Abstract
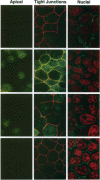
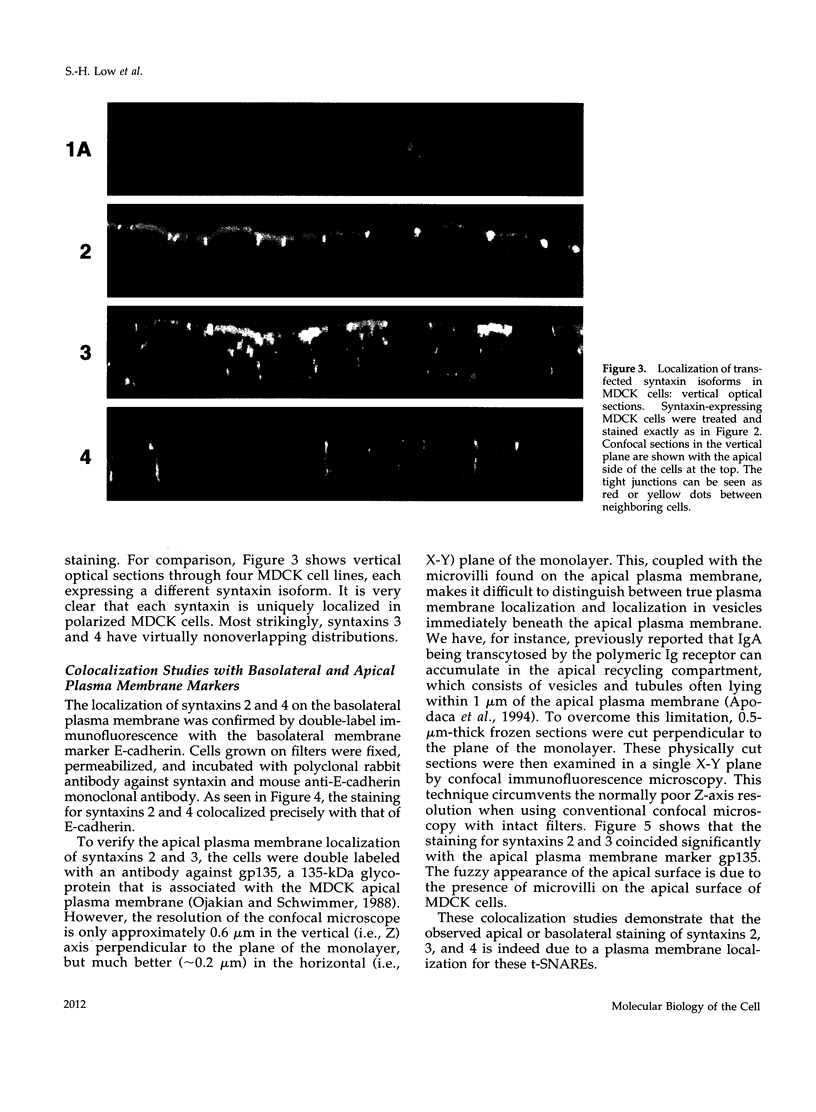
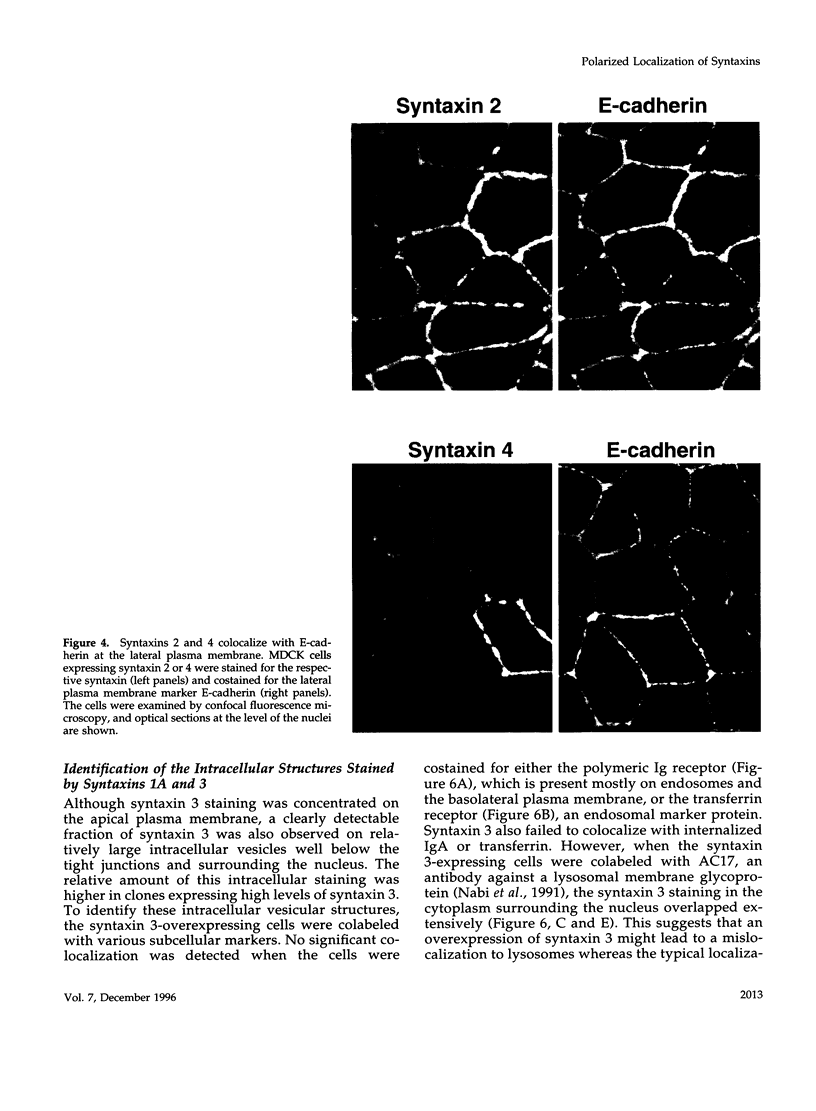
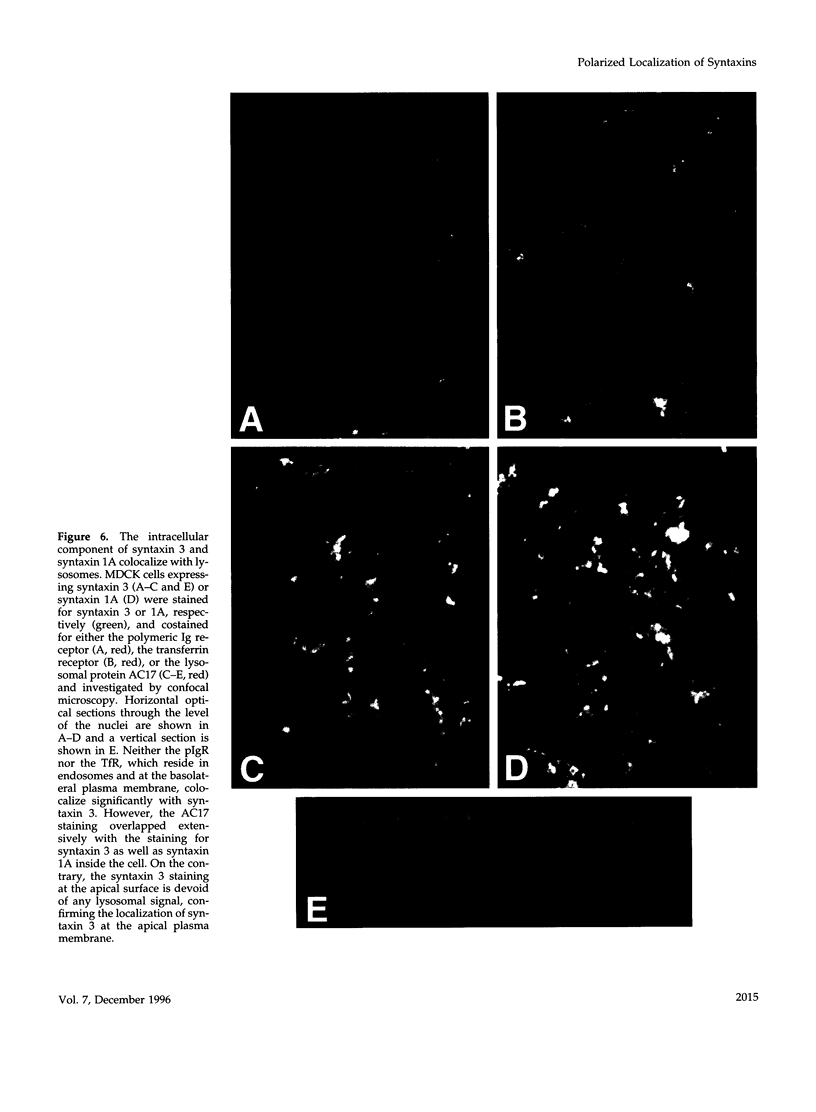
Syntaxins, integral membrane proteins that are part of the ubiquitous membrane fusion machinery, are thought to act as target membrane receptors during the process of vesicle docking and fusion. Several isoforms of the syntaxin family have been previously identified in mammalian cells, some of which are localized to the plasma membrane. We investigated the subcellular localization of these putative plasma membrane syntaxins in polarized epithelial cells, which are characterized by the presence of distinct apical and basolateral plasma membrane domains. Syntaxins 2, 3, and 4 were found to be endogenously present in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. The localization of syntaxins 1A, 1B, 2, 3, and 4 in stably transfected Madin-Darby canine kidney cell lines was studied with confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Each syntaxin isoform was found to have a unique pattern of localization. Syntaxins 1A and 1B were present only in intracellular structures, with little or no apparent plasma membrane staining. In contrast, syntaxin 2 was found on both the apical and basolateral surface, whereas the plasma membrane localization of syntaxins 3 and 4 were restricted to the apical or basolateral domains, respectively. Syntaxins are therefore the first known components of the plasma membrane fusion machinery that are differentially localized in polarized cells, suggesting that they may play a central role in targeting specificity.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya U., Jacobs R., Peters J. M., Watson N., Farquhar M. G., Malhotra V. The formation of Golgi stacks from vesiculated Golgi membranes requires two distinct fusion events. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apodaca G., Cardone M. H., Whiteheart S. W., DasGupta B. R., Mostov K. E. Reconstitution of transcytosis in SLO-permeabilized MDCK cells: existence of an NSF-dependent fusion mechanism with the apical surface of MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1996 Apr 1;15(7):1471–1481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apodaca G., Katz L. A., Mostov K. E. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of IgA in MDCK cells is via apical recycling endosomes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):67–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K. SNAREs and the specificity of transport vesicle targeting. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;7(4):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boll W., Partin J. S., Katz A. I., Caplan M. J., Jamieson J. D. Distinct pathways for basolateral targeting of membrane and secretory proteins in polarized epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8592–8596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitfeld P. P., Casanova J. E., Harris J. M., Simister N. E., Mostov K. E. Expression and analysis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells using retroviral vectors. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:329–337. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C. B., Roth M. G. A single amino acid change in the cytoplasmic domain alters the polarized delivery of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):413–421. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Bennett M. K., Peterson K. E., Scheller R. H. Protein-protein interactions contributing to the specificity of intracellular vesicular trafficking. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Synaptic vesicle biogenesis, docking, and fusion: a molecular description. Physiol Rev. 1996 Jan;76(1):1–29. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1996.76.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Nelson W. J. Origins of cell polarity. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler K., Lafont F., Parton R. G., Simons K. Annexin XIIIb: a novel epithelial specific annexin is implicated in vesicular traffic to the apical plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1043–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler K., Simons K. The role of N-glycans in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90380-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaisano H. Y., Ghai M., Malkus P. N., Sheu L., Bouquillon A., Bennett M. K., Trimble W. S. Distinct cellular locations of the syntaxin family of proteins in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Dec;7(12):2019–2027. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.12.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackam D. J., Rotstein O. D., Bennett M. K., Klip A., Grinstein S., Manolson M. F. Characterization and subcellular localization of target membrane soluble NSF attachment protein receptors (t-SNAREs) in macrophages. Syntaxins 2, 3, and 4 are present on phagosomal membranes. J Immunol. 1996 Jun 1;156(11):4377–4383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D. A., Ojakian G. K. Studies on the development and maintenance of epithelial cell surface polarity with monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L. Targeting of membrane and secretory proteins to the apical domain in epithelial cells. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;2(6):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikonen E., Tagaya M., Ullrich O., Montecucco C., Simons K. Different requirements for NSF, SNAP, and Rab proteins in apical and basolateral transport in MDCK cells. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):571–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S., Yamamoto A., Inoue A., Inoue Y., Akagawa K., Kawamura Y., Kawamoto K., Tashiro Y. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of the HPC-1 antigen in rat cerebellum. J Neurocytol. 1993 Nov;22(11):995–1005. doi: 10.1007/BF01218356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A., Wickner W., Haas A. Sec18p (NSF)-driven release of Sec17p (alpha-SNAP) can precede docking and fusion of yeast vacuoles. Cell. 1996 Apr 5;85(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Altschuler Y., Chapin S. J., Enrich C., Low S. H., Luton F., Richman-Eisenstat J., Singer K. L., Tang K., Weimbs T. Regulation of protein traffic in polarized epithelial cells: the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor model. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1995;60:775–781. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1995.060.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Cardone M. H. Regulation of protein traffic in polarized epithelial cells. Bioessays. 1995 Feb;17(2):129–138. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K., Apodaca G., Aroeti B., Okamoto C. Plasma membrane protein sorting in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):577–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabi I. R., Le Bivic A., Fambrough D., Rodriguez-Boulan E. An endogenous MDCK lysosomal membrane glycoprotein is targeted basolaterally before delivery to lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1573–1584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojakian G. K., Schwimmer R. The polarized distribution of an apical cell surface glycoprotein is maintained by interactions with the cytoskeleton of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2377–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto C. T., Shia S. P., Bird C., Mostov K. E., Roth M. G. The cytoplasmic domain of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor contains two internalization signals that are distinct from its basolateral sorting signal. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9925–9932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabouille C., Levine T. P., Peters J. M., Warren G. An NSF-like ATPase, p97, and NSF mediate cisternal regrowth from mitotic Golgi fragments. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran V., Chawla A., Roche P. A. Identification of a novel syntaxin- and synaptobrevin/VAMP-binding protein, SNAP-23, expressed in non-neuronal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 7;271(23):13300–13303. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.23.13300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Powell S. K. Polarity of epithelial and neuronal cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:395–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Warren G. Implications of the SNARE hypothesis for intracellular membrane topology and dynamics. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):220–233. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. Protein sorting by transport vesicles. Science. 1996 Apr 12;272(5259):227–234. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5259.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saucan L., Palade G. E. Membrane and secretory proteins are transported from the Golgi complex to the sinusoidal plasmalemma of hepatocytes by distinct vesicular carriers. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(4):733–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze K. L., Broadie K., Perin M. S., Bellen H. J. Genetic and electrophysiological studies of Drosophila syntaxin-1A demonstrate its role in nonneuronal secretion and neurotransmission. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90414-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Wandinger-Ness A. Polarized sorting in epithelia. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90357-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel G. J., Tagaya M., Woodman P. G. Association of the fusion protein NSF with clathrin-coated vesicle membranes. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 15;15(4):745–752. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Siliciano J. D., Mooseker M. S., Goodenough D. A. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., De Camilli P., Niemann H., Jahn R. Membrane fusion machinery: insights from synaptic proteins. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C. The synaptic vesicle cycle: a cascade of protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):645–653. doi: 10.1038/375645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volchuk A., Wang Q., Ewart H. S., Liu Z., He L., Bennett M. K., Klip A. Syntaxin 4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: regulation by insulin and participation in insulin-dependent glucose transport. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Jul;7(7):1075–1082. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.7.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walch-Solimena C., Blasi J., Edelmann L., Chapman E. R., von Mollard G. F., Jahn R. The t-SNAREs syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 are present on organelles that participate in synaptic vesicle recycling. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L. NSF-independent fusion mechanisms. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):475–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]