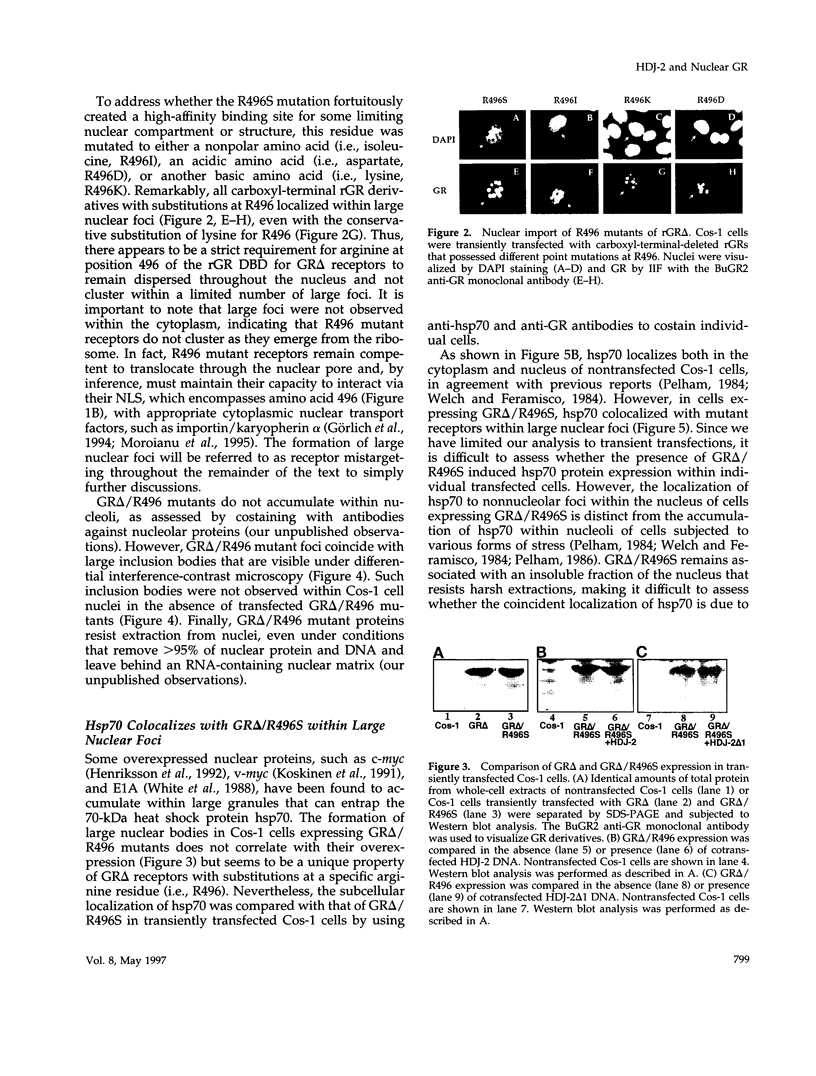
Abstract
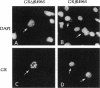
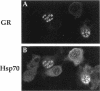
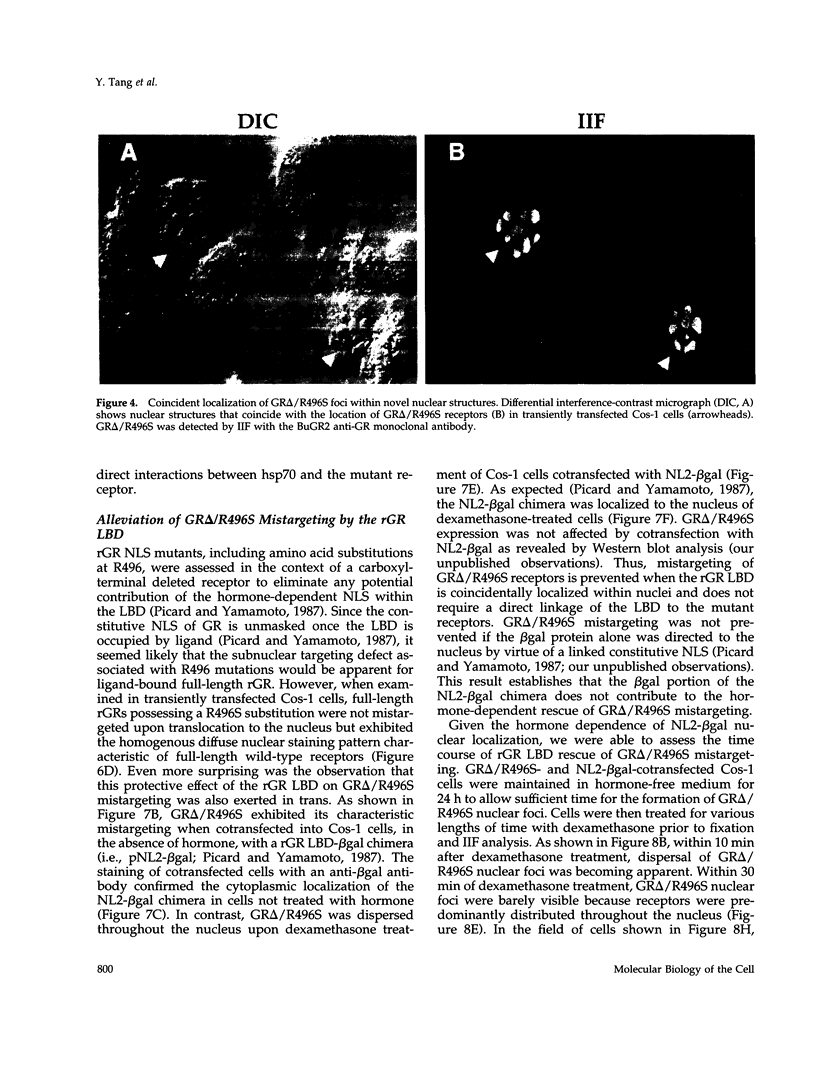
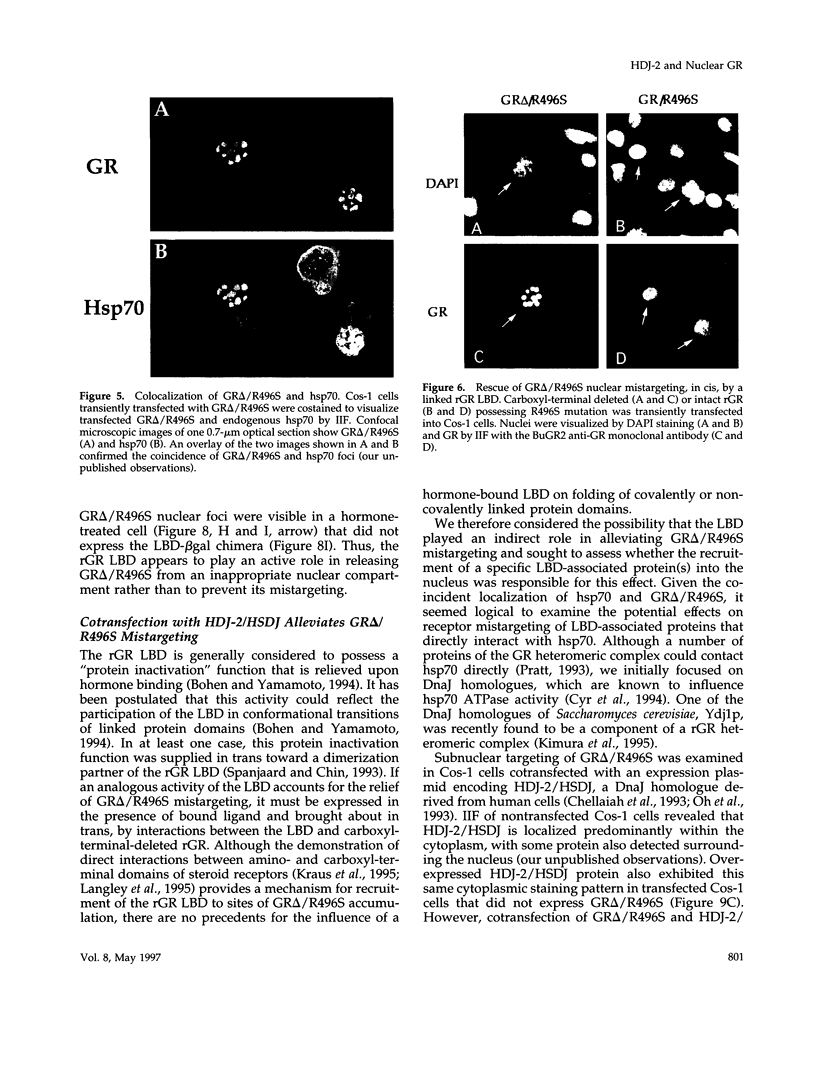
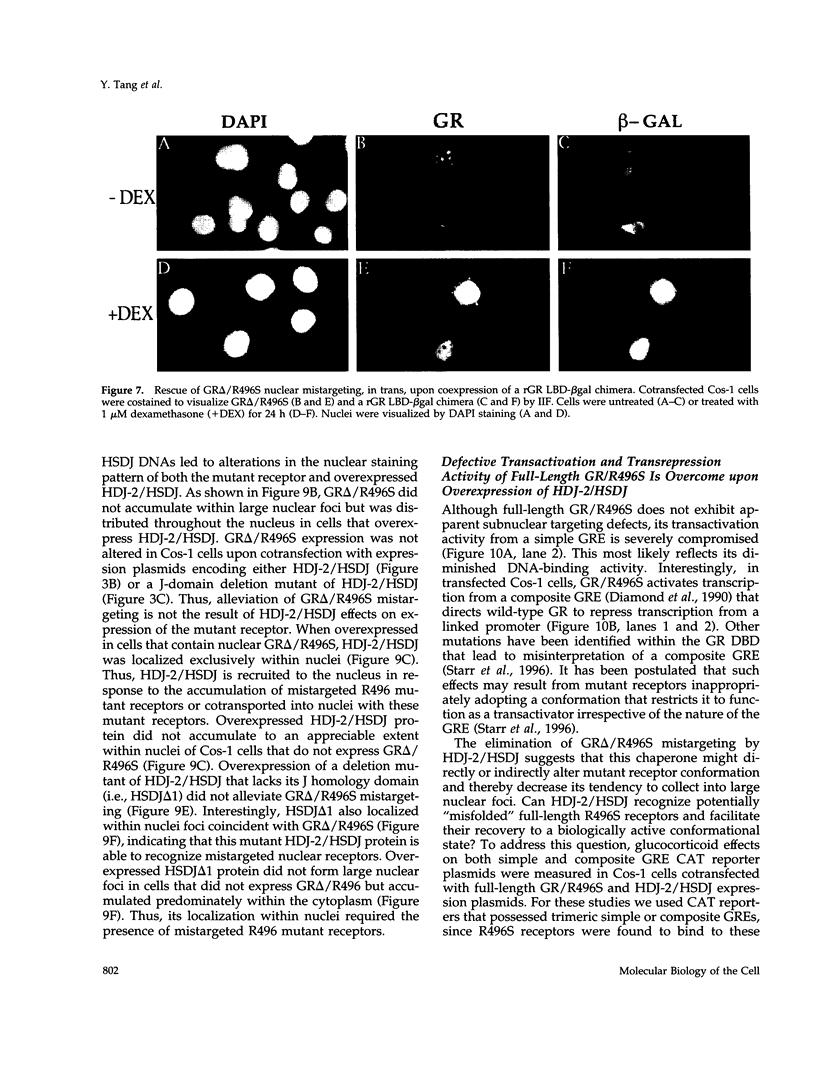
All steroid receptors possess a bipartite nuclear localization signal sequence (NLS) that localizes within the second zinc finger of their DNA-binding domain. Fine-structure mapping of the rat glucocorticoid receptor (rGS) NLS identified a composite signal composed of three distinct proto-NLSs that function effectively when present in unique pairs. At least one of the rGR proto-NLSs appears to influence receptor trafficking within the nucleus, as revealed by a unique nuclear staining pattern of receptors possessing a point mutation (i.e., arginine at position 496; R496), at proto-NLS, pNLS-2. Specifically, carboxyl-terminal-truncated rGRs possessing various point mutations at R496 localized within a limited number of large foci in nuclei of transiently transfected COS-1 cells. R496 mutations did not affect subnuclear targeting when present in full-length rGR, reflecting a protective effect of the receptor's ligand-binding domain that can be exerted in cis and in trans. The effects of rGR R496 mutations on subnuclear targeting were not autonomous because we also observed a coincident localization of hsp70, the 70-kDa heat shock protein, within nuclear foci that include r496 mutant receptors. The elimination of R496 mistargeting by overexpression of an hsp70 partner (i.e., the DnaJ homologue, HDJ-2/HSDJ) suggests that the hsp70/DnaJ chaperone system is mobilized to specific sites within the nucleus in response to inappropriate targeting or folding of specific mutant receptors. HDJ-2/HSDJ overexpression also corrects defective transactivation and transrepression activity of R496 mutant GRs. Thus, molecular chaperones, such as members of the hsp70 and DnaJ families, may survey the nucleus for misfolded proteins and actively participate in their refolding into biologically active conformational states.
Full text
PDF


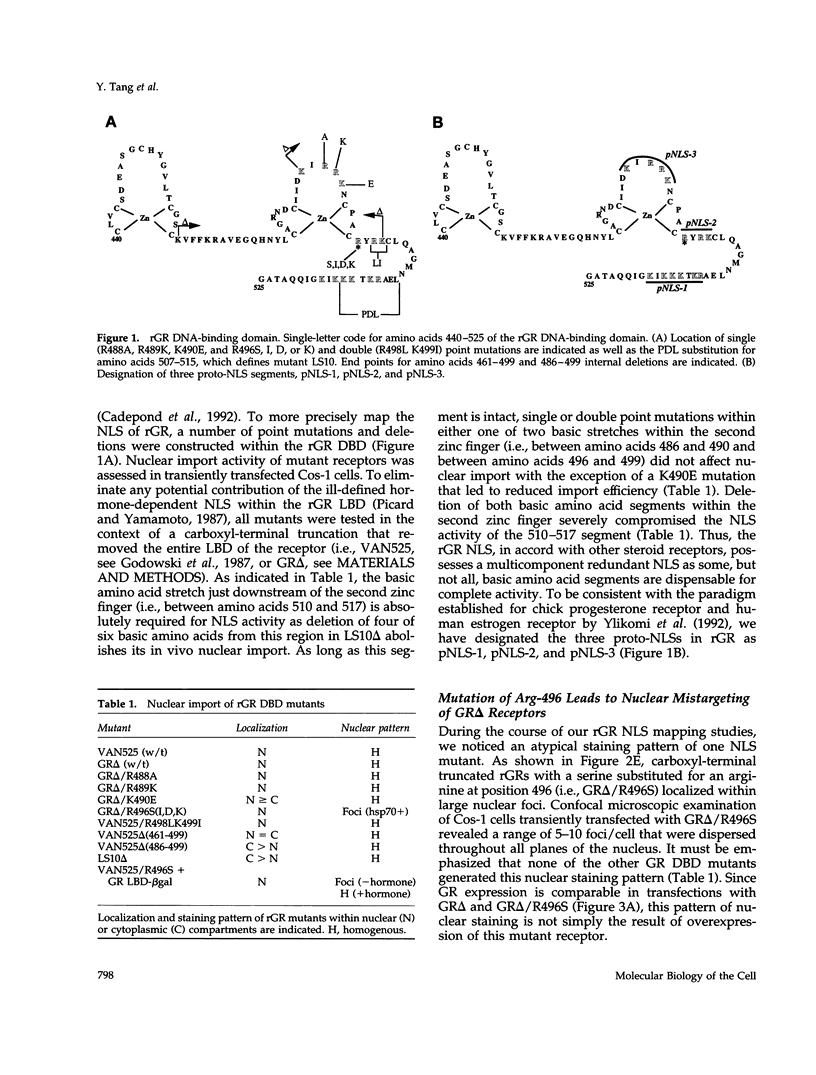
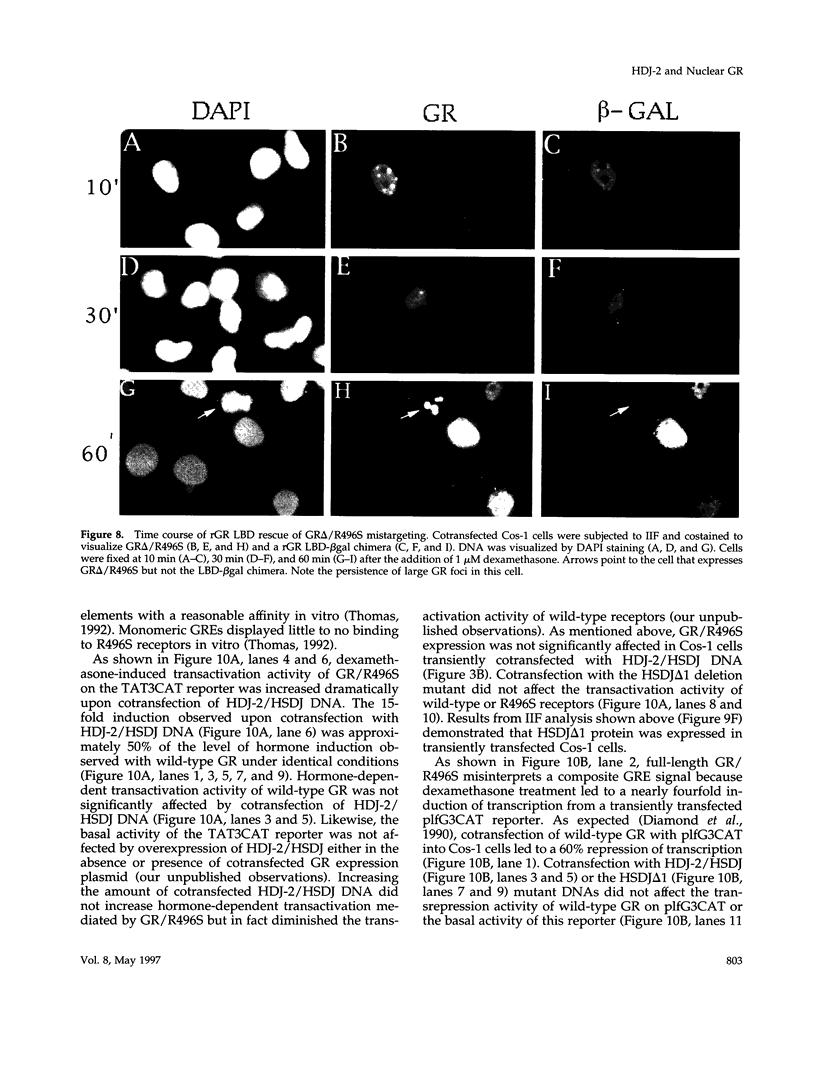
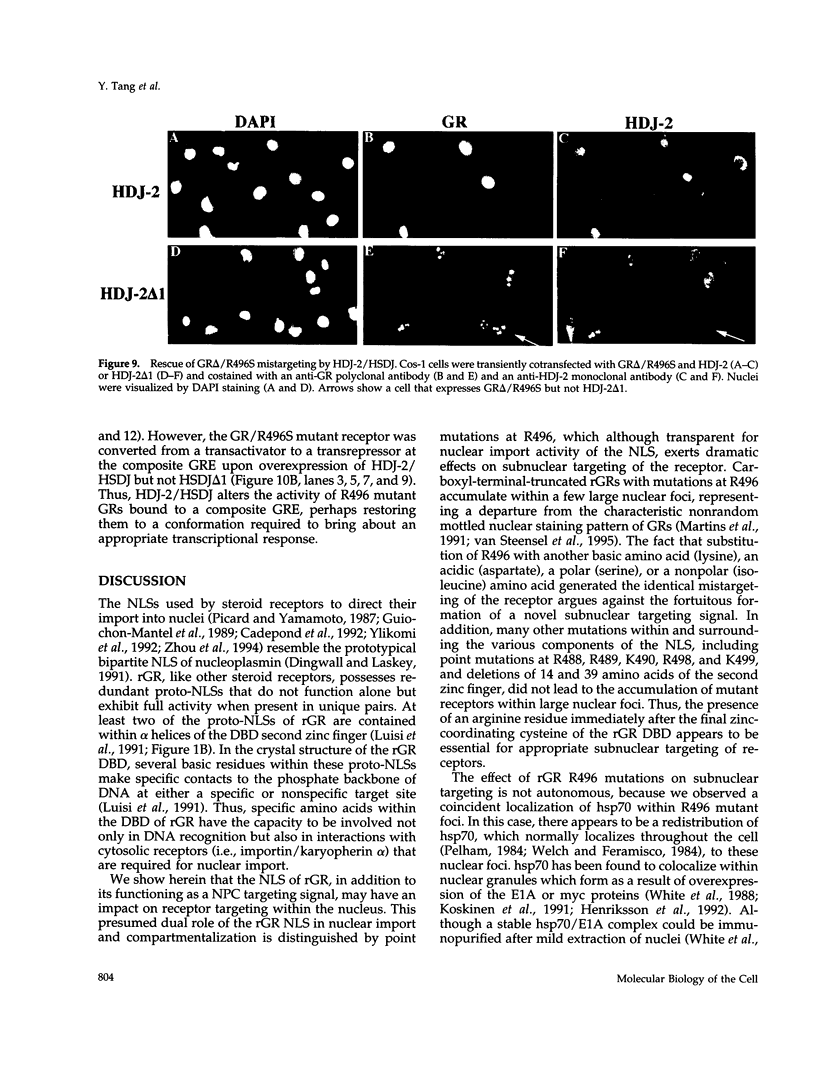
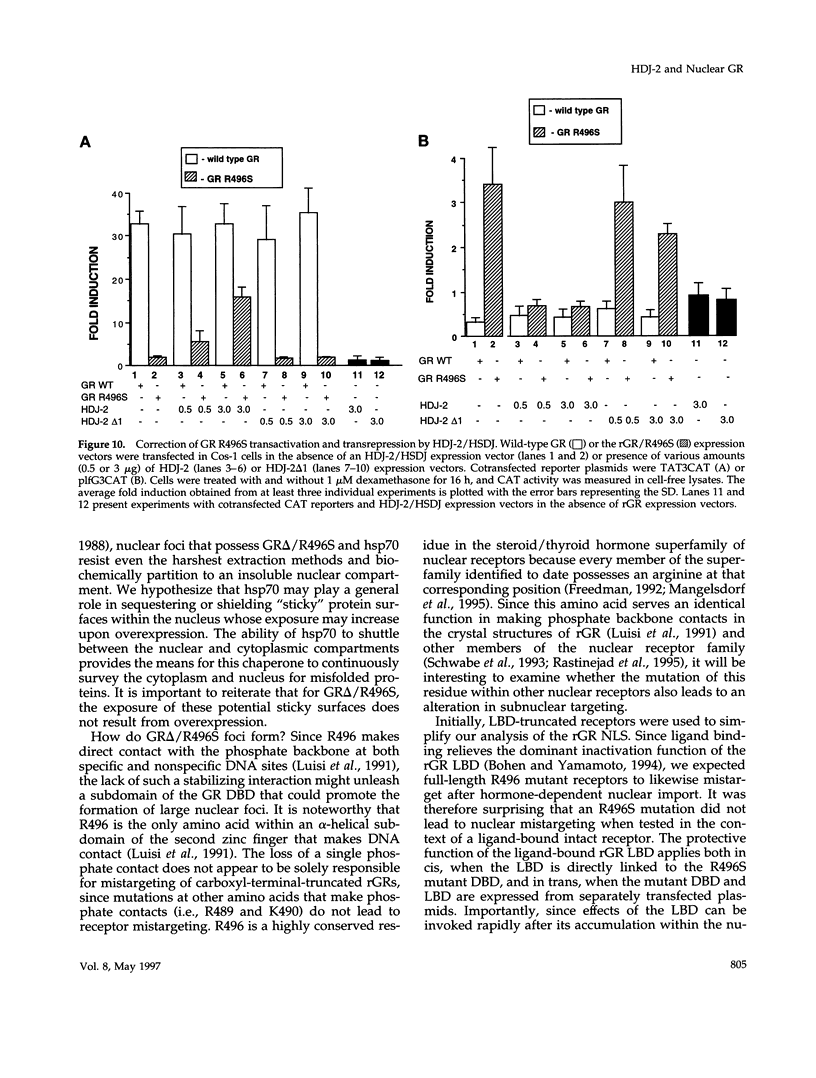




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Lobl T. J., Mitchell M. A., Gerace L. Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear location sequence. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):276–279. doi: 10.1038/337276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohen S. P., Kralli A., Yamamoto K. R. Hold 'em and fold 'em: chaperones and signal transduction. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1303–1304. doi: 10.1126/science.7761850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadepond F., Gasc J. M., Delahaye F., Jibard N., Schweizer-Groyer G., Segard-Maurel I., Evans R., Baulieu E. E. Hormonal regulation of the nuclear localization signals of the human glucocorticosteroid receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jul;201(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Langley E., Wilson E. M., Vidal J. Hormone-dependent transactivation by the human androgen receptor is regulated by a dnaJ protein. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5251–5257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellaiah A., Davis A., Mohanakumar T. Cloning of a unique human homologue of the Escherichia coli DNAJ heat shock protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 18;1174(1):111–113. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90103-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cidlowski J. A., Bellingham D. L., Powell-Oliver F. E., Lubahn D. B., Sar M. Novel antipeptide antibodies to the human glucocorticoid receptor: recognition of multiple receptor forms in vitro and distinct localization of cytoplasmic and nuclear receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1427–1437. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr D. M. Cooperation of the molecular chaperone Ydj1 with specific Hsp70 homologs to suppress protein aggregation. FEBS Lett. 1995 Feb 13;359(2-3):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr D. M., Langer T., Douglas M. G. DnaJ-like proteins: molecular chaperones and specific regulators of Hsp70. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr D. M., Lu X., Douglas M. G. Regulation of Hsp70 function by a eukaryotic DnaJ homolog. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20927–20931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalman F. C., Scherrer L. C., Taylor L. P., Akil H., Pratt W. B. Localization of the 90-kDa heat shock protein-binding site within the hormone-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor by peptide competition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3482–3490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Sanders S. L., Feldheim D. A., Schekman R. Assembly of yeast Sec proteins involved in translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum into a membrane-bound multisubunit complex. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):806–808. doi: 10.1038/349806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J. Structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:495–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P. Anatomy of the steroid receptor zinc finger region. Endocr Rev. 1992 May;13(2):129–145. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-2-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman J., Nimmesgern E., Ohtsuka K., Hartl F. U. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):111–117. doi: 10.1038/370111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Independent modes of transcriptional activation by the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):775–787. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gametchu B., Harrison R. W. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):274–279. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Loosfelt H., Lescop P., Sar S., Atger M., Perrot-Applanat M., Milgrom E. Mechanisms of nuclear localization of the progesterone receptor: evidence for interaction between monomers. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1147–1154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E. Isolation of a protein that is essential for the first step of nuclear protein import. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Vogel F., Mills A. D., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A. Distinct functions for the two importin subunits in nuclear protein import. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):246–248. doi: 10.1038/377246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Amrein H., Maniatis T. An amino acid sequence motif sufficient for subnuclear localization of an arginine/serine-rich splicing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11524–11528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson M., Classon M., Axelson H., Klein G., Thyberg J. Nuclear colocalization of c-myc protein and hsp70 in cells transfected with human wild-type and mutant c-myc genes. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Dec;203(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90012-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard K. J., Holley S. J., Yamamoto K. R., Distelhorst C. W. Mapping the HSP90 binding region of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11928–11935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höhfeld J., Hartl F. U. Post-translational protein import and folding. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höhfeld J., Minami Y., Hartl F. U. Hip, a novel cochaperone involved in the eukaryotic Hsc70/Hsp40 reaction cycle. Cell. 1995 Nov 17;83(4):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto N., Matsuoka Y., Kurihara T., Kohno K., Miyagi M., Sakiyama F., Okada Y., Tsunasawa S., Yoneda Y. Antibodies against 70-kD heat shock cognate protein inhibit mediated nuclear import of karyophilic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1047–1061. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenster G., Trapman J., Brinkmann A. O. Nuclear import of the human androgen receptor. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):761–768. doi: 10.1042/bj2930761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Yahara I., Lindquist S. Role of the protein chaperone YDJ1 in establishing Hsp90-mediated signal transduction pathways. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1362–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.7761857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskinen P. J., Sistonen L., Evan G., Morimoto R., Alitalo K. Nuclear colocalization of cellular and viral myc proteins with HSP70 in myc-overexpressing cells. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):842–851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.842-851.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus W. L., McInerney E. M., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Ligand-dependent, transcriptionally productive association of the amino- and carboxyl-terminal regions of a steroid hormone nuclear receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 19;92(26):12314–12318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley E., Zhou Z. X., Wilson E. M. Evidence for an anti-parallel orientation of the ligand-activated human androgen receptor dimer. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 15;270(50):29983–29990. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.50.29983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt H., Page A. W., Weier H. U., Bestor T. H. A targeting sequence directs DNA methyltransferase to sites of DNA replication in mammalian nuclei. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90561-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bingham P. M. Arginine/serine-rich domains of the su(wa) and tra RNA processing regulators target proteins to a subnuclear compartment implicated in splicing. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Neupert W. Mechanisms of protein import across the mitochondrial outer membrane. Trends Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;6(2):56–61. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(96)81015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Thummel C., Beato M., Herrlich P., Schütz G., Umesono K., Blumberg B., Kastner P., Mark M., Chambon P. The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):835–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90199-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins V. R., Pratt W. B., Terracio L., Hirst M. A., Ringold G. M., Housley P. R. Demonstration by confocal microscopy that unliganded overexpressed glucocorticoid receptors are distributed in a nonrandom manner throughout all planes of the nucleus. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):217–225. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Paschal B., Evans J., Gerace L. Inhibition of nuclear protein import by nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP and identification of the small GTPase Ran/TC4 as an essential transport factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1649–1659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud N., Goldfarb D. S. Multiple pathways in nuclear transport: the import of U2 snRNP occurs by a novel kinetic pathway. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):215–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Walter S., Yang P., Hayes S., O'Hare P. Conformational alteration of Oct-1 upon DNA binding dictates selectivity in differential interactions with related transcriptional coactivators. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Aug;16(8):4404–4413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.8.4404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Blobel G., Radu A. Previously identified protein of uncertain function is karyopherin alpha and together with karyopherin beta docks import substrate at nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2008–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S., Iwahori A., Kato S. Human cDNA encoding DnaJ protein homologue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 18;1174(1):114–116. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Hsp70 accelerates the recovery of nucleolar morphology after heat shock. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3095–3100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J. M., Skalicky J. J., Donaldson L. W., McIntosh L. P., Alber T., Graves B. J. Modulation of transcription factor Ets-1 DNA binding: DNA-induced unfolding of an alpha helix. Science. 1995 Sep 29;269(5232):1866–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.7569926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Kumar V., Chambon P., Yamamoto K. R. Signal transduction by steroid hormones: nuclear localization is differentially regulated in estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. Cell Regul. 1990 Feb;1(3):291–299. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Jolly D. J., Pratt D. V., Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Cadepond F. M., Schweizer-Groyer G., Catelli M. G., Evans R. M., Baulieu E. E. A region in the steroid binding domain determines formation of the non-DNA-binding, 9 S glucocorticoid receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding, and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21455–21458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi M., Hamilton B. J., DeFranco D. v-mos oncoproteins affect the nuclear retention and reutilization of glucocorticoid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1279–1288. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Moore M. S., Blobel G. The peptide repeat domain of nucleoporin Nup98 functions as a docking site in transport across the nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Perlmann T., Evans R. M., Sigler P. B. Structural determinants of nuclear receptor assembly on DNA direct repeats. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):203–211. doi: 10.1038/375203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M., Blobel G. Protein import into nuclei: association and dissociation reactions involving transport substrate, transport factors, and nucleoporins. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Wente S. R. Pores for thought: nuclear pore complex proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;4(10):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G., Dobberstein B. Common principles of protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Chapman L., Finch J. T., Rhodes D. The crystal structure of the estrogen receptor DNA-binding domain bound to DNA: how receptors discriminate between their response elements. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90390-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Thomas J. O. The transport of proteins into the nucleus requires the 70-kilodalton heat shock protein or its cytosolic cognate. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2186–2192. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulga N., Roberts P., Gu Z., Spitz L., Tabb M. M., Nomura M., Goldfarb D. S. In vivo nuclear transport kinetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a role for heat shock protein 70 during targeting and translocation. J Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;135(2):329–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Sadler I., Osborne M. A. Yeast proteins that recognize nuclear localization sequences. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):983–989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Toft D. O. Steroid receptors and their associated proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):4–11. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8446107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers J. P., DeFranco D. B. Effects of okadaic acid, a protein phosphatase inhibitor, on glucocorticoid receptor-mediated enhancement. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;6(1):26–34. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.1.1310797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanjaard R. A., Chin W. W. Reconstitution of ligand-mediated glucocorticoid receptor activity by trans-acting functional domains. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):12–16. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8446102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr D. B., Matsui W., Thomas J. R., Yamamoto K. R. Intracellular receptors use a common mechanism to interpret signaling information at response elements. Genes Dev. 1996 May 15;10(10):1271–1283. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.10.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo A., Korszun R., Hartl F. U., Flanagan J. A zinc finger-like domain of the molecular chaperone DnaJ is involved in binding to denatured protein substrates. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 15;15(2):408–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Richmond T. J. DNA binding-induced conformational change of the yeast transcriptional activator PRTF. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90373-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y., DeFranco D. B. ATP-dependent release of glucocorticoid receptors from the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):1989–2001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urda L. A., Yen P. M., Simons S. S., Jr, Harmon J. M. Region-specific antiglucocorticoid receptor antibodies selectively recognize the activated form of the ligand-occupied receptor and inhibit the binding of activated complexes to deoxyribonucleic acid. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Feb;3(2):251–260. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Nuclear and nucleolar localization of the 72,000-dalton heat shock protein in heat-shocked mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Spector D., Welch W. Differential distribution of the adenovirus E1A proteins and colocalization of E1A with the 70-kilodalton cellular heat shock protein in infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4153–4166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4153-4166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T. How ATP drives proteins across membranes. Science. 1994 Nov 18;266(5188):1197–1198. doi: 10.1126/science.7973701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., DeFranco D. B. Assessment of glucocorticoid receptor-heat shock protein 90 interactions in vivo during nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Jan;10(1):3–13. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.1.8838140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., DeFranco D. B. Differential roles of heat shock protein 70 in the in vitro nuclear import of glucocorticoid receptor and simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5088–5098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylikomi T., Bocquel M. T., Berry M., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P. Cooperation of proto-signals for nuclear accumulation of estrogen and progesterone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3681–3694. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z. X., Sar M., Simental J. A., Lane M. V., Wilson E. M. A ligand-dependent bipartite nuclear targeting signal in the human androgen receptor. Requirement for the DNA-binding domain and modulation by NH2-terminal and carboxyl-terminal sequences. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13115–13123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steensel B., Brink M., van der Meulen K., van Binnendijk E. P., Wansink D. G., de Jong L., de Kloet E. R., van Driel R. Localization of the glucocorticoid receptor in discrete clusters in the cell nucleus. J Cell Sci. 1995 Sep;108(Pt 9):3003–3011. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.9.3003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]