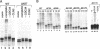Abstract
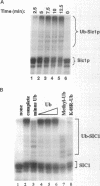
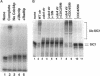
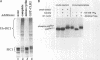
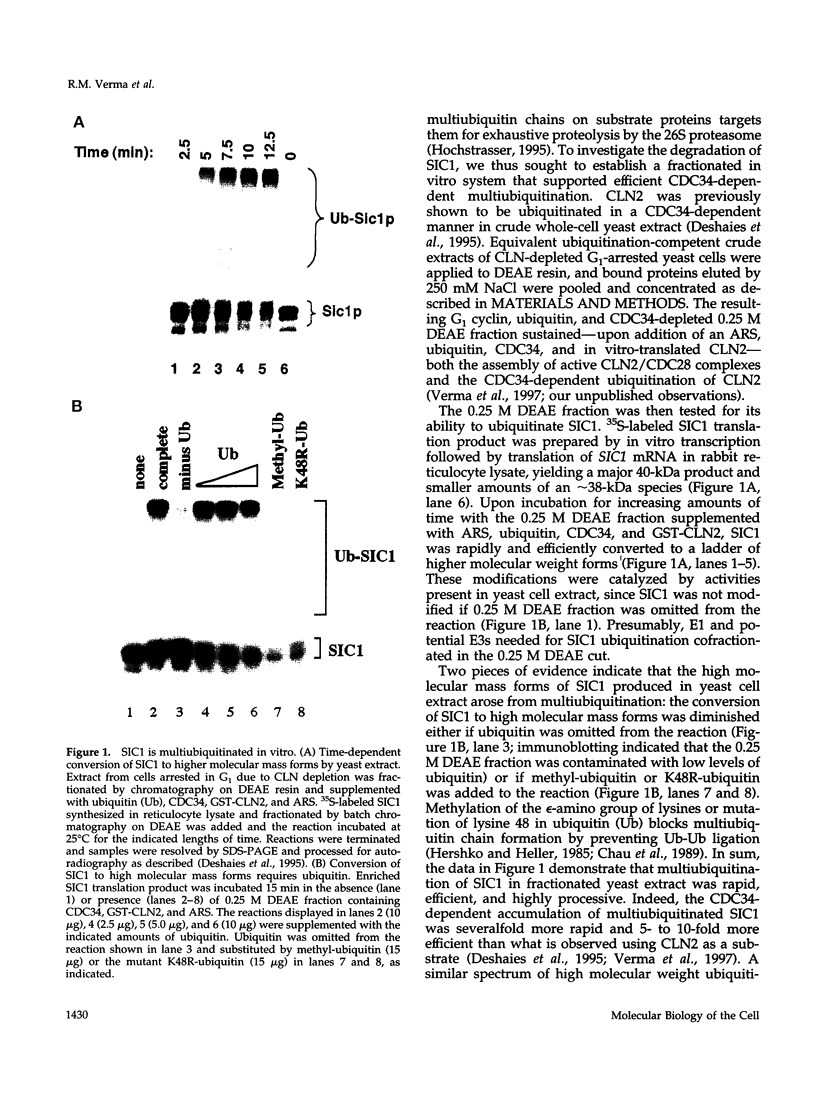
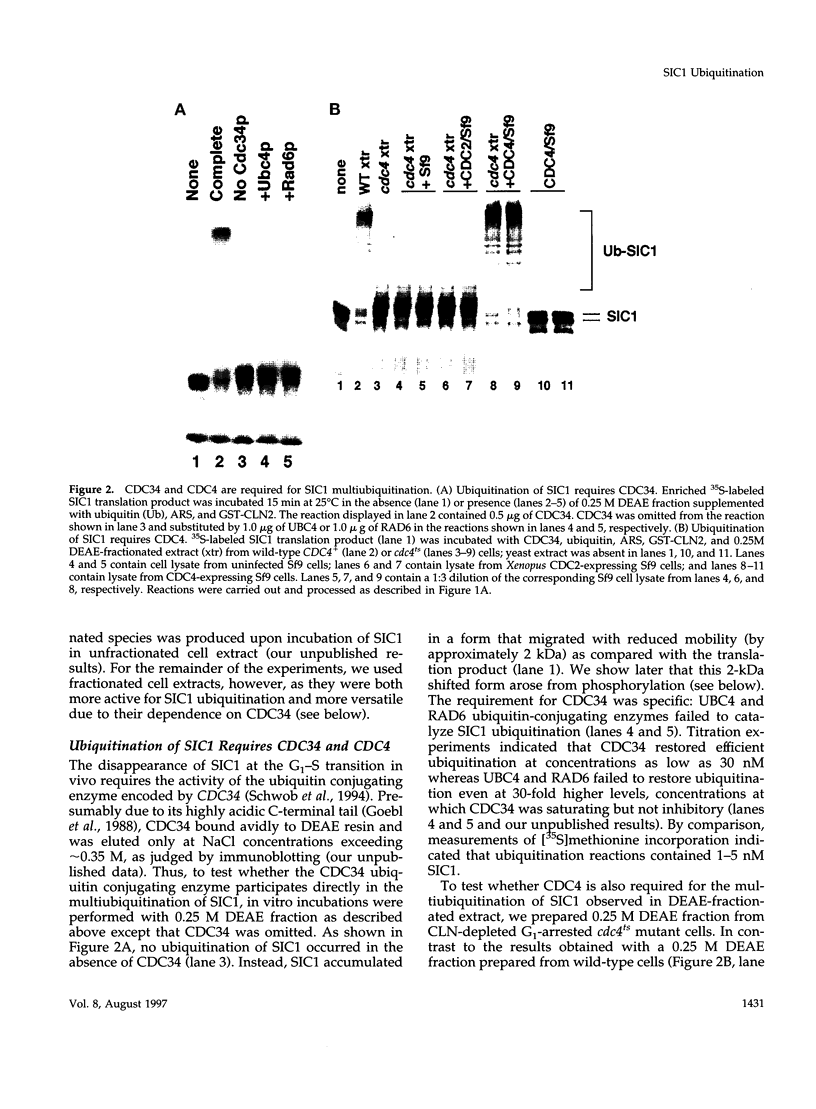
Traversal from G1 to S-phase in cycling cells of budding yeast is dependent on the destruction of the S-phase cyclin/CDK inhibitor SIC1. Genetic data suggest that SIC1 proteolysis is mediated by the ubiquitin pathway and requires the action of CDC34, CDC4, CDC53, SKP1, and CLN/CDC28. As a first step in defining the functions of the corresponding gene products, we have reconstituted SIC1 multiubiquitination in DEAE-fractionated yeast extract. Multiubiquitination depends on cyclin/CDC28 protein kinase and the CDC34 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Ubiquitin chain formation is abrogated in cdc4ts mutant extracts and assembly restored by the addition of exogenous CDC4, suggesting a direct role for this protein in SIC1 multiubiquitination. Deletion analysis of SIC1 indicates that the N-terminal 160 residues are both necessary and sufficient to serve as substrate for CDC34-dependent ubiquitination. The complementary C-terminal segment of SIC1 binds to the S-phase cyclin CLB5, indicating a modular structure for SIC1.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. D., Sellers W. R., Sharma S. K., Wu A. D., Nalin C. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr Identification of a cyclin-cdk2 recognition motif present in substrates and p21-like cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;16(12):6623–6633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.12.6623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai C., Sen P., Hofmann K., Ma L., Goebl M., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996 Jul 26;86(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Gregori L., Xu Y., Chau V. The bacterially expressed yeast CDC34 gene product can undergo autoubiquitination to form a multiubiquitin chain-linked protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5668–5675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel B., Wünning I., Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3179–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers E. P., Callis J. Utility of polyhistidine-tagged ubiquitin in the purification of ubiquitin-protein conjugates and as an affinity ligand for the purification of ubiquitin-specific hydrolases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21645–21649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau V., Tobias J. W., Bachmair A., Marriott D., Ecker D. J., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1576–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2538923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Chau V., Kirschner M. Ubiquitination of the G1 cyclin Cln2p by a Cdc34p-dependent pathway. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):303–312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Kirschner M. G1 cyclin-dependent activation of p34CDC28 (Cdc28p) in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirick L., Böhm T., Nasmyth K. Roles and regulation of Cln-Cdc28 kinases at the start of the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 2;14(19):4803–4813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. D., Toyn J. H., Johnson A. L., Johnston L. H. P40SDB25, a putative CDK inhibitor, has a role in the M/G1 transition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1640–1653. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G., Yochem J., Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A., Byers B. The yeast cell cycle gene CDC34 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1331–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2842867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H. Occurrence of a polyubiquitin structure in ubiquitin-protein conjugates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M. Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Localization of the E6-AP regions that direct human papillomavirus E6 binding, association with p53, and ubiquitination of associated proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4918–4927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. R., Kikuchi A., Fujii-Nakata T., Turck C. W., Murray A. W. Members of the NAP/SET family of proteins interact specifically with B-type cyclins. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(3):661–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Schleiffer A., Ammerer G., Nasmyth K. Switching transcription on and off during the yeast cell cycle: Cln/Cdc28 kinases activate bound transcription factor SBF (Swi4/Swi6) at start, whereas Clb/Cdc28 kinases displace it from the promoter in G2. Genes Dev. 1996 Jan 15;10(2):129–141. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambright D. G., Sondek J., Bohm A., Skiba N. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.0 A crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):311–319. doi: 10.1038/379311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini N. J., Reed S. I. Direct induction of G1-specific transcripts following reactivation of the Cdc28 kinase in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):557–567. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias N., Johnson S. L., Winey M., Adams A. E., Goetsch L., Pringle J. R., Byers B., Goebl M. G. Cdc53p acts in concert with Cdc4p and Cdc34p to control the G1-to-S-phase transition and identifies a conserved family of proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;16(12):6634–6643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.12.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D. An inhibitor of p34CDC28 protein kinase activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):216–219. doi: 10.1126/science.8421781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Jones C. A., Reed S. I. Dual regulation of the yeast CDC28-p40 protein kinase complex: cell cycle, pheromone, and nutrient limitation effects. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):927–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J., Nambudripad R., Smith T. F. The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):297–300. doi: 10.1038/371297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugroho T. T., Mendenhall M. D. An inhibitor of yeast cyclin-dependent protein kinase plays an important role in ensuring the genomic integrity of daughter cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3320–3328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Rogers S. W. PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Jul;21(7):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Nuber U., Huibregtse J. M. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1-E2-E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):81–83. doi: 10.1038/373081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. L., Yang Q. H., Futcher A. B. Linkage of replication to start by the Cdk inhibitor Sic1. Science. 1996 Apr 26;272(5261):560–562. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5261.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob E., Böhm T., Mendenhall M. D., Nasmyth K. The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the G1 to S transition in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondek J., Bohm A., Lambright D. G., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a G-protein beta gamma dimer at 2.1A resolution. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):369–374. doi: 10.1038/379369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart E., Kobayashi H., Harrison D., Hunt T. Destruction of Xenopus cyclins A and B2, but not B1, requires binding to p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):584–594. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 imposes the requirement for Cln G1 cyclin function at Start. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7772–7776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma R., Chi Y., Deshaies R. J. Cell-free ubiquitination of cell cycle regulators in budding yeast extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1997;283:366–376. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(97)83030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall M. A., Coleman D. E., Lee E., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Posner B. A., Gilman A. G., Sprang S. R. The structure of the G protein heterotrimer Gi alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems A. R., Lanker S., Patton E. E., Craig K. L., Nason T. F., Mathias N., Kobayashi R., Wittenberg C., Tyers M. Cdc53 targets phosphorylated G1 cyclins for degradation by the ubiquitin proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1996 Aug 9;86(3):453–463. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Kobayashi R., Galaktionov K., Beach D. p19Skp1 and p45Skp2 are essential elements of the cyclin A-CDK2 S phase kinase. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]