Abstract
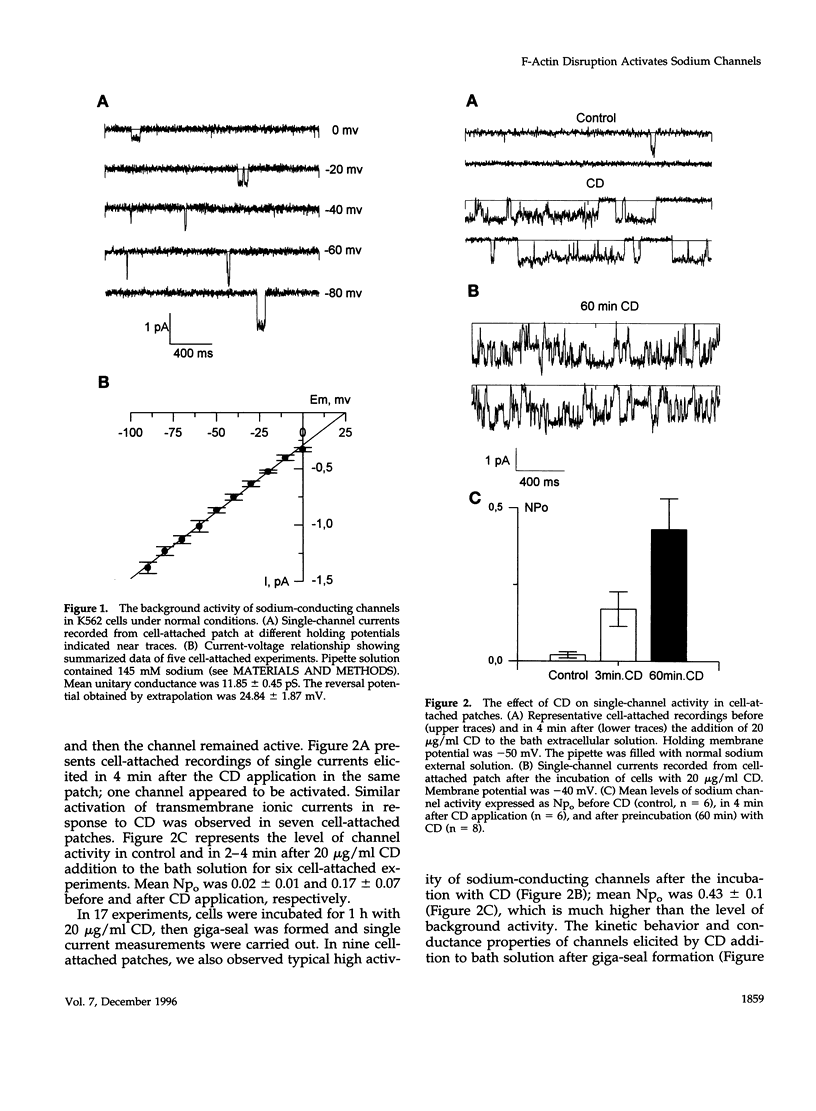
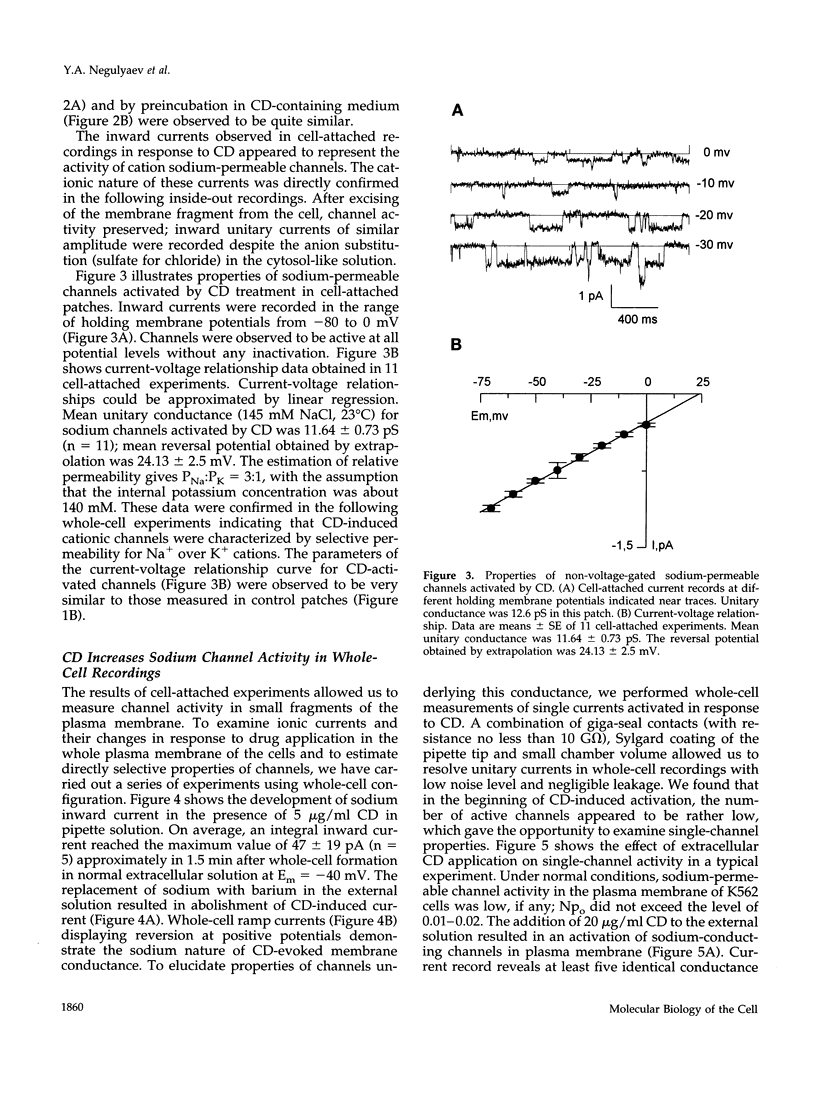
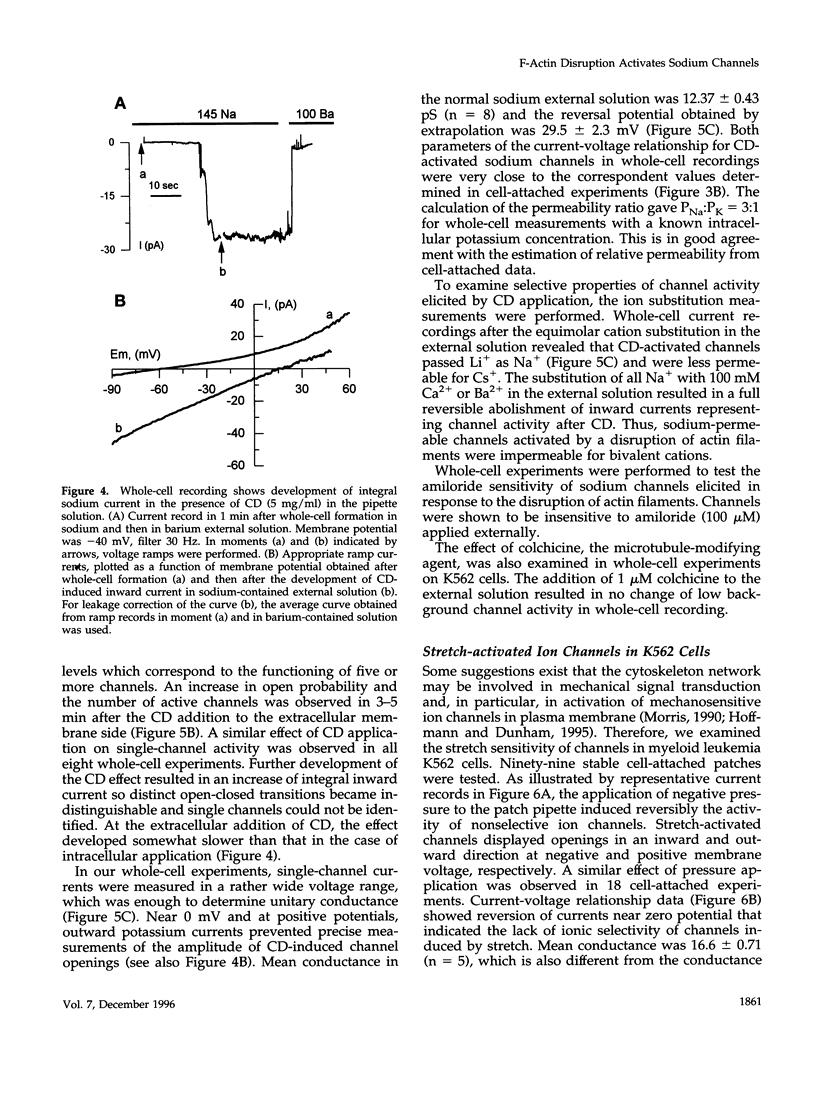
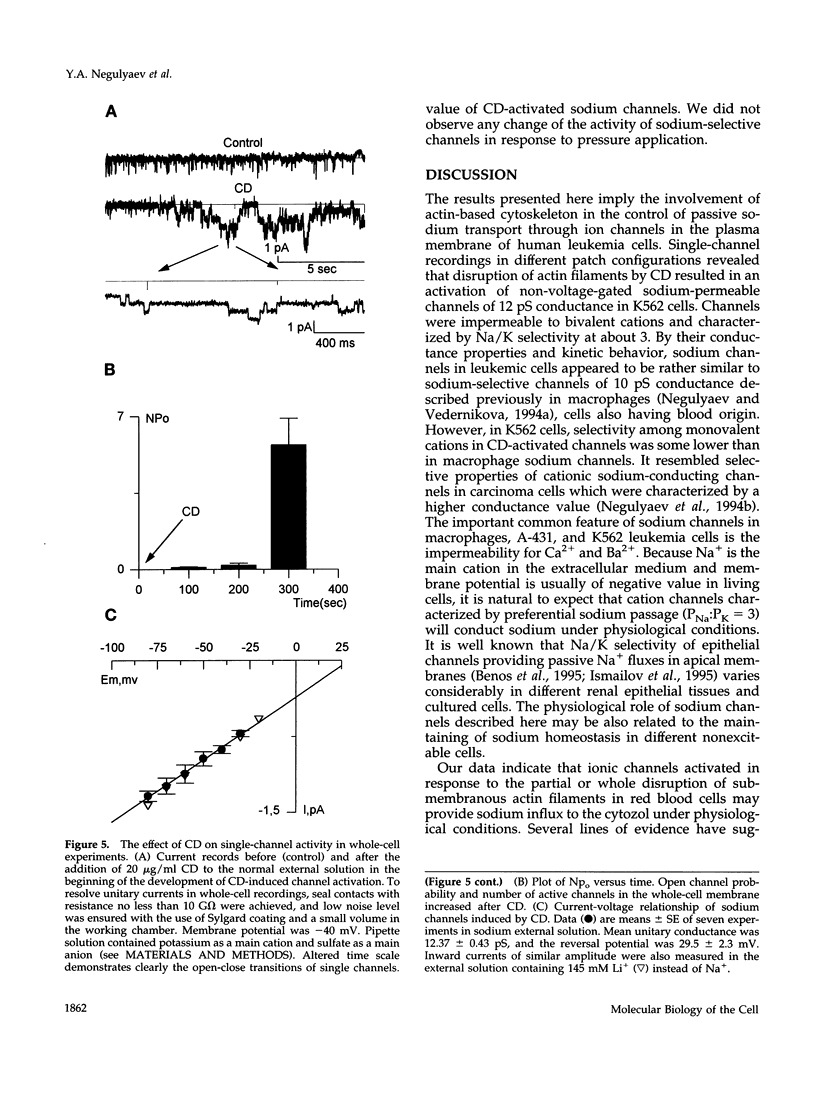
With the use of the patch clamp technique, the role of cytoskeleton in the regulation of ion channels in plasma membrane of leukemic K562 cells was examined. Single-channel measurements have indicated that disruption of actin filaments with cytochalasin D (CD) resulted in a considerable increase of the activity of non-voltage-gated sodium-permeable channels of 12 pS unitary conductance. Background activity of these channels was low; open probability (po) did not exceed 0.01-0.02. After CD, po grew at least 10-20 times. Cell-attached and whole-cell recordings showed that activation of sodium channels was elicited within 1-3 min after the addition of 10-20 micrograms/ml CD to the bath extracellular solution or in the presence of 5 micrograms/ml CD in the intracellular pipette solution. Preincubation of K562 cells with CD during 1 h also increased drastically the activity of 12 pS sodium channels. Whole-cell measurements confirmed that CD-activated channels were permeable to monovalent cations (preferentially to Na+ and Li+), but not to bivalent cations (Ca2+, Ba2+). Colchicine (1 microM), which affect microtubules, did not alter background channel activity. Our data indicate that actin filaments organization plays an important role in the regulation of sodium-permeable channels which may participate in providing passive Na+ influx in red blood cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balke C. W., Wier W. G. Modulation of L-type calcium channels by sodium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basudev H., Romano-Silva M. A., Brammer M. J., Campbell I. C. Effects of sodium on PKC translocation; relationship to neurotransmitter release. Neuroreport. 1995 Mar 27;6(5):809–812. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199503270-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Awayda M. S., Ismailov I. I., Johnson J. P. Structure and function of amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels. J Membr Biol. 1995 Jan;143(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00232519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Stow J. L., Prat A. G., Ausiello D. A. Actin filaments regulate epithelial Na+ channel activity. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):C882–C888. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.5.C882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., Carraway C. A. Signaling, mitogenesis and the cytoskeleton: where the action is. Bioessays. 1995 Feb;17(2):171–175. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devarajan P., Scaramuzzino D. A., Morrow J. S. Ankyrin binds to two distinct cytoplasmic domains of Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):2965–2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddette D. W., Frieden C. Actin polymerization. The mechanism of action of cytochalasin D. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15974–15980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Eckert B. K., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cytosolic free Na+ in individual fibroblasts and lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19458–19467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. D., Jurevicius J. A., Hume J. R. Intracellular Na+ modulates the cAMP-dependent regulation of ion channels in the heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6946–6950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. K., Dunham P. B. Membrane mechanisms and intracellular signalling in cell volume regulation. Int Rev Cytol. 1995;161:173–262. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J. Biochemical status of renal epithelial Na+ channels determines apparent channel conductance, ion selectivity, and amiloride sensitivity. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):1789–1800. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80049-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I., Almonte C., Mollard P., Garber S. S. Modulation of a volume-regulated chloride current by F-actin. J Membr Biol. 1995 Oct;147(3):283–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00234526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Hitt A. L. Cytoskeleton--plasma membrane interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):955–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1439807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Mechanosensitive ion channels of E. coli activated by amphipaths. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):261–263. doi: 10.1038/348261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. E. Mechanosensitive ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(2):93–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01872883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. Influence of sodium on the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor system of human platelets. Role for intraplatelet sodium in receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3913–3919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negulyaev YuA, Vedernikova E. A., Mozhayeva G. N. Several types of sodium-conducting channel in human carcinoma A-431 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Aug 24;1194(1):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90217-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negulyaev Y. A., Vedernikova E. A. Sodium-selective channels in membranes of rat macrophages. J Membr Biol. 1994 Feb;138(1):37–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00211067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat A. G., Bertorello A. M., Ausiello D. A., Cantiello H. F. Activation of epithelial Na+ channels by protein kinase A requires actin filaments. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C224–C233. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Bar-Sagi D., O'Brodovich H., Merilainen J., Lehto V. P., Canessa C. M., Rossier B. C., Downey G. P. An SH3 binding region in the epithelial Na+ channel (alpha rENaC) mediates its localization at the apical membrane. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4440–4450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M. Action of cytochalasin D on cytoskeletal networks. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):79–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiebert E. M., Mills J. W., Stanton B. A. Actin-based cytoskeleton regulates a chloride channel and cell volume in a renal cortical collecting duct cell line. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7081–7089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Saccomani G., Joe E. H., Angelides K. J., Benos D. J. Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel is linked to the cytoskeleton in renal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokabe M., Sachs F., Jing Z. Q. Quantitative video microscopy of patch clamped membranes stress, strain, capacitance, and stretch channel activation. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):722–728. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82285-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan Y., Elmer L., Davis J., Bennett V., Angelides K. Ankyrin and spectrin associate with voltage-dependent sodium channels in brain. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):177–180. doi: 10.1038/333177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Miyazaki K., Ikeda M., Kawaguchi Y., Sakai O. F-actin network may regulate a Cl- channel in renal proximal tubule cells. J Membr Biol. 1993 May;134(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00233473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Renterghem C., Lazdunski M. A new non-voltage-dependent, epithelial-like Na+ channel in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Oct;419(3-4):401–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00371123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


