Abstract
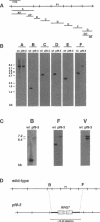
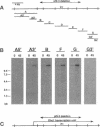
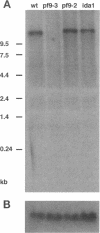
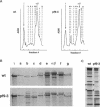
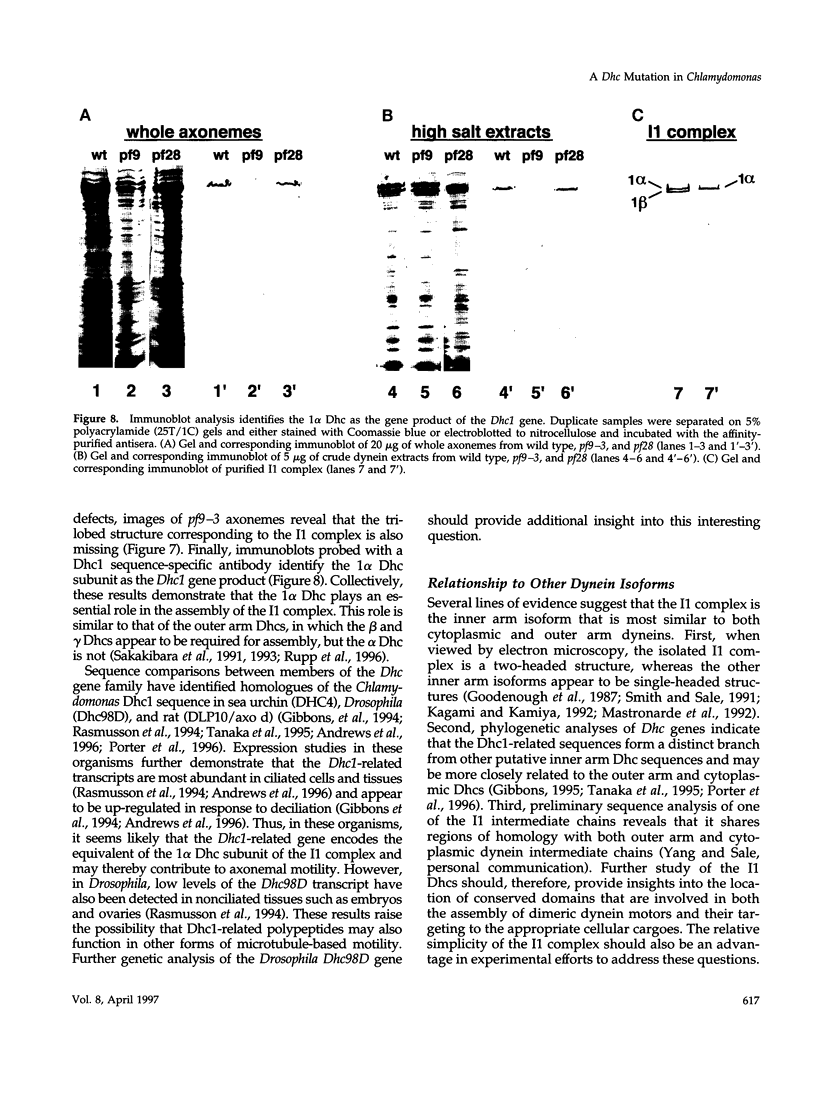
Multiple members of the dynein heavy chain (Dhc) gene family have been recovered in several organisms, but the relationships between these sequences and the Dhc isoforms that they encode are largely unknown. To identify Dhc loci and determine the specific functions of the individual Dhc isoforms, we have screened a collection of motility mutants generated by insertional mutagenesis in Chlamydomonas. In this report, we characterize one strain, pf9-3, in which the insertion event was accompanied by a deletion of approximately 13 kb of genomic DNA within the transcription unit of the Dhc1 gene. Northern blot analysis confirms that pf9-3 is a null mutation. Biochemical and structural studies of isolated axonemes demonstrate that the pf9-3 mutant fails to assemble the I1 inner arm complex, a two-headed dynein isoform composed of two Dhcs (1 alpha and 1 beta) and three intermediate chains. To determine if the Dhc1 gene product corresponds to one of the Dhcs of the I1 complex, antibodies were generated against a Dhc1-specific peptide sequence. Immunoblot analysis reveals that the Dhc1 gene encodes the 1 alpha Dhc subunit. These studies thus, identify the first inner arm Dhc locus to be described in any organism and further demonstrate that the 1 alpha Dhc subunit plays an essential role in the assembly of the I1 inner arm complex.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews K. L., Nettesheim P., Asai D. J., Ostrowski L. E. Identification of seven rat axonemal dynein heavy chain genes: expression during ciliated cell differentiation. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Jan;7(1):71–79. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai D. J., Beckwith S. M., Kandl K. A., Keating H. H., Tjandra H., Forney J. D. The dynein genes of Paramecium tetraurelia. Sequences adjacent to the catalytic P-loop identify cytoplasmic and axonemal heavy chain isoforms. J Cell Sci. 1994 Apr;107(Pt 4):839–847. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.4.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokaw C. J., Kamiya R. Bending patterns of Chlamydomonas flagella: IV. Mutants with defects in inner and outer dynein arms indicate differences in dynein arm function. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm D. A convenient moderate-scale procedure for obtaining DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Biotechniques. 1989 Jan;7(1):21–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criswell P. S., Ostrowski L. E., Asai D. J. A novel cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain: expression of DHC1b in mammalian ciliated epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1996 Jul;109(Pt 7):1891–1898. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.7.1891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuchy R., Purton S., Rochaix J. D. The argininosuccinate lyase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an important tool for nuclear transformation and for correlating the genetic and molecular maps of the ARG7 locus. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2803–2809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutcher S. Genetic nomenclature guide. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Trends Genet. 1995 Mar;:18–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersold W. T. Chlamydomonas reinhardi: heterozygous diploid strains. Science. 1967 Jul 28;157(3787):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3787.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández E., Schnell R., Ranum L. P., Hussey S. C., Silflow C. D., Lefebvre P. A. Isolation and characterization of the nitrate reductase structural gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6449–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner L. C., O'Toole E., Perrone C. A., Giddings T., Porter M. E. Components of a "dynein regulatory complex" are located at the junction between the radial spokes and the dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1311–1325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B. H., Asai D. J., Tang W. J., Hays T. S., Gibbons I. R. Phylogeny and expression of axonemal and cytoplasmic dynein genes in sea urchins. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jan;5(1):57–70. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R. Dynein family of motor proteins: present status and future questions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;32(2):136–144. doi: 10.1002/cm.970320214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Gebhart B., Mermall V., Mitchell D. R., Heuser J. E. High-pressure liquid chromatography fractionation of Chlamydomonas dynein extracts and characterization of inner-arm dynein subunits. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90676-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. S., Levine R. P. Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1665–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumpel N. J., Purton S. Playing tag with Chlamydomonas. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;4(8):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermacher G., Sale W. S. Regulation of dynein-driven microtubule sliding by an axonemal kinase and phosphatase in Chlamydomonas flagella. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;32(2):106–109. doi: 10.1002/cm.970320207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermacher G., Sale W. S. Regulation of flagellar dynein by phosphorylation of a 138-kD inner arm dynein intermediate chain. J Cell Biol. 1997 Jan 13;136(1):167–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes J. A., Dutcher S. K. Cellular asymmetry in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Sci. 1989 Oct;94(Pt 2):273–285. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbaur E. L., Vallee R. B. DYNEINS: molecular structure and cellular function. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. R., Habermacher G., Glass D. B., Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Regulation of Chlamydomonas flagellar dynein by an axonemal protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1683–1692. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. W., Silflow C. D., Thompson M. D., Ranum L. P., Lefebvre P. A. Extragenic suppression and synthetic lethality among Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutants resistant to anti-microtubule drugs. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):567–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Wolf H. The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):181–186. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Kurimoto E., Muto E. Two types of Chlamydomonas flagellar mutants missing different components of inner-arm dynein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):441–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Kagami O., Yagi T., Kamiya R. Isolation of two species of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagellar mutants, ida5 and ida6, that lack a newly identified heavy chain of the inner dynein arm. Cell Struct Funct. 1993 Dec;18(6):371–377. doi: 10.1247/csf.18.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L. High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1228–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. J., Dutcher S. K. Phosphoregulation of an inner dynein arm complex in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is altered in phototactic mutant strains. J Cell Biol. 1997 Jan 13;136(1):177–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. J., Inwood W. B., O'Toole E. T., Power J., Dutcher S. K. The bop2-1 mutation reveals radial asymmetry in the inner dynein arm region of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1255–1266. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. M., Otter T., Witman G. B. Purification and characterization of Chlamydomonas flagellar dyneins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:291–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE R. P., EBERSOLD W. T. The genetics and cytology of Chlamydomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1960;14:197–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.14.100160.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDizet M., Piperno G. The light chain p28 associates with a subset of inner dynein arm heavy chains in Chlamydomonas axonemes. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Jun;6(6):697–711. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.6.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDizet M., Piperno G. ida4-1, ida4-2, and ida4-3 are intron splicing mutations affecting the locus encoding p28, a light chain of Chlamydomonas axonemal inner dynein arms. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Jun;6(6):713–723. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppes R. A new class of arginine-requiring mutants in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;104(2):172–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00272799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastronarde D. N., O'Toole E. T., McDonald K. L., McIntosh J. R., Porter M. E. Arrangement of inner dynein arms in wild-type and mutant flagella of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1145–1162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVittie A. Flagellum mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Aug;71(3):525–540. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-3-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R., Brown K. S. Sequence analysis of the Chlamydomonas alpha and beta dynein heavy chain genes. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):635–644. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R. Cell and molecular biology of flagellar dyneins. Int Rev Cytol. 1994;155:141–180. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R., Kang Y. Identification of oda6 as a Chlamydomonas dynein mutant by rescue with the wild-type gene. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):835–842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Savereide P. B., Lefebvre P. A. The CRY1 gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: structure and use as a dominant selectable marker for nuclear transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4011–4019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G. Isolation of a sixth dynein subunit adenosine triphosphatase of Chlamydomonas axonemes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):133–140. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):379–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Ramanis Z. The proximal portion of Chlamydomonas flagella contains a distinct set of inner dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):701–709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E. Axonemal dyneins: assembly, organization, and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;8(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Johnson K. A. Characterization of the ATP-sensitive binding of Tetrahymena 30 S dynein to bovine brain microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6575–6581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Knott J. A., Gardner L. C., Mitchell D. R., Dutcher S. K. Mutations in the SUP-PF-1 locus of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identify a regulatory domain in the beta-dynein heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1495–1507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Knott J. A., Myster S. H., Farlow S. J. The dynein gene family in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Genetics. 1996 Oct;144(2):569–585. doi: 10.1093/genetics/144.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Power J., Dutcher S. K. Extragenic suppressors of paralyzed flagellar mutations in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identify loci that alter the inner dynein arms. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1163–1176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmusson K., Serr M., Gepner J., Gibbons I., Hays T. S. A family of dynein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jan;5(1):45–55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp G., O'Toole E., Gardner L. C., Mitchell B. F., Porter M. E. The sup-pf-2 mutations of Chlamydomonas alter the activity of the outer dynein arms by modification of the gamma-dynein heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;135(6 Pt 2):1853–1865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.6.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., GRANICK S. Nutritional studies with Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):831–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara H., Mitchell D. R., Kamiya R. A Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein mutant missing the alpha heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):615–622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara H., Takada S., King S. M., Witman G. B., Kamiya R. A Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein mutant with a truncated beta heavy chain. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):653–661. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell R. A., Lefebvre P. A. Isolation of the Chlamydomonas regulatory gene NIT2 by transposon tagging. Genetics. 1993 Jul;134(3):737–747. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., Ranum L. P. The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2389–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. F., Lefebvre P. A. PF16 encodes a protein with armadillo repeats and localizes to a single microtubule of the central apparatus in Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;132(3):359–370. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Microtubule binding and translocation by inner dynein arm subtype I1. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;18(4):258–268. doi: 10.1002/cm.970180403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. F., Sale W. S. Regulation of dynein-driven microtubule sliding by the radial spokes in flagella. Science. 1992 Sep 11;257(5076):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1387971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam L. W., Lefebvre P. A. Cloning of flagellar genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by DNA insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):375–384. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Zhang Z., Hirokawa N. Identification and molecular evolution of new dynein-like protein sequences in rat brain. J Cell Sci. 1995 May;108(Pt 5):1883–1893. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.5.1883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisberg E. A., Grissom P. M., McIntosh J. R. Mammalian cells express three distinct dynein heavy chains that are localized to different cytoplasmic organelles. J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(4):831–842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.4.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson C. G., King S. M., Koutoulis A., Pazour G. J., Witman G. B. The 78,000 M(r) intermediate chain of Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein isa WD-repeat protein required for arm assembly. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(1):169–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson C. G., King S. M., Witman G. B. Molecular analysis of the gamma heavy chain of Chlamydomonas flagellar outer-arm dynein. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):497–506. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. D., Velleca M. A., Curry A. M., Rosenbaum J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Chlamydomonas gene coding for radial spoke protein 3: flagellar mutation pf-14 is an ochre allele. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):235–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B., Carlson K., Berliner J., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas flagella. I. Isolation and electrophoretic analysis of microtubules, matrix, membranes, and mastigonemes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):507–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. Isolation of Chlamydomonas flagella and flagellar axonemes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:280–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B., Plummer J., Sander G. Chlamydomonas flagellar mutants lacking radial spokes and central tubules. Structure, composition, and function of specific axonemal components. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):729–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]