Abstract
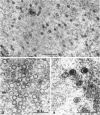
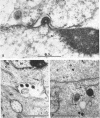
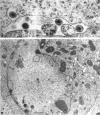
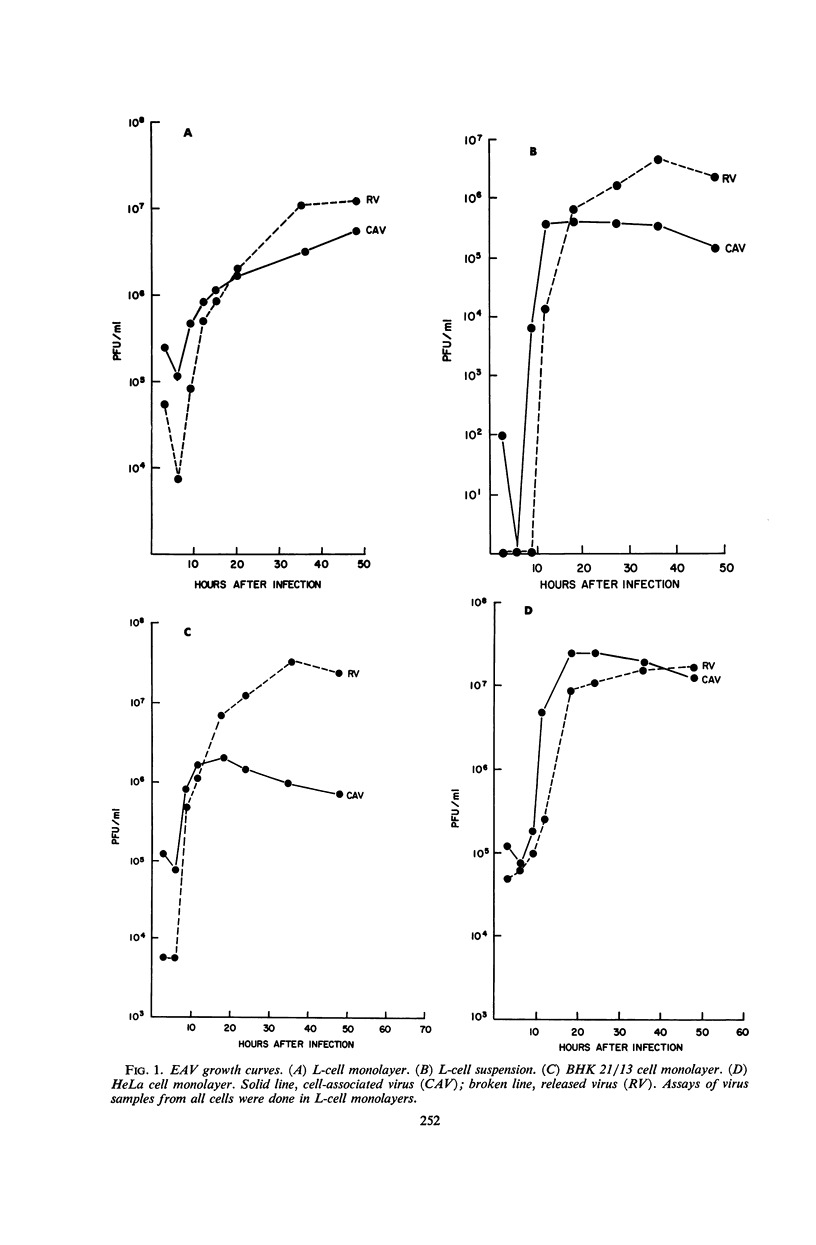
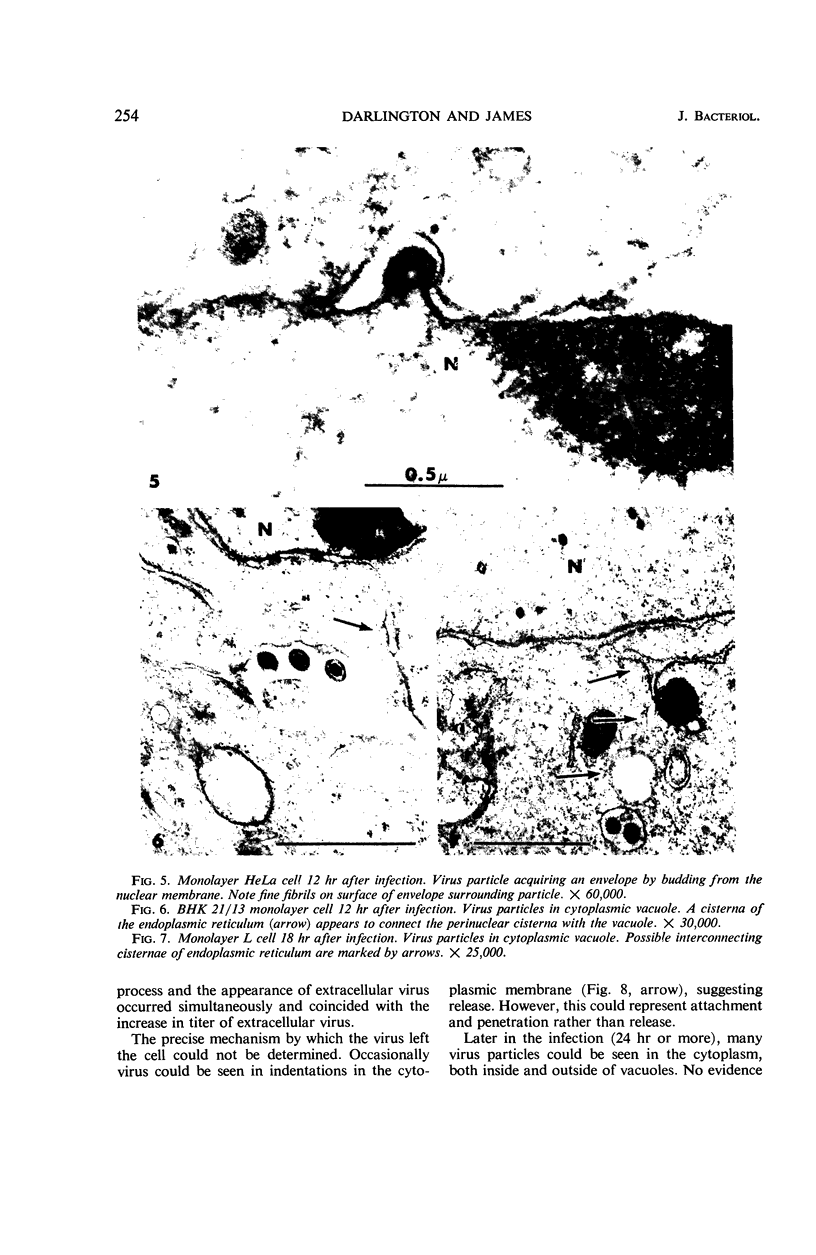
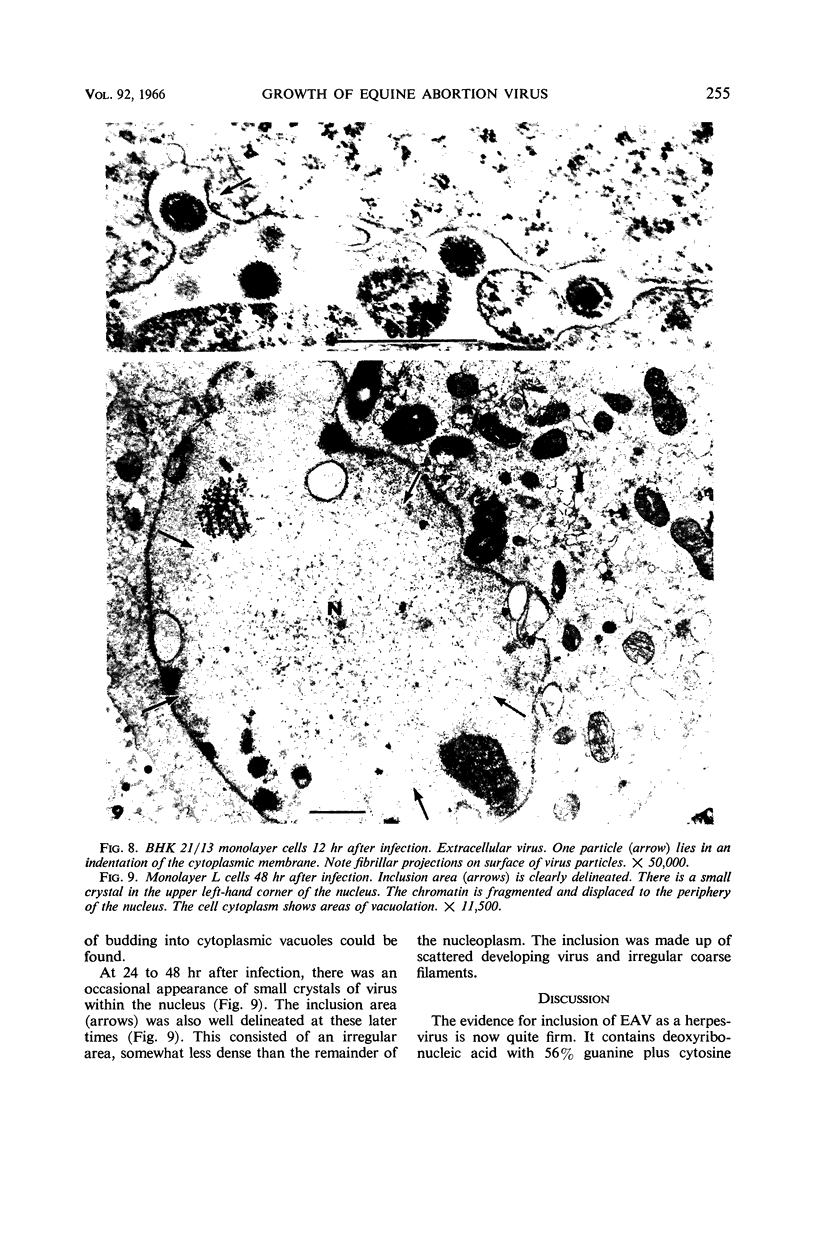
Darlington, R. W. (St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn.), and C. James. Biological and morphological aspects of the growth of equine abortion virus. J. Bacteriol. 92:250–257. 1966.—The growth of equine abortion virus (EAV) was studied by bioassay and electron microscopy in L-cell monolayer and suspension cultures, and in HeLa and BHK 21/13 cell monolayers. Results of virus assay (plaque-forming units) indicated that production of cell-associated virus (CAV) began at 6 to 9 hr after infection in all of the cell strains used. Virus release occurred 1 to 2 hr later. By 15 to 20 hr after infection, the amount of released virus (RV) equaled or surpassed that of CAV in all cells other than the HeLa cells, where the amount of RV did not equal CAV until 48 hr after infection. Electron microscopy of infected cells revealed no differences in the morphology of virus development in any of the cells used. Developing virus particles were first detected in cell nuclei at 9 hr after infection. At 12 hr, virus particles could be seen budding from the inner nuclear envelope. Budding into cytoplasmic vacuoles was not seen. Budding virus, virus in cytoplasmic vacuoles, and extracellular virus were all approximately 145 mμ in diameter, and were indistinguishable morphologically. These results indicated that EAV is quite similar to herpes simplex virus with respect to growth and morphology, and that the inner nuclear membrane is the principal site of virus envelopment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARHELGER R. B., DARLINGTON R. W., RANDALL C. C. An electron microscopic study of equine abortion virus infection in hamster liver. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jun;42:703–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER P., MELNICK J. L., MAYOR H. D. A MORPHOLOGIC COMPARISON BETWEEN THE DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF HERPES ZOSTER AND HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:11–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANS J. T., CROWE M. E., DOLL E. R., MCCOLLUM W. H. Isolation of a filterable agent causing arteritis of horses and abortion by mares; its differentiation from the equine abortion (influenza) virus. Cornell Vet. 1957 Jan;47(1):3–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARLINGTON R. W., RANDALL C. C. The nucleic acid content of equine abortion virus. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:322–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science. 1955 Sep 16;122(3168):501–514. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3168.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A. Observations on the mode of release of herpes virus from infected HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1962 Mar;12:589–597. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANDSON R. A. A NEW MAGAGLAS, D.E.R.(R) 732, EMBEDMENT FOR ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:704–709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES I. H., WATSON D. H. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE ATTACHMENT AND PENETRATION OF HERPES VIRUS IN BHK21 CELLS. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:112–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUCHLER R. J., MERCHANT D. J. Propagation of strain L (Earle) cells in agitated fluid suspension cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Aug-Sep;92(4):803–806. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L., MIDULLA M., WIMBERLY I., BARRERA-ORO J. G., LEVY B. M. A NEW MEMBER OF THE HERPESVIRUS GROUP ISOLATED FROM SOUTH AMERICAN MARMOSETS. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:596–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ROSE H. M., HOLDEN M., JONES E. P. Electron microscopic observations on the development of herpes simplex virus. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:643–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Simple dispositions in cells in situ. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Nov 25;1(6):567–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.6.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLUMMER G. SEROLOGICAL COMPARISON OF THE HERPES VIRUSES. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Apr;45:135–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLUMMER G., WATERSON A. P. Equine herpes viruses. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:412–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL C. C., LAWSON L. A. Adaptation of equine abortion virus to Earle's L cells in serum-free medium with plaque formation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jul;110:487–489. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECZKO E., MAYR A. UBER DIE FEINSTRUKTUR EINES VOM PFERD ISOLIERTEN VIRUS DER HERPESGRUPPE. (KURZE MITTEILUNG) Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1963 Aug 26;13:591–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOEHNER R. L., GENTRY G. A., RANDALL C. C. SOME PHYSICOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EQUINE ABORTION VIRUS NUCLEIC ACID. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:394–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M., MACPHERSON I. SYRIAN HAMSTER FIBROBLAST CELL LINE BHK21 AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1355–1357. doi: 10.1038/2031355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]