Abstract
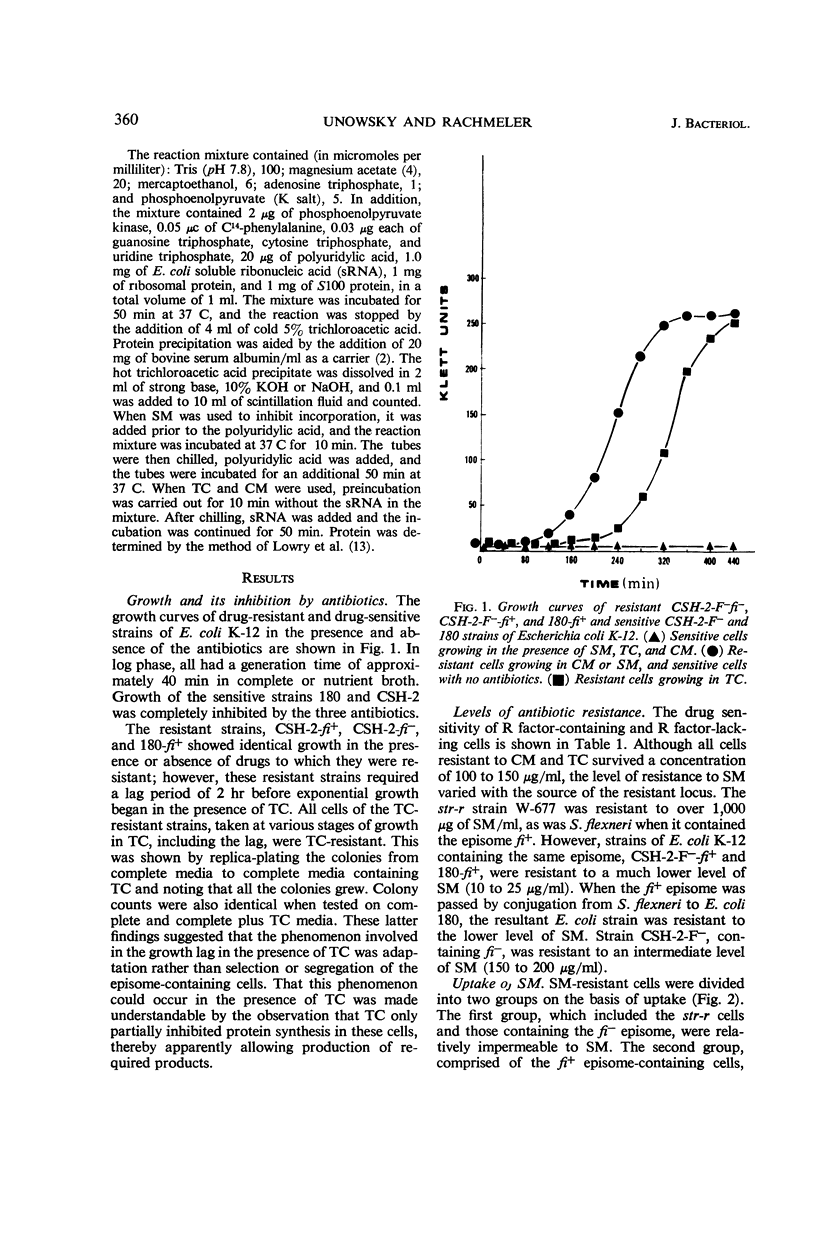
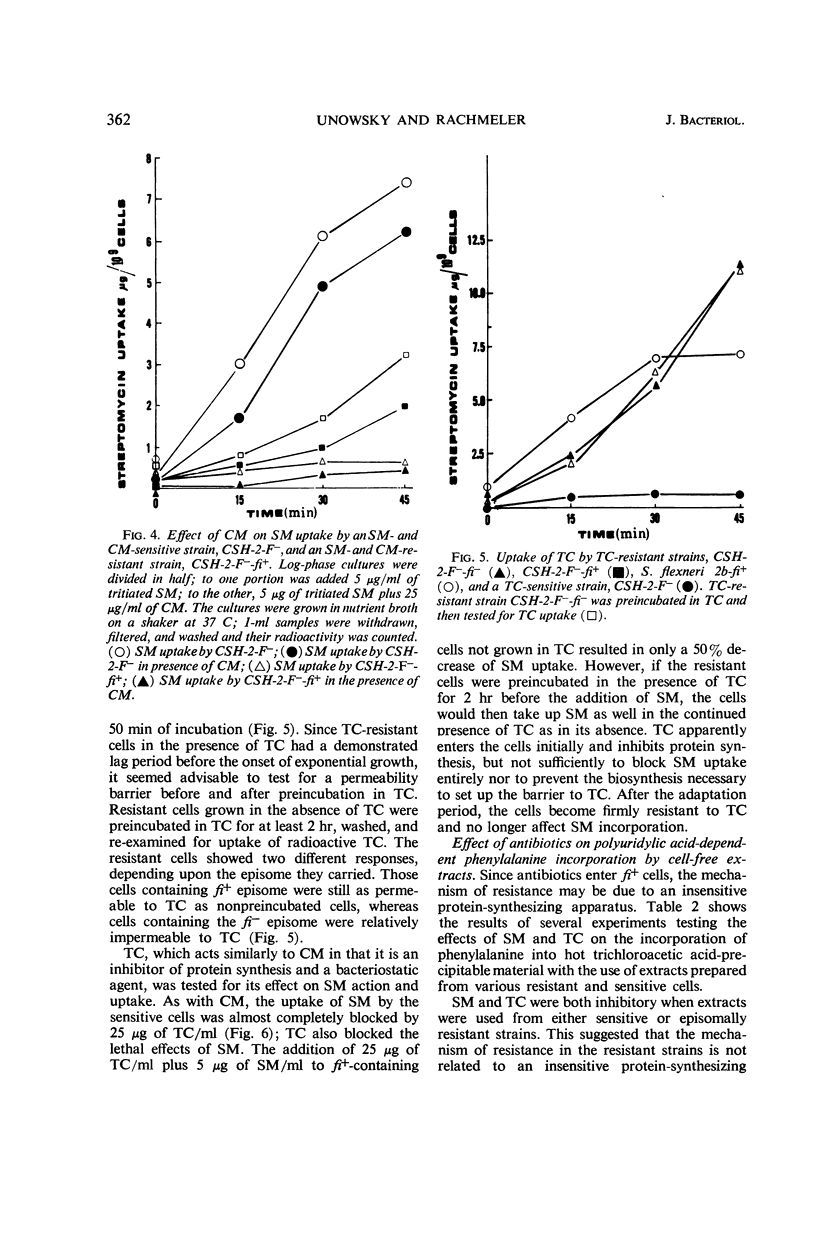
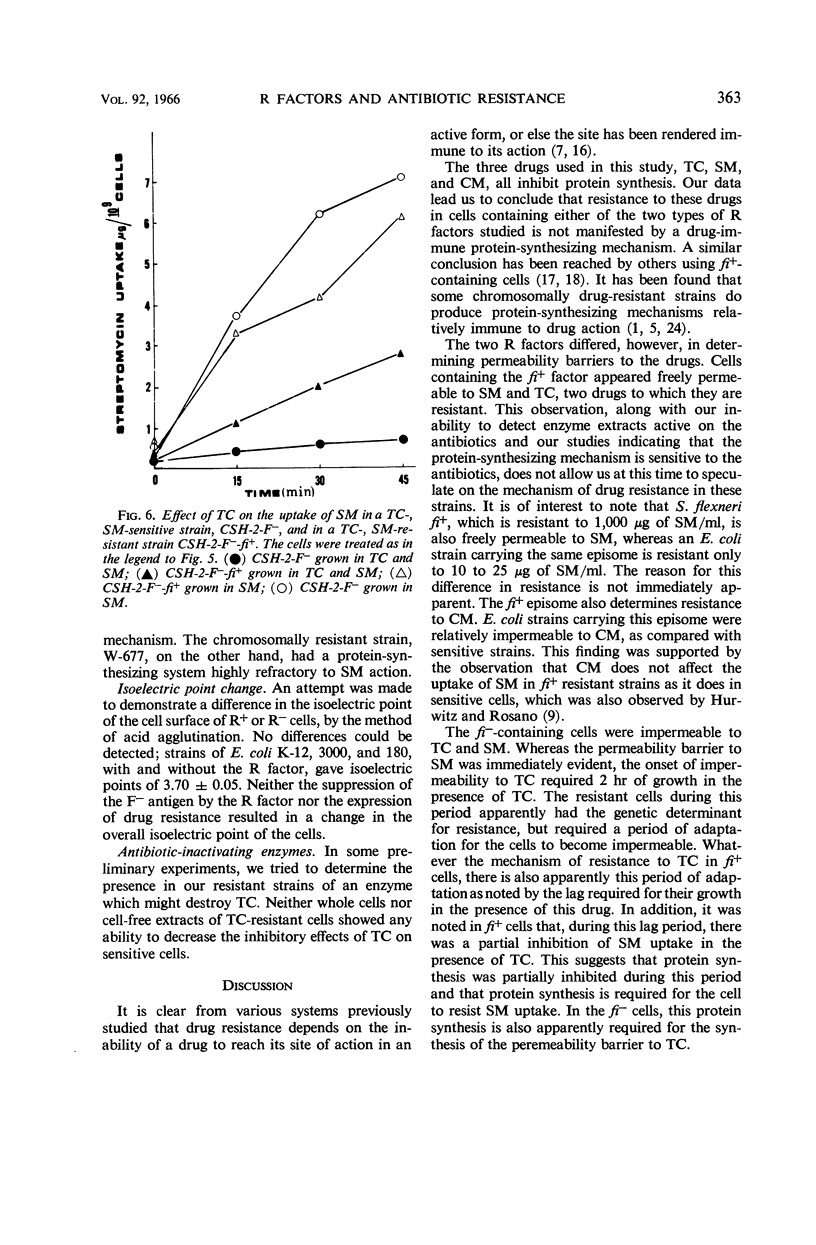
Unowsky, Joel (Northwestern University Medical School, Chicago, Ill.), and Martin Rachmeler. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance determined by resistance-transfer factors. J. Bacteriol. 92:358–365. 1966.—This study was concerned with the mechanism of expression of drug resistance carried by resistance-transfer (R) factors of two types: fi− (negative fertility inhibition) and fi+ (positive fertility inhibition). The levels of drug resistance determined by R factors used in this study were similar to those reported by other investigators. A new finding was that Escherichia coli carrying the fi− episome was resistant to 150 to 200 μg/ml of streptomycin. The growth kinetics of R factor-containing cells were similar in the presence or absence of streptomycin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline, but a period of adaptation was necessary before cells began exponential growth in the presence of tetracycline. By use of radioactive antibiotics, it was shown that cells containing the fi− episome were impermeable to tetracycline and streptomycin, whereas cells containing the fi+ episome were impermeable only to chloramphenicol. Cell-free extracts from fi+ and fi− cells were sensitive to the antibiotics tested in the polyuridylic acid-stimulated incorporation of phenylalanine into protein.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock T. D. CHLORAMPHENICOL. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Mar;25(1):32–48. doi: 10.1128/br.25.1.32-48.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX E. C., WHITE J. R., FLAKS J. G. STREPTOMYCIN ACTION AND THE RIBOSOME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:703–709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DATTA N. Transmissible drug resistance in an epidemic strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1962 Sep;60:301–310. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J. E. STUDIES ON THE RIBOSOMES OF STREPTOMYCIN-SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:659–664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J., GILBERT W., GORINI L. STREPTOMYCIN, SUPPRESSION, AND THE CODE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN T. J., GODFREY A. RESISTANCE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI TO TETRACYCLINES. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:54–60. doi: 10.1042/bj0940054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIROTA Y., NISHIMURA Y., ORSKOV F., ORSKOV I. EFFECT OF DRUG-RESISTANCE FACTOR R ON THE F PROPERTIES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:341–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.341-351.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Accumulation of label from C14-streptomycin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1193–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1193-1201.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Chloramphenicol-sensitive and-insensitive phases of the lethal action of streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1202–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1202-1209.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., HARADA K., HASHIMOTO H., EGAWA R. Drug-resistance of enteric bacteria. 5. Drug-resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from human being. Jpn J Exp Med. 1961 Feb;31:53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYED H. S. BIOCHEMICAL MECHANISMS OF DRUG RESISTANCE. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:347–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO S., MIZUNO D. MECHANISM OF CHLORAMPHENICOL AND TETRACYCLINE RESISTANCE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Apr;35:125–133. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKRANZ H. S. BASIS OF STREPTOMYCIN RESISTANCE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI WITH A "MULTIPLE DRUG RESISTANCE" EPISOME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:342–345. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ D. UPTAKE AND BINDING OF CHLORAMPHENICOL BY SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT ORGANISMS. Nature. 1964 Jul 18;203:257–258. doi: 10.1038/203257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., FUKASAWA T. Episome-mediated transfer of drug resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. I. Transfer of resistance factors by conjugation. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:669–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.669-678.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., NISHIDA H., OGATA C., ARAI T., SATO S. EPISOME-MEDIATED TRANSFER OF DRUG RESISTANCE IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. VII. TWO TYPES OF NATURALLY OCCURRING R FACTORS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:716–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.716-726.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., OGATA C., SATO S. EPISOME-MEDIATED TRANSFER OF DRUG RESISTANCE IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. 8. SIX-DRUG-RESISTANCE R FACTOR. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:922–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.922-928.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE A. D., HAHN F. E. MODE OF ACTION OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. IX. EFFECTS OF CHLORAMPHENICOL UPON A RIBOSOMAL AMINO ACID POLYMERIZATION SYSTEM AND ITS BINDING TO BACTERIAL RIBOSOME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:146–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


