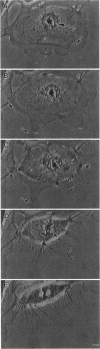
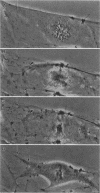
Abstract
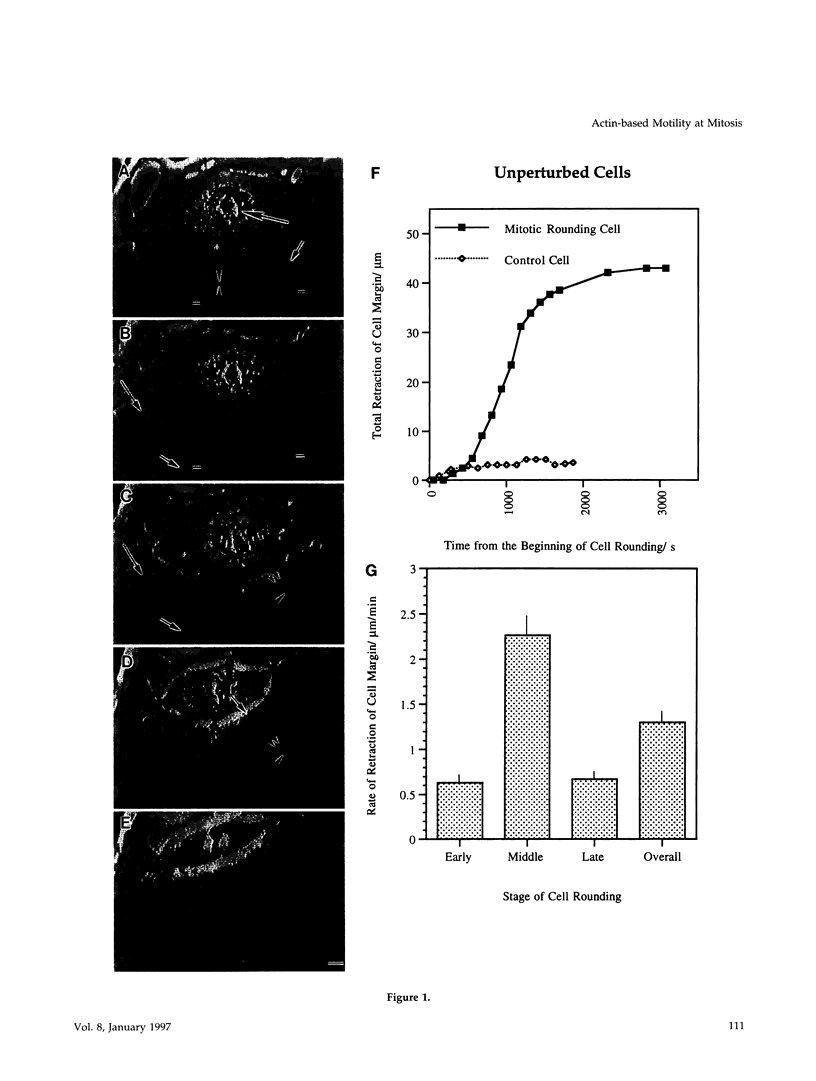
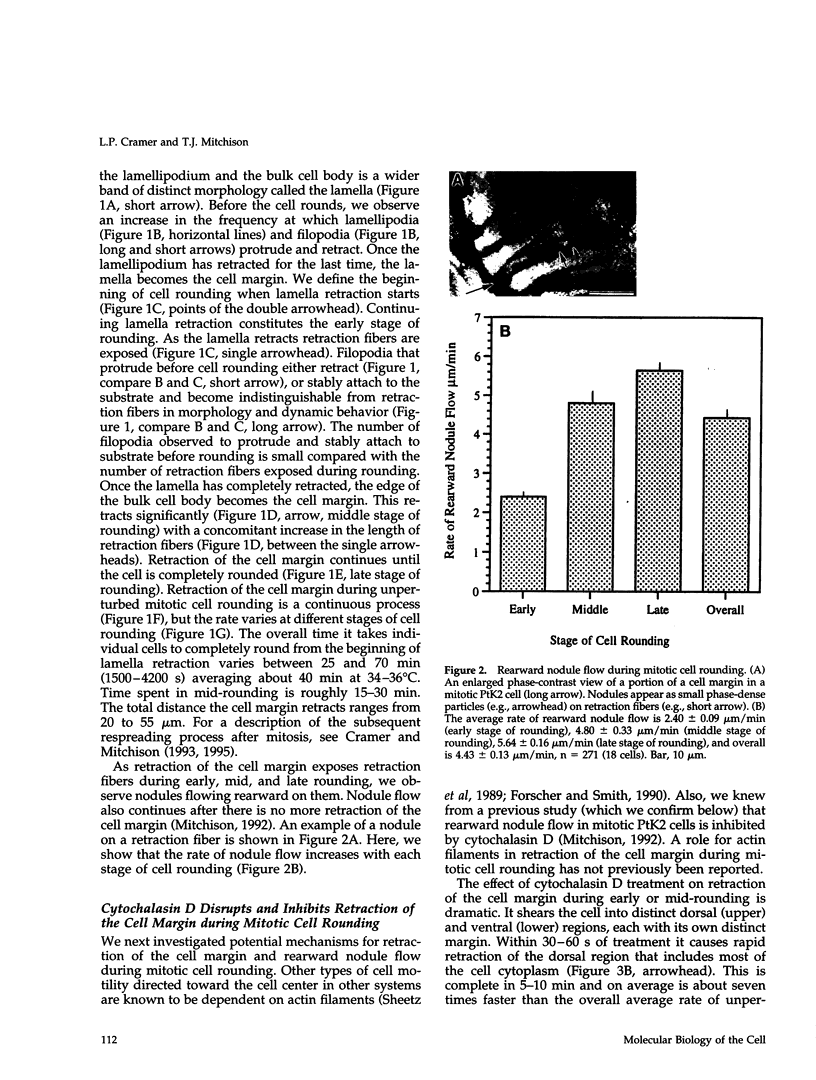
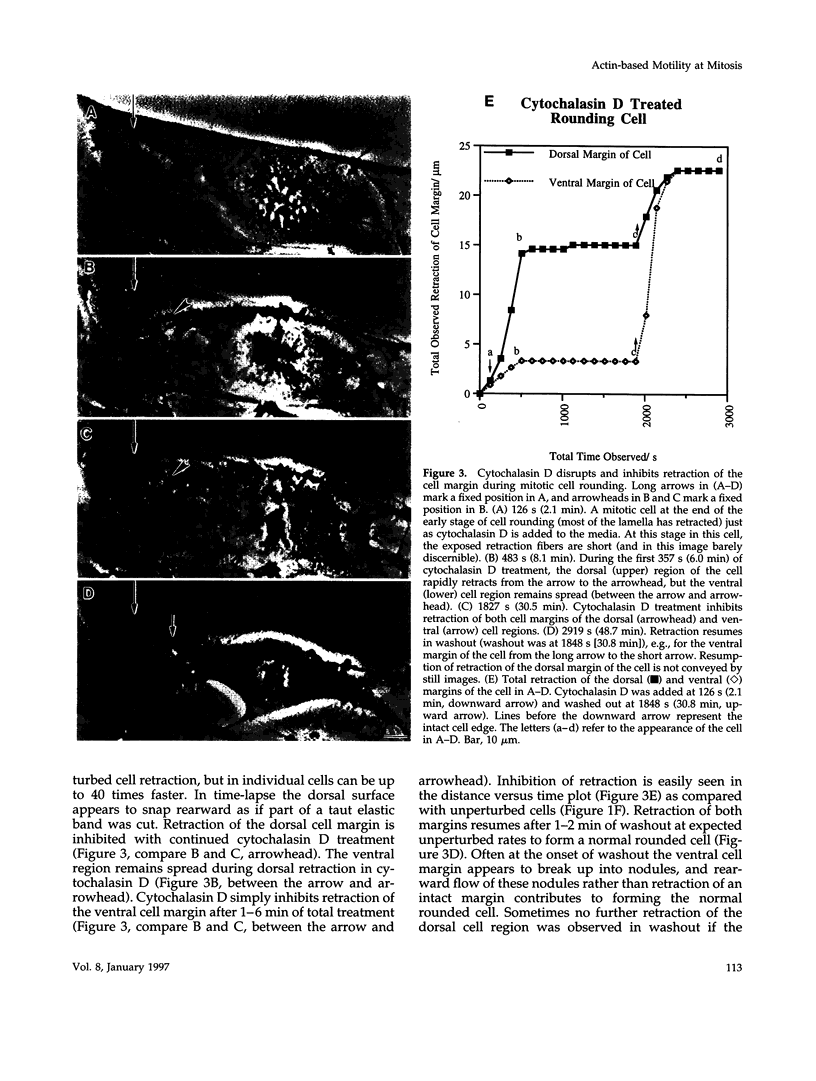
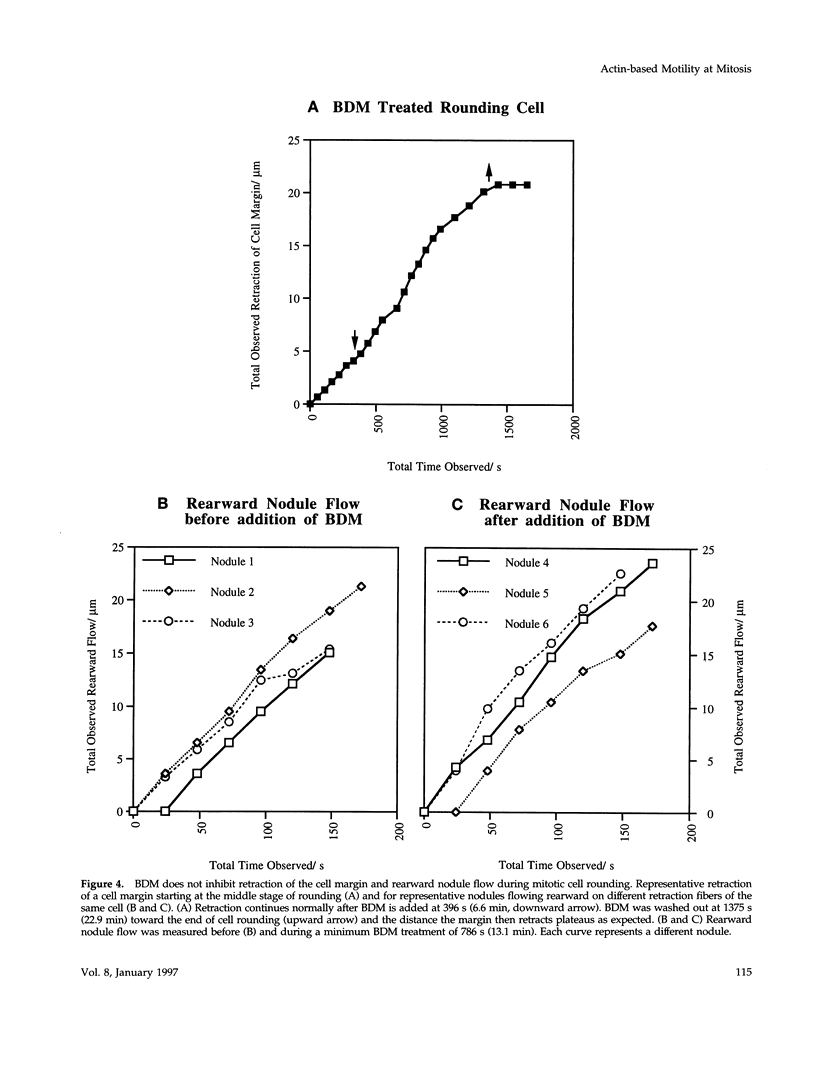
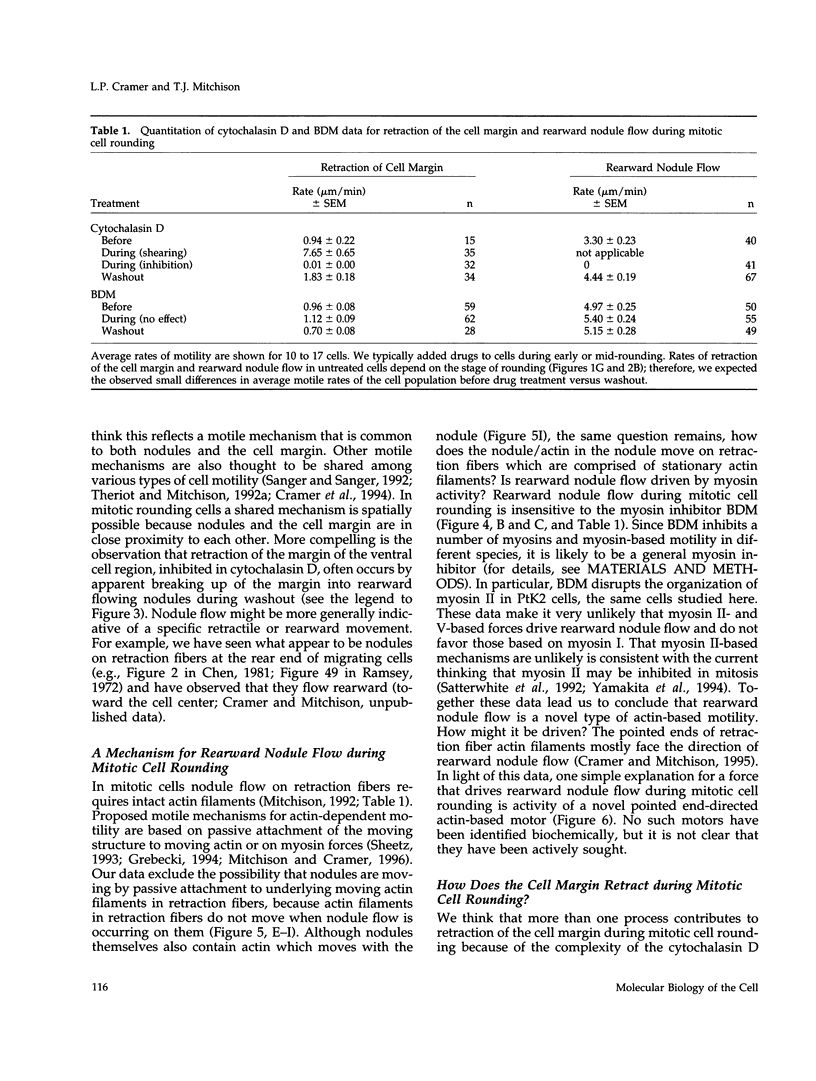
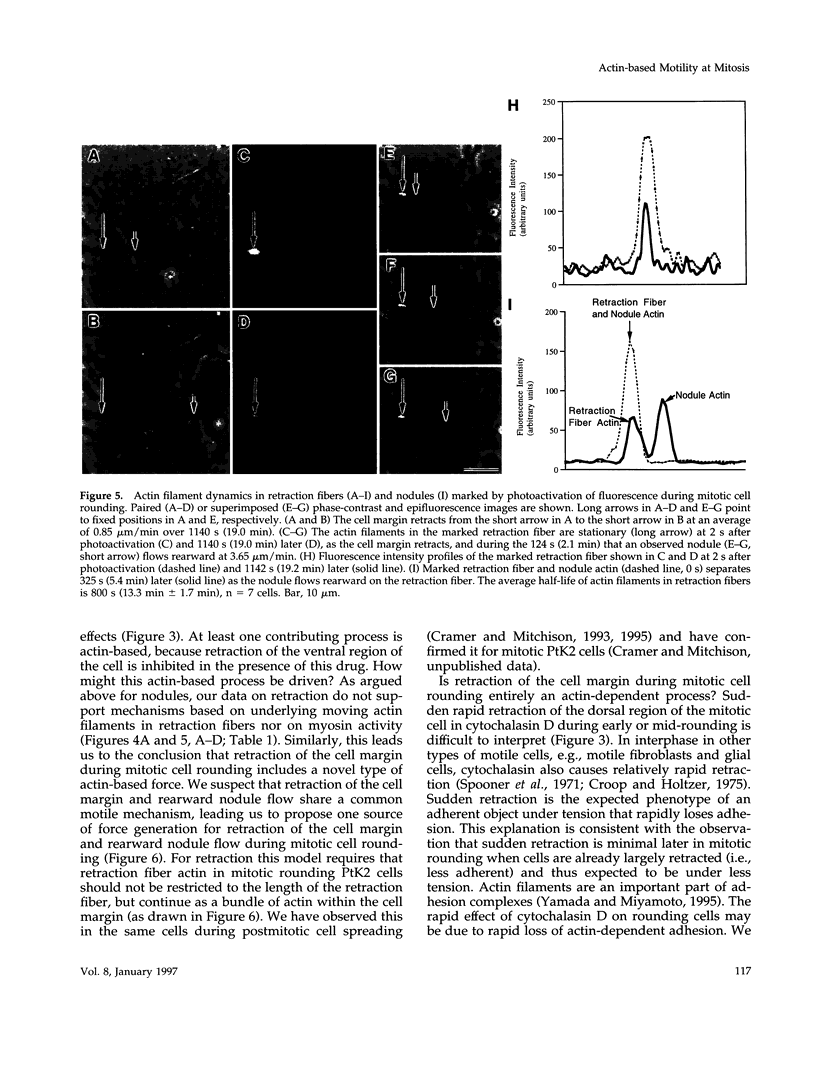
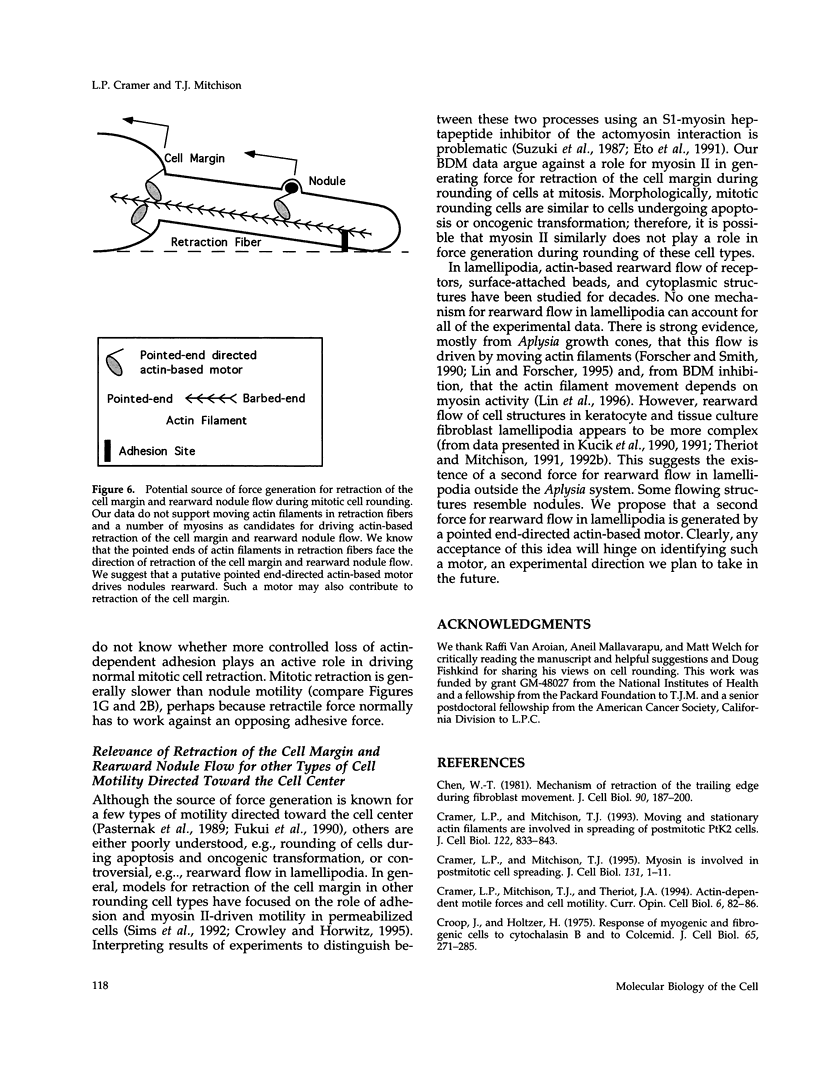
We have studied two types of cell motility directed toward the cell center: retraction of the cell margin and rearward flow of small cytoplasmic nodules during mitotic cell rounding in Potoroo tridactylis kidney (PtK2) cells by time-lapse video microscopy, drug treatments, and photoactivation of fluorescence. Nodules flow rearward on thin, actin-rich fibers (retraction fibers) exposed as the cell margin retracts. Retraction of the cell margin and rearward flow of nodules require intact actin filaments, but are insensitive to an inhibitor of myosin function (butanedione monoxime). Using photoactivation of fluorescence marking, we have determined that actin filaments in the majority of retraction fibers remain stationary while the cell margin retracts and nodules flow rearward. The pointed ends of retraction fiber actin filaments face the cell center. We argue that nodule motility is driven by a novel actin-based force that perhaps also partially contributes to retraction of the cell margin during cell rounding at mitosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen W. T. Mechanism of retraction of the trailing edge during fibroblast movement. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):187–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer L. P., Mitchison T. J., Theriot J. A. Actin-dependent motile forces and cell motility. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer L., Mitchison T. J. Moving and stationary actin filaments are involved in spreading of postmitotic PtK2 cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):833–843. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croop J., Holtzer H. Response of myogenic and fibrogenic cells to cytochalasin B and to colcemid. I. Light microscope observations. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):271–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley E., Horwitz A. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and cytoskeletal tension regulate the release of fibroblast adhesions. J Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;131(2):525–537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Morita F., Nishi N., Tokura S., Ito T., Takahashi K. Actin polymerization promoted by a heptapeptide, an analog of the actin-binding S site on myosin head. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18233–18236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Structure and function of the cytoskeleton of a Dictyostelium myosin-defective mutant. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):367–378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. Location of cellular adhesions to solid substrata. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):97–114. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Takemori S. Butanedione monoxime suppresses contraction and ATPase activity of rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1989 Apr;105(4):638–643. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucik D. F., Elson E. L., Sheetz M. P. Cell migration does not produce membrane flow. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1617–1622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucik D. F., Kuo S. C., Elson E. L., Sheetz M. P. Preferential attachment of membrane glycoproteins to the cytoskeleton at the leading edge of lamella. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):1029–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. H., Espreafico E. M., Mooseker M. S., Forscher P. Myosin drives retrograde F-actin flow in neuronal growth cones. Neuron. 1996 Apr;16(4):769–782. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. H., Forscher P. Growth cone advance is inversely proportional to retrograde F-actin flow. Neuron. 1995 Apr;14(4):763–771. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Kiehart D. P. Fly division. J Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;131(1):1–5. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J. Actin based motility on retraction fibers in mitotic PtK2 cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(2):135–151. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak C., Spudich J. A., Elson E. L. Capping of surface receptors and concomitant cortical tension are generated by conventional myosin. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):549–551. doi: 10.1038/341549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey W. S. Locomotion of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jun;72(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. M., Reingold A. M., Sanger J. W. Cell surface changes during mitosis and cytokinesis of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(3):409–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00228425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Sanger J. M. Cell motility. Beads, bacteria and actin. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):442–442. doi: 10.1038/357442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite L. L., Lohka M. J., Wilson K. L., Scherson T. Y., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L., Pollard T. D. Phosphorylation of myosin-II regulatory light chain by cyclin-p34cdc2: a mechanism for the timing of cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):595–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Glycoprotein motility and dynamic domains in fluid plasma membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:417–431. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Turney S., Qian H., Elson E. L. Nanometre-level analysis demonstrates that lipid flow does not drive membrane glycoprotein movements. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):284–288. doi: 10.1038/340284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J. R., Karp S., Ingber D. E. Altering the cellular mechanical force balance results in integrated changes in cell, cytoskeletal and nuclear shape. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):1215–1222. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Yamada K. M., Wessells N. K. Microfilaments and cell locomotion. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):595–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki R., Nishi N., Tokura S., Morita F. F-actin-binding synthetic heptapeptide having the amino acid sequence around the SH1 cysteinyl residue of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11410–11412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. Actin microfilament dynamics in locomoting cells. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):126–131. doi: 10.1038/352126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. Comparison of actin and cell surface dynamics in motile fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):367–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. The nucleation-release model of actin filament dynamics in cell motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Miyamoto S. Integrin transmembrane signaling and cytoskeletal control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;7(5):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakita Y., Yamashiro S., Matsumura F. In vivo phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II during mitosis of cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):129–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]