Abstract
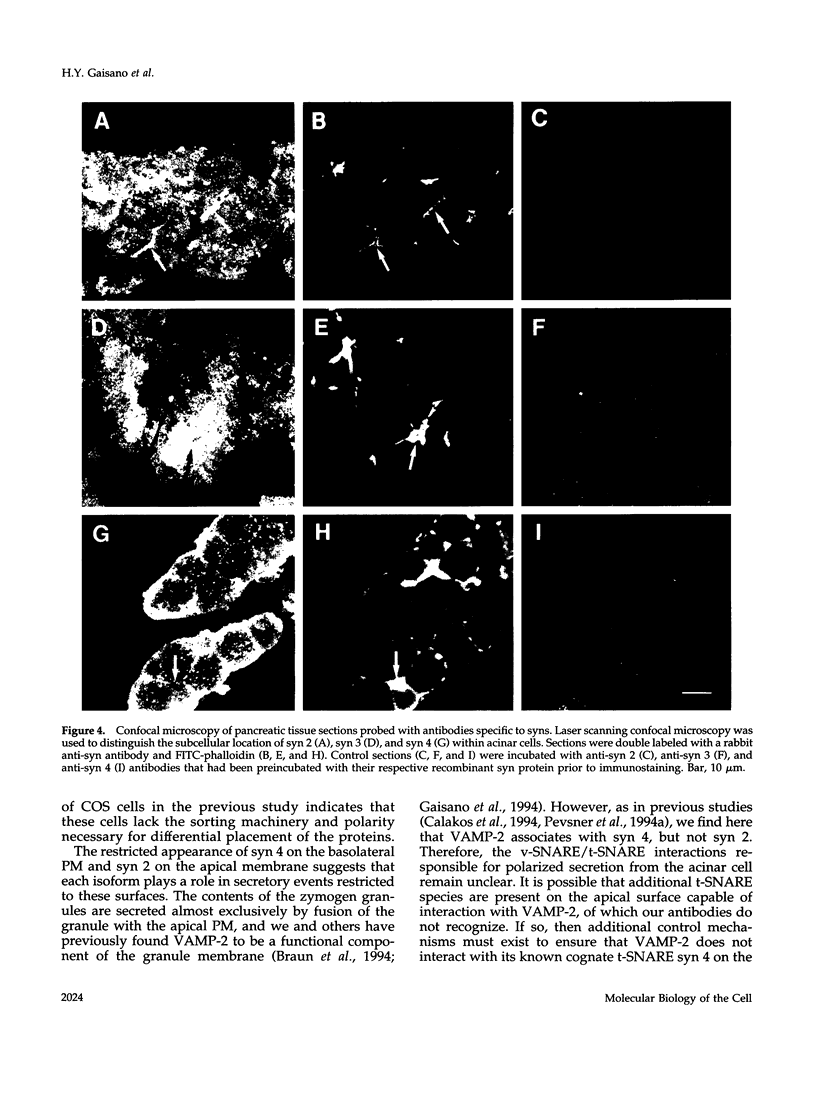
Syntaxins are cytoplasmically oriented integral membrane soluble NEM-sensitive factor receptors (SNAREs; soluble NEM-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors) thought to serve as targets for the assembly of protein complexes important in regulating membrane fusion. The SNARE hypothesis predicts that the fidelity of vesicle traffic is controlled in part by the correct recognition of vesicle SNAREs with their cognate target SNARE partner. Here, we show that in the exocrine acinar cell of the pancreas, multiple syntaxin isoforms are expressed and that they appear to reside in distinct membrane compartments. Syntaxin 2 is restricted to the apical plasma membrane whereas syntaxin 4 is found most abundantly on the basolateral membranes. Surprisingly, syntaxin 3 was found to be localized to a vesicular compartment, the zymogen granule membrane. In addition, we show that these proteins are capable of specific interaction with vesicle SNARE proteins. Their nonoverlapping locations support the general principle of the SNARE hypothesis and provide new insights into the mechanisms of polarized secretion in epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. L., McNiven M. A. Vesicle dynamics during regulated secretion in a novel pancreatic acinar cell in vitro model. Eur J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;66(1):25–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvan P., Castle J. D. Phasic release of newly synthesized secretory proteins in the unstimulated rat exocrine pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):243–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudoin A. R., Grondin G. Zymogen granules of the pancreas and the parotid gland and their role in cell secretion. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;132:177–222. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62456-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. A molecular description of synaptic vesicle membrane trafficking. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:63–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J. E., Fritz B. A., Wong S. M., Lowe A. W. Identification of a vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)-like membrane protein in zymogen granules of the rat exocrine pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5328–5335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Bennett M. K., Peterson K. E., Scheller R. H. Protein-protein interactions contributing to the specificity of intracellular vesicular trafficking. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascher C., Matteson J., Balch W. E. Syntaxin 5 regulates endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29363–29366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardson J. M., MacLean C. M., Law G. J. Synthetic peptides of the rab3 effector domain stimulate a membrane fusion event involved in regulated exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 29;320(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81656-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Trimble W. S., Scheller R. H. Two vesicle-associated membrane protein genes are differentially expressed in the rat central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11061–11064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaisano H. Y., Klueppelberg U. G., Pinon D. I., Pfenning M. A., Powers S. P., Miller L. J. Novel tool for the study of cholecystokinin-stimulated pancreatic enzyme secretion. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):321–325. doi: 10.1172/JCI113877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaisano H. Y., Sheu L., Foskett J. K., Trimble W. S. Tetanus toxin light chain cleaves a vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) isoform 2 in rat pancreatic zymogen granules and inhibits enzyme secretion. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17062–17066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Hirling H., Scheller R. H. Mammalian vesicle trafficking proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 8;271(10):5671–5679. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.10.5671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikonen E., Tagaya M., Ullrich O., Montecucco C., Simons K. Different requirements for NSF, SNAP, and Rab proteins in apical and basolateral transport in MDCK cells. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):571–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampel M., Kern H. F. Acute interstitial pancreatitis in the rat induced by excessive doses of a pancreatic secretagogue. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1977 Mar 11;373(2):97–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00432156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew S., Hammel I., Galli S. J. Cytoplasmic granule formation in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Evidence for formation of immature granules (condensing vacuoles) by aggregation and fusion of progranules of unit size, and for reductions in membrane surface area and immature granule volume during granule maturation. Cell Tissue Res. 1994 Nov;278(2):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00414176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyler G. A., Higgins G. A., Hart R. A., Battenberg E., Billingsley M., Bloom F. E., Wilson M. C. The identification of a novel synaptosomal-associated protein, SNAP-25, differentially expressed by neuronal subpopulations. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3039–3052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Hsu S. C., Braun J. E., Calakos N., Ting A. E., Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. Specificity and regulation of a synaptic vesicle docking complex. Neuron. 1994 Aug;13(2):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Hsu S. C., Scheller R. H. n-Sec1: a neural-specific syntaxin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Warren G. Implications of the SNARE hypothesis for intracellular membrane topology and dynamics. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):220–233. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul K., Lang J., Montecucco C., Weller U., Regazzi R., Catsicas S., Wollheim C. B., Halban P. A. SNAP-25 is expressed in islets of Langerhans and is involved in insulin release. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1019–1028. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya M., Toyonaga S., Takahashi M., Yamamoto A., Fujiwara T., Akagawa K., Moriyama Y., Mizushima S. Syntaxin 1 (HPC-1) is associated with chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):15930–15933. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.15930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. VAMP-1: a synaptic vesicle-associated integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walch-Solimena C., Blasi J., Edelmann L., Chapman E. R., von Mollard G. F., Jahn R. The t-SNAREs syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 are present on organelles that participate in synaptic vesicle recycling. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler M. B., Sheu L., Ghai M., Bouquillon A., Grondin G., Weller U., Beaudoin A. R., Bennett M. K., Trimble W. S., Gaisano H. Y. Characterization of SNARE protein expression in beta cell lines and pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1996 Apr;137(4):1340–1348. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.4.8625909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L. NSF-independent fusion mechanisms. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):475–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]