Abstract
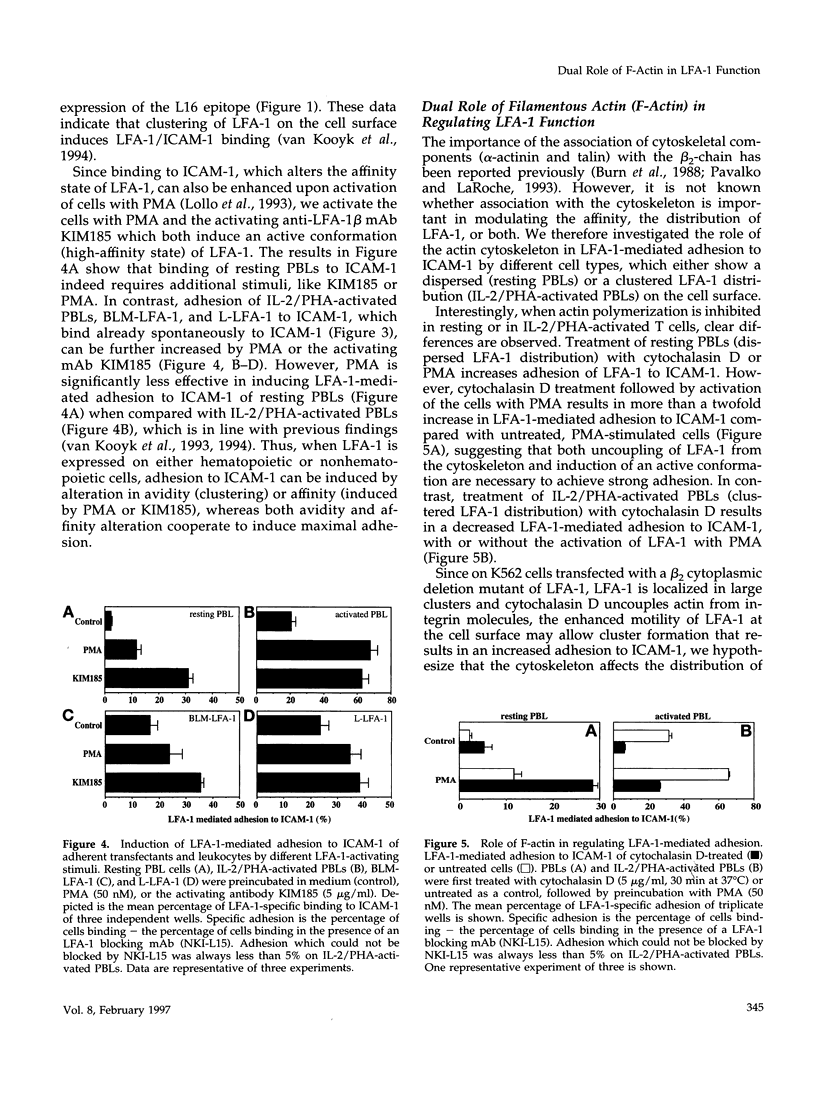
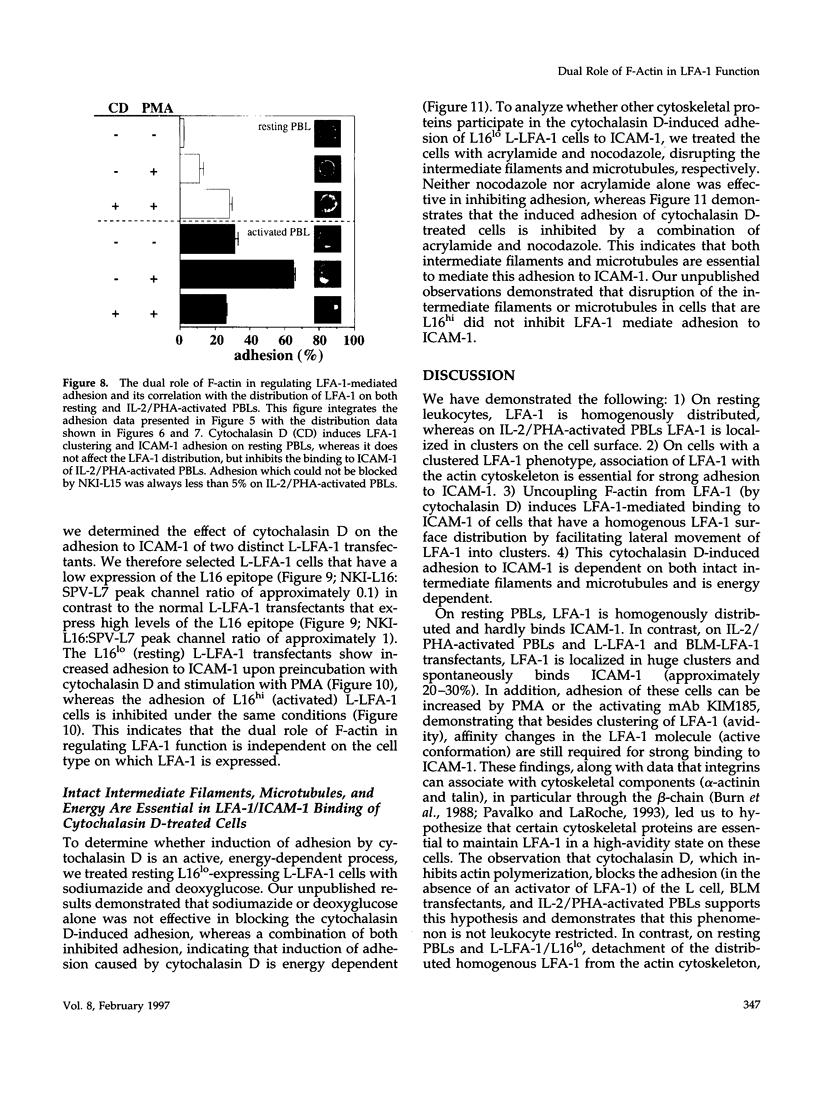
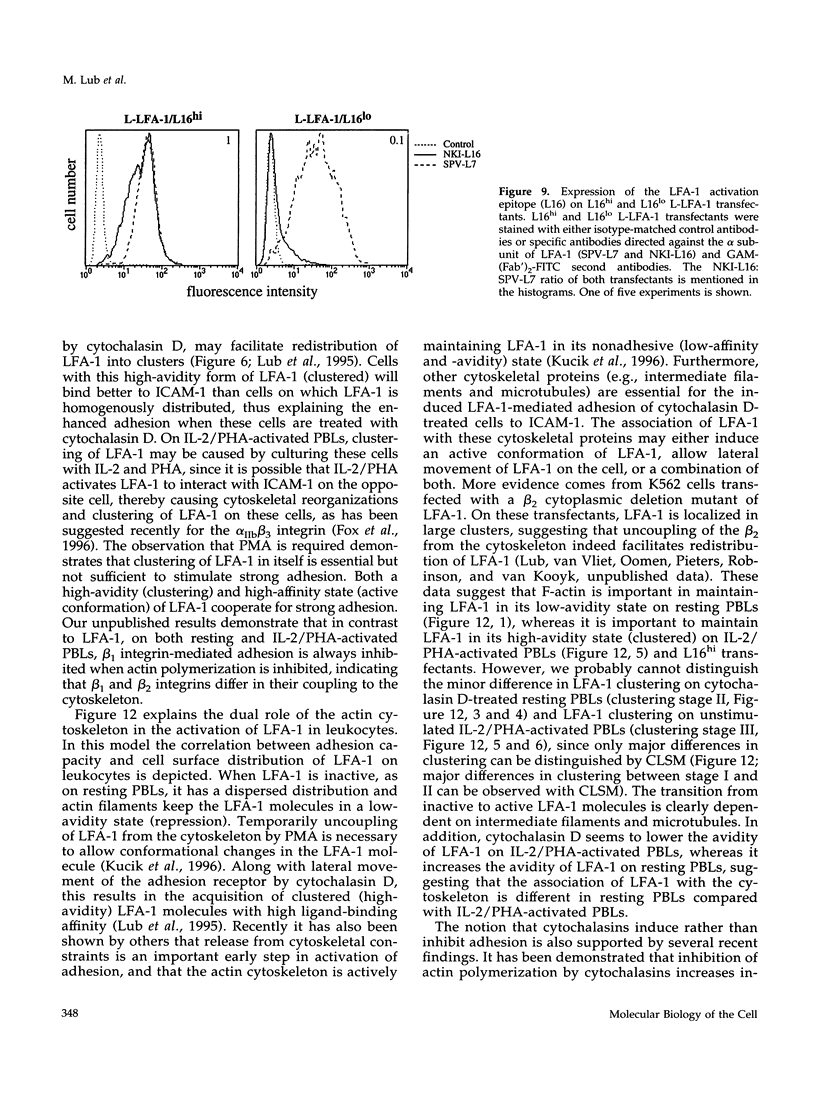
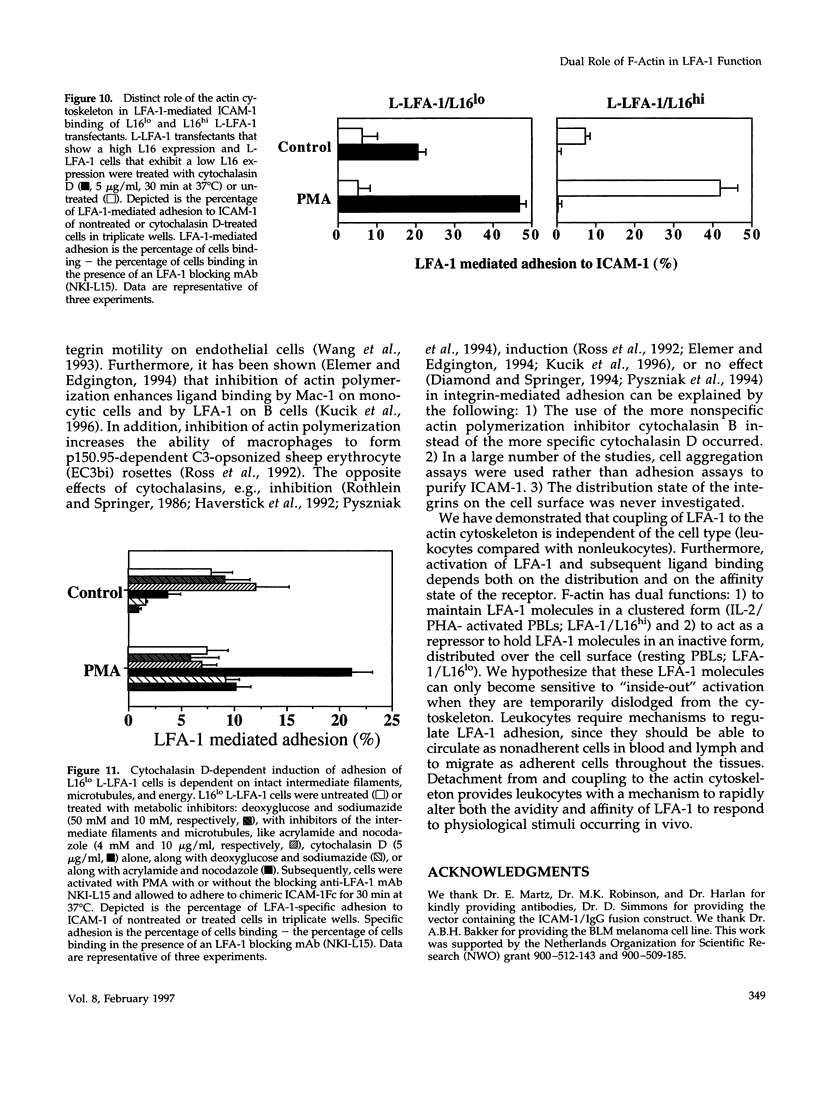
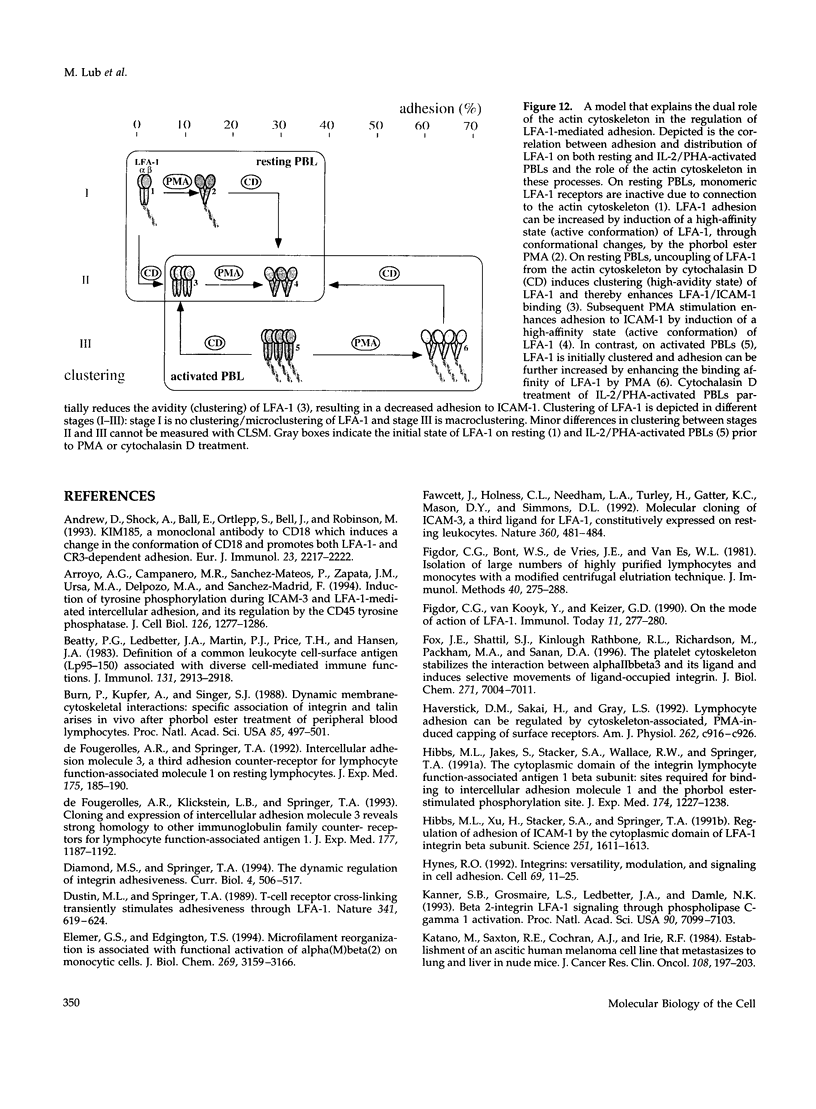
Intracellular signals are required to activate the leukocyte-specific adhesion receptor lymphocyte function-associated molecule-1 (LFA-1; CD11a/CD18) to bind its ligand, intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). In this study, we investigated the role of the cytoskeleton in LFA-1 activation and demonstrate that filamentous actin (F-actin) can both enhance and inhibit LFA-1-mediated adhesion, depending on the distribution of LFA-1 on the cell surface. We observed that LFA-1 is already clustered on the cell surface of interleukin-2/phytohemagglutinin-activated lymphocytes. These cells bind strongly ICAM-1 and disruption of the actin cytoskeleton inhibits adhesion. In contrast to interleukin-2/phytohemagglutinin-activated peripheral blood lymphocytes, resting lymphocytes, which display a homogenous cell surface distribution of LFA-1, respond poorly to intracellular signals to bind ICAM-1, unless the actin cytoskeleton is disrupted. On resting peripheral blood lymphocytes, uncoupling of LFA-1 from the actin cytoskeleton induces clustering of LFA-1 and this, along with induction of a high-affinity form of LFA-1, via "inside-out" signaling, results in enhanced binding to ICAM-1, which is dependent on intact intermediate filaments, microtubules, and metabolic energy. We hypothesize that linkage of LFA-1 to cytoskeletal elements prevents movement of LFA-1 over the cell surface, thus inhibiting clustering and strong ligand binding. Release from these cytoskeletal elements allows lateral movement and activation of LFA-1, resulting in ligand binding and "outside-in" signaling, that subsequently stimulates actin polymerization and stabilizes cell adhesion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew D., Shock A., Ball E., Ortlepp S., Bell J., Robinson M. KIM185, a monoclonal antibody to CD18 which induces a change in the conformation of CD18 and promotes both LFA-1- and CR3-dependent adhesion. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2217–2222. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo A. G., Campanero M. R., Sánchez-Mateos P., Zapata J. M., Ursa M. A., del Pozo M. A., Sánchez-Madrid F. Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation during ICAM-3 and LFA-1-mediated intercellular adhesion, and its regulation by the CD45 tyrosine phosphatase. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1277–1286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty P. G., Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Price T. H., Hansen J. A. Definition of a common leukocyte cell-surface antigen (Lp95-150) associated with diverse cell-mediated immune functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2913–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn P., Kupfer A., Singer S. J. Dynamic membrane-cytoskeletal interactions: specific association of integrin and talin arises in vivo after phorbol ester treatment of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Springer T. A. The dynamic regulation of integrin adhesiveness. Curr Biol. 1994 Jun 1;4(6):506–517. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elemer G. S., Edgington T. S. Microfilament reorganization is associated with functional activation of alpha M beta 2 on monocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3159–3166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett J., Holness C. L., Needham L. A., Turley H., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y., Simmons D. L. Molecular cloning of ICAM-3, a third ligand for LFA-1, constitutively expressed on resting leukocytes. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):481–484. doi: 10.1038/360481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figdor C. G., Bont W. S., De Vries J. E., Van Es W. L. Isolation of large numbers of highly purified lymphocytes and monocytes with a modified centrifugal elutriation technique. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(3):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figdor C. G., van Kooyk Y., Keizer G. D. On the mode of action of LFA-1. Immunol Today. 1990 Aug;11(8):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90112-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Shattil S. J., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Richardson M., Packham M. A., Sanan D. A. The platelet cytoskeleton stabilizes the interaction between alphaIIbbeta3 and its ligand and induces selective movements of ligand-occupied integrin. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):7004–7011. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.7004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Sakai H., Gray L. S. Lymphocyte adhesion can be regulated by cytoskeleton-associated, PMA-induced capping of surface receptors. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C916–C926. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Jakes S., Stacker S. A., Wallace R. W., Springer T. A. The cytoplasmic domain of the integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 beta subunit: sites required for binding to intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and the phorbol ester-stimulated phosphorylation site. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Xu H., Stacker S. A., Springer T. A. Regulation of adhesion of ICAM-1 by the cytoplasmic domain of LFA-1 integrin beta subunit. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1611–1613. doi: 10.1126/science.1672776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Grosmaire L. S., Ledbetter J. A., Damle N. K. Beta 2-integrin LFA-1 signaling through phospholipase C-gamma 1 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7099–7103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katano M., Saxton R. E., Cochran A. J., Irie R. F. Establishment of an ascitic human melanoma cell line that metastasizes to lung and liver in nude mice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1984;108(2):197–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00402467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer G. D., Borst J., Figdor C. G., Spits H., Miedema F., Terhorst C., De Vries J. E. Biochemical and functional characteristics of the human leukocyte membrane antigen family LFA-1, Mo-1 and p150,95. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Nov;15(11):1142–1148. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer G. D., Visser W., Vliem M., Figdor C. G. A monoclonal antibody (NKI-L16) directed against a unique epitope on the alpha-chain of human leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 induces homotypic cell-cell interactions. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1393–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucik D. F., Dustin M. L., Miller J. M., Brown E. J. Adhesion-activating phorbol ester increases the mobility of leukocyte integrin LFA-1 in cultured lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1996 May 1;97(9):2139–2144. doi: 10.1172/JCI118651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kürzinger K., Reynolds T., Germain R. N., Davignon D., Martz E., Springer T. A. A novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1): cellular distribution, quantitative expression, and structure. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis R. C., Bennett R. I., Hogg N. A novel LFA-1 activation epitope maps to the I domain. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1519–1527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollo B. A., Chan K. W., Hanson E. M., Moy V. T., Brian A. A. Direct evidence for two affinity states for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 on activated T cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21693–21700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lub M., van Kooyk Y., Figdor C. G. Ins and outs of LFA-1. Immunol Today. 1995 Oct;16(10):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. LFA-1 and other accessory molecules functioning in adhesions of T and B lymphocytes. Hum Immunol. 1987 Jan;18(1):3–37. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavalko F. M., LaRoche S. M. Activation of human neutrophils induces an interaction between the integrin beta 2-subunit (CD18) and the actin binding protein alpha-actinin. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3795–3807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter K., O'Toole T. E. Modulation of cell adhesion by changes in alpha L beta 2 (LFA-1, CD11a/CD18) cytoplasmic domain/cytoskeleton interaction. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):315–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyszniak A. M., Welder C. A., Takei F. Cell surface distribution of high-avidity LFA-1 detected by soluble ICAM-1-coated microspheres. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5241–5249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. K., Andrew D., Rosen H., Brown D., Ortlepp S., Stephens P., Butcher E. C. Antibody against the Leu-CAM beta-chain (CD18) promotes both LFA-1- and CR3-dependent adhesion events. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1080–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Reed W., Dalzell J. G., Becker S. E., Hogg N. Macrophage cytoskeleton association with CR3 and CR4 regulates receptor mobility and phagocytosis of iC3b-opsonized erythrocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Feb;51(2):109–117. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Springer T. A. The requirement for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 in homotypic leukocyte adhesion stimulated by phorbol ester. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1132–1149. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Krensky A. M., Ware C. F., Robbins E., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Springer T. A. Three distinct antigens associated with human T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7489–7493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Functional cloning of ICAM-2, a cell adhesion ligand for LFA-1 homologous to ICAM-1. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):61–64. doi: 10.1038/339061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazeux R., Hoffman P. A., Tomita J. K., Dickinson E. S., Jasman R. L., St John T., Gallatin W. M. Cloning and characterization of a new intercellular adhesion molecule ICAM-R. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):485–488. doi: 10.1038/360485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Butler J. P., Ingber D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1124–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.7684161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Klickstein L. B., Springer T. A. Cloning and expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 3 reveals strong homology to other immunoglobulin family counter-receptors for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1187–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Springer T. A. Intercellular adhesion molecule 3, a third adhesion counter-receptor for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 on resting lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):185–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kooyk Y., Weder P., Heije K., Figdor C. G. Extracellular Ca2+ modulates leukocyte function-associated antigen-1 cell surface distribution on T lymphocytes and consequently affects cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.6.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kooyk Y., van de Wiel-van Kemenade E., Weder P., Huijbens R. J., Figdor C. G. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 dominates very late antigen 4 in binding of activated T cells to endothelium. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):185–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kooyk Y., van de Wiel-van Kemenade P., Weder P., Kuijpers T. W., Figdor C. G. Enhancement of LFA-1-mediated cell adhesion by triggering through CD2 or CD3 on T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):811–813. doi: 10.1038/342811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]