Abstract
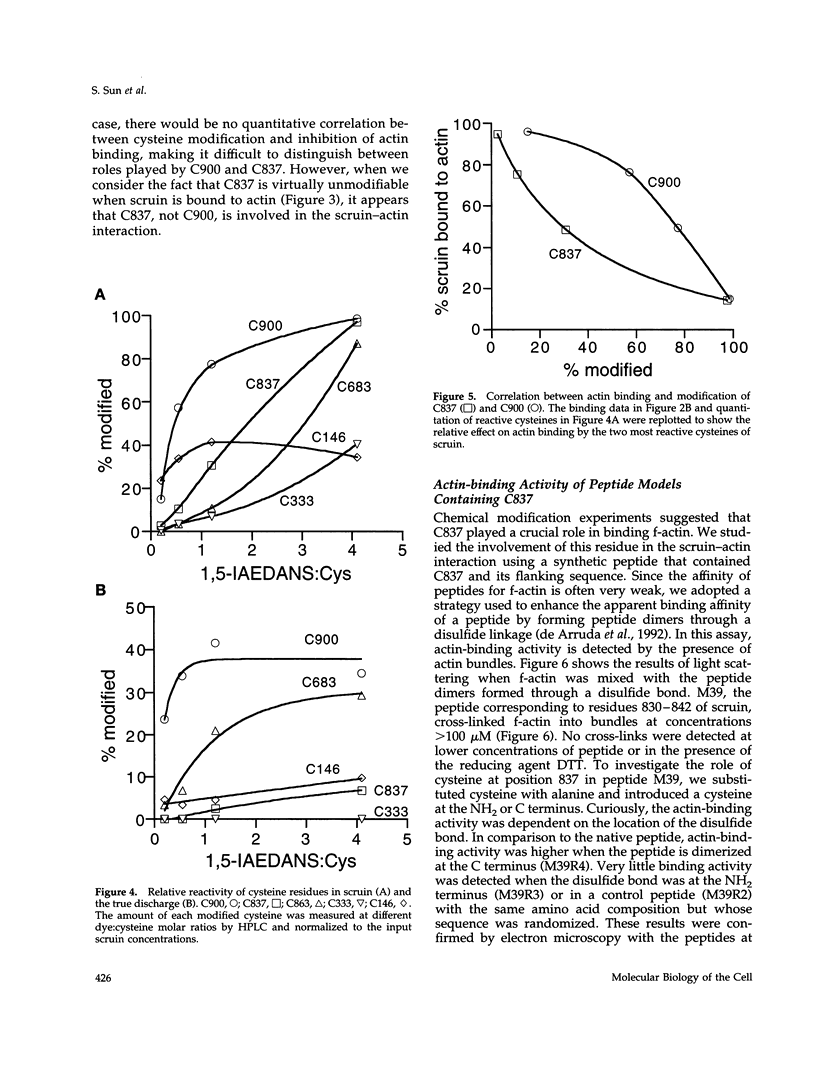
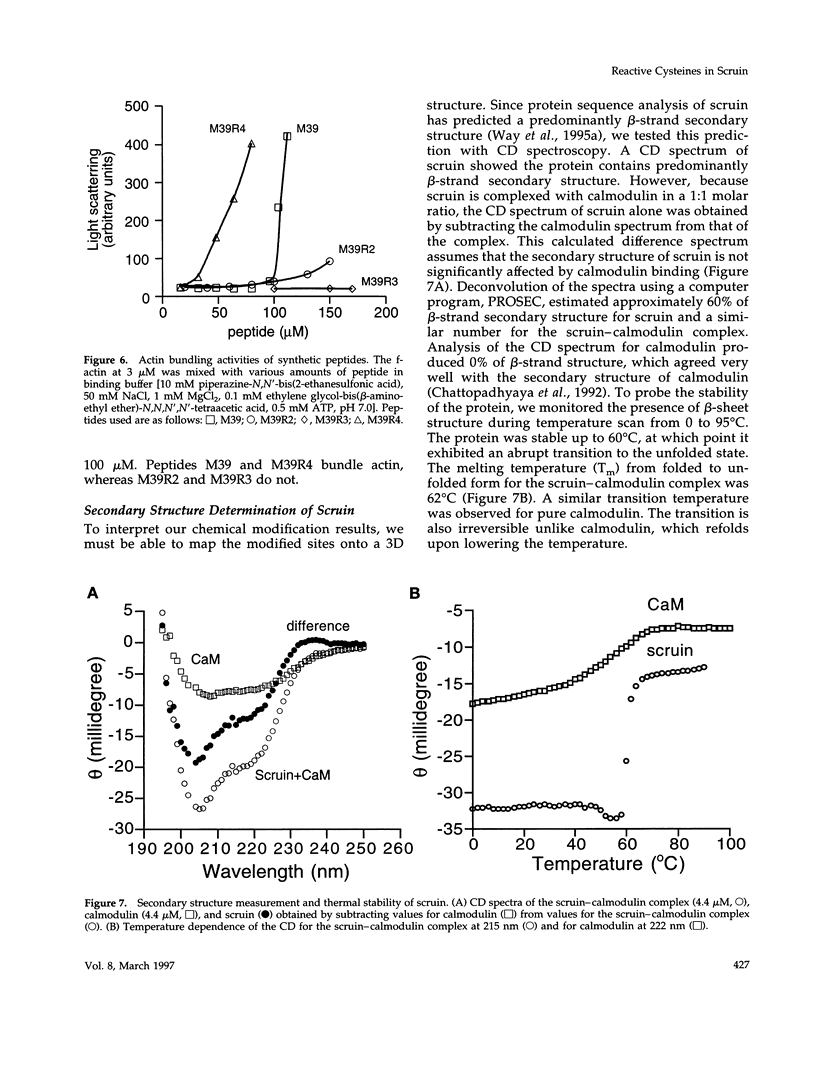
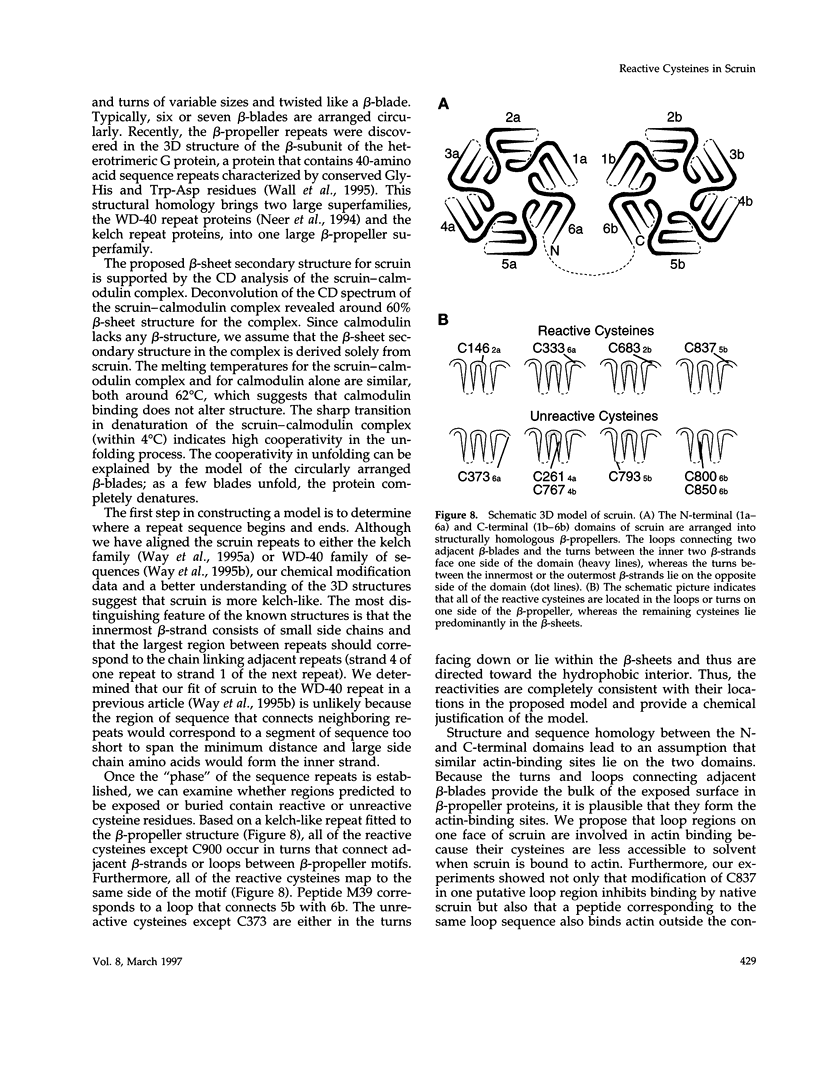
In the acrosomal process of Limulus sperm, the beta-propeller protein scruin cross-links actin into a crystalline bundle. To confirm that scruin has the topology of a beta-propeller protein and to understand how scruin binds actin, we compared the solvent accessibility of cysteine residues in scruin and the acrosomal process by chemical modification with (1,5-IAEDANS). In soluble scruin, the two most reactive cysteines of soluble scruin are C837 and C900, whereas C146, C333, and C683 are moderately reactive. This pattern of reactivity is consistent with the topology of a typical beta-propeller protein; all of the reactive cysteines map to putative loops and turns whereas the unreactive cysteines lie within the predicted interior of the protein. The chemical reactivities of cysteine in the acrosomal process implicate C837 at an actin-binding site. In contrast to soluble scruin, in the acrosomal process, C837 is completely unreactive while the other cysteines become less reactive. Binding studies of chemically modified scruin correlate the extent of modification at C837 with the extent of inhibition of actin binding. Furthermore, peptides corresponding to residues flanking C837 bind actin and narrow a possible actin-binding region to a KQK sequence. On the basis of these studies, our results suggest that an actin-binding site lies in the C-terminal domain of scruin and involves a putative loop defined by C837.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bork P., Doolittle R. F. Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 11;236(5):1277–1282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyaya R., Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Calmodulin structure refined at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1177–1192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90324-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Edds K. T. Evidence for fascin cross-links between the actin filaments in coelomocyte filopodia. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):490–494. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Tilney L. G., Bonder E. M., Frankl P. A change in twist of actin provides the force for the extension of the acrosomal process in Limulus sperm: the false-discharge reaction. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):324–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Tilney L. G. How to build a bend into an actin bundle. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 5;175(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering D. S., Matsudaira P. Cysteine scanning mutagenesis at 40 of 76 positions in villin headpiece maps the F-actin binding site and structural features of the domain. Biochemistry. 1996 Oct 1;35(39):12677–12685. doi: 10.1021/bi9615699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Vancompernolle K., Huet C., Goethals M., Finidori J., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. An actin-binding site containing a conserved motif of charged amino acid residues is essential for the morphogenic effect of villin. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90535-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Phillips S. E., Yadav K. D., Knowles P. F. Crystal structure of a free radical enzyme, galactose oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 20;238(5):794–814. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J., Nambudripad R., Smith T. F. The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):297–300. doi: 10.1038/371297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C., DeRosier D. A 13-A map of the actin-scruin filament from the limulus acrosomal process. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):337–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. C., Way M., Sakai J., Matsudaira P. Characterization of the actin cross-linking properties of the scruin-calmodulin complex from the acrosomal process of Limulus sperm. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 2;271(5):2651–2657. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.5.2651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. F., Agris J. M., Jakana J., Matsudaira P., Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of a single filament in the Limulus acrosomal bundle: scruin binds to homologous helix-loop-beta motifs in actin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(3):341–350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G. Actin filaments in the acrosomal reaction of Limulus sperm. Motion generated by alterations in the packing of the filaments. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):289–310. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Colman P. M. Three-dimensional structure of the neuraminidase of influenza virus A/Tokyo/3/67 at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall M. A., Coleman D. E., Lee E., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Posner B. A., Gilman A. G., Sprang S. R. The structure of the G protein heterotrimer Gi alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Sanders M., Chafel M., Tu Y. H., Knight A., Matsudaira P. beta-Scruin, a homologue of the actin crosslinking protein scruin, is localized to the acrosomal vesicle of Limulus sperm. J Cell Sci. 1995 Oct;108(Pt 10):3155–3162. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.10.3155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Sanders M., Garcia C., Sakai J., Matsudaira P. Sequence and domain organization of scruin, an actin-cross-linking protein in the acrosomal process of Limulus sperm. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):51–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Arruda M. V., Bazari H., Wallek M., Matsudaira P. An actin footprint on villin. Single site substitutions in a cluster of basic residues inhibit the actin severing but not capping activity of villin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13079–13085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]