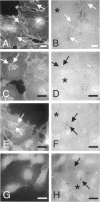
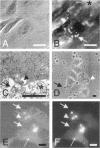
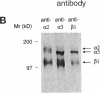
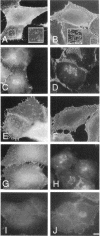
Abstract
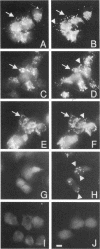
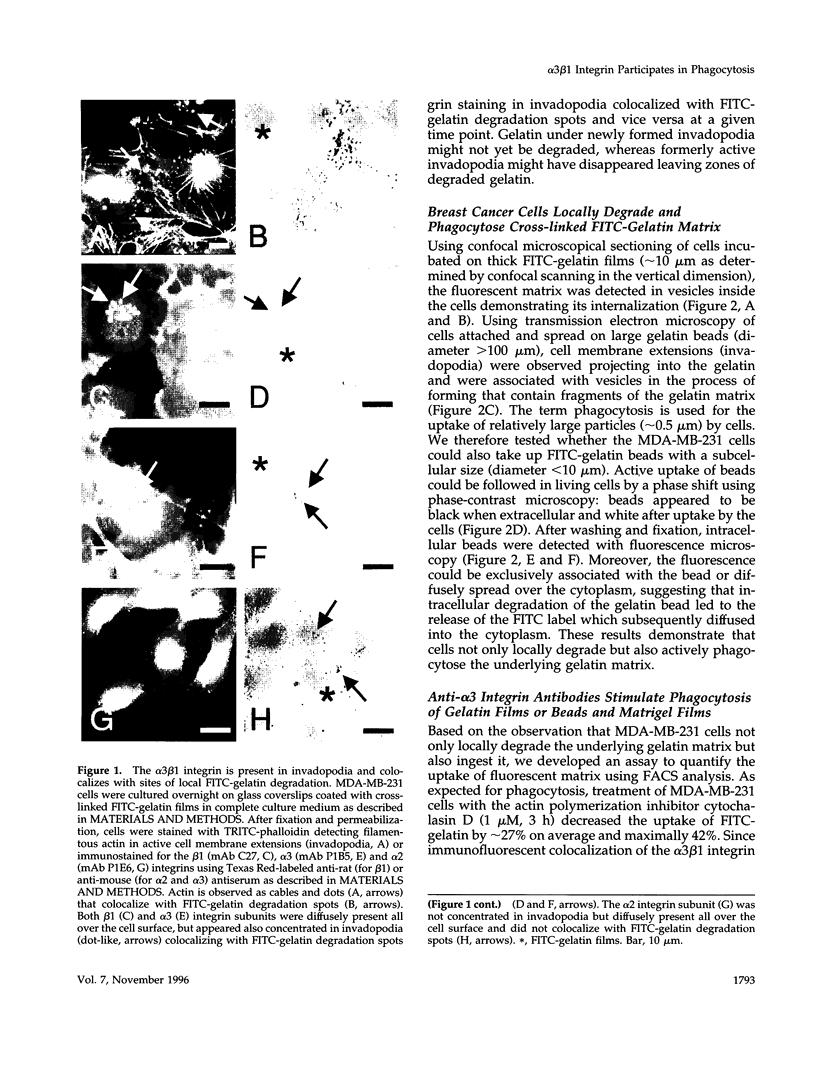
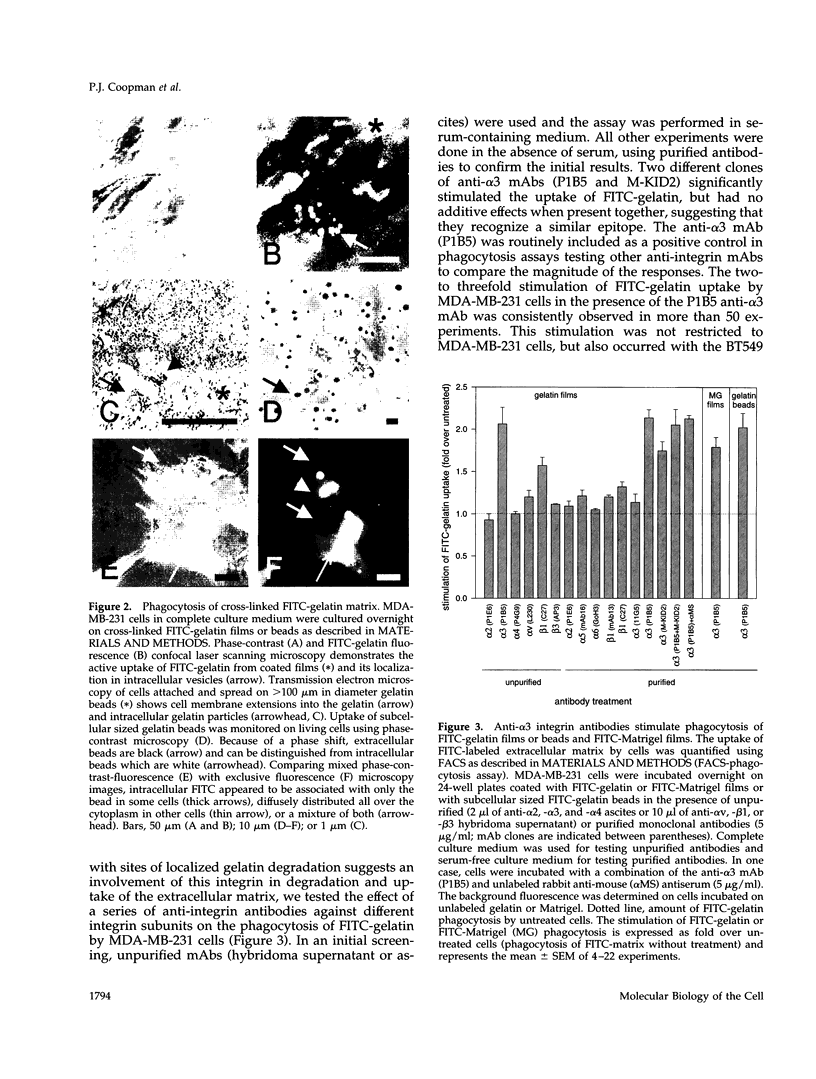
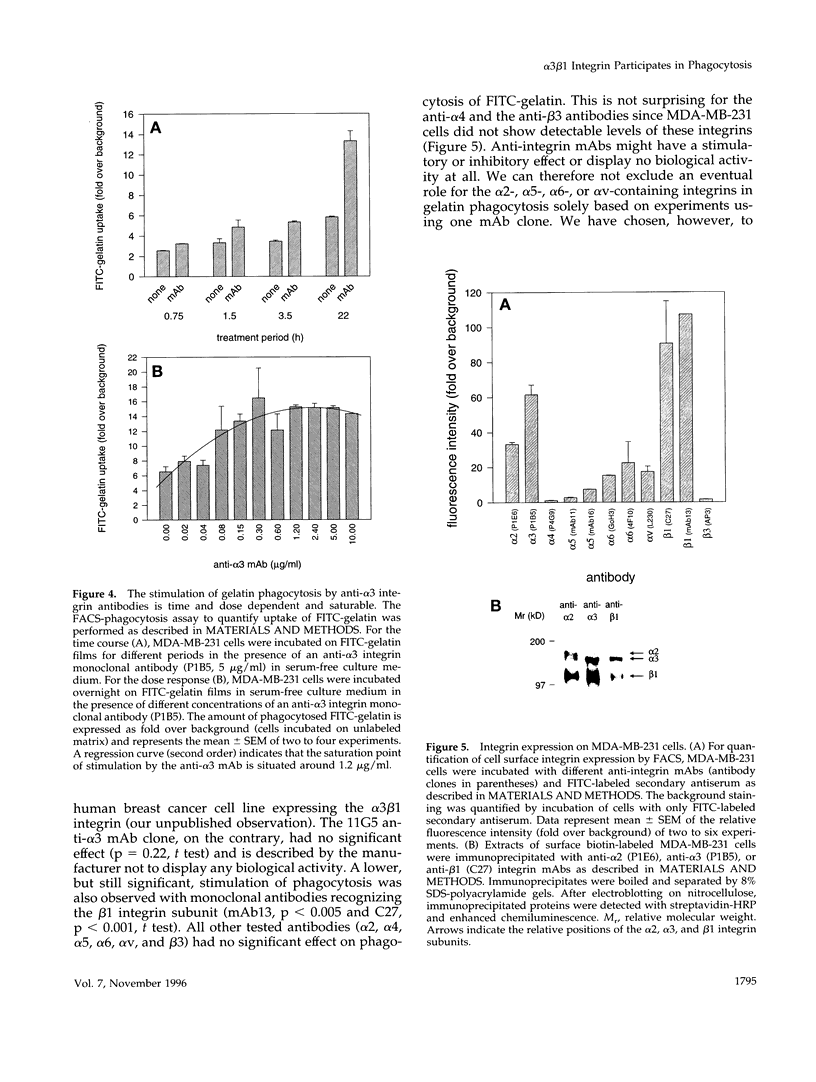
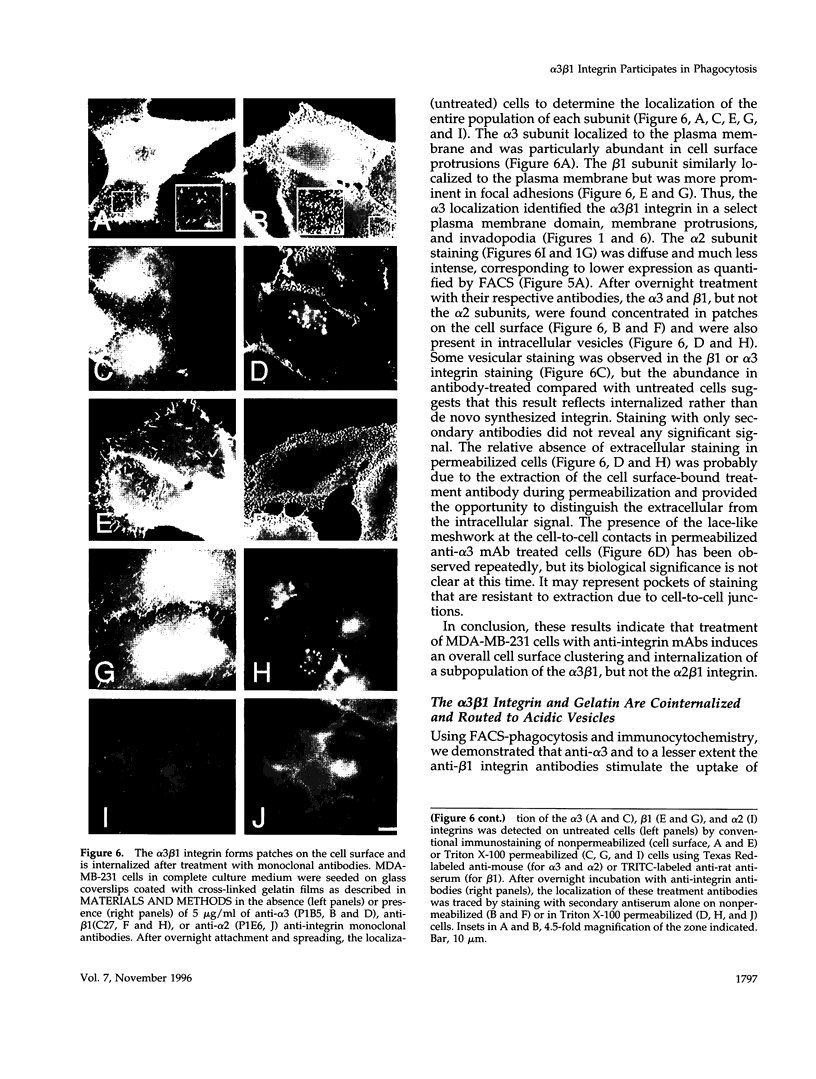
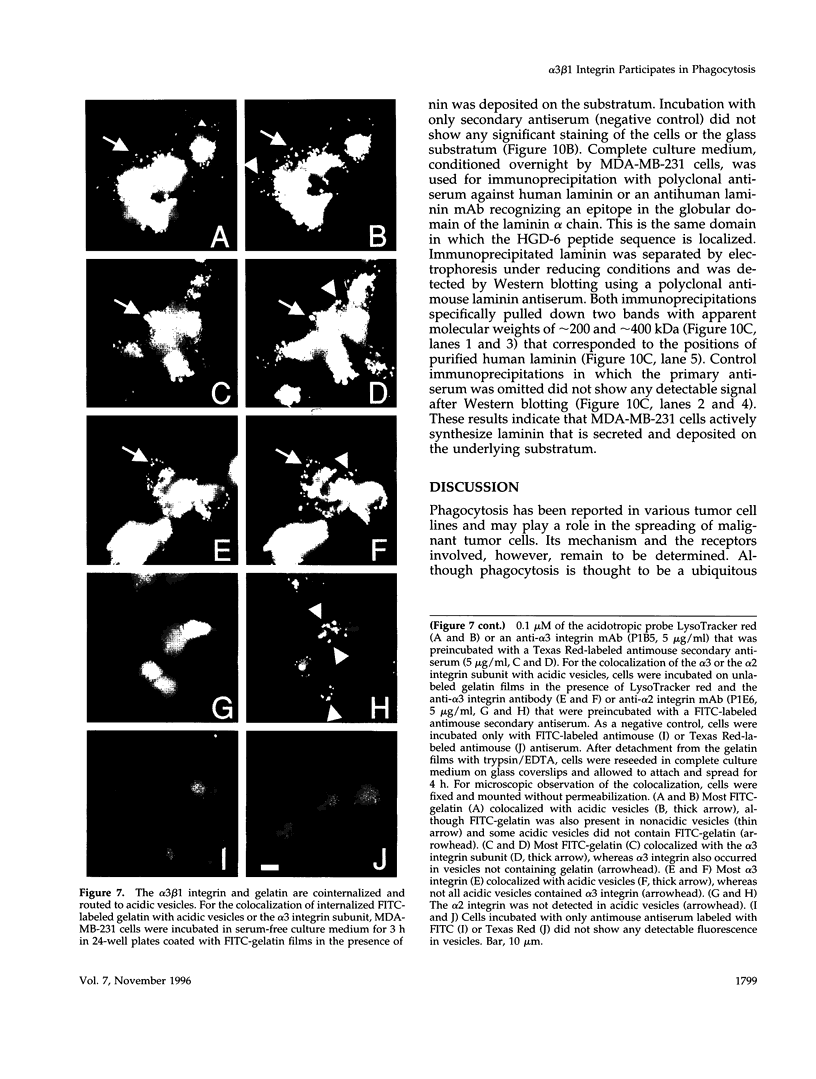
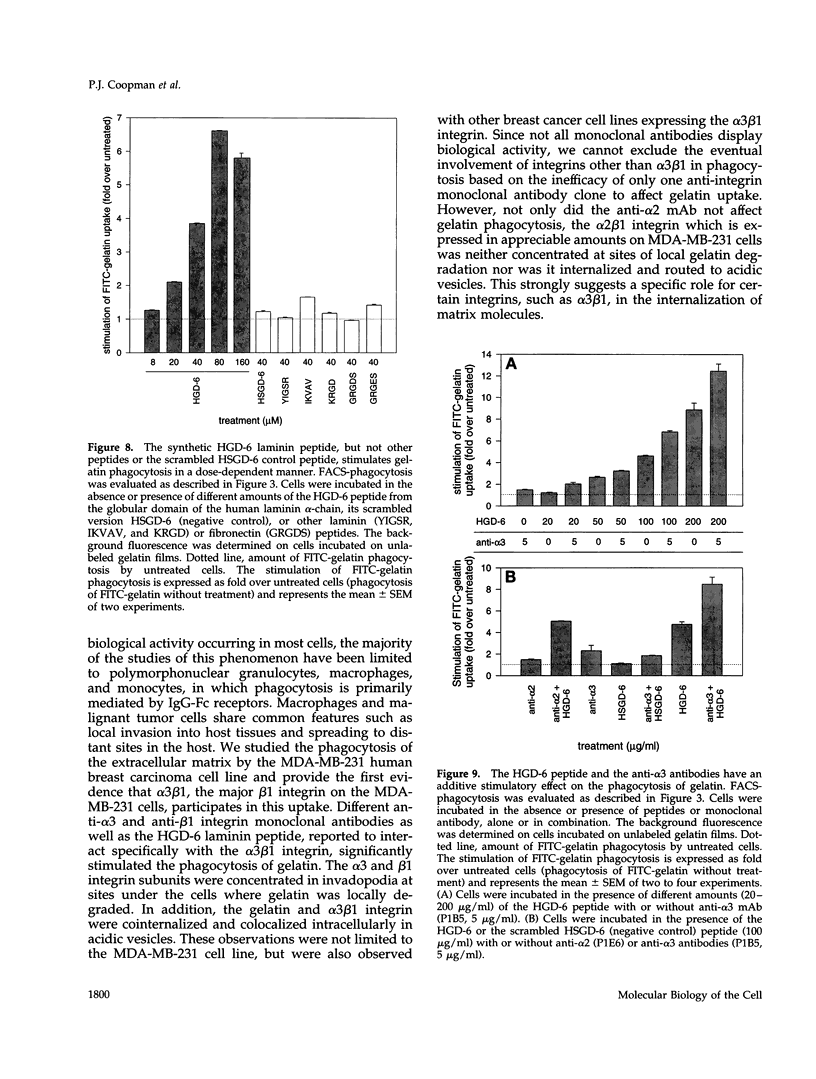
The mechanisms and receptors involved in phagocytosis by nonhematopoietic cells are not well understood. The involvement of the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin in phagocytosis of the extracellular matrix by human breast cancer cells was studied. The possible role of this integrin was suggested since alpha 3 and beta 1 but not alpha 2 subunits are concentrated at membrane sites where local degradation of fluorescently labeled gelatin occurs. Strikingly, anti-alpha 3 integrin monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) stimulate the phagocytosis of fluorescently labeled gelatin films, gelatin beads, and Matrigel films in a quantitative phagocytosis assay. Stimulation of the gelatin uptake by the anti-alpha 3 mAb is dose responsive, saturable, and time dependent. Antibodies against other integrin subunits have a lower stimulatory effect (anti-beta 1) or no significant effect (anti-alpha 2, -alpha 5, -alpha 6, and -alpha v) on gelatin phagocytosis. The synthetic HGD-6 human laminin peptide that binds specifically the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin, but not the scrambled HSGD-6 control peptide, also markedly stimulates gelatin uptake in a dose-responsive way. Furthermore, the stimulatory effects of the HGD-6 peptide and the anti-alpha 3 mAb are additive, suggesting that they might promote phagocytosis in different ways. Other laminin (YIGSR, IKVAV) and fibronectin (GRGDS) peptides have no effect on gelatin phagocytosis. Immunofluorescence shows that the alpha 3 and the beta 1, but not the alpha 2 integrin subunit, concentrate into patches on the cell surface after treatment with their respective mAbs. And, both gelatin and the alpha 3 beta 1 but not the alpha 2 beta 1 integrin are cointernalized and routed to acidic vesicles such as lysosomes. In conclusion, we demonstrate that human breast cancer cells locally degrade and phagocytose the extracellular matrix and show for the first time that the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin participates in this phagocytosis. We hypothesize that the anti-alpha 3 antibodies and the laminin peptide HGD-6 activate the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin, which results in a downstream signaling cascade stimulating phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berdichevsky F., Alford D., D'Souza B., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Branching morphogenesis of human mammary epithelial cells in collagen gels. J Cell Sci. 1994 Dec;107(Pt 12):3557–3568. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.12.3557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes R., Bjerkvig R., Laerum O. D. Phagocytic capacity of normal and malignant rat glial cells in culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Feb;78(2):279–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blystone S. D., Lindberg F. P., LaFlamme S. E., Brown E. J. Integrin beta 3 cytoplasmic tail is necessary and sufficient for regulation of alpha 5 beta 1 phagocytosis by alpha v beta 3 and integrin-associated protein. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(3):745–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack J. F., Kleinman H. K., Takahashi T., O'Shea J. J., Brown E. J. Connective tissue proteins and phagocytic cell function. Laminin enhances complement and Fc-mediated phagocytosis by cultured human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):912–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Circulating integrins: alpha 5 beta 1, alpha 6 beta 4 and Mac-1, but not alpha 3 beta 1, alpha 4 beta 1 or LFA-1. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):405–410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Goodwin J. L. Fibronectin receptors of phagocytes. Characterization of the Arg-Gly-Asp binding proteins of human monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):777–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J. Phagocytosis. Bioessays. 1995 Feb;17(2):109–117. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J. The role of extracellular matrix proteins in the control of phagocytosis. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 May;39(5):579–591. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreno M. P., Gresham H. D., Brown E. J. Isolation of leukocyte response integrin: a novel RGD-binding protein involved in regulation of phagocytic function. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Oct;69(1):43–51. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Ryan M. C., Gahr P. J. Epiligrin, a new cell adhesion ligand for integrin alpha 3 beta 1 in epithelial basement membranes. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90092-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Salomon D. R., Wadsworth S., Hong M. J., Mojcik C. F., Otto S., Shevach E. M., Coligan J. E. Alpha 3 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 1 integrins mediate laminin/merosin binding and function as costimulatory molecules for human thymocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):500–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. T. Proteolytic activity of specialized surface protrusions formed at rosette contact sites of transformed cells. J Exp Zool. 1989 Aug;251(2):167–185. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402510206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coopman P., Nuydens R., Leunissen J., De Brabander M., Bortier H., Foidart J. M., Mareel M. Laminin binding and internalization by human and murine mammary gland cell lines in vitro. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;56(2):251–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppolino M., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S., Dedhar S. Identification of a novel form of the alpha 3 integrin subunit: covalent association with transferrin receptor. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 15;306(Pt 1):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj3060129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Jewell K., Rojiani M., Gray V. The receptor for the basement membrane glycoprotein entactin is the integrin alpha 3/beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18908–18914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwel G. O., de Melker A. A., Hogervorst F., Jaspars L. H., Fles D. L., Kuikman I., Lindblom A., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Sonnenberg A. Distinct and overlapping ligand specificities of the alpha 3A beta 1 and alpha 6A beta 1 integrins: recognition of laminin isoforms. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):203–215. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Urry L. A., Hemler M. E. Receptor functions for the integrin VLA-3: fibronectin, collagen, and laminin binding are differentially influenced by Arg-Gly-Asp peptide and by divalent cations. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):169–181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaietta G., Redelmeier T. E., Jackson M. R., Tamura R. N., Quaranta V. Quantitative measurement of alpha 6 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 4 integrin internalization under cross-linking conditions: a possible role for alpha 6 cytoplasmic domains. J Cell Sci. 1994 Dec;107(Pt 12):3339–3349. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.12.3339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Dickerson K., Argraves W. S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Subunit structure of a laminin-binding integrin and localization of its binding site on laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19034–19038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Sriramarao P., Furcht L. T., Skubitz A. P. A synthetic peptide derived from the carboxy terminus of the laminin A chain represents a binding site for the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):449–459. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. Signal transduction of phagocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;5(3):93–99. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham H. D., Goodwin J. L., Allen P. M., Anderson D. C., Brown E. J. A novel member of the integrin receptor family mediates Arg-Gly-Asp-stimulated neutrophil phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1935–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Brownson N. E., Fields G. B., Skubitz A. P. Laminin peptides stimulate human neutrophil motility. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5447–5456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Varner J. A. Adhesion molecules in cancer: the role of integrins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;5(5):812–818. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90030-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T., Mueller S. C., Yeh Y., Chen W. T. Invadopodia promote proteolysis of a wide variety of extracellular matrix proteins. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Feb;158(2):299–308. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041580212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larjava H., Lyons J. G., Salo T., Mäkelä M., Koivisto L., Birkedal-Hansen H., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M., Heino J. Anti-integrin antibodies induce type IV collagenase expression in keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Oct;157(1):190–200. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Plutner H. Internalization and degradation of macrophage Fc receptors bound to polyvalent immune complexes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Synergistic roles for receptor occupancy and aggregation in integrin transmembrane function. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):883–885. doi: 10.1126/science.7846531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsky W. L., Chen W. T. Proteases of cell adhesion proteins in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Aug;4(4):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsky W. L., Kelly T., Lin C. Y., Yeh Y., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Mueller S. C., Chen W. T. Binding and localization of M(r) 72,000 matrix metalloproteinase at cell surface invadopodia. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 1;53(13):3159–3164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montcourrier P., Mangeat P. H., Valembois C., Salazar G., Sahuquet A., Duperray C., Rochefort H. Characterization of very acidic phagosomes in breast cancer cells and their association with invasion. J Cell Sci. 1994 Sep;107(Pt 9):2381–2391. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.9.2381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller S. C., Chen W. T. Cellular invasion into matrix beads: localization of beta 1 integrins and fibronectin to the invadopodia. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):213–225. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller S. C., Kelly T., Dai M. Z., Dai H. N., Chen W. T. Dynamic cytoskeleton-integrin associations induced by cell binding to immobilized fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3455–3464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller S. C., Yeh Y., Chen W. T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane proteins mediates cellular invasion by transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1309–1325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opdenakker G., Van Damme J. Cytokines and proteases in invasive processes: molecular similarities between inflammation and cancer. Cytokine. 1992 Jul;4(4):251–258. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panetti T. S., McKeown-Longo P. J. The alpha v beta 5 integrin receptor regulates receptor-mediated endocytosis of vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11492–11495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Professional and non-professional phagocytes: an introduction. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;5(3):85–87. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raub T. J., Kuentzel S. L. Kinetic and morphological evidence for endocytosis of mammalian cell integrin receptors by using an anti-fibronectin receptor beta subunit monoclonal antibody. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Oct;184(2):407–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J., Dransfield I., Hogg N., Haslett C. Vitronectin receptor-mediated phagocytosis of cells undergoing apoptosis. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):170–173. doi: 10.1038/343170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriramarao P., Steffner P., Gehlsen K. R. Biochemical evidence for a homophilic interaction of the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22036–22041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Aznavoorian S., Liotta L. A. Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:541–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington B. E., Carter W. G. Modulation of epidermal differentiation by epiligrin and integrin alpha 3 beta 1. J Cell Sci. 1995 Feb;108(Pt 2):831–838. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.2.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington B. E., Takada Y., Carter W. G. Interaction of integrins alpha 3 beta 1 and alpha 2 beta 1: potential role in keratinocyte intercellular adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):523–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Peteghem M. C., Mareel M. M., De Bruyne G. K. Phagocytic capacity of invasive malignant cells in three-dimensional culture. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1980;34(2):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02892417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. Identification of multiple cell adhesion receptors for collagen and fibronectin in human fibrosarcoma cells possessing unique alpha and common beta subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1873–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman J. B., Chen A., Hemler M. E. Investigation of the role of beta 1 integrins in cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1995 Nov;108(Pt 11):3635–3644. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.11.3635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman J. B., Pasqualini R., Takada Y., Hemler M. E. The function and distinctive regulation of the integrin VLA-3 in cell adhesion, spreading, and homotypic cell aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8651–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke M. S., Skubitz A. P. Human keratinocytes adhere to multiple distinct peptide sequences of laminin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Jul;97(1):141–146. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12479311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Chung A. E., McDonald J. A. A novel role for alpha 3 beta 1 integrins in extracellular matrix assembly. J Cell Sci. 1995 Jun;108(Pt 6):2511–2523. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.6.2511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Miyamoto S. Integrin transmembrane signaling and cytoskeletal control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;7(5):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylänne J., Huuskonen J., O'Toole T. E., Ginsberg M. H., Virtanen I., Gahmberg C. G. Mutation of the cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 3 subunit. Differential effects on cell spreading, recruitment to adhesion plaques, endocytosis, and phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9550–9557. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga I. G., Vink J., Dekker S. K., Mihm M. C., Jr, Byers H. R. Role of alpha 3 beta 1 and alpha 2 beta 1 integrins in melanoma cell migration. Melanoma Res. 1993 Dec;3(6):435–441. doi: 10.1097/00008390-199311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]