Abstract
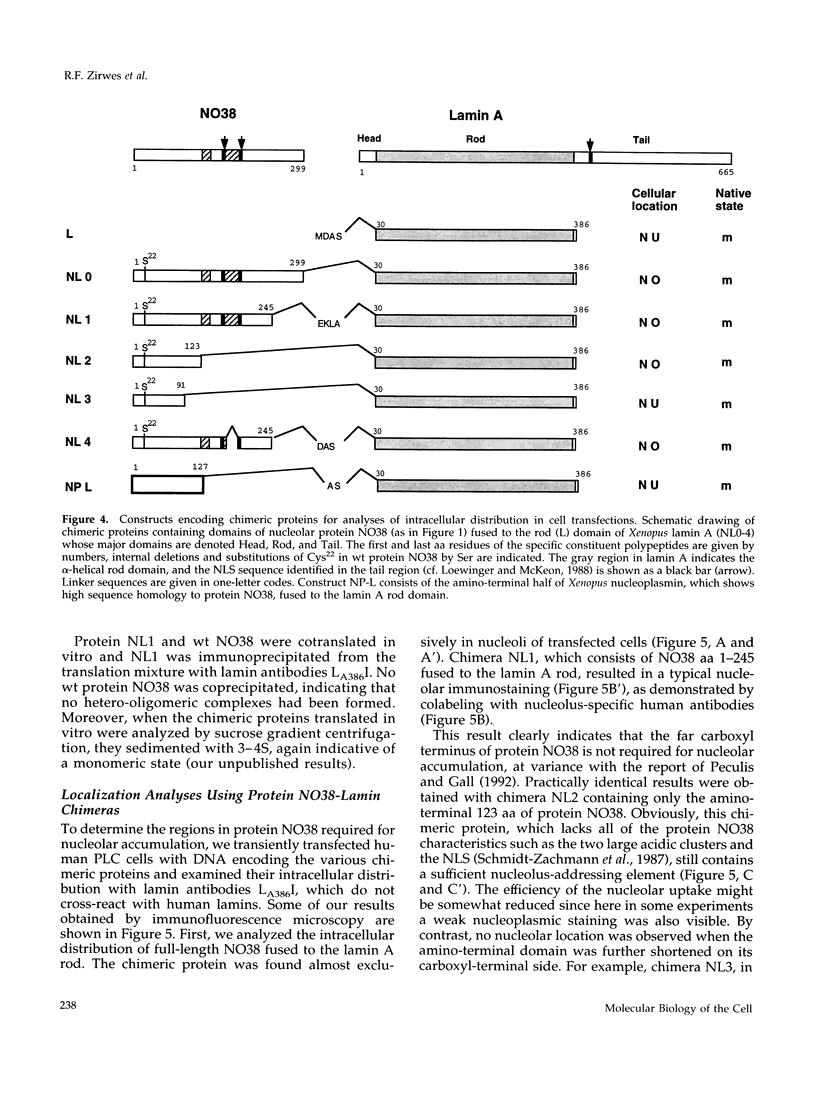
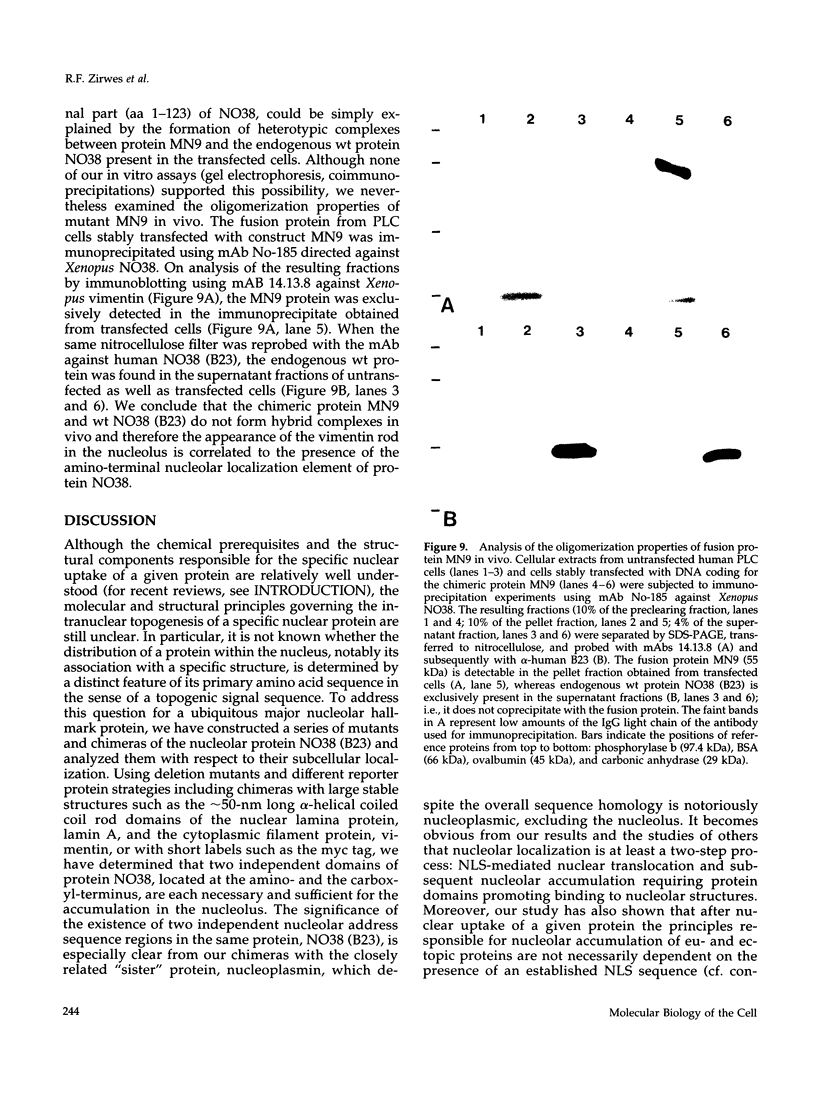
To identify the element(s) in nucleolar proteins which determine nucleolus-specific topogenesis, we have used different kinds of cDNA constructs encoding various chimeric combinations of mutants of the constitutive nucleolar protein NO38 (B23): 1) with an amino terminally placed short "myc tag"; 2) with two different carboxyl terminally attached large alpha-helical coiled coil structures, the lamin A rod domain or the rod domain of vimentin; 3) with the sequence-related nucleoplasmic histone-binding protein nucleo-plasmin; and 4) with the soluble cytoplasmic protein pyruvate kinase. To avoid the problem of formation of complexes with endogenous wild-type (wt) molecules and "piggyback" localization, special care was taken to secure that the mutants and chimeras used did not oligomerize as is typical of protein NO38 (B23). Using microinjection and transfection of cultured cells, we found that the segment comprising the amino-terminal 123 amino acids (aa) alone was sufficient to effect nucleolar accumulation of the construct molecules, including the chimeras with the entire rod domains of lamin A and vimentin. However, when the amino-terminal 109 aa were deleted, the molecules still associated with the nucleolus. The results of further deletion experiments and of domain swaps with nucleoplasmin all point to the topogenic importance of two independent molecular regions located at both the amino- and carboxyl-terminal end. Our definition of dominant elements determining the nucleolar localization of protein NO38 (B23) as well as of diverse nonnucleolar proteins will help to identify its local binding partner(s) and functions, the construction of probes examining other proteins or sequence elements within the nucleolar microenvironment, and the generation of cells with an altered nuclear architecture.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Gerace L. Cytosolic proteins that specifically bind nuclear location signals are receptors for nuclear import. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):837–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90431-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge W. Improved system for capillary microinjection into living cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jul;140(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader B. L., Magin T. M., Freudenmann M., Stumpp S., Franke W. W. Intermediate filaments formed de novo from tail-less cytokeratins in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1293–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessing M., Rüther U., Franke W. W. Ectopic synthesis of epidermal cytokeratins in pancreatic islet cells of transgenic mice interferes with cytoskeletal order and insulin production. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. K., Aldrich M., Cook R. G., Busch H. Amino acid sequence of protein B23 phosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1868–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. K., Chan W. Y., Yung B. Y., Cook R. G., Aldrich M. B., Ku D., Goldknopf I. L., Busch H. Amino acid sequence of a specific antigenic peptide of protein B23. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14335–14341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. K. Characterization and cellular localization of nucleophosmin/B23 in HeLa cells treated with selected cytotoxic agents (studies of B23-translocation mechanism). Exp Cell Res. 1992 Nov;203(1):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90053-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. K., Liu Q. R., Durban E. The major phosphorylation site of nucleophosmin (B23) is phosphorylated by a nuclear kinase II. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):549–552. doi: 10.1042/bj2700549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. Y., Liu Q. R., Borjigin J., Busch H., Rennert O. M., Tease L. A., Chan P. K. Characterization of the cDNA encoding human nucleophosmin and studies of its role in normal and abnormal growth. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1033–1039. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. H., Olson M. O. A single gene codes for two forms of rat nucleolar protein B23 mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11732–11737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Travers A. A. Protein motifs that recognize structural features of DNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Identification of sequences important in the nucleolar localization of human immunodeficiency virus Rev: relevance of nucleolar localization to function. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):881–885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.881-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créancier L., Prats H., Zanibellato C., Amalric F., Bugler B. Determination of the functional domains involved in nucleolar targeting of nucleolin. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1239–1250. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV tat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18019–18023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Dilworth S. M., Black S. J., Kearsey S. E., Cox L. S., Laskey R. A. Nucleoplasmin cDNA sequence reveals polyglutamic acid tracts and a cluster of sequences homologous to putative nuclear localization signals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckelt A., Herrmann H., Franke W. W. Assembly of a tail-less mutant of the intermediate filament protein, vimentin, in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;58(2):319–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Hurt E. C. Nuclear transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein N., Chan P. K., Mond J. J. Identification of numatrin, the nuclear matrix protein associated with induction of mitogenesis, as the nucleolar protein B23. Implication for the role of the nucleolus in early transduction of mitogenic signals. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10608–10612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Grund C., Osborn M., Weber K. The intermediate-sized filaments in rat kangaroo PtK2 cells. I. Morphology in situ. Cytobiologie. 1978 Aug;17(2):365–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieffers C., Krohne G. In vitro reconstitution of recombinant lamin A and a lamin A mutant lacking the carboxy-terminal tail. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;55(2):191–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P., Bagni C., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Lapeyre B. Identification of a segment of the small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein-associated protein GAR1 that is sufficient for nucleolar accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18499–18506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Mattaj I. W. Nucleocytoplasmic transport. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1513–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E. Isolation of a protein that is essential for the first step of nuclear protein import. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Vogel F., Mills A. D., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A. Distinct functions for the two importin subunits in nuclear protein import. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):246–248. doi: 10.1038/377246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtz D., Tanaka R. A., Hartwig J., McKeon F. The CaaX motif of lamin A functions in conjunction with the nuclear localization signal to target assembly to the nuclear envelope. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90753-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C. Importins/karyopherins meet nucleoporins. Cell. 1996 Feb 23;84(4):509–515. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang C., Sinskey A. J., Lodish H. F. Oxidized redox state of glutathione in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1992 Sep 11;257(5076):1496–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.1523409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügle B., Kleinschmidt J. A., Franke W. W. The 22 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. II. Immunological characterization and localization of their proteins in tissues and cultured cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügle B., Scheer U., Franke W. W. Ribocharin: a nuclear Mr 40,000 protein specific to precursor particles of the large ribosomal subunit. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):615–627. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitten G. T., Nigg E. A. The CaaX motif is required for isoprenylation, carboxyl methylation, and nuclear membrane association of lamin B2. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):13–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Dingwall C., Maier G., Franke W. W. Molecular characterization of a karyophilic, histone-binding protein: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and expression of nuclear protein N1/N2 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3547–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Birchmeier W. Microinjection of fluorescently labeled proteins into living cells with emphasis on cytoskeletal proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;75:209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Waizenegger I., Höger T. H. The conserved carboxy-terminal cysteine of nuclear lamins is essential for lamin association with the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., Stick R., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Differential expression of nuclear lamin proteins during chicken development. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):577–587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Kaiser P., Seiter A., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W., Rehm H., Knaus P., Prior P., Betz H., Reinke H. Synaptophysin: molecular organization and mRNA expression as determined from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3261–3268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Topogenesis and sorting of synaptophysin: synthesis of a synaptic vesicle protein from a gene transfected into nonneuroendocrine cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bingham P. M. Arginine/serine-rich domains of the su(wa) and tra RNA processing regulators target proteins to a subnuclear compartment implicated in splicing. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. R., Chan P. K. Formation of nucleophosmin/B23 oligomers requires both the amino- and the carboxyl-terminal domains of the protein. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 15;200(3):715–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewinger L., McKeon F. Mutations in the nuclear lamin proteins resulting in their aberrant assembly in the cytoplasm. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2301–2309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur H., Walter G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the carboxy terminus of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.483-491.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Hisatake K., Kondo T., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Nishimura T., Muramatsu M. Mouse rRNA gene transcription factor mUBF requires both HMG-box1 and an acidic tail for nucleolar accumulation: molecular analysis of the nucleolar targeting mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3695–3704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makkerh J. P., Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Comparative mutagenesis of nuclear localization signals reveals the importance of neutral and acidic amino acids. Curr Biol. 1996 Aug 1;6(8):1025–1027. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00648-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mears W. E., Lam V., Rice S. A. Identification of nuclear and nucleolar localization signals in the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP27. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):935–947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.935-947.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J., Georgatos S. D. Type B lamins remain associated with the integral nuclear envelope protein p58 during mitosis: implications for nuclear reassembly. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1888–1898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messmer B., Dreyer C. Requirements for nuclear translocation and nucleolar accumulation of nucleolin of Xenopus laevis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;61(2):369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Morimoto R. I. Mutational analysis of the human HSP70 protein: distinct domains for nucleolar localization and adenosine triphosphate binding. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1947–1962. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. A G protein involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport: the role of Ran. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The two steps of nuclear import, targeting to the nuclear envelope and translocation through the nuclear pore, require different cytosolic factors. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90613-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. Use of peptide tagging to detect proteins expressed from cloned genes: deletion mapping functional domains of Drosophila hsp 70. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3087–3093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panté N., Aebi U. Toward the molecular dissection of protein import into nuclei. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;8(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peculis B. A., Gall J. G. Localization of the nucleolar protein NO38 in amphibian oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaye I. K., Toku S., Tanaka T. Sequence requirement for nucleolar localization of rat ribosomal protein L31. Eur J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;69(2):151–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Pollard K. M., Penning C. A., Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Busch H., Tan E. M. Monoclonal autoantibody from a (New Zealand black x New Zealand white)F1 mouse and some human scleroderma sera target an Mr 34,000 nucleolar protein of the U3 RNP particle. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):793–800. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. R., Eckelt A., Nimmrich V., Janssen K. P., Schliwa M., Herrmann H., Franke W. W. Truncation mutagenesis of the non-alpha-helical carboxyterminal tail domain of vimentin reveals contributions to cellular localization but not to filament assembly. Eur J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;66(2):136–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Benavente R. Functional and dynamic aspects of the mammalian nucleolus. Bioessays. 1990 Jan;12(1):14–21. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Weisenberger D. The nucleolus. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):354–359. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Franke W. W. DNA cloning and amino acid sequence determination of a major constituent protein of mammalian nucleoli. Correspondence of the nucleoplasmin-related protein NO38 to mammalian protein B23. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):417–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00303035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Hügle-Dörr B., Franke W. W. A constitutive nucleolar protein identified as a member of the nucleoplasmin family. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1881–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Zachmann M. S., Nigg E. A. Protein localization to the nucleolus: a search for targeting domains in nucleolin. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jul;105(Pt 3):799–806. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Lipsius E., Kruppa J. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting of human ribosomal protein S6. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Dec;6(12):1875–1885. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.12.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Nam S. H., Nosaka T., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Blobel G. The first membrane spanning region of the lamin B receptor is sufficient for sorting to the inner nuclear membrane. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):631–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soullam B., Worman H. J. The amino-terminal domain of the lamin B receptor is a nuclear envelope targeting signal. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stick R., Angres B., Lehner C. F., Nigg E. A. The fates of chicken nuclear lamin proteins during mitosis: evidence for a reversible redistribution of lamin B2 between inner nuclear membrane and elements of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):397–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Dual roles for transcription and translation factors in the RNA storage particles of Xenopus oocytes. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;3(3):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90080-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troyanovsky S. M., Eshkind L. G., Troyanovsky R. B., Leube R. E., Franke W. W. Contributions of cytoplasmic domains of desmosomal cadherins to desmosome assembly and intermediate filament anchorage. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):561–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdez B. C., Perlaky L., Henning D., Saijo Y., Chan P. K., Busch H. Identification of the nuclear and nucleolar localization signals of the protein p120. Interaction with translocation protein B23. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23776–23783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Mélèse T. Multiple regions of NSR1 are sufficient for accumulation of a fusion protein within the nucleolus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1081–1091. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung B. Y., Chan P. K. Identification and characterization of a hexameric form of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 16;925(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]