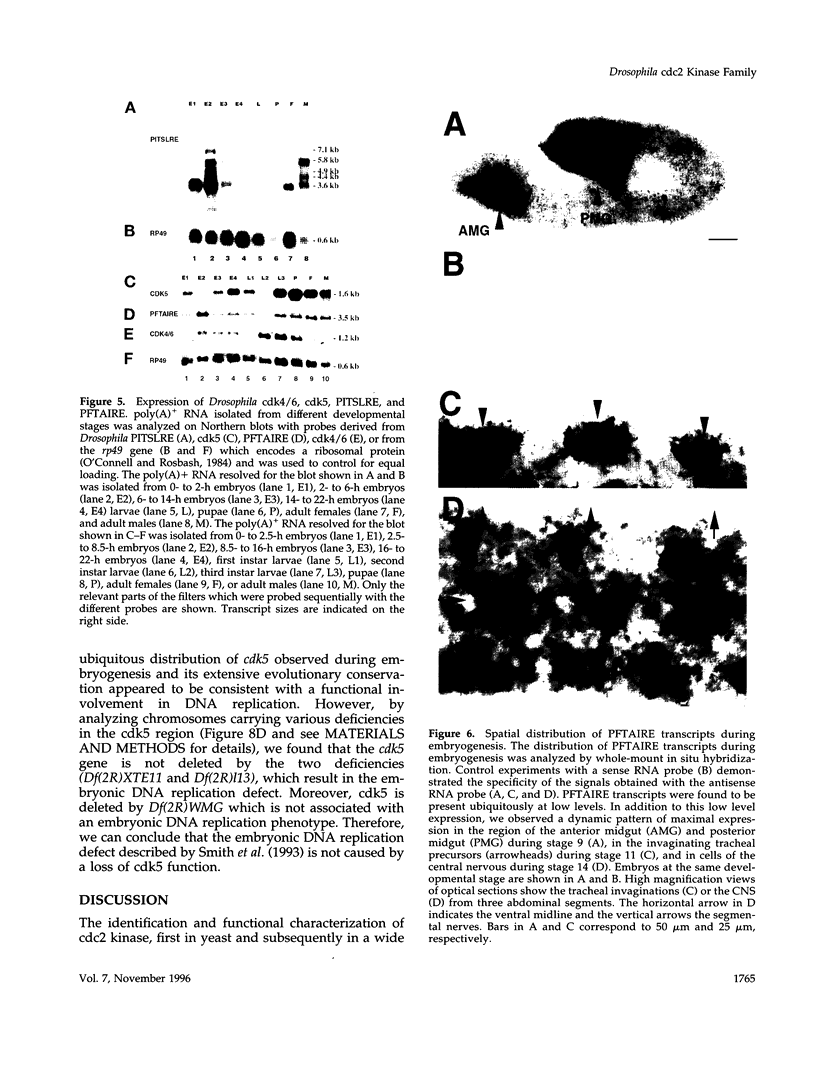
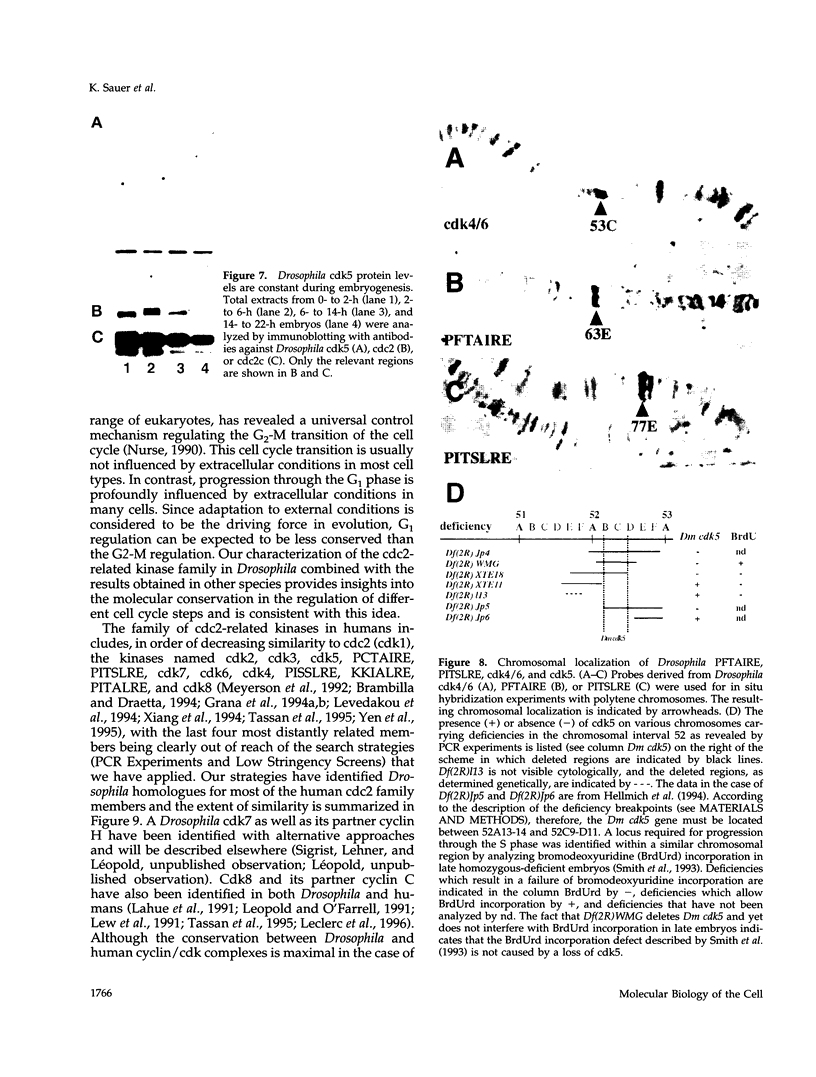
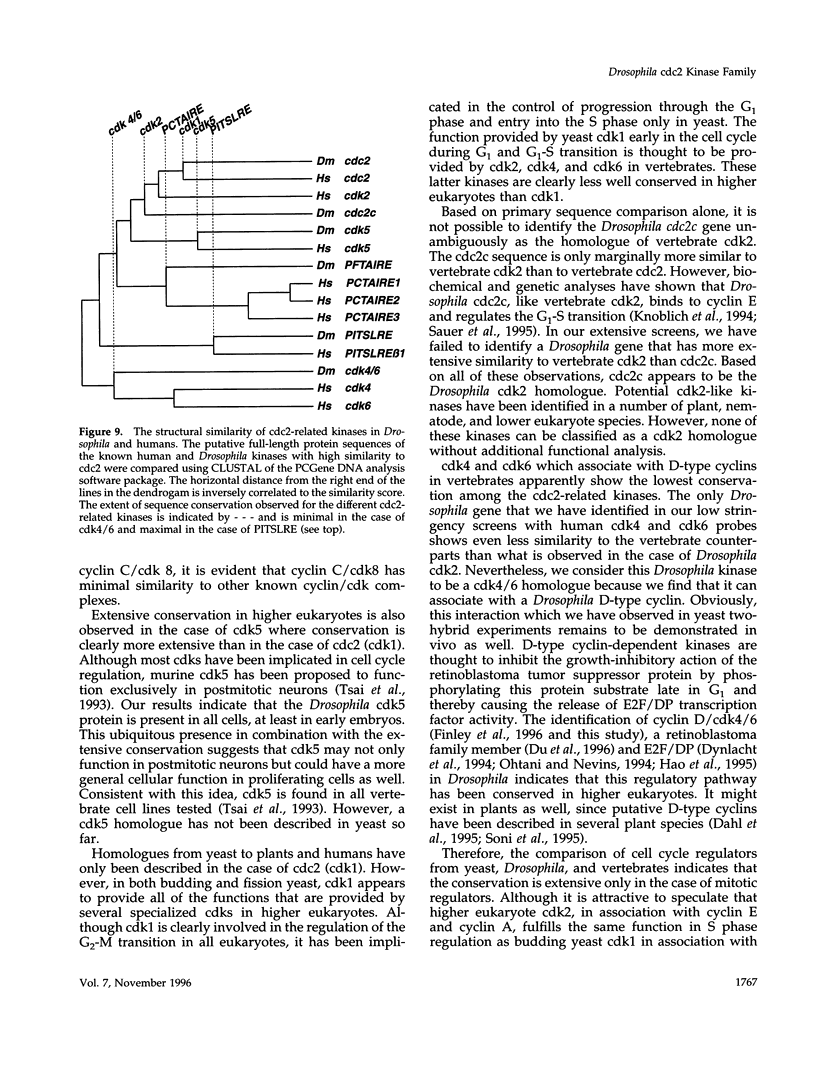
In addition to the previously identified Drosophila cdc2 and cdc2c genes, we have identified four additional cdc2-related genes with low stringency and polymerase chain reaction approaches. Sequence comparisons suggest that the four putative kinases represent the Drosophila homologues of vertebrate cdk4/6, cdk5, PCTAIRE, and PITSLRE kinases. Although the similarity between human and Drosophila homologues is extensive in the case of cdk5, PCTAIRE, and PITSLRE kinases (78%, 58%, and 65% identity in the kinase domain), only limited conservation is observed for Drosophila cdk4/6 (47% identity). However, like vertebrate cdk4 and cdk6, Drosophila cdk4/6 binds also to a D-type cyclin according to the results of two-hybrid experiments in yeast. Northern blot analysis indicated that the four Drosophila kinases are expressed throughout embryogenesis. Expression in early embryogenesis appeared to be ubiquitous according to in situ hybridization. Abundant expression already at the start of embryogenesis and long before neuron differentiation was also observed in the case of cdk5 protein, which has been described as predominantly neuron specific in mice. Sequence conservation and expression pattern, therefore, suggest that all of these kinases perform important cellular functions.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates S., Bonetta L., MacAllan D., Parry D., Holder A., Dickson C., Peters G. CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3) are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla R., Draetta G. Molecular cloning of PISSLRE, a novel putative member of the cdk family of protein serine/threonine kinases. Oncogene. 1994 Oct;9(10):3037–3041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunnell B. A., Adams D. E., Kidd V. J. Transient expression of a p58 protein kinase cDNA enhances mammalian glycosyltransferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudy M., Vässin H., Brand M., Tuma R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. daughterless, a Drosophila gene essential for both neurogenesis and sex determination, has sequence similarities to myc and the achaete-scute complex. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtot C., Fankhauser C., Simanis V., Lehner C. F. The Drosophila cdc25 homolog twine is required for meiosis. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):405–416. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl M., Meskiene I., Bögre L., Ha D. T., Swoboda I., Hubmann R., Hirt H., Heberle-Bors E. The D-type alfalfa cyclin gene cycMs4 complements G1 cyclin-deficient yeast and is induced in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Plant Cell. 1995 Nov;7(11):1847–1857. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.11.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Vidal M., Xie J. E., Dyson N. RBF, a novel RB-related gene that regulates E2F activity and interacts with cyclin E in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1996 May 15;10(10):1206–1218. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.10.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Brook A., Dembski M., Yenush L., Dyson N. DNA-binding and trans-activation properties of Drosophila E2F and DP proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6359–6363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley R. L., Jr, Brent R. Interaction mating reveals binary and ternary connections between Drosophila cell cycle regulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12980–12984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley R. L., Jr, Thomas B. J., Zipursky S. L., Brent R. Isolation of Drosophila cyclin D, a protein expressed in the morphogenetic furrow before entry into S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 2;93(7):3011–3015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.7.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervasi C., Szaro B. G. The Xenopus laevis homologue to the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk5) is expressed in embryos by gastrulation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995 Nov;33(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña X., Claudio P. P., De Luca A., Sang N., Giordano A. PISSLRE, a human novel CDC2-related protein kinase. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):2097–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña X., De Luca A., Sang N., Fu Y., Claudio P. P., Rosenblatt J., Morgan D. O., Giordano A. PITALRE, a nuclear CDC2-related protein kinase that phosphorylates the retinoblastoma protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3834–3838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao X. F., Alphey L., Bandara L. R., Lam E. W., Glover D., La Thangue N. B. Functional conservation of the cell cycle-regulating transcription factor DRTF1/E2F and its pathway of control in Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Sci. 1995 Sep;108(Pt 9):2945–2954. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.9.2945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmich M. R., Kennison J. A., Hampton L. L., Battey J. F. Cloning and characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster CDK5 homolog. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmich M. R., Pant H. C., Wada E., Battey J. F. Neuronal cdc2-like kinase: a cdc2-related protein kinase with predominantly neuronal expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10867–10871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoblich J. A., Sauer K., Jones L., Richardson H., Saint R., Lehner C. F. Cyclin E controls S phase progression and its down-regulation during Drosophila embryogenesis is required for the arrest of cell proliferation. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):107–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Ishiguro K., Omori A., Takamatsu M., Arioka M., Imahori K., Uchida T. A cdc2-related kinase PSSALRE/cdk5 is homologous with the 30 kDa subunit of tau protein kinase II, a proline-directed protein kinase associated with microtubule. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 6;335(2):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80723-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti J. M., Xiang J., Heath L. S., Campana D., Kidd V. J. PITSLRE protein kinase activity is associated with apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahue E. E., Smith A. V., Orr-Weaver T. L. A novel cyclin gene from Drosophila complements CLN function in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2166–2175. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc V., Tassan J. P., O'Farrell P. H., Nigg E. A., Léopold P. Drosophila Cdk8, a kinase partner of cyclin C that interacts with the large subunit of RNA polymerase II. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Apr;7(4):505–513. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Drosophila cdc2 homologs: a functional homolog is coexpressed with a cognate variant. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3573–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levedakou E. N., He M., Baptist E. W., Craven R. J., Cance W. G., Welcsh P. L., Simmons A., Naylor S. L., Leach R. J., Lewis T. B. Two novel human serine/threonine kinases with homologies to the cell cycle regulating Xenopus MO15, and NIMA kinases: cloning and characterization of their expression pattern. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):1977–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew J., Winkfein R. J., Paudel H. K., Wang J. H. Brain proline-directed protein kinase is a neurofilament kinase which displays high sequence homology to p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25922–25926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léopold P., O'Farrell P. H. An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90043-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Levine M. S., Hafen E., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A conserved DNA sequence in homoeotic genes of the Drosophila Antennapedia and bithorax complexes. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):428–433. doi: 10.1038/308428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Enders G. H., Wu C. L., Su L. K., Gorka C., Nelson C., Harlow E., Tsai L. H. A family of human cdc2-related protein kinases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2909–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Harlow E. Identification of G1 kinase activity for cdk6, a novel cyclin D partner. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2077–2086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani K., Nevins J. R. Functional properties of a Drosophila homolog of the E2F1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1603–1612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda T., Cleveland J. L., Downing J. R. PCTAIRE-1 and PCTAIRE-3, two members of a novel cdc2/CDC28-related protein kinase gene family. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2249–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Hunter T. Cell regulation. Innocent bystanders or chosen collaborators? Curr Biol. 1995 Nov 1;5(11):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R., Adamczewski J. P., Seroz T., Vermeulen W., Tassan J. P., Schaeffer L., Nigg E. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M. The MO15 cell cycle kinase is associated with the TFIIH transcription-DNA repair factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1093–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer K., Knoblich J. A., Richardson H., Lehner C. F. Distinct modes of cyclin E/cdc2c kinase regulation and S-phase control in mitotic and endoreduplication cycles of Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 1;9(11):1327–1339. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiekhattar R., Mermelstein F., Fisher R. P., Drapkin R., Dynlacht B., Wessling H. C., Morgan D. O., Reinberg D. Cdk-activating kinase complex is a component of human transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):283–287. doi: 10.1038/374283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
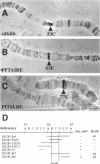
- Smith A. V., King J. A., Orr-Weaver T. L. Identification of genomic regions required for DNA replication during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genetics. 1993 Nov;135(3):817–829. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. V., Orr-Weaver T. L. The regulation of the cell cycle during Drosophila embryogenesis: the transition to polyteny. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):997–1008. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soni R., Carmichael J. P., Shah Z. H., Murray J. A. A family of cyclin D homologs from plants differentially controlled by growth regulators and containing the conserved retinoblastoma protein interaction motif. Plant Cell. 1995 Jan;7(1):85–103. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassan J. P., Jaquenoud M., Léopold P., Schultz S. J., Nigg E. A. Identification of human cyclin-dependent kinase 8, a putative protein kinase partner for cyclin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8871–8875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Takahashi T., Caviness V. S., Jr, Harlow E. Activity and expression pattern of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in the embryonic mouse nervous system. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1029–1040. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood E. M., Briot A. S., Doll K. Z., Ludwiczak R. L., Otteson D. C., Tower J., Vessey K. B., Yu K. Genetics of 51D-52A, a region containing several maternal-effect genes and two maternal-specific transcripts in Drosophila. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):639–650. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang J., Lahti J. M., Grenet J., Easton J., Kidd V. J. Molecular cloning and expression of alternatively spliced PITSLRE protein kinase isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15786–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Kenessey A., Lee S. C., Dickson D. W. The distribution and biochemical properties of a Cdc2-related kinase, KKIALRE, in normal and Alzheimer brains. J Neurochem. 1995 Dec;65(6):2577–2584. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65062577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]