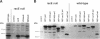Abstract
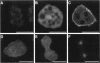
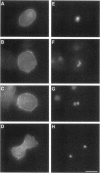
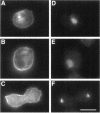
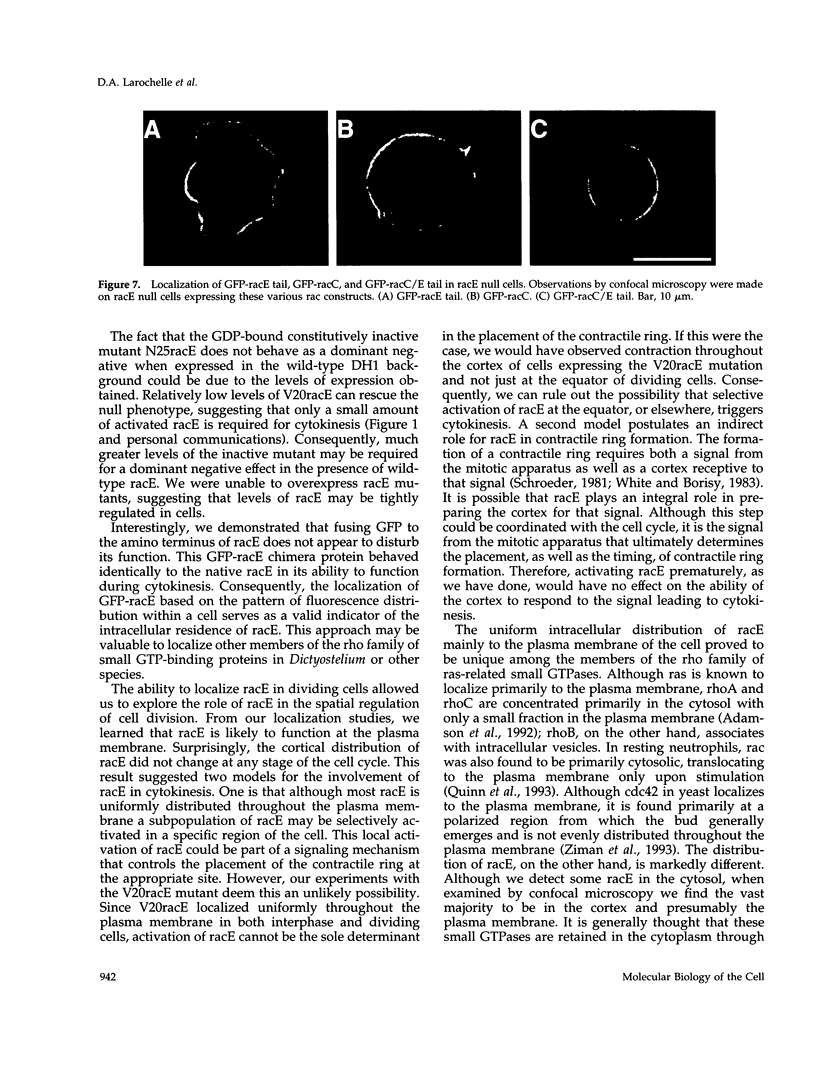
The small GTPase racE is essential for cytokinesis in Dictyostelium but its precise role in cell division is not known. To determine the molecular mechanism of racE function, we undertook a mutational analysis of racE. The exogenous expression of either wild-type racE or a constitutively active V20racE mutant effectively rescues the cytokinesis deficiency of racE null cells. In contrast, a constitutively inactive N25racE mutant fails to rescue the cytokinesis deficiency. Thus, cytokinesis requires only the activation of racE by GTP and not the inactivation of racE by hydrolysis of GTP. To determine the spatial distribution of racE, we created a fusion protein with GFP at the amino terminus of racE. Remarkably, GFP-racE fusion protein was fully competent to rescue the phenotype of racE null cells and, therefore, must reside in the same location as native racE. We found that GFP-racE localized to the plasma membrane of the cell throughout the entire cell cycle. Furthermore, constitutively active and inactive GFP-racE fusion proteins also localized to the plasma membrane. We mapped the domain required for plasma membrane localization to the carboxyl-terminal 40 amino acids of racE. This domain, however, is not sufficient to confer racE function onto a closely related GTPase. Taken together, these results suggest that racE functions at the cell cortex but it is not involved in determining the timing or placement of the contractile ring.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson P., Paterson H. F., Hall A. Intracellular localization of the P21rho proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):617–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns C. G., Reedy M., Heuser J., De Lozanne A. Expression of light meromyosin in Dictyostelium blocks normal myosin II function. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(3):605–612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush J., Franek K., Cardelli J. Cloning and characterization of seven novel Dictyostelium discoideum rac-related genes belonging to the rho family of GTPases. Gene. 1993 Dec 22;136(1-2):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90448-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Gorvel J. P., Stelzer E., Simons K., Gruenberg J., Zerial M. Hypervariable C-terminal domain of rab proteins acts as a targeting signal. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):769–772. doi: 10.1038/353769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. H., Benson D. R., Schultz P. G. Probing the structure and mechanism of Ras protein with an expanded genetic code. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):806–809. doi: 10.1126/science.8430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann D., Brill S., Garrett M. D., Totty N., Hsuan J., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim L., Hall A. Bcr encodes a GTPase-activating protein for p21rac. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):400–402. doi: 10.1038/351400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutartre H., Davoust J., Gorvel J. P., Chavrier P. Cytokinesis arrest and redistribution of actin-cytoskeleton regulatory components in cells expressing the Rho GTPase CDC42Hs. J Cell Sci. 1996 Feb;109(Pt 2):367–377. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.2.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. L., Feig L. A. Dominant inhibitory mutations in the Mg(2+)-binding site of RasH prevent its activation by GTP. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4822–4829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishkind D. J., Wang Y. L. New horizons for cytokinesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;7(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Self A. J., van Oers C., Hall A. Identification of distinct cytoplasmic targets for ras/R-ras and rho regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Farnsworth C. C. Role of protein modification reactions in programming interactions between ras-related GTPases and cell membranes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:181–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Cadwallader K., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A CAAX or a CAAL motif and a second signal are sufficient for plasma membrane targeting of ras proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4033–4039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A polybasic domain or palmitoylation is required in addition to the CAAX motif to localize p21ras to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90294-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden N., Loh H. Y., Chia W., Lim L. A dominant inhibitory version of the small GTP-binding protein Rac disrupts cytoskeletal structures and inhibits developmental cell shape changes in Drosophila. Development. 1995 Mar;121(3):903–914. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.3.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim R., Tsien R. Y. Engineering green fluorescent protein for improved brightness, longer wavelengths and fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Curr Biol. 1996 Feb 1;6(2):178–182. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00450-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Itoh T., Takai Y. Regulation of cytoplasmic division of Xenopus embryo by rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI). J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1187–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma R., Ahmed S., Best A., Lim L. The Ras-related protein Cdc42Hs and bradykinin promote formation of peripheral actin microspikes and filopodia in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):1942–1952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larochelle D. A., Vithalani K. K., De Lozanne A. A novel member of the rho family of small GTP-binding proteins is specifically required for cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1321–1329. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi I., Hamaguchi Y., Fujimoto H., Morii N., Mishima M., Narumiya S. A rho-like protein is involved in the organisation of the contractile ring in dividing sand dollar eggs. Zygote. 1993 Nov;1(4):325–331. doi: 10.1017/s0967199400001659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. L., Schaber M. D., Mosser S. D., Rands E., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Marshall M. S., Pompliano D. L., Gibbs J. B. Sequence dependence of protein isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14603–14610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. T., Evans T., Loetterle L. R., Jesaitis A. J., Bokoch G. M. Translocation of Rac correlates with NADPH oxidase activation. Evidence for equimolar translocation of oxidase components. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20983–20987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. The origin of cleavage forces in dividing eggs. A mechanism in two steps. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jul;134(1):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. A transformation vector for dictyostelium discoideum with a new selectable marker bsr. Plasmid. 1993 Sep;30(2):150–154. doi: 10.1006/plas.1993.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaishi K., Sasaki T., Kameyama T., Tsukita S., Tsukita S., Takai Y. Translocation of activated Rho from the cytoplasm to membrane ruffling area, cell-cell adhesion sites and cleavage furrows. Oncogene. 1995 Jul 6;11(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Abramson P. D., Spudich J. A. The neck region of the myosin motor domain acts as a lever arm to generate movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4459–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Borisy G. G. On the mechanisms of cytokinesis in animal cells. J Theor Biol. 1983 Mar 21;101(2):289–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Signal transduction and actin filament organization. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;8(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziman M., Preuss D., Mulholland J., O'Brien J. M., Botstein D., Johnson D. I. Subcellular localization of Cdc42p, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae GTP-binding protein involved in the control of cell polarity. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1307–1316. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]