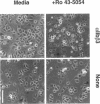
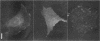
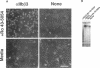
Abstract
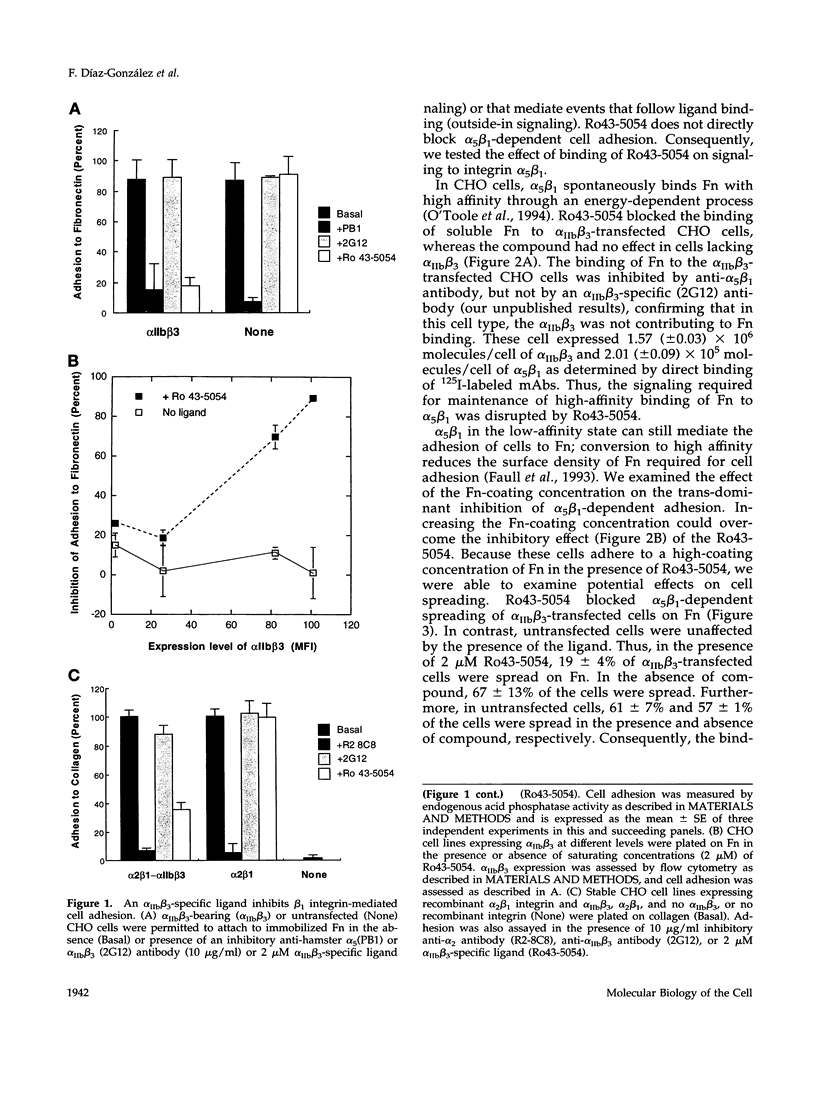
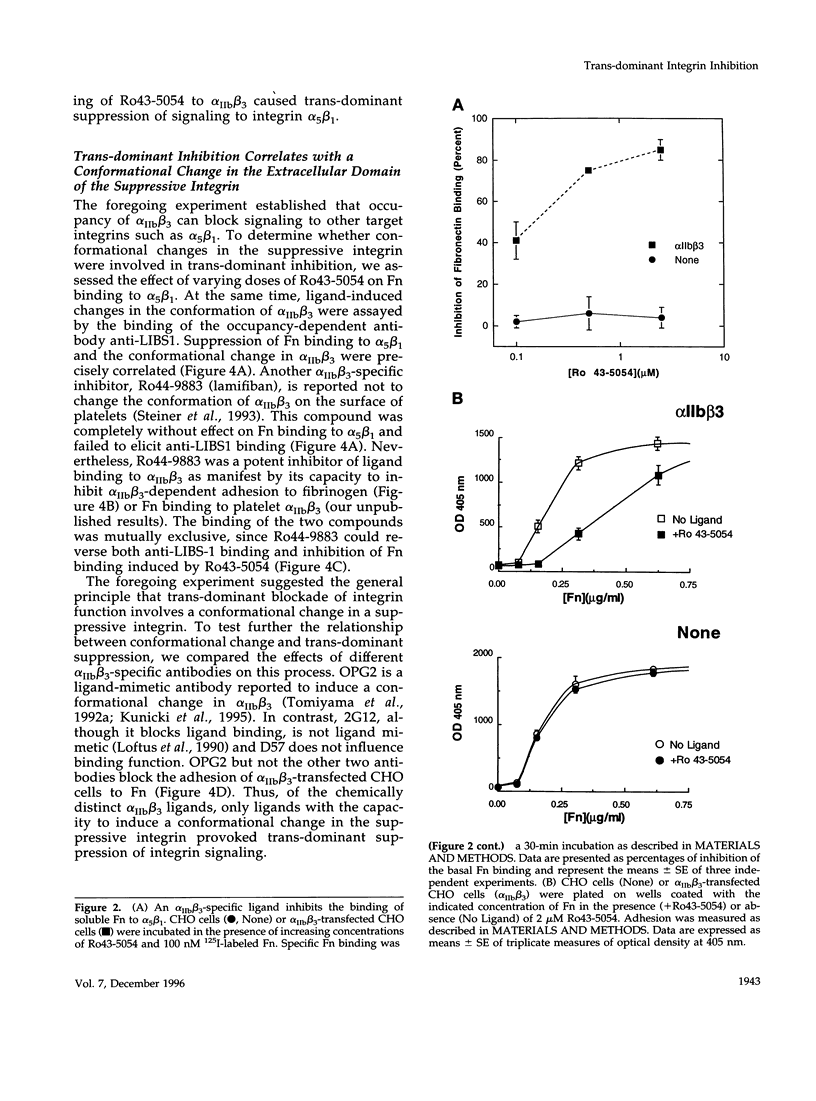
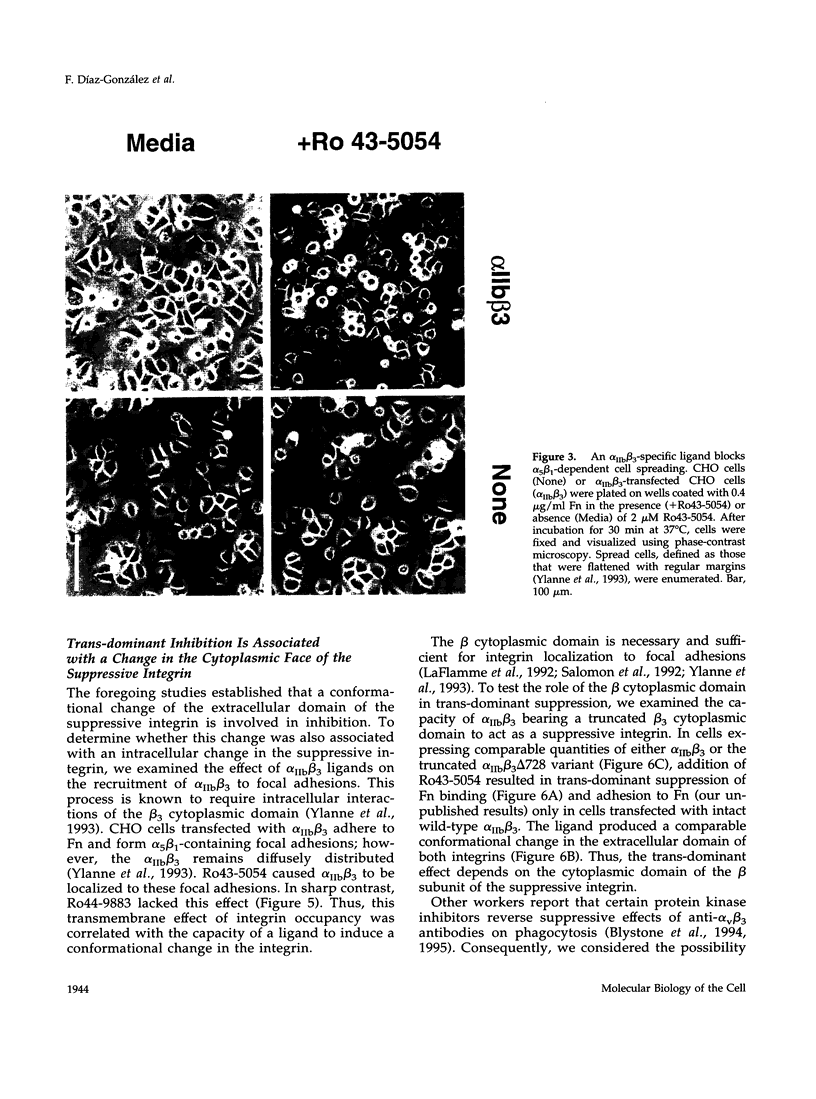
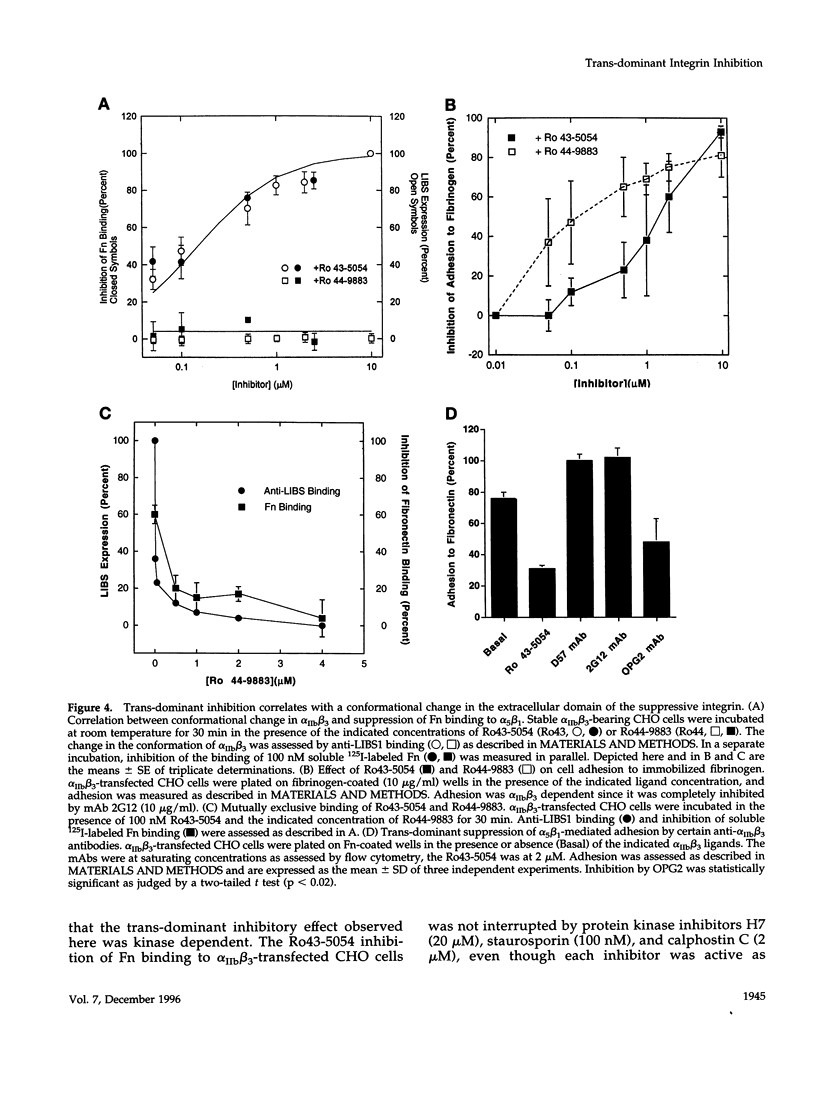
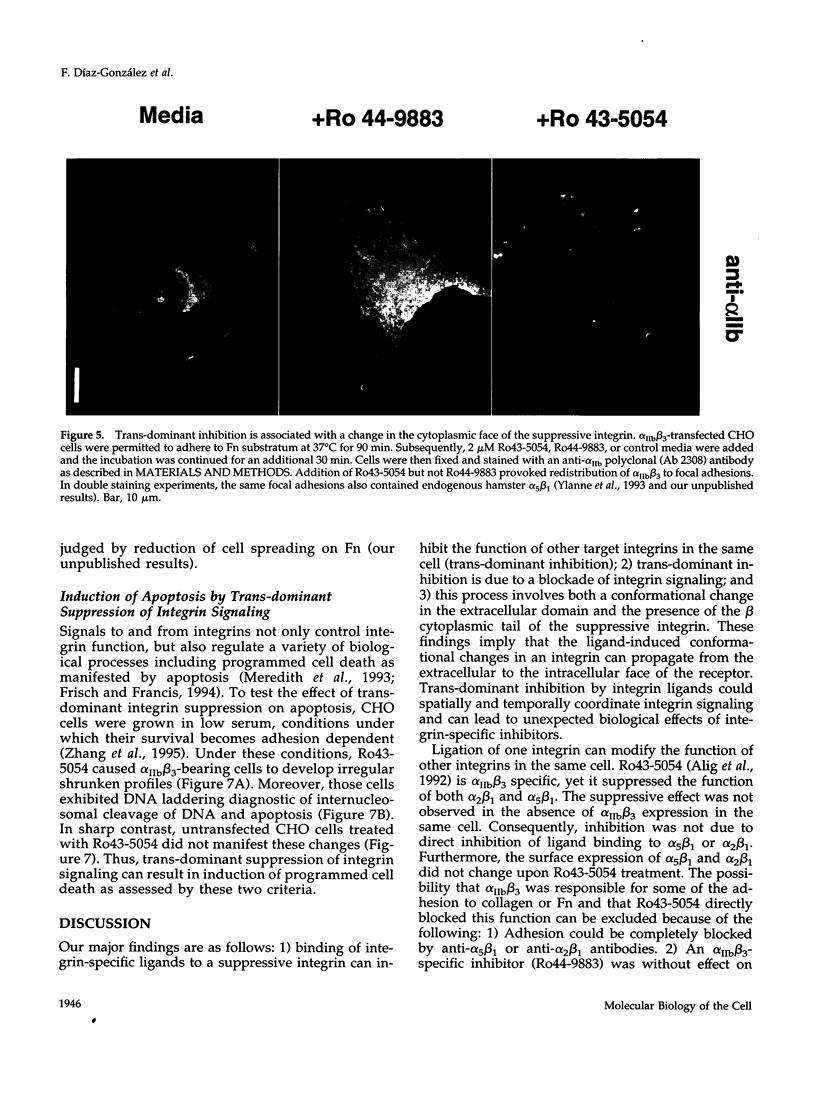
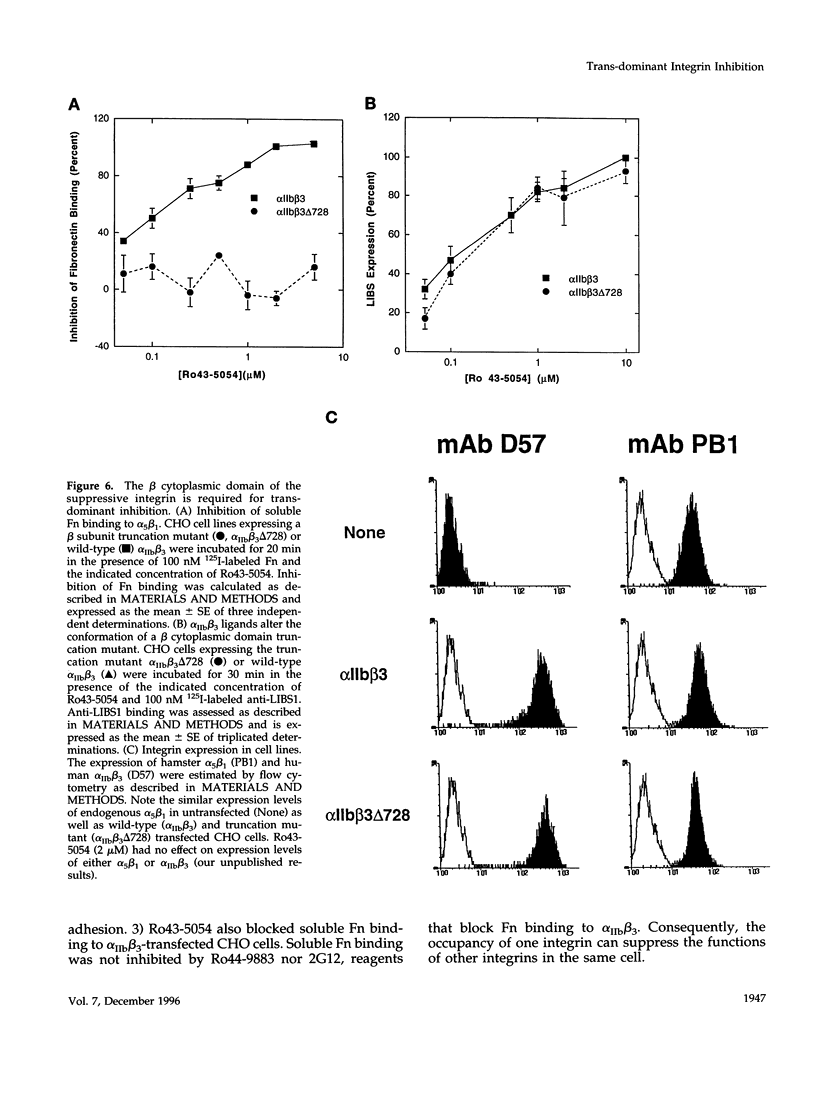
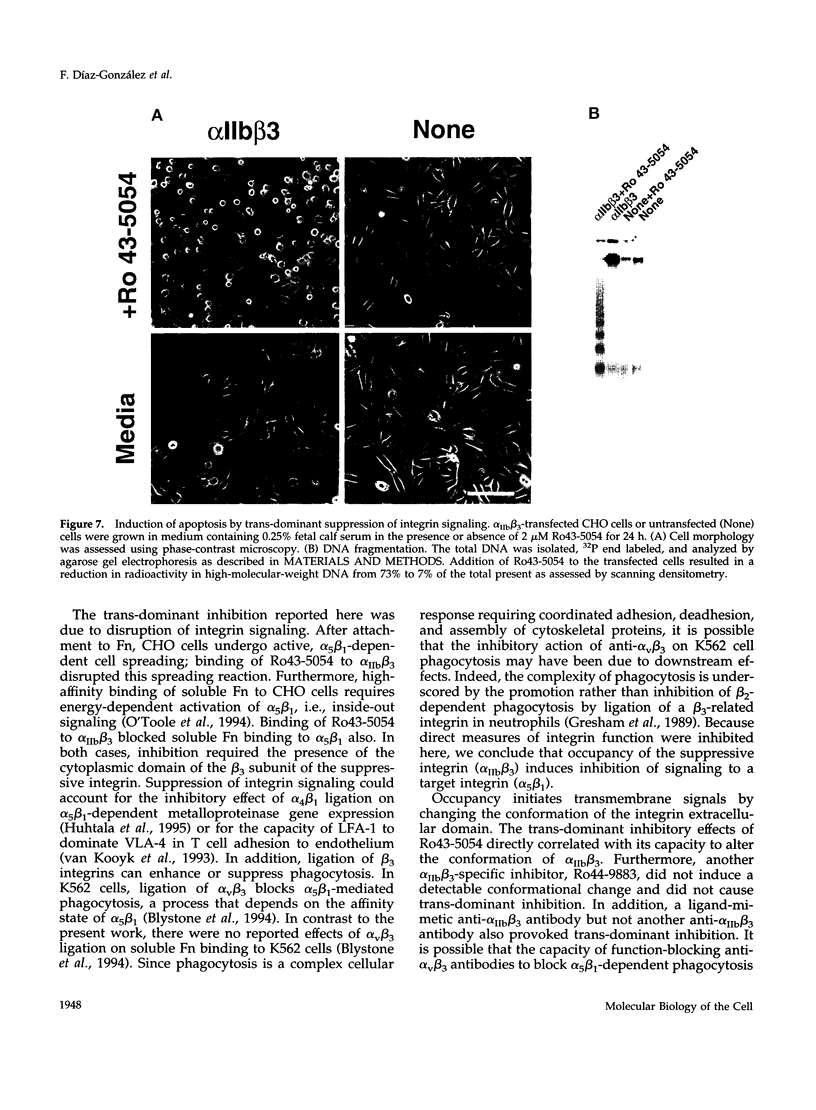
Occupancy of integrin adhesion receptors can alter the functions of other integrins and cause partition of the ligand-occupied integrin into focal adhesions. Ligand binding also changes the conformation of integrin extracellular domains. To explore the relationship between ligand-induced conformational change and integrin signaling, we examined the effect of ligands specific for integrin alpha IIb beta 3 on the functions of target integrins alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha 2 beta 1. We report that binding of integrin-specific ligands to a suppressive integrin can inhibit the function of other target integrins (trans-dominant inhibition). Trans-dominant inhibition is due to a blockade of integrin signaling. Furthermore, this inhibition involves both a conformational change in the extracellular domain and the presence of the beta cytoplasmic tail in the suppressive integrin. Similarly, ligand-induced recruitment of alpha IIb beta 3 to focal adhesions also involves a conformational rearrangement of its extracellular domain. These findings imply that the ligand-induced conformational changes can propagate from an integrin's extracellular to its intracellular face. Trans-dominant inhibition by integrin ligands may coordinate integrin signaling and can lead to unexpected biological effects of integrin-specific inhibitors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alig L., Edenhofer A., Hadváry P., Hürzeler M., Knopp D., Müller M., Steiner B., Trzeciak A., Weller T. Low molecular weight, non-peptide fibrinogen receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1992 Nov 13;35(23):4393–4407. doi: 10.1021/jm00101a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blystone S. D., Graham I. L., Lindberg F. P., Brown E. J. Integrin alpha v beta 3 differentially regulates adhesive and phagocytic functions of the fibronectin receptor alpha 5 beta 1. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):1129–1137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blystone S. D., Lindberg F. P., LaFlamme S. E., Brown E. J. Integrin beta 3 cytoplasmic tail is necessary and sufficient for regulation of alpha 5 beta 1 phagocytosis by alpha v beta 3 and integrin-associated protein. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(3):745–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briesewitz R., Kern A., Marcantonio E. E. Assembly and function of integrin receptors is dependent on opposing alpha and beta cytoplasmic domains. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Aug;6(8):997–1010. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.8.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briesewitz R., Kern A., Marcantonio E. E. Ligand-dependent and -independent integrin focal contact localization: the role of the alpha chain cytoplasmic domain. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jun;4(6):593–604. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.6.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Clark R. A., Cheresh D. A. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.7512751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Strömblad S., Klemke R., Visscher D., Sarkar F. H., Cheresh D. A. Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest. 1995 Oct;96(4):1815–1822. doi: 10.1172/JCI118227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. J., Juliano R. L. Monoclonal antibodies to distinctive epitopes on the alpha and beta subunits of the fibronectin receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Aug;177(2):303–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. J., Juliano R. L. Selective inhibition of fibronectin-mediated cell adhesion by monoclonal antibodies to a cell-surface glycoprotein. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1448–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.4012302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. P., O'Toole T. E., Shipley T., Forsyth J., LaFlamme S. E., Yamada K. M., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H. "Inside-out" signal transduction inhibited by isolated integrin cytoplasmic domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18307–18310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conforti G., Dominguez-Jimenez C., Zanetti A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cremona O., Marchisio P. C., Dejana E. Human endothelial cells express integrin receptors on the luminal aspect of their membrane. Blood. 1992 Jul 15;80(2):437–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. A point mutation of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene (NHE1) and amplification of the mutated allele confer amiloride resistance upon chronic acidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4508–4512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X., Gu M., Weisel J. W., Nagaswami C., Bennett J. S., Bowditch R., Ginsberg M. H. Long range propagation of conformational changes in integrin alpha IIb beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23087–23092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faull R. J., Kovach N. L., Harlan J. M., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of integrin alpha 5 beta 1: regulation of the functional response by soluble fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):155–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Cohen I., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Roberts J., Lam S. C., Ginsberg M. H. Selective inhibition of integrin function by antibodies specific for ligand-occupied receptor conformers. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6346–6352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Lam S. C., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Loftus J. C., Ginsberg M. H. Occupancy of an adhesive glycoprotein receptor modulates expression of an antigenic site involved in cell adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12397–12402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Forsyth J., Lightsey A., Chediak J., Plow E. F. Reduced surface expression and binding of fibronectin by thrombin-stimulated thrombasthenic platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):619–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI110808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham H. D., Goodwin J. L., Allen P. M., Anderson D. C., Brown E. J. A novel member of the integrin receptor family mediates Arg-Gly-Asp-stimulated neutrophil phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1935–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. E., Diaz-Gonzalez F., Leong L., Wu C., McDonald J. A., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H. Breaking the integrin hinge. A defined structural constraint regulates integrin signaling. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):6571–6574. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.6571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. E., O'Toole T. E., Ylänne J., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H. The conserved membrane-proximal region of an integrin cytoplasmic domain specifies ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12411–12417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhtala P., Humphries M. J., McCarthy J. B., Tremble P. M., Werb Z., Damsky C. H. Cooperative signaling by alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha 4 beta 1 integrins regulates metalloproteinase gene expression in fibroblasts adhering to fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):867–879. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. Signal transduction by integrins and its role in the regulation of tumor growth. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994 Mar;13(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00690416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer N., Fitzgerald L. A., Wolf D., Cheresh D. A., Phillips D. R. Adhesive properties of the beta 3 integrins: comparison of GP IIb-IIIa and the vitronectin receptor individually expressed in human melanoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):451–461. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouns W. C., Hadvary P., Haering P., Steiner B. Conformational modulation of purified glycoprotein (GP) IIb-IIIa allows proteolytic generation of active fragments from either active or inactive GPIIb-IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18844–18851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Ely K. R., Kunicki T. C., Tomiyama Y., Annis D. S. The exchange of Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) and Arg-Tyr-Asp (RYD) binding sequences in a recombinant murine Fab fragment specific for the integrin alpha IIb beta 3 does not alter integrin recognition. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 14;270(28):16660–16665. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.28.16660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Orchekowski R., Annis D., Honda Y. Variability of integrin alpha 2 beta 1 activity on human platelets. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2693–2703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFlamme S. E., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Regulation of fibronectin receptor distribution. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):437–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFlamme S. E., Thomas L. A., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M. Single subunit chimeric integrins as mimics and inhibitors of endogenous integrin functions in receptor localization, cell spreading and migration, and matrix assembly. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1287–1298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffenburger D. A. Models for receptor-mediated cell phenomena: adhesion and migration. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:387–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., O'Toole T. E., Plow E. F., Glass A., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Ginsberg M. H. A beta 3 integrin mutation abolishes ligand binding and alters divalent cation-dependent conformation. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):915–918. doi: 10.1126/science.2392682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Smith J. W., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion: the extracellular face. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25235–25238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukashev M. E., Sheppard D., Pytela R. Disruption of integrin function and induction of tyrosine phosphorylation by the autonomously expressed beta 1 integrin cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18311–18314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith J. E., Jr, Fazeli B., Schwartz M. A. The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):953–961. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Synergistic roles for receptor occupancy and aggregation in integrin transmembrane function. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):883–885. doi: 10.1126/science.7846531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Katagiri Y., Faull R. J., Peter K., Tamura R., Quaranta V., Loftus J. C., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin cytoplasmic domains mediate inside-out signal transduction. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(6):1047–1059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.6.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Du X. P., Glass A. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of the alpha IIb beta 3 integrin (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) is an intrinsic property of the receptor. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):883–893. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Plow E. F., Glass A. A., Harper J. R., Ginsberg M. H. Efficient surface expression of platelet GPIIb-IIIa requires both subunits. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):14–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Mandelman D., Forsyth J., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Modulation of the affinity of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (GPIIb-IIIa) by the cytoplasmic domain of alpha IIb. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):845–847. doi: 10.1126/science.1948065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parise L. V., Helgerson S. L., Steiner B., Nannizzi L., Phillips D. R. Synthetic peptides derived from fibrinogen and fibronectin change the conformation of purified platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12597–12602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., McEver R. P., Coller B. S., Woods V. L., Jr, Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. Related binding mechanisms for fibrinogen, fibronectin, von Willebrand factor, and thrombospondin on thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Reed J. C. Anchorage dependence, integrins, and apoptosis. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):477–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D., Ayalon O., Patel-King R., Hynes R. O., Geiger B. Extrajunctional distribution of N-cadherin in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1992 May;102(Pt 1):7–17. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Schaller M. D., Ginsberg M. H. Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:549–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly J. L., Hsueh A. J. Microscale autoradiographic method for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of apoptotic DNA fragmentation. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Mar;154(3):519–526. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyama Y., Brojer E., Ruggeri Z. M., Shattil S. J., Smiltneck J., Gorski J., Kumar A., Kieber-Emmons T., Kunicki T. J. A molecular model of RGD ligands. Antibody D gene segments that direct specificity for the integrin alpha IIb beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18085–18092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyama Y., Tsubakio T., Piotrowicz R. S., Kurata Y., Loftus J. C., Kunicki T. J. The Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) recognition site of platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa on nonactivated platelets is accessible to high-affinity macromolecules. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2303–2312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. J., Hughes P. E., O'Toole T. E., Ginsberg M. H. The inner world of cell adhesion: integrin cytoplasmic domains. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;4(4):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods V. L., Jr, Oh E. H., Mason D., McMillan R. Autoantibodies against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex in patients with chronic ITP. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Keivens V. M., O'Toole T. E., McDonald J. A., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin activation and cytoskeletal interaction are essential for the assembly of a fibronectin matrix. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90184-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylänne J., Chen Y., O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Takada Y., Ginsberg M. H. Distinct functions of integrin alpha and beta subunit cytoplasmic domains in cell spreading and formation of focal adhesions. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):223–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Vuori K., Reed J. C., Ruoslahti E. The alpha 5 beta 1 integrin supports survival of cells on fibronectin and up-regulates Bcl-2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 20;92(13):6161–6165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.6161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kooyk Y., van de Wiel-van Kemenade E., Weder P., Huijbens R. J., Figdor C. G. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 dominates very late antigen 4 in binding of activated T cells to endothelium. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):185–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]