Abstract
Since the time when I was a postdoctoral fellow under the supervision of Dr. Howard Green, then at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, I have been interested in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying growth, differentiation, and development in the mammalian ectoderm. The ectoderm gives rise to epidermal keratinocytes and to neurons, which are the only two cell types of the body that devote most of their protein-synthesizing machinery to developing an elaborate cytoskeletal architecture composed of 10-nm intermediate filaments (IFs). Our interest is in understanding the architecture of the cytoskeleton in keratinocytes and in neurons, and in elucidating how perturbations in this architecture can lead to degenerative diseases of the skin and the nervous system. I will concentrate on the intermediate filament network of the skin and its associated genetic disorders, since this has been a long-standing interest of my laboratory at the University of Chicago.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi U., Cohn J., Buhle L., Gerace L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):560–564. doi: 10.1038/323560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
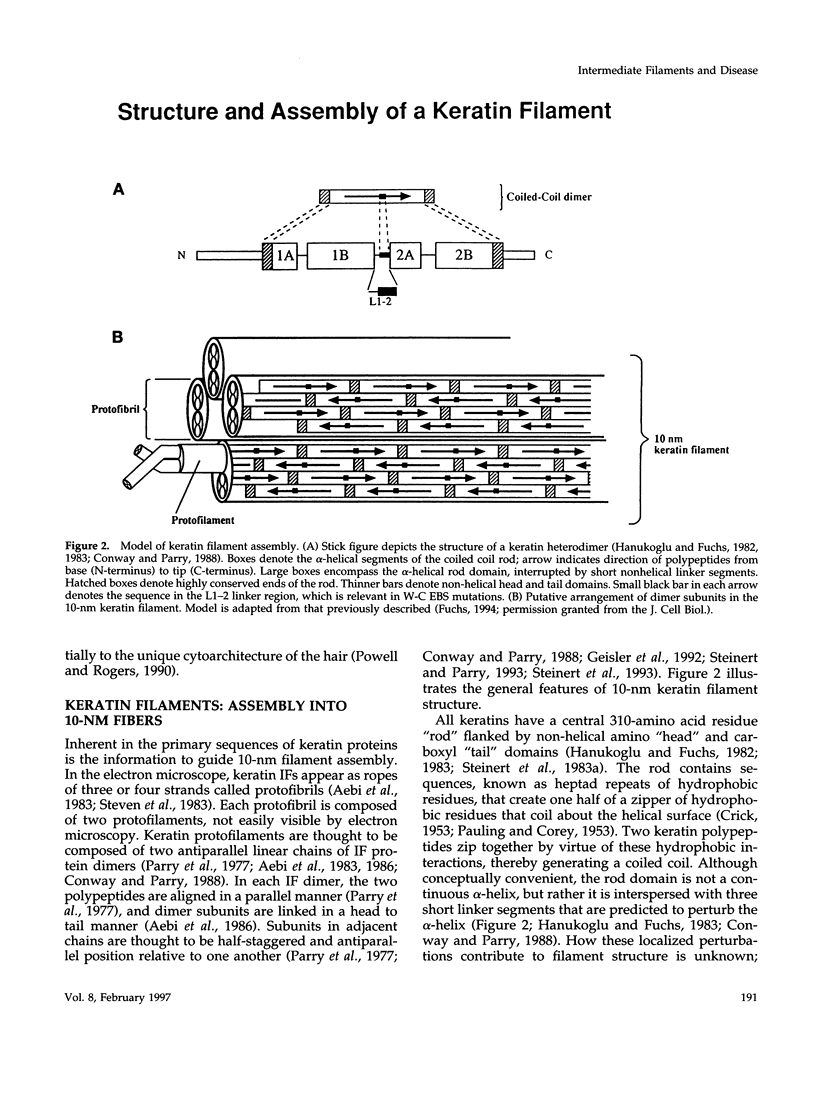
- Aebi U., Fowler W. E., Rew P., Sun T. T. The fibrillar substructure of keratin filaments unraveled. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1131–1143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers K., Fuchs E. Expression of mutant keratin cDNAs in epithelial cells reveals possible mechanisms for initiation and assembly of intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers K., Fuchs E. The expression of mutant epidermal keratin cDNAs transfected in simple epithelial and squamous cell carcinoma lines. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):791–806. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen E., Yu Q. C., Fuchs E. Mice expressing a mutant desmosomal cadherin exhibit abnormalities in desmosomes, proliferation, and epidermal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1367–1382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton-Lamprecht I., Schnyder U. W. Epidermolysis bullosa herpetiformis Dowling-Meara. Report of a case and pathomorphogenesis. Dermatologica. 1982 Apr;164(4):221–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifas J. M., Rothman A. L., Epstein E. H., Jr Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: evidence in two families for keratin gene abnormalities. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1202–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.1720261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden P. E., Haley J. L., Kansky A., Rothnagel J. A., Jones D. O., Turner R. J. Mutation of a type II keratin gene (K6a) in pachyonychia congenita. Nat Genet. 1995 Jul;10(3):363–365. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Bernier G., Mathieu M., Rossant J., Kothary R. The mouse dystonia musculorum gene is a neural isoform of bullous pemphigoid antigen 1. Nat Genet. 1995 Jul;10(3):301–306. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. M., Cheng J., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr, Niemi K. M., Fuchs E. Genetic analysis of a severe case of Dowling-Meara epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Feb;106(2):327–334. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12342985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. M., Yu Q. C., Fine J. D., Fuchs E. The genetic basis of Weber-Cockayne epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7414–7418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. M., Yu Q. C., LeBlanc-Straceski J., Christiano A., Pulkkinen L., Kucherlapati R. S., Uitto J., Fuchs E. Mutations in the non-helical linker segment L1-2 of keratin 5 in patients with Weber-Cockayne epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Cell Sci. 1994 Apr;107(Pt 4):765–774. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.4.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y., Anton-Lamprecht I., Yu Q. C., Jäckel A., Zabel B., Ernst J. P., Fuchs E. A human keratin 14 "knockout": the absence of K14 leads to severe epidermolysis bullosa simplex and a function for an intermediate filament protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2574–2587. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Bonifas J. M., Matsumura K., Ikeda S., Leyden W. A., Epstein E. H., Jr Keratin 14 gene mutations in patients with epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Oct;105(4):629–632. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12323846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J., Syder A. J., Yu Q. C., Letai A., Paller A. S., Fuchs E. The genetic basis of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: a disorder of differentiation-specific epidermal keratin genes. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipev C. C., Korge B. P., Markova N., Bale S. J., DiGiovanna J. J., Compton J. G., Steinert P. M. A leucine----proline mutation in the H1 subdomain of keratin 1 causes epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Uitto J. Molecular complexity of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Revelations from the paradigms of epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol. 1996 Feb;5(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
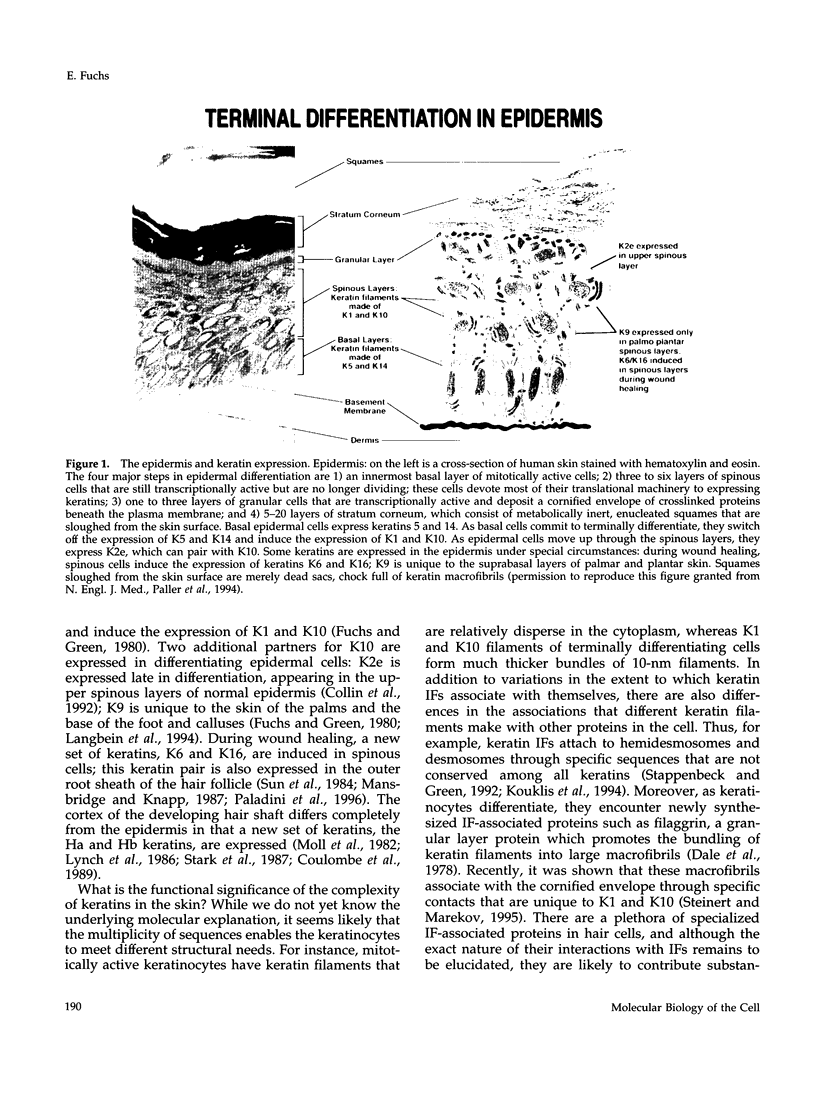
- Collin C., Moll R., Kubicka S., Ouhayoun J. P., Franke W. W. Characterization of human cytokeratin 2, an epidermal cytoskeletal protein synthesized late during differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Sep;202(1):132–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., DiGiovanna J. J., Santucci S. K., Kearns K. S., Amos C. I., Abangan D. L., Korge B. P., McBride O. W., Steinert P. M., Bale S. J. Linkage of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis to the type II keratin gene cluster on chromosome 12q. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):301–305. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Chan Y. M., Albers K., Fuchs E. Deletions in epidermal keratins leading to alterations in filament organization in vivo and in intermediate filament assembly in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3049–3064. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Hutton M. E., Letai A., Hebert A., Paller A. S., Fuchs E. Point mutations in human keratin 14 genes of epidermolysis bullosa simplex patients: genetic and functional analyses. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1301–1311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90051-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Hutton M. E., Vassar R., Fuchs E. A function for keratins and a common thread among different types of epidermolysis bullosa simplex diseases. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1661–1674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Kopan R., Fuchs E. Expression of keratin K14 in the epidermis and hair follicle: insights into complex programs of differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2295–2312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté F., Collard J. F., Julien J. P. Progressive neuronopathy in transgenic mice expressing the human neurofilament heavy gene: a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90158-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Holbrook K. A., Steinert P. M. Assembly of stratum corneum basic protein and keratin filaments in macrofibrils. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):729–731. doi: 10.1038/276729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong W., Ryynänen M., Uitto J. Identification of a leucine-to-proline mutation in the keratin 5 gene in a family with the generalized Köbner type of epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(2):94–102. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J., Yu Q. C., Fuchs E. Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;134(2):559–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. V., Coppock S. M., Green H., Cleveland D. W. Two distinct classes of keratin genes and their evolutionary significance. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Byrne C. The epidermis: rising to the surface. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Oct;4(5):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Esteves R. A., Coulombe P. A. Transgenic mice expressing a mutant keratin 10 gene reveal the likely genetic basis for epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6906–6910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Intermediate filaments and disease: mutations that cripple cell strength. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):511–516. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Keratins and the skin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:123–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Weber K. Intermediate filaments: structure, dynamics, function, and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:345–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gache Y., Chavanas S., Lacour J. P., Wiche G., Owaribe K., Meneguzzi G., Ortonne J. P. Defective expression of plectin/HD1 in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1996 May 15;97(10):2289–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI118671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod D. R. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):30–40. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Schünemann J., Weber K. Chemical cross-linking indicates a staggered and antiparallel protofilament of desmin intermediate filaments and characterizes one higher-level complex between protofilaments. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):841–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges-Labouesse E., Messaddeq N., Yehia G., Cadalbert L., Dierich A., Le Meur M. Absence of integrin alpha 6 leads to epidermolysis bullosa and neonatal death in mice. Nat Genet. 1996 Jul;13(3):370–373. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L., Degenstein L., Dowling J., Yu Q. C., Wollmann R., Perman B., Fuchs E. Gene targeting of BPAG1: abnormalities in mechanical strength and cell migration in stratified epithelia and neurologic degeneration. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld M., Weber K. Modulation of keratin intermediate filament assembly by single amino acid exchanges in the consensus sequence at the C-terminal end of the rod domain. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):351–362. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld M., Weber K. The coiled coil of in vitro assembled keratin filaments is a heterodimer of type I and II keratins: use of site-specific mutagenesis and recombinant protein expression. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1199–1210. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy E., Holmes S. C., Belgaid C. E., Stephenson A. M., Mclean W. H., Rees J. L., Munro C. S. A gene for monilethrix is closely linked to the type II keratin gene cluster at 12q13. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2399–2402. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovnanian A., Pollack E., Hilal L., Rochat A., Prost C., Barrandon Y., Goossens M. A missense mutation in the rod domain of keratin 14 associated with recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):327–332. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. M., Sheils D. M., Farrar G. J., Kumar-Singh R., Kenna P. F., Mansergh F. C., Jordan S. A., Young M., Humphries P. A mutation (Met-->Arg) in the type I keratin (K14) gene responsible for autosomal dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(1):37–42. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly P., Thomine E., Gilbert D., Verdier S., Delpech A., Prost C., Lebbe C., Lauret P., Tron F. Overlapping distribution of autoantibody specificities in paraneoplastic pemphigus and pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jul;103(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12389680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman M. F., Heeres K., Pas H. H., van Luyn M. J., Elema J. D., Corden L. D., Smith F. J., McLean W. H., Ramaekers F. C., Burton M. Effects of keratin 14 ablation on the clinical and cellular phenotype in a kindred with recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Nov;107(5):764–769. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12365805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimonis V., DiGiovanna J. J., Yang J. M., Doyle S. Z., Bale S. J., Compton J. G. A mutation in the V1 end domain of keratin 1 in non-epidermolytic palmar-plantar keratoderma. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Dec;103(6):764–769. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12412771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima Y., Inoue S., Yaoita H. Abnormal organization of keratin intermediate filaments in cultured keratinocytes of epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281(1):5–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00424265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouklis P. D., Hutton E., Fuchs E. Making a connection: direct binding between keratin intermediate filaments and desmosomal proteins. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):1049–1060. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer H., Zeeuwen P., McLean W. H., Mariman E. C., Lane E. B., van de Kerkhof C. M., Ropers H. H., Steijlen P. M. Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens is caused by mutations in the keratin 2e gene. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Sep;103(3):286–289. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12394414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku N. O., Michie S., Oshima R. G., Omary M. B. Chronic hepatitis, hepatocyte fragility, and increased soluble phosphoglycokeratins in transgenic mice expressing a keratin 18 conserved arginine mutant. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(5):1303–1314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.5.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Rugg E. L., Navsaria H., Leigh I. M., Heagerty A. H., Ishida-Yamamoto A., Eady R. A. A mutation in the conserved helix termination peptide of keratin 5 in hereditary skin blistering. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):244–246. doi: 10.1038/356244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langbein L., Heid H. W., Moll I., Franke W. W. Molecular characterization of the body site-specific human epidermal cytokeratin 9: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence, and tissue specificity of gene expression. Differentiation. 1994 Jan;55(2):164–164. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1994.5520164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letai A., Coulombe P. A., Fuchs E. Do the ends justify the mean? Proline mutations at the ends of the keratin coiled-coil rod segment are more disruptive than internal mutations. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1181–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letai A., Coulombe P. A., McCormick M. B., Yu Q. C., Hutton E., Fuchs E. Disease severity correlates with position of keratin point mutations in patients with epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3197–3201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd C., Yu Q. C., Cheng J., Turksen K., Degenstein L., Hutton E., Fuchs E. The basal keratin network of stratified squamous epithelia: defining K15 function in the absence of K14. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(5):1329–1344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.5.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Lane E. B. Retrovirus-mediated transgenic keratin expression in cultured fibroblasts: specific domain functions in keratin stabilization and filament formation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):681–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90114-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M. H., O'Guin W. M., Hardy C., Mak L., Sun T. T. Acidic and basic hair/nail ("hard") keratins: their colocalization in upper cortical and cuticle cells of the human hair follicle and their relationship to "soft" keratins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2593–2606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansbridge J. N., Knapp A. M. Changes in keratinocyte maturation during wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Sep;89(3):253–263. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12471216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean W. H., Morley S. M., Lane E. B., Eady R. A., Griffiths W. A., Paige D. G., Harper J. I., Higgins C., Leigh I. M. Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens--a disease involving keratin 2e. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Sep;103(3):277–281. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12394307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean W. H., Pulkkinen L., Smith F. J., Rugg E. L., Lane E. B., Bullrich F., Burgeson R. E., Amano S., Hudson D. L., Owaribe K. Loss of plectin causes epidermolysis bullosa with muscular dystrophy: cDNA cloning and genomic organization. Genes Dev. 1996 Jul 15;10(14):1724–1735. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.14.1724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean W. H., Rugg E. L., Lunny D. P., Morley S. M., Lane E. B., Swensson O., Dopping-Hepenstal P. J., Griffiths W. A., Eady R. A., Higgins C. Keratin 16 and keratin 17 mutations cause pachyonychia congenita. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):273–278. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Seperack P. K., Strobel M. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Novel myosin heavy chain encoded by murine dilute coat colour locus. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):709–713. doi: 10.1038/349709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Berger F. G., Cox D. R., Crosby J. L., Davisson M. T., Ferrara D., Fuchs E., Hart C., Hunihan L., Lalley P. A. A family of type I keratin genes and the homeobox-2 gene complex are closely linked to the rex locus on mouse chromosome 11. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):454–462. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Sun T. T. The 50- and 58-kdalton keratin classes as molecular markers for stratified squamous epithelia: cell culture studies. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):244–251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owaribe K., Kartenbeck J., Stumpp S., Magin T. M., Krieg T., Diaz L. A., Franke W. W. The hemidesmosomal plaque. I. Characterization of a major constituent protein as a differentiation marker for certain forms of epithelia. Differentiation. 1990 Dec;45(3):207–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B. Compound helical configurations of polypeptide chains: structure of proteins of the alpha-keratin type. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):59–61. doi: 10.1038/171059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paladini R. D., Takahashi K., Bravo N. S., Coulombe P. A. Onset of re-epithelialization after skin injury correlates with a reorganization of keratin filaments in wound edge keratinocytes: defining a potential role for keratin 16. J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;132(3):381–397. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paller A. S., Syder A. J., Chan Y. M., Yu Q. C., Hutton E., Tadini G., Fuchs E. Genetic and clinical mosaicism in a type of epidermal nevus. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 24;331(21):1408–1415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411243312103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Crewther W. G., Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P. Structure of alpha-keratin: structural implication of the amino acid sequences of the type I and type II chain segments. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 25;113(2):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell B. C., Rogers G. E. Cyclic hair-loss and regrowth in transgenic mice overexpressing an intermediate filament gene. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1485–1493. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis A., Hennies H. C., Langbein L., Digweed M., Mischke D., Drechsler M., Schröck E., Royer-Pokora B., Franke W. W., Sperling K. Keratin 9 gene mutations in epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (EPPK). Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):174–179. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard G., De Laurenzi V., Didona B., Bale S. J., Compton J. G. Keratin 13 point mutation underlies the hereditary mucosal epithelial disorder white sponge nevus. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):453–455. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Fuchs E., Le Beau M. M., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B. Three epidermal and one simple epithelial type II keratin genes map to human chromosome 12. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;57(1):33–38. doi: 10.1159/000133109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., RayChaudhury A., Shows T. B., Le Beau M. M., Fuchs E. A group of type I keratin genes on human chromosome 17: characterization and expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):722–736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothnagel J. A., Dominey A. M., Dempsey L. D., Longley M. A., Greenhalgh D. A., Gagne T. A., Huber M., Frenk E., Hohl D., Roop D. R. Mutations in the rod domains of keratins 1 and 10 in epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1128–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothnagel J. A., Traupe H., Wojcik S., Huber M., Hohl D., Pittelkow M. R., Saeki H., Ishibashi Y., Roop D. R. Mutations in the rod domain of keratin 2e in patients with ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens. Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):485–490. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugg E. L., McLean W. H., Allison W. E., Lunny D. P., Macleod R. I., Felix D. H., Lane E. B., Munro C. S. A mutation in the mucosal keratin K4 is associated with oral white sponge nevus. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):450–452. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugg E. L., McLean W. H., Lane E. B., Pitera R., McMillan J. R., Dopping-Hepenstal P. J., Navsaria H. A., Leigh I. M., Eady R. A. A functional "knockout" of human keratin 14. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2563–2573. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugg E. L., Morley S. M., Smith F. J., Boxer M., Tidman M. J., Navsaria H., Leigh I. M., Lane E. B. Missing links: Weber-Cockayne keratin mutations implicate the L12 linker domain in effective cytoskeleton function. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):294–300. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhrberg C., Hajibagheri M. A., Simon M., Dooley T. P., Watt F. M. Envoplakin, a novel precursor of the cornified envelope that has homology to desmoplakin. J Cell Biol. 1996 Aug;134(3):715–729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.3.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. J., Eady R. A., Leigh I. M., McMillan J. R., Rugg E. L., Kelsell D. P., Bryant S. P., Spurr N. K., Geddes J. F., Kirtschig G. Plectin deficiency results in muscular dystrophy with epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):450–457. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R. Cell adhesion molecules as targets of autoantibodies in pemphigus and pemphigoid, bullous diseases due to defective epidermal cell adhesion. Adv Immunol. 1993;53:291–325. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60503-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stappenbeck T. S., Green K. J. The desmoplakin carboxyl terminus coaligns with and specifically disrupts intermediate filament networks when expressed in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1197–1209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark H. J., Breitkreutz D., Limat A., Bowden P., Fusenig N. E. Keratins of the human hair follicle: "hyperproliferative" keratins consistently expressed in outer root sheath cells in vivo and in vitro. Differentiation. 1987;35(3):236–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Marekov L. N., Fraser R. D., Parry D. A. Keratin intermediate filament structure. Crosslinking studies yield quantitative information on molecular dimensions and mechanism of assembly. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):436–452. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Marekov L. N. The proteins elafin, filaggrin, keratin intermediate filaments, loricrin, and small proline-rich proteins 1 and 2 are isodipeptide cross-linked components of the human epidermal cornified cell envelope. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17702–17711. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.17702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. Structural features of epidermal keratin filaments reassembled in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):86s–90s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M. The two-chain coiled-coil molecule of native epidermal keratin intermediate filaments is a type I-type II heterodimer. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8766–8774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Sybert V. P., Wijsman E. M., Ehrlich P., Spencer A. A keratin 14 mutational hot spot for epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Dowling-Meara: implications for diagnosis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Aug;101(2):240–243. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12365079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Hainfeld J. F., Trus B. L., Wall J. S., Steinert P. M. Epidermal keratin filaments assembled in vitro have masses-per-unit-length that scale according to average subunit mass: structural basis for homologous packing of subunits in intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1939–1944. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens H. P., Kelsell D. P., Bryant S. P., Bishop D. T., Dawber R. P., Spurr N. K., Leigh I. M. Linkage of monilethrix to the trichocyte and epithelial keratin gene cluster on 12q11-q13. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Apr;106(4):795–797. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12346400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syder A. J., Yu Q. C., Paller A. S., Giudice G., Pearson R., Fuchs E. Genetic mutations in the K1 and K10 genes of patients with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Correlation between location and disease severity. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1533–1542. doi: 10.1172/JCI117132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchard D., Blanchet-Bardon C., Serova O., Langbein L., Narod S., Janin N., Goguel A. F., Bernheim A., Franke W. W., Lenoir G. M. Epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma cosegregates with a keratin 9 mutation in a pedigree with breast and ovarian cancer. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):106–110. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttam J., Hutton E., Coulombe P. A., Anton-Lamprecht I., Yu Q. C., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr, Fine J. D., Fuchs E. The genetic basis of epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 20;93(17):9079–9084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.9079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Coulombe P. A., Degenstein L., Albers K., Fuchs E. Mutant keratin expression in transgenic mice causes marked abnormalities resembling a human genetic skin disease. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):365–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90645-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Rosenberg M., Ross S., Tyner A., Fuchs E. Tissue-specific and differentiation-specific expression of a human K14 keratin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1563–1567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal F., Aberdam D., Miquel C., Christiano A. M., Pulkkinen L., Uitto J., Ortonne J. P., Meneguzzi G. Integrin beta 4 mutations associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nat Genet. 1995 Jun;10(2):229–234. doi: 10.1038/ng0695-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Gromov D., Donovan A., Castañn M. J., Fuchs E. Expression of plectin mutant cDNA in cultured cells indicates a role of COOH-terminal domain in intermediate filament association. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):607–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. K., Coulombe P. A., Fuchs E. The roles of K5 and K14 head, tail, and R/K L L E G E domains in keratin filament assembly in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):401–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z., Cork L. C., Griffin J. W., Cleveland D. W. Increased expression of neurofilament subunit NF-L produces morphological alterations that resemble the pathology of human motor neuron disease. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90157-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Matsuki M., Konishi K., Yasuno H. A novel mutation of Leu122 to Phe at a highly conserved hydrophobic residue in the helix initiation motif of keratin 14 in epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jul;3(7):1171–1172. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.7.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Dowling J., Yu Q. C., Kouklis P., Cleveland D. W., Fuchs E. An essential cytoskeletal linker protein connecting actin microfilaments to intermediate filaments. Cell. 1996 Aug 23;86(4):655–665. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Neut R., Krimpenfort P., Calafat J., Niessen C. M., Sonnenberg A. Epithelial detachment due to absence of hemidesmosomes in integrin beta 4 null mice. Nat Genet. 1996 Jul;13(3):366–369. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]