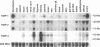Abstract
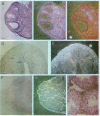
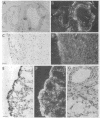
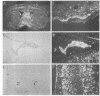
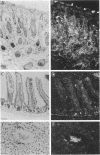
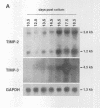
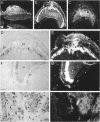
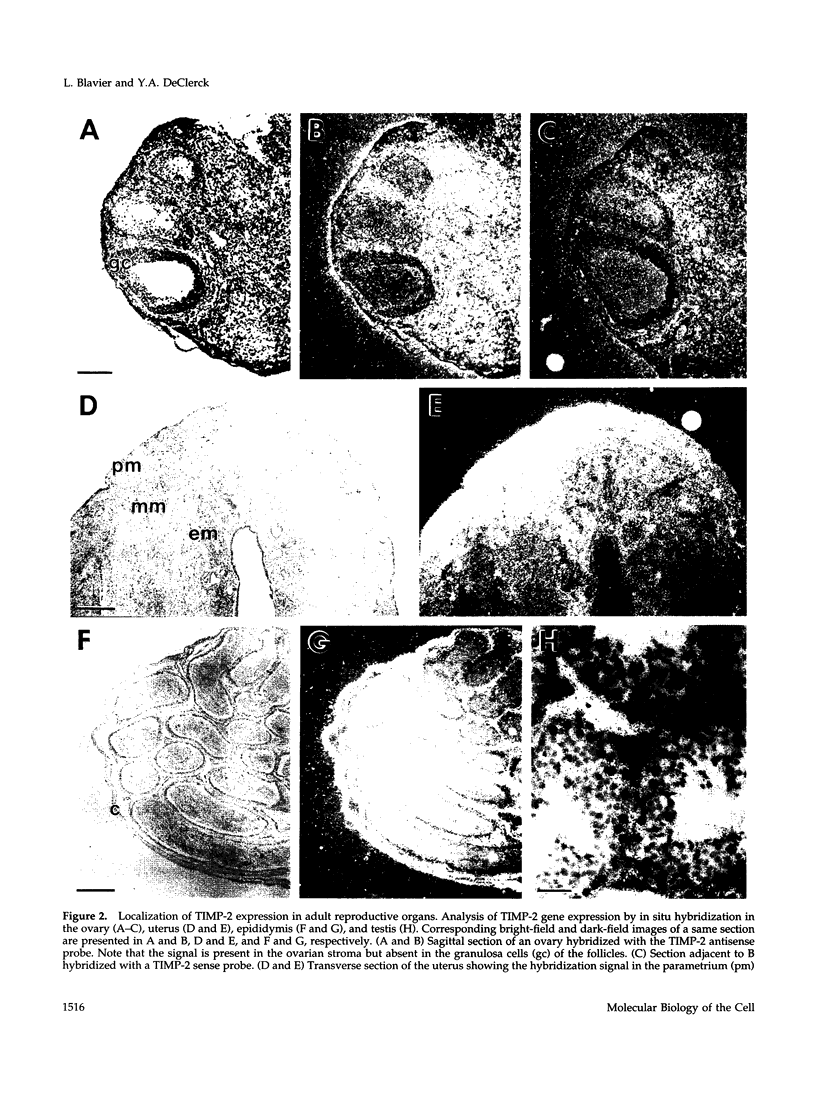
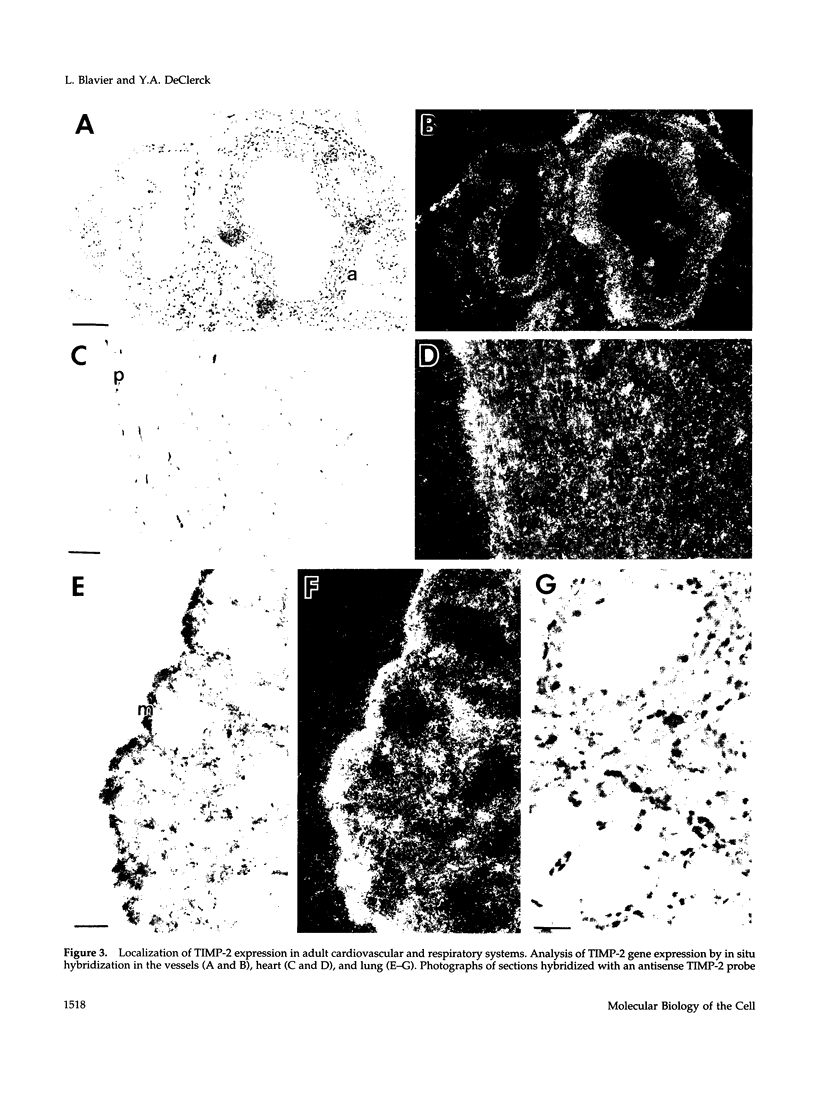
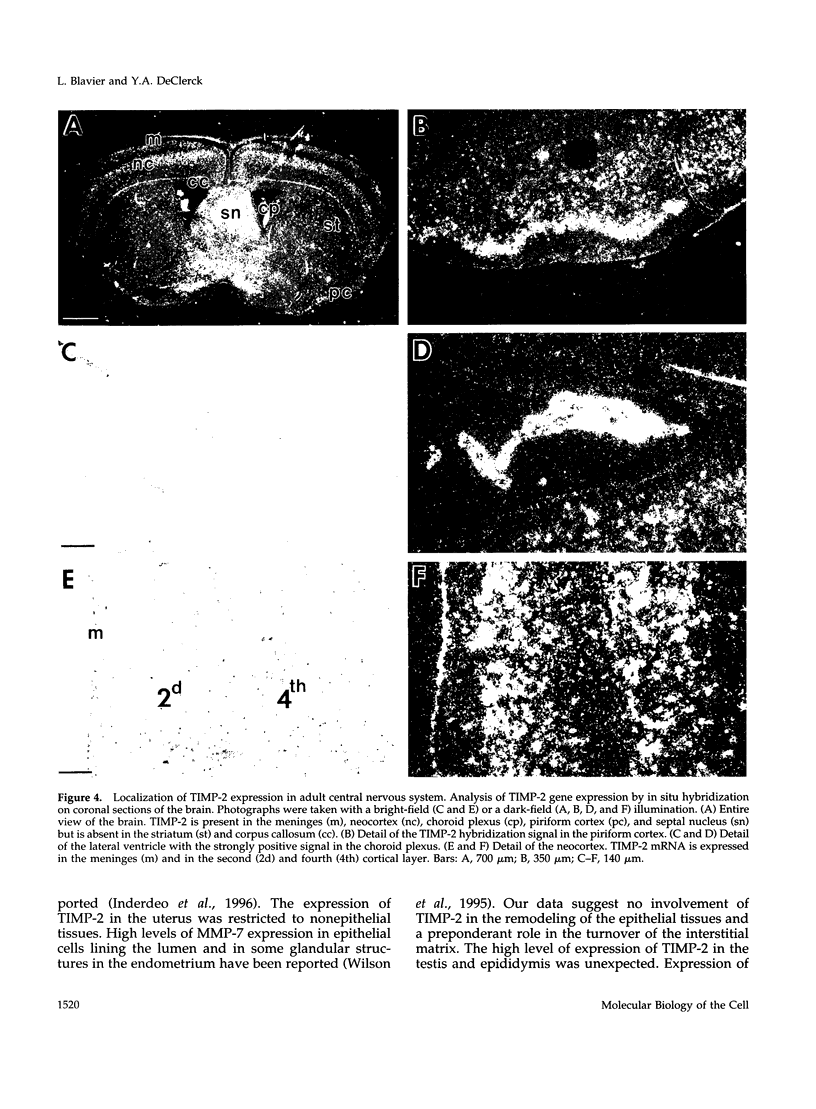
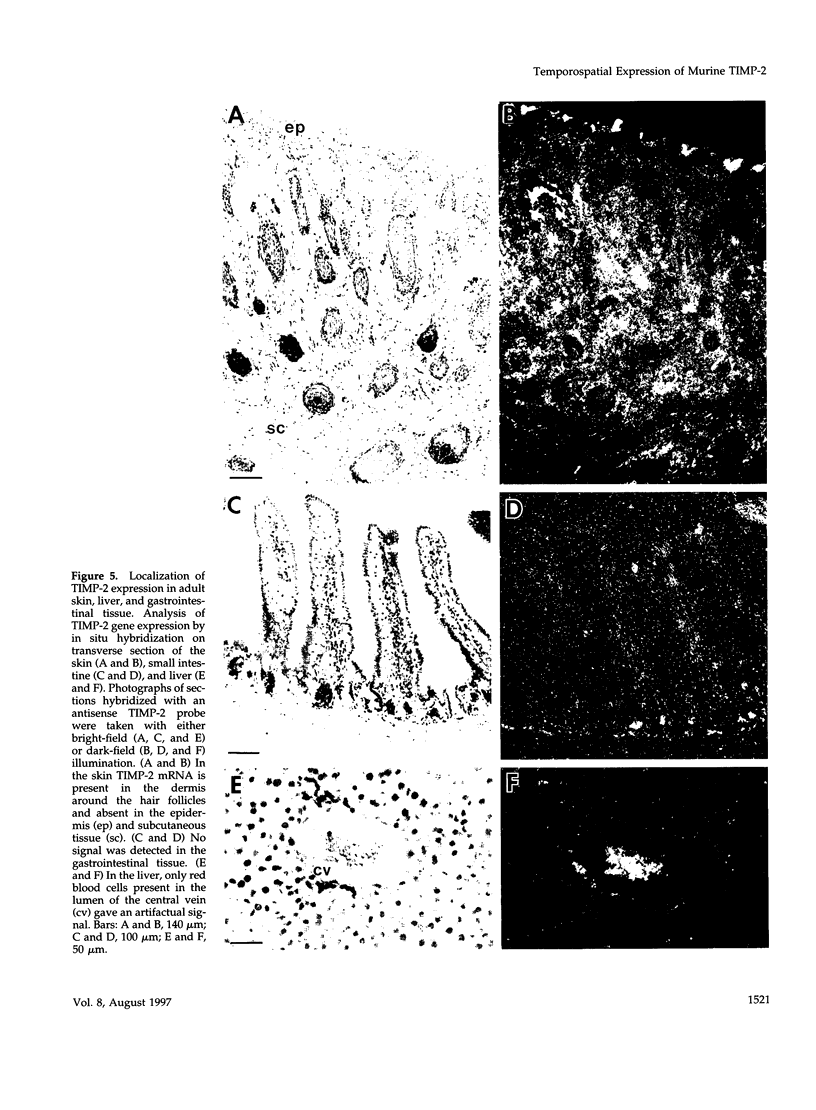
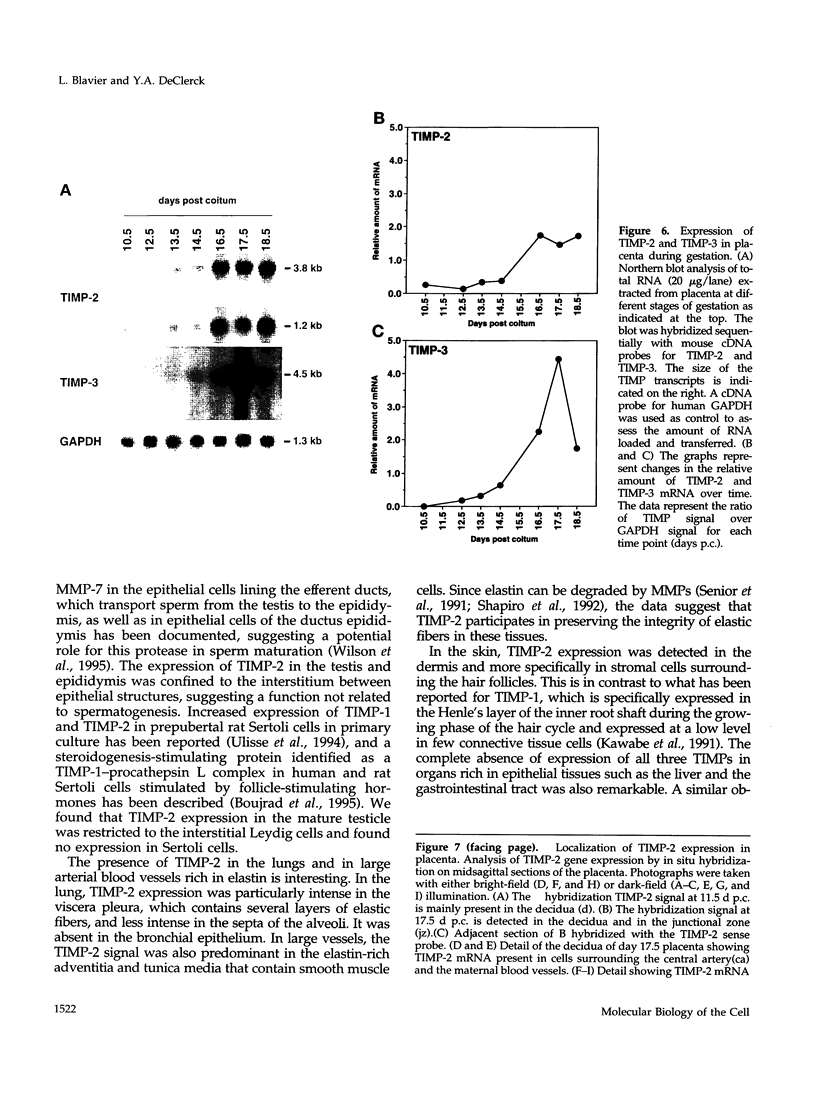
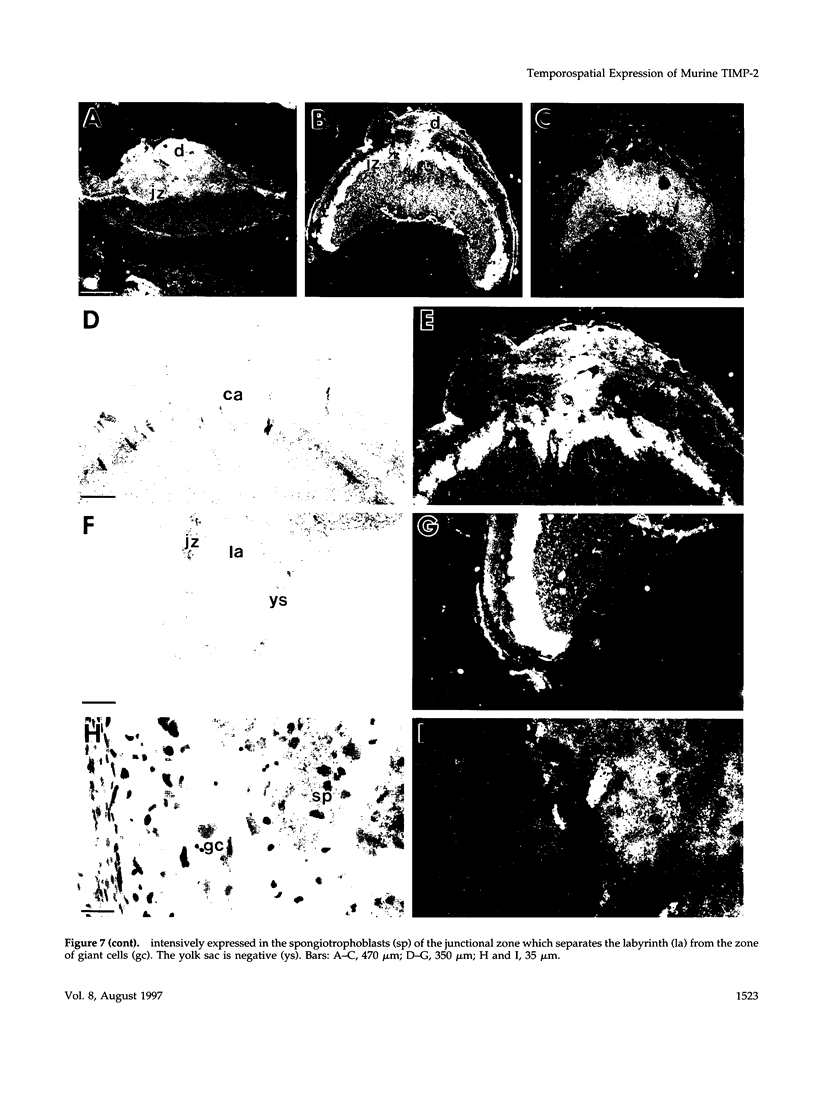
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) is a member of a family of inhibitors of matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. A better insight into the role of this inhibitor during development and in organ function was obtained by examining the temporospatial expression of TIMP-2 in mice. Northern blot analysis indicated high levels of TIMP-2 mRNA in the lung, skin, reproductive organs, and brain. Lower levels of expression were found in all other organs with the exception of the liver and gastrointestinal tissue, which were negative of these tissues with complete absence of TIMP-2 mRNA in the epithelium. In the testis, TIMP-2 was present in the Leydig cells, and in the brain, it was expressed in pia matter and in neuronal tissues. TIMP-2 expression in the placenta increased during late gestation and was particularly abundant in spongiotrophoblasts In mouse embryo (day 10.5-18.5), TIMP-2 mRNA was abundant in mesenchymal tissues that surrounded developing epithelia and maturing skeleton. The pattern of expression significantly differs from that observed with TIMP-1 and TIMP-3, therefore, suggesting specific roles for each inhibitor during tissue remodeling and development.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agren M. S. Gelatinase activity during wound healing. Br J Dermatol. 1994 Nov;131(5):634–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1994.tb04974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander C. M., Hansell E. J., Behrendtsen O., Flannery M. L., Kishnani N. S., Hawkes S. P., Werb Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development. 1996 Jun;122(6):1723–1736. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.6.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apte S. S., Hayashi K., Seldin M. F., Mattei M. G., Hayashi M., Olsen B. R. Gene encoding a novel murine tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP), TIMP-3, is expressed in developing mouse epithelia, cartilage, and muscle, and is located on mouse chromosome 10. Dev Dyn. 1994 Jul;200(3):177–197. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002000302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backstrom J. R., Lim G. P., Cullen M. J., Tökés Z. A. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is synthesized in neurons of the human hippocampus and is capable of degrading the amyloid-beta peptide (1-40). J Neurosci. 1996 Dec 15;16(24):7910–7919. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-24-07910.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Moore W. G., Bodden M. K., Windsor L. J., Birkedal-Hansen B., DeCarlo A., Engler J. A. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4(2):197–250. doi: 10.1177/10454411930040020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blavier L., Delaissé J. M. Matrix metalloproteinases are obligatory for the migration of preosteoclasts to the developing marrow cavity of primitive long bones. J Cell Sci. 1995 Dec;108(Pt 12):3649–3659. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.12.3649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone T. C., Johnson M. J., De Clerck Y. A., Langley K. E. cDNA cloning and expression of a metalloproteinase inhibitor related to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau N., Sympson C. J., Werb Z., Bissell M. J. Suppression of ICE and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):891–893. doi: 10.1126/science.7531366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boujrad N., Ogwuegbu S. O., Garnier M., Lee C. H., Martin B. M., Papadopoulos V. Identification of a stimulator of steroid hormone synthesis isolated from testis. Science. 1995 Jun 16;268(5217):1609–1612. doi: 10.1126/science.7777858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cañete-Soler R., Gui Y. H., Linask K. K., Muschel R. J. Developmental expression of MMP-9 (gelatinase B) mRNA in mouse embryos. Dev Dyn. 1995 Sep;204(1):30–40. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002040105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Darby J. A., Fuller K. Mammalian collagenase predisposes bone surfaces to osteoclastic resorption. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(3):671–675. doi: 10.1007/BF00214590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C. C., Chua B. H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mRNA for collagenase and TIMP in human skin fibroblasts. Connect Tissue Res. 1990;25(2):161–170. doi: 10.3109/03008209009006990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clerck Y. A., Darville M. I., Eeckhout Y., Rousseau G. G. Characterization of the promoter of the gene encoding human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2). Gene. 1994 Feb 25;139(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90753-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty A. J., Lyons A., Smith B. J., Wright E. M., Stephens P. E., Harris T. J., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Sequence of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and its identity to erythroid-potentiating activity. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):66–69. doi: 10.1038/318066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flenniken A. M., Williams B. R. Developmental expression of the endogenous TIMP gene and a TIMP-lacZ fusion gene in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1094–1106. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Wilhelm S., He C. S. Human 72-kilodalton type IV collagenase forms a complex with a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases designated TIMP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8207–8211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Strongin A., Collier I. E., Genrich L. T., Marmer B. L. Interaction of 92-kDa type IV collagenase with the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases prevents dimerization, complex formation with interstitial collagenase, and activation of the proenzyme with stromelysin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4583–4591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J., Wang M., Liu Y. E., Raymond L. A., Rosen C., Shi Y. E. Molecular cloning and characterization of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 4. J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 29;271(48):30375–30380. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.48.30375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammani K., Blakis A., Morsette D., Bowcock A. M., Schmutte C., Henriet P., DeClerck Y. A. Structure and characterization of the human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 gene. J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 11;271(41):25498–25505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.41.25498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey M. B., Leco K. J., Arcellana-Panlilio M. Y., Zhang X., Edwards D. R., Schultz G. A. Proteinase expression in early mouse embryos is regulated by leukaemia inhibitory factor and epidermal growth factor. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):1005–1014. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Yamashita K., Ohuchi E., Shinagawa A. Cell growth-promoting activity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2). J Cell Sci. 1994 Sep;107(Pt 9):2373–2379. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.9.2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Yamashita K., Tanzawa K., Uchijima E., Iwata K. Growth-promoting activity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) for a wide range of cells. A possible new growth factor in serum. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 17;298(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inderdeo D. S., Edwards D. R., Han V. K., Khokha R. Temporal and spatial expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases during the natural ovulatory cycle of the mouse. Biol Reprod. 1996 Sep;55(3):498–508. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod55.3.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T. T., Rea T. J., Flenniken A. M., Williams B. R., Groppi V. E., Buhl A. E. Localization of TIMP in cycling mouse hair. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):877–879. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoh H., Sato H., Tsunezuka Y., Takino T., Kawashima A., Okada Y., Seiki M. MT-MMP, the cell surface activator of proMMP-2 (pro-gelatinase A), is expressed with its substrate in mouse tissue during embryogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1996 May;109(Pt 5):953–959. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.5.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lala P. K., Graham C. H. Mechanisms of trophoblast invasiveness and their control: the role of proteases and protease inhibitors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Dec;9(4):369–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00049525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lala P. K., Hamilton G. S. Growth factors, proteases and protease inhibitors in the maternal-fetal dialogue. Placenta. 1996 Nov;17(8):545–555. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(96)80071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leco K. J., Apte S. S., Taniguchi G. T., Hawkes S. P., Khokha R., Schultz G. A., Edwards D. R. Murine tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4 (Timp-4): cDNA isolation and expression in adult mouse tissues. FEBS Lett. 1997 Jan 20;401(2-3):213–217. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(96)01474-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leco K. J., Hayden L. J., Sharma R. R., Rocheleau H., Greenberg A. H., Edwards D. R. Differential regulation of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA expression in normal and Ha-ras-transformed murine fibroblasts. Gene. 1992 Aug 15;117(2):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90731-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leco K. J., Khokha R., Pavloff N., Hawkes S. P., Edwards D. R. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) is an extracellular matrix-associated protein with a distinctive pattern of expression in mouse cells and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9352–9360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Guerne P. A. Interleukin-6 induces the synthesis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1/erythroid potentiating activity (TIMP-1/EPA). J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2017–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbaix E., Donnez J., Courtoy P. J., Eeckhout Y. Progesterone regulates the activity of collagenase and related gelatinases A and B in human endometrial explants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11789–11793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattot V., Raes M. B., Henriet P., Eeckhout Y., Stehelin D., Vandenbunder B., Desbiens X. Expression of interstitial collagenase is restricted to skeletal tissue during mouse embryogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1995 Feb;108(Pt 2):529–535. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.2.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. N., Unsworth E. J., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 inhibits bFGF-induced human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Nov;157(2):351–358. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müntener M., Hsu Y. C. Development of trophoblast and placenta of the mouse. A reinvestigation with regard to the in vitro culture of mouse trophoblast and placenta. Acta Anat (Basel) 1977;98(3):241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Hogan B. L., Wills A. J., Heath J. K., Edwards D. R. Developmental expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) RNA. Development. 1989 Mar;105(3):575–583. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.3.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polette M., Nawrocki B., Pintiaux A., Massenat C., Maquoi E., Volders L., Schaaps J. P., Birembaut P., Foidart J. M. Expression of gelatinases A and B and their tissue inhibitors by cells of early and term human placenta and gestational endometrium. Lab Invest. 1994 Dec;71(6):838–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reponen P., Leivo I., Sahlberg C., Apte S. S., Olsen B. R., Thesleff I., Tryggvason K. 92-kDa type IV collagenase and TIMP-3, but not 72-kDa type IV collagenase or TIMP-1 or TIMP-2, are highly expressed during mouse embryo implantation. Dev Dyn. 1995 Apr;202(4):388–396. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reponen P., Sahlberg C., Huhtala P., Hurskainen T., Thesleff I., Tryggvason K. Molecular cloning of murine 72-kDa type IV collagenase and its expression during mouse development. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7856–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers W. H., Osteen K. G., Matrisian L. M., Navre M., Giudice L. C., Gorstein F. Expression and localization of matrilysin, a matrix metalloproteinase, in human endometrium during the reproductive cycle. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Jan;168(1 Pt 1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(12)90922-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Fliszar C. J., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Human 92- and 72-kilodalton type IV collagenases are elastases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. D., Griffin G. L., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Welgus H. G., Senior R. M., Ley T. J. Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, and bacterial expression of a murine macrophage metalloelastase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4664–4671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Onisto M., Levy A. T., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) mRNA expression in tumor cell lines and human tumor tissues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13933–13938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). A new member of the metalloproteinase inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17374–17378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulisse S., Farina A. R., Piersanti D., Tiberio A., Cappabianca L., D'Orazi G., Jannini E. A., Malykh O., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., D'Armiento M. Follicle-stimulating hormone increases the expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 and induces TIMP-1 AP-1 site binding complex(es) in prepubertal rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1994 Dec;135(6):2479–2487. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.6.7988435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse P., Denhardt D. T., Khokha R. Temporal expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in mouse reproductive tissues during gestation. Mol Reprod Dev. 1993 Jul;35(3):219–226. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080350302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. L., Heppner K. J., Rudolph L. A., Matrisian L. M. The metalloproteinase matrilysin is preferentially expressed by epithelial cells in a tissue-restricted pattern in the mouse. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Jul;6(7):851–869. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.7.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr The family of matrix metalloproteinases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Sep 6;732:11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb24720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]