Abstract
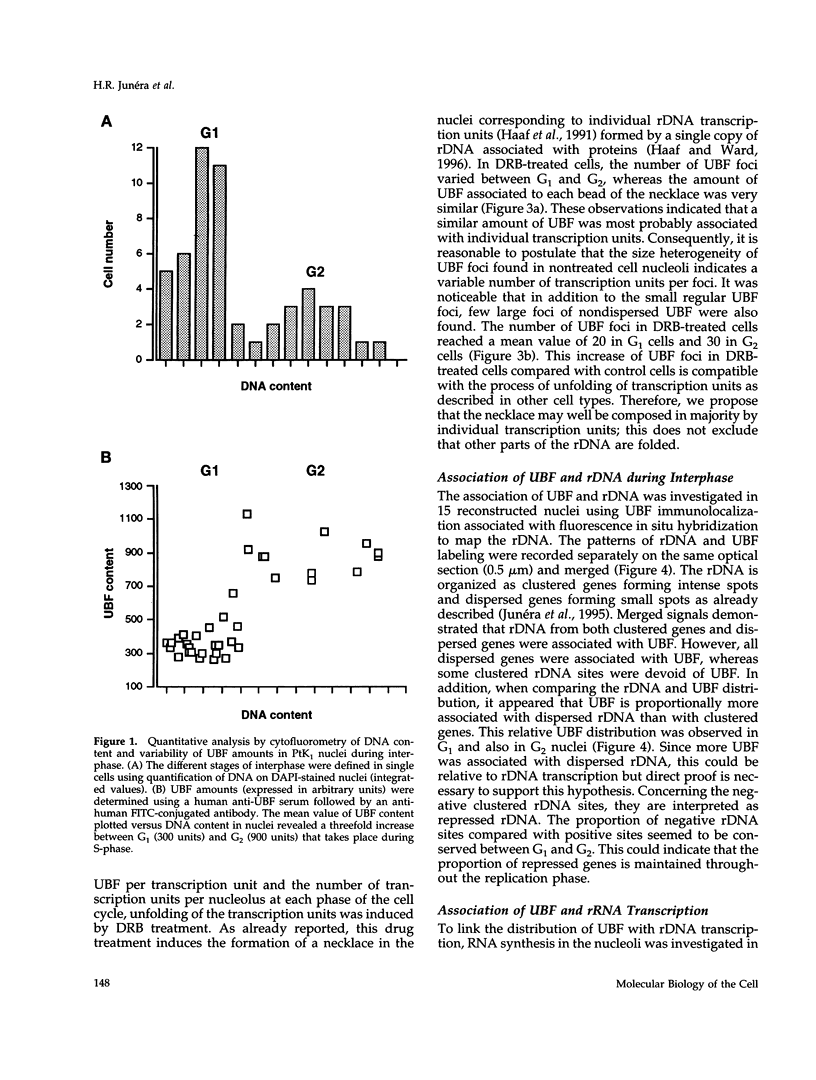
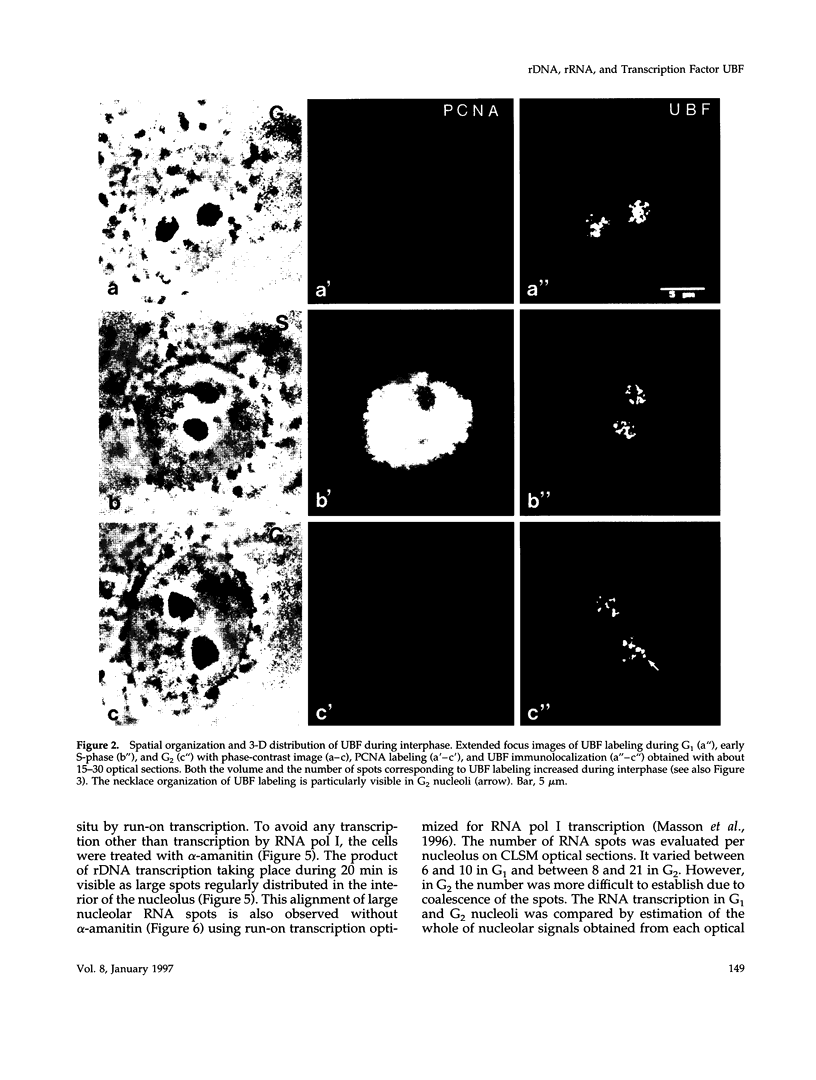
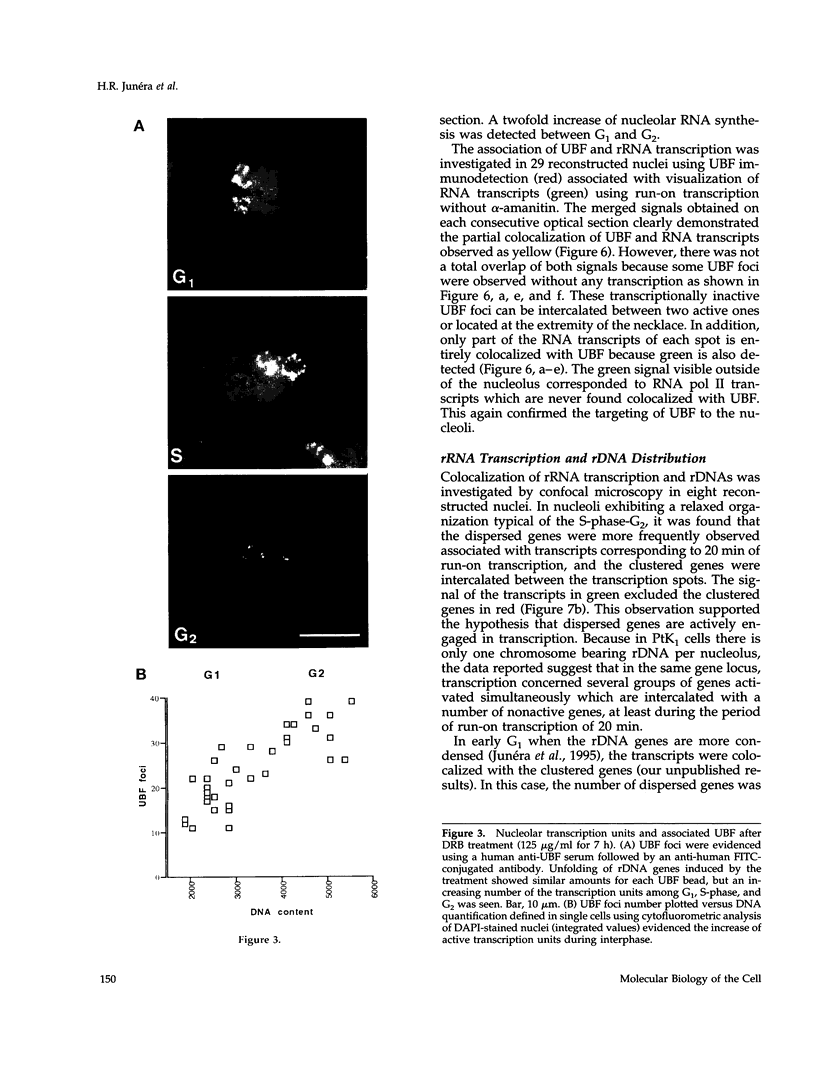
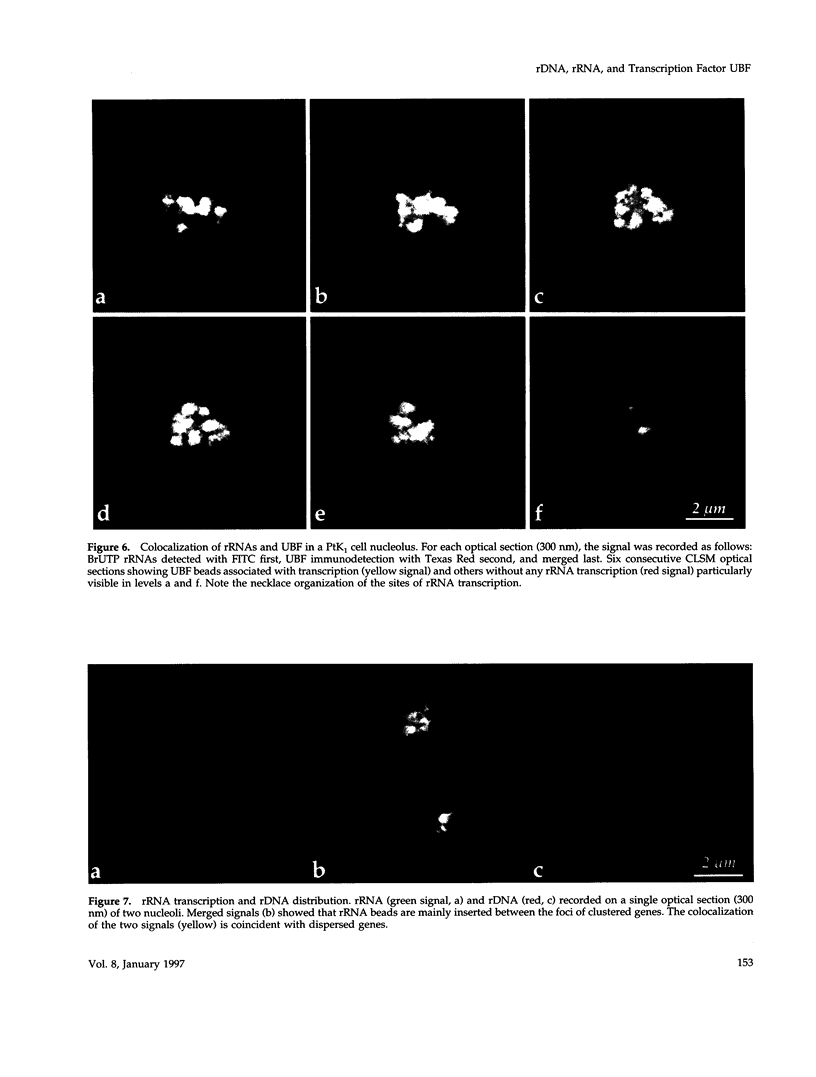
The distribution of the ribosomal genes (rDNA) and the upstream binding factor (UBF), correlatively with their RNA transcripts, was investigated in G1, S-phase, and G2. rDNA was distributed in nucleoli, with alternate sites of clustered and dispersed genes. UBF was found associated with some but not all clustered genes and proportionally more with dispersed genes. It was distributed in several foci that were more numerous and heterogeneous in size during G2 than G1. We suggest that UBF associated with rDNA during S-phase because its nucleolar amount increased during that time and remained stable in G2. 5,6-Dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole treatment indicated a similar amount of UBF per transcription unit, and consequently heterogeneous size of the UBF foci can represent a variable number of transcription units per foci. Direct visualization of the transcripts demonstrated that only part of UBF is associated with active transcription and that rDNA distribution varied with transcription. We propose that in the same rDNA locus three types of configuration coexist that are correlated with gene activity: 1) clustered genes without UBF; 2) clustered genes with UBF, of which some are associated with transcription; and 3) dispersed genes with UBF and transcription. These results support the hypothesis that rDNA transcription involved several steps of regulation acting successively and locally in the same locus to promote the repressed clustered genes to become actively transcribed dispersed genes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazett-Jones D. P., Leblanc B., Herfort M., Moss T. Short-range DNA looping by the Xenopus HMG-box transcription factor, xUBF. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1134–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.8178172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H., Tjian R. Molecular mechanisms governing species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Hempel W. M., Taylor L. J., Rogalsky V., Todorov G., Rothblum L. I. Activity of RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF blocked by Rb gene product. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):177–180. doi: 10.1038/374177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer T., Kurz A., Zirbel R., Dietzel S., Rinke B., Schröck E., Speicher M. R., Mathieu U., Jauch A., Emmerich P. Role of chromosome territories in the functional compartmentalization of the cell nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:777–792. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glibetic M., Taylor L., Larson D., Hannan R., Sells B., Rothblum L. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF is the product of a primary response gene. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4209–4212. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Hayman D. L., Schmid M. Quantitative determination of rDNA transcription units in vertebrate cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Mar;193(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90540-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Ward D. C. Inhibition of RNA polymerase II transcription causes chromatin decondensation, loss of nucleolar structure, and dispersion of chromosomal domains. Exp Cell Res. 1996 Apr 10;224(1):163–173. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannan R. D., Luyken J., Rothblum L. I. Regulation of rDNA transcription factors during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by adrenergic agents. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):8290–8297. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.8290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. C., Hautmann M., Thompson M. M., Rothblum L. I., Haystead T. A., Owens G. K. Angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy of rat vascular smooth muscle is associated with increased 18 S rRNA synthesis and phosphorylation of the rRNA transcription factor, upstream binding factor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):25096–25101. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.25096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatake K., Nishimura T., Maeda Y., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Muramatsu M. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNA and the gene for mouse transcription factor UBF. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4631–4637. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozák P., Cook P. R., Schöfer C., Mosgöller W., Wachtler F. Site of transcription of ribosomal RNA and intranucleolar structure in HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 1994 Feb;107(Pt 2):639–648. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junéra H. R., Masson C., Géraud G., Hernandez-Verdun D. The three-dimensional organization of ribosomal genes and the architecture of the nucleoli vary with G1, S and G2 phases. J Cell Sci. 1995 Nov;108(Pt 11):3427–3441. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.11.3427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. Dual role of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: trans-activator and antirepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. E., Xie W., Glibetic M., O'Mahony D., Sells B. H., Rothblum L. I. Coordinated decreases in rRNA gene transcription factors and rRNA synthesis during muscle cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7933–7936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Carter K. C., Xing X. Probing functional organization within the nucleus: is genome structure integrated with RNA metabolism? Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:807–818. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch A. R., Mosgöller W., Shi M., Heslop-Harrison J. S. Different patterns of rDNA organization at interphase in nuclei of wheat and rye. J Cell Sci. 1992 Apr;101(Pt 4):751–757. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson C., Bouniol C., Fomproix N., Szöllösi M. S., Debey P., Hernandez-Verdun D. Conditions favoring RNA polymerase I transcription in permeabilized cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996 Jul 10;226(1):114–125. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Stefanovsky V. Y. Promotion and regulation of ribosomal transcription in eukaryotes by RNA polymerase I. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1995;50:25–66. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60810-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Hanada K., Maeda Y., Song C. Z., Hisatake K., Muramatsu M. Regulation of mouse UBF gene by multiple growth-related control elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 15;205(2):1217–1225. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam C. D., Copenhaver G. P., Denton M. L., Pikaard C. S. The RNA polymerase I transactivator upstream binding factor requires its dimerization domain and high-mobility-group (HMG) box 1 to bend, wrap, and positively supercoil enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6476–6488. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. J., Shaw P. J. Localization of ribosomal and telomeric DNA sequences in intact plant nuclei by in-situ hybridization and three-dimensional optical microscopy. J Microsc. 1990 Jan;157(Pt 1):83–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb02949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendón M. C., Rodrigo R. M., Goenechea L. G., García-Herdugo G., Valdivia M. M., Moreno F. J. Characterization and immunolocalization of a nucleolar antigen with anti-NOR serum in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90187-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Fortel I., Junéra H. R., Géraud G., Hernandez-Verdun D. Three-dimensional organization of the ribosomal genes and Ag-NOR proteins during interphase and mitosis in PtK1 cells studied by confocal microscopy. Chromosoma. 1993 Feb;102(3):146–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00387729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez J. L., Gelpi C., Juarez C., Hardin J. A. Anti-NOR 90. A new autoantibody in scleroderma that recognizes a 90-kDa component of the nucleolus-organizing region of chromatin. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2579–2584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel P., André C., Comai L., Hernandez-Verdun D. The rDNA transcription machinery is assembled during mitosis in active NORs and absent in inactive NORs. J Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;133(2):235–246. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel P., André C., Masson C., Géraud G., Hernandez-Verdun D. Localization of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor hUBF during the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):327–337. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. J., Highett M. I., Beven A. F., Jordan E. G. The nucleolar architecture of polymerase I transcription and processing. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2896–2906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07289.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Kuhn A., Sander E. E., Grummt I. Activation of mammalian ribosomal gene transcription requires phosphorylation of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Jul 25;23(14):2593–2599. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.14.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Schnapp A., Kuhn A., Rosenbauer H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription factor mUBF is phosphorylated by casein kinase II in the C-terminal hyperacidic tail which is essential for transactivation. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2211–2218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wansink D. G., Schul W., van der Kraan I., van Steensel B., van Driel R., de Jong L. Fluorescent labeling of nascent RNA reveals transcription by RNA polymerase II in domains scattered throughout the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):283–293. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatsepina O. V., Voit R., Grummt I., Spring H., Semenov M. V., Trendelenburg M. F. The RNA polymerase I-specific transcription initiation factor UBF is associated with transcriptionally active and inactive ribosomal genes. Chromosoma. 1993 Nov;102(9):599–611. doi: 10.1007/BF00352307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









