Abstract
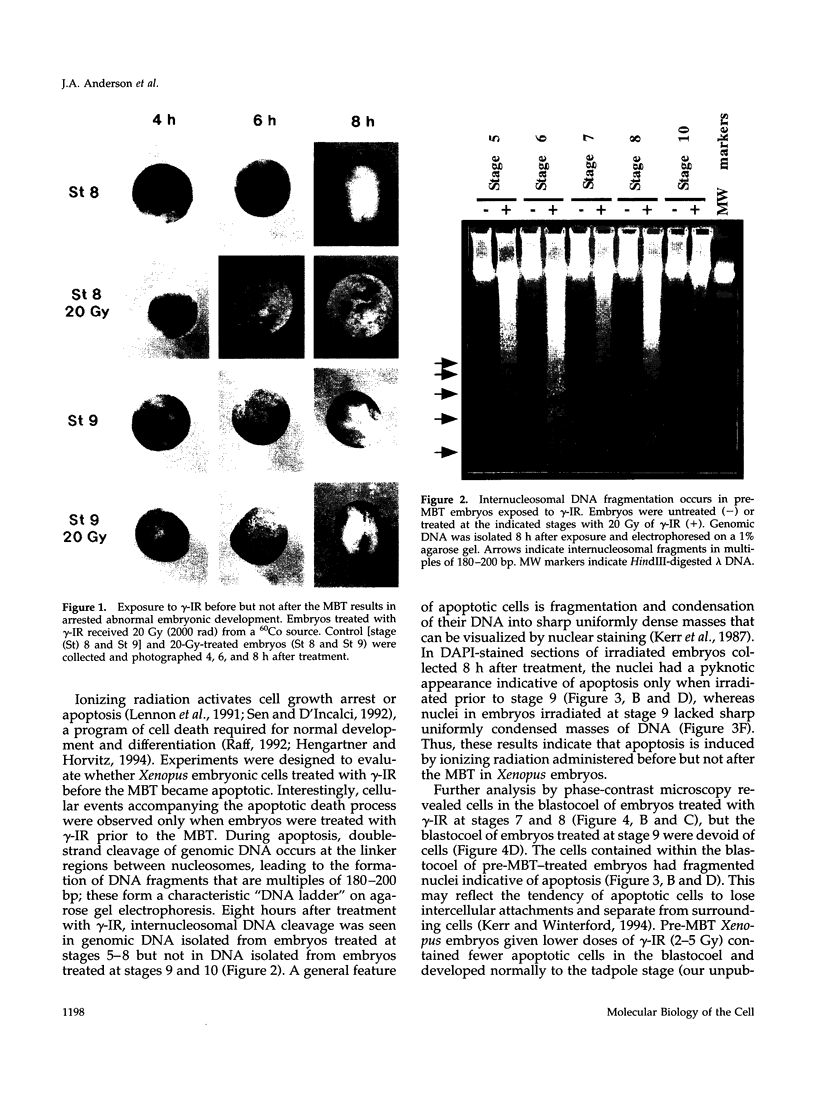
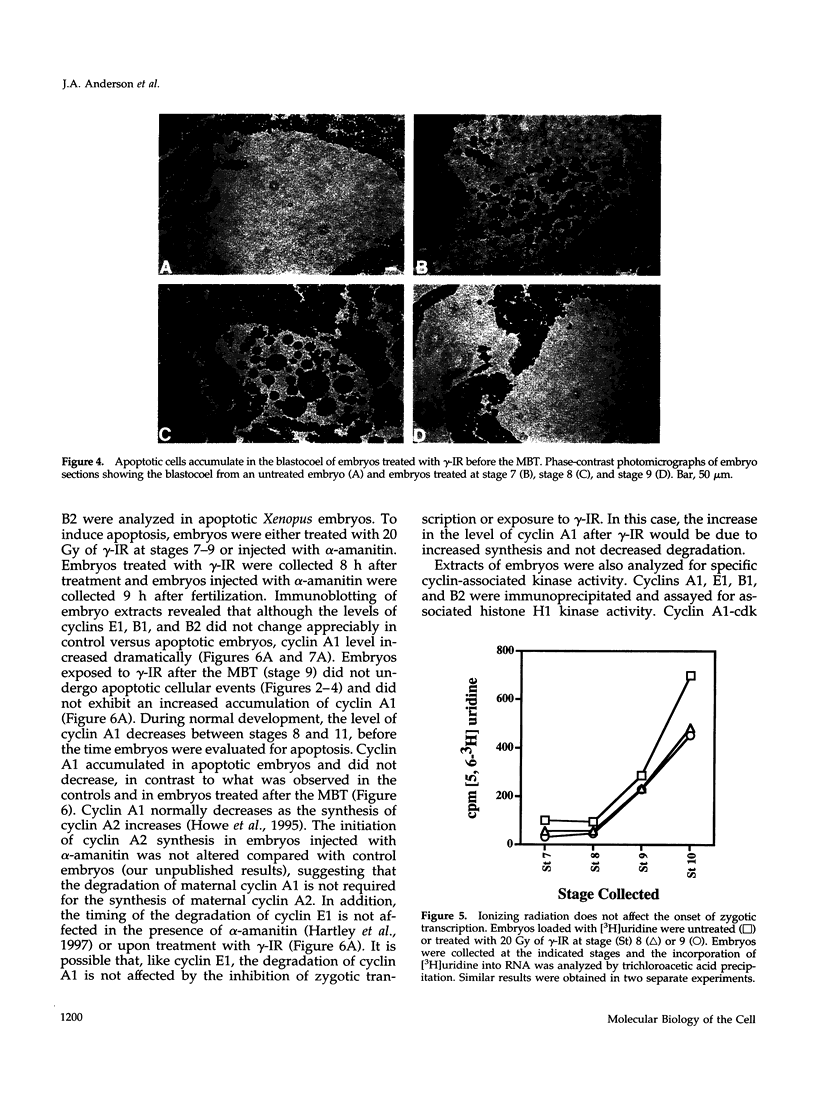
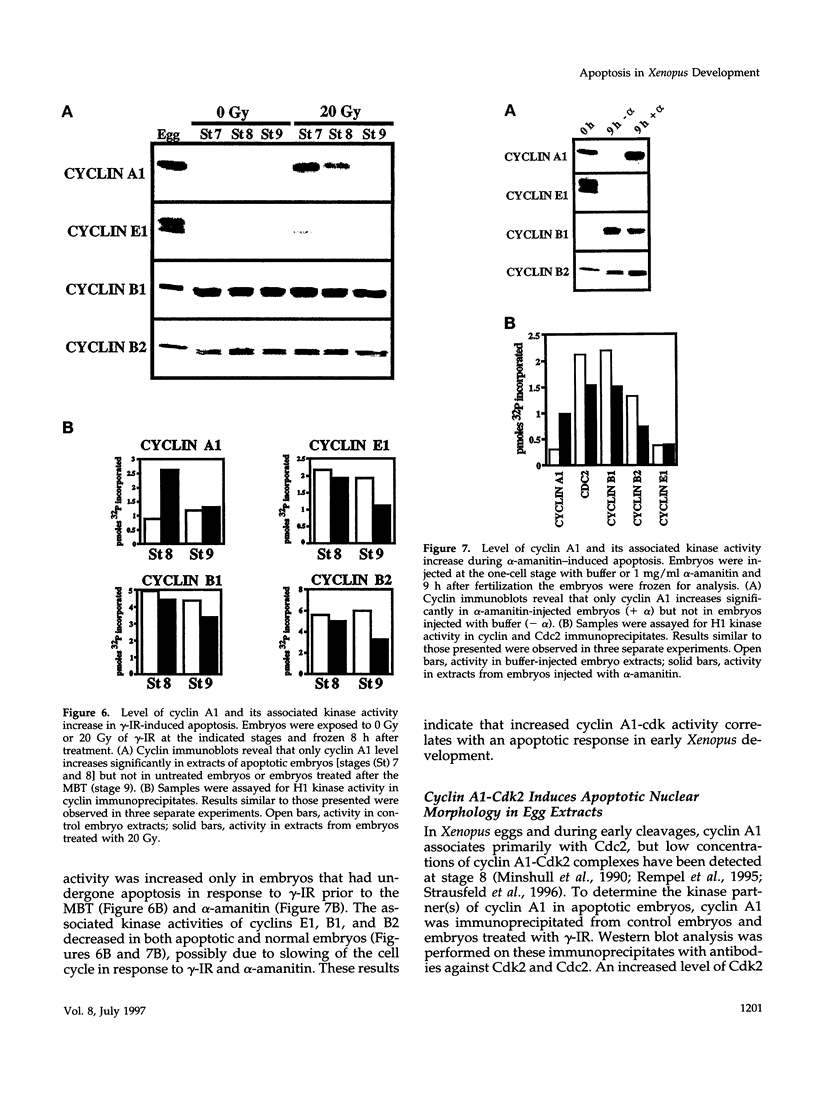
After the twelfth cell division in Xenopus embryos, zygotic gene transcription is activated, cells become motile, and cell division becomes asynchronous. This developmental change is termed the midblastula transition. High doses of gamma-irradiation (gamma-IR) before the midblastula transition induced apoptotic cell death and increased the levels of cyclin A1 and cyclin A1-Cdk2 activity. The addition of recombinant cyclin A1-Cdk2 induced the formation of apoptotic nuclei in Xenopus egg extracts, suggesting a role for cyclin A1-Cdk2 in apoptosis. Hallmarks of apoptosis, such as internucleosomal DNA fragmentation, pyknotic and uniformly condensed nuclei, and loss of intercellular attachments, were evident in embryos exposed to gamma-IR before the midblastula transition. Apoptotic cells accumulated in the blastocoel, suggesting that before the midblastula transition Xenopus embryos use apoptosis to eliminate cells containing damaged DNA. However, embryos treated with the same dose of gamma-IR after the midblastula transition developed normally and exhibited no signs of apoptosis, no change in cyclin A1 level, and no increase in cyclin A1-Cdk2 activity. These results indicate that there is a change in the response to DNA damage at the midblastula transition in Xenopus embryos.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends M. J., Morris R. G., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis. The role of the endonuclease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):593–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal N., Houle A., Melnykovych G. Apoptosis: mode of cell death induced in T cell leukemia lines by dexamethasone and other agents. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):211–216. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.2004665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchou T., Kranenburg O., van Dam H., Roelen D., Zantema A., Hall F. L., van der Eb A. Increased cyclin A and decreased cyclin D levels in adenovirus 5 E1A-transformed rodent cell lines. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1765–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelles C., Helmberg A., Karin M. p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of transcriptional activation of p53-target genes. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):220–223. doi: 10.1038/370220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. J., Harmon B. V., Souvlis T., Pope J. H., Kerr J. F. Effects of cycloheximide on B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemic and normal lymphocytes in vitro: induction of apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 1991 Sep;64(3):518–522. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Reyes J., Tata J. R. Cloning, characterization and expression of two Xenopus bcl-2-like cell-survival genes. Gene. 1995 Jun 9;158(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Distinct roles of cdk2 and cdc2 in RP-A phosphorylation during the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):983–994. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnie N. J., Gottlieb T. M., Blunt T., Jeggo P. A., Jackson S. P. DNA-dependent protein kinase activity is absent in xrs-6 cells: implications for site-specific recombination and DNA double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):320–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Estus S., Johnson E. M., Jr Analysis of cell cycle-related gene expression in postmitotic neurons: selective induction of Cyclin D1 during programmed cell death. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90276-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazitt Y., Erdos G. W. Fluctuations and ultrastructural localization of oncoproteins and cell cycle regulatory proteins during growth and apoptosis of synchronized AGF cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):950–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley R. S., Rempel R. E., Maller J. L. In vivo regulation of the early embryonic cell cycle in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1996 Feb 1;173(2):408–419. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans cell survival gene ced-9 encodes a functional homolog of the mammalian proto-oncogene bcl-2. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):665–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang A. T., Cohen K. J., Barrett J. F., Bergstrom D. A., Dang C. V. Participation of cyclin A in Myc-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6875–6879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. A., Howell M., Hunt T., Newport J. W. Identification of a developmental timer regulating the stability of embryonic cyclin A and a new somatic A-type cyclin at gastrulation. Genes Dev. 1995 May 15;9(10):1164–1176. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.10.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Maller J. L. Elimination of cdc2 phosphorylation sites in the cdc25 phosphatase blocks initiation of M-phase. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1337–1350. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Burne J. F., King M. P., Miyashita T., Reed J. C., Raff M. C. Bcl-2 blocks apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):365–369. doi: 10.1038/361365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Meichle A., Steiner P., Pagano M., Finke K., Botz J., Wessbecher J., Draetta G., Eilers M. Differential modulation of cyclin gene expression by MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Harmon B., Searle J. An electron-microscope study of cell deletion in the anuran tadpole tail during spontaneous metamorphosis with special reference to apoptosis of striated muscle fibers. J Cell Sci. 1974 May;14(3):571–585. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.3.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Winterford C. M., Harmon B. V. Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer. 1994 Apr 15;73(8):2013–2026. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940415)73:8<2013::aid-cncr2820730802>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King K. L., Cidlowski J. A. Cell cycle and apoptosis: common pathways to life and death. J Cell Biochem. 1995 Jun;58(2):175–180. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240580206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoblich J. A., Lehner C. F. Synergistic action of Drosophila cyclins A and B during the G2-M transition. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):65–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L. J., Prives C. p53: puzzle and paradigm. Genes Dev. 1996 May 1;10(9):1054–1072. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.9.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranenburg O., van der Eb A. J., Zantema A. Cyclin D1 is an essential mediator of apoptotic neuronal cell death. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):46–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik Y. A., Cole S., Cooke C. A., Nelson W. G., Earnshaw W. C. Nuclear events of apoptosis in vitro in cell-free mitotic extracts: a model system for analysis of the active phase of apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):7–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon S. V., Martin S. J., Cotter T. G. Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in human tumour cell lines by widely diverging stimuli. Cell Prolif. 1991 Mar;24(2):203–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1991.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu V. F., Weaver D. T. The ionizing radiation-induced replication protein A phosphorylation response differs between ataxia telangiectasia and normal human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7222–7231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Hematopoietic cells from mice deficient in wild-type p53 are more resistant to induction of apoptosis by some agents. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Lennon S. V., Bonham A. M., Cotter T. G. Induction of apoptosis (programmed cell death) in human leukemic HL-60 cells by inhibition of RNA or protein synthesis. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1859–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikrantz W., Gisselbrecht S., Tam S. W., Schlegel R. Activation of cyclin A-dependent protein kinases during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3754–3758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikrantz W., Schlegel R. Apoptosis and the cell cycle. J Cell Biochem. 1995 Jun;58(2):160–174. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240580205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikrantz W., Schlegel R. Suppression of apoptosis by dominant negative mutants of cyclin-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 26;271(17):10205–10209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.17.10205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden J. S., Agard D. A., Sedat J. W., Alberts B. M. Direct cell lineage analysis in Drosophila melanogaster by time-lapse, three-dimensional optical microscopy of living embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):505–516. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Golsteyn R., Hill C. S., Hunt T. The A- and B-type cyclin associated cdc2 kinases in Xenopus turn on and off at different times in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2865–2875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Wang H. G., Lin H. K., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Cell cycle extracts. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:581–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Farschon D. M., Reed J. C. Cell-free apoptosis in Xenopus egg extracts: inhibition by Bcl-2 and requirement for an organelle fraction enriched in mitochondria. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: II. Control of the onset of transcription. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., MacFarlane M., Fearnhead H., Cohen G. M. Cdc2 activation is not required for thymocyte apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 15;202(3):1400–1406. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F. A., Hochegger K., Fröschl G., Tiefenbacher R., Pavelka M. Chromatin condensation during apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of lamin A+B, without enhanced activation of cdc2 kinase. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):827–837. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ongkeko W., Ferguson D. J., Harris A. L., Norbury C. Inactivation of Cdc2 increases the level of apoptosis induced by DNA damage. J Cell Sci. 1995 Aug;108(Pt 8):2897–2904. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.8.2897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. B. Xenopus laevis: Practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Solutions and protocols. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rempel R. E., Sleight S. B., Maller J. L. Maternal Xenopus Cdk2-cyclin E complexes function during meiotic and early embryonic cell cycles that lack a G1 phase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6843–6855. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. L., Philpott K. L., Brooks S. F. Apoptosis: the cell cycle and cell death. Curr Biol. 1993 Jun 1;3(6):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle J., Lawson T. A., Abbott P. J., Harmon B., Kerr J. F. An electron-microscope study of the mode of cell death induced by cancer-chemotherapeutic agents in populations of proliferating normal and neoplastic cells. J Pathol. 1975 Jul;116(3):129–138. doi: 10.1002/path.1711160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumaran M., Lin H. K., Miyashita T., Wang H. G., Krajewski S., Reed J. C., Hoffman B., Liebermann D. Immediate early up-regulation of bax expression by p53 but not TGF beta 1: a paradigm for distinct apoptotic pathways. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1791–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen S., D'Incalci M. Apoptosis. Biochemical events and relevance to cancer chemotherapy. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80914-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Nishioka W. K., Th'ng J., Bradbury E. M., Litchfield D. W., Greenberg A. H. Premature p34cdc2 activation required for apoptosis. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1143–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.8108732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U. P., Howell M., Descombes P., Chevalier S., Rempel R. E., Adamczewski J., Maller J. L., Hunt T., Blow J. J. Both cyclin A and cyclin E have S-phase promoting (SPF) activity in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Sci. 1996 Jun;109(Pt 6):1555–1563. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.6.1555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchang F., Gusse M., Soussi T., Méchali M. Stabilization and expression of high levels of p53 during early development in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):163–172. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S. Death by suicide: one way to go in mammalian cellular development? New Biol. 1991 Feb;3(2):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L. Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):786–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Stillman B. Anatomy of a DNA replication fork revealed by reconstitution of SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):207–212. doi: 10.1038/369207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Maller J. L. Role for cyclin A in the dependence of mitosis on completion of DNA replication. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):314–317. doi: 10.1038/354314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Grunwald D., Wilder S., Kimchi A., May E., Lawrence J. J., May P., Oren M. p53-mediated cell death: relationship to cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S., Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]











