Abstract
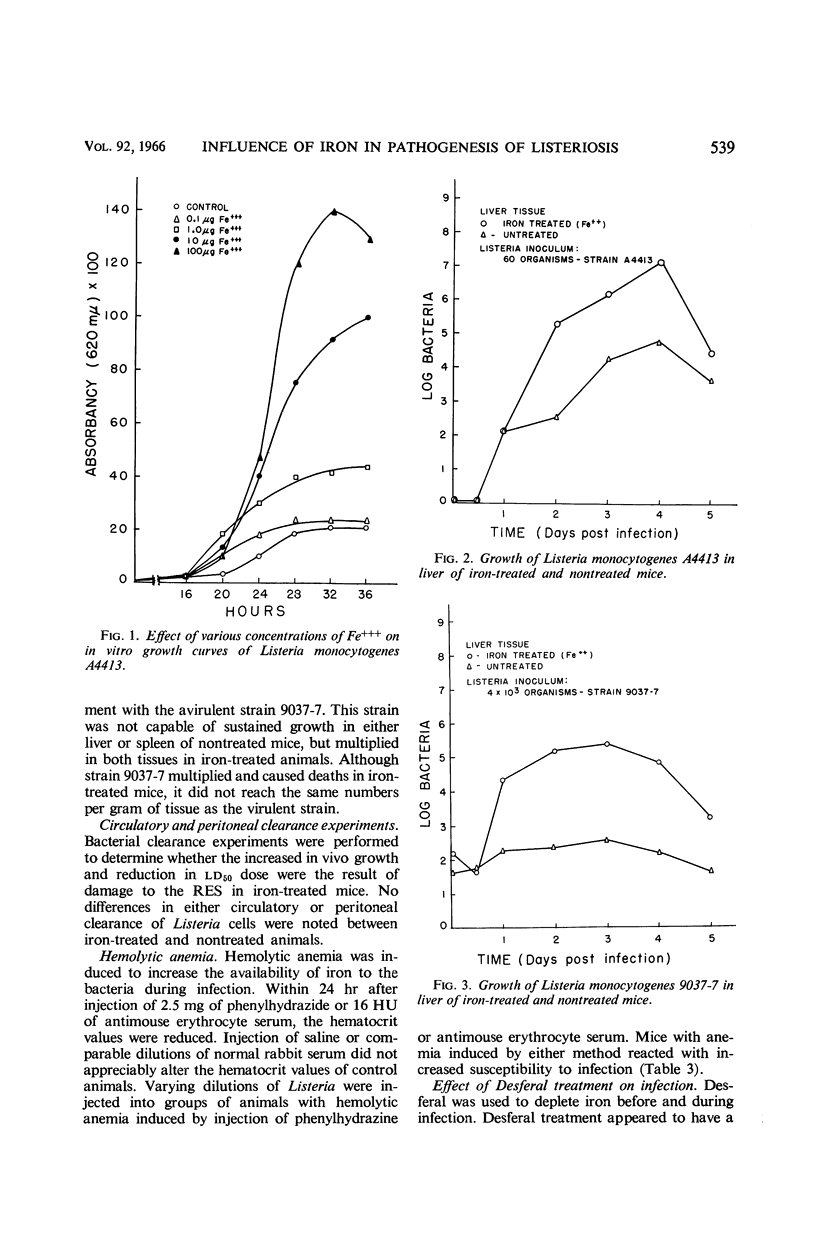
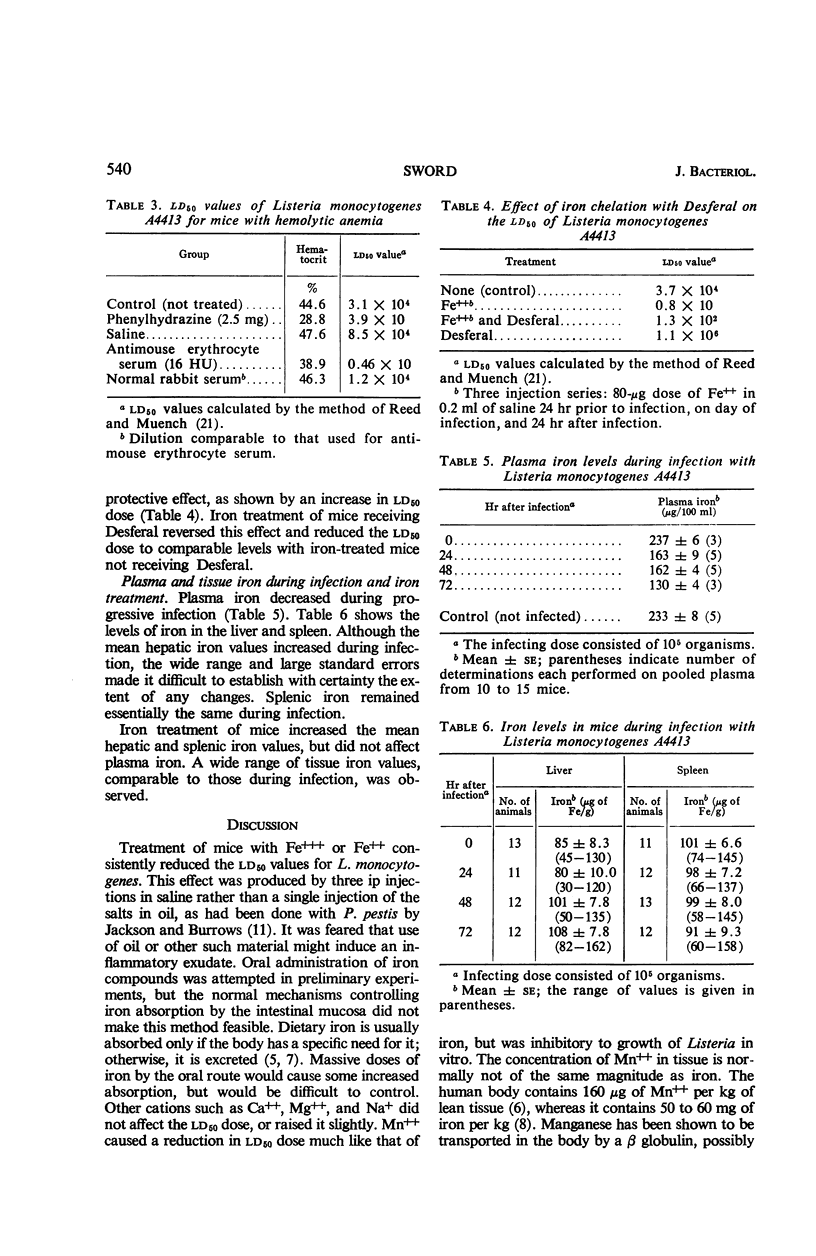
Sword, C. P. (The University of Kansas, Lawrence). Mechanisms of pathogenesis in Listeria monocytogenes infection. I. Influence of iron. J. Bacteriol. 92: 536–542. 1966.—The effects of ferric and ferrous iron as well as other cations on Listeria infection in mice were studied. Iron compounds caused a reduction in the ld50 dose of Listeria, and, when added to a synthetic medium, proved stimulatory for in vitro growth of the organism. Bacterial counts on spleen and liver tissue from iron-treated mice showed that iron injections caused more rapid growth of bacteria and resulted in higher numbers of organisms in the tissue. The reticuloendothelial system did not appear to be impaired by this treatment. Immunized animals were not affected by iron treatment during challenge. Mice with experimentally induced hemolytic anemia showed increased susceptibility to listeriosis, whereas those treated with Desferal, a specific iron-chelating agent, appeared more resistant. Iron proved stimulatory for the avirulent strain, 9037–7, and resulted in an ld50 of 1.3 × 104 organisms in iron-treated animals. Growth of L. monocytogenes and mortality from experimental infection appeared to be correlated with availability of iron to the bacteria. The results suggest that host iron metabolism may play a part in the onset and progress of Listeria infections.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG A. S., SWORD C. P. CELLULAR RESISTANCE IN LISTERIOSIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:258–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong B. A., Sword C. P. Electron microscopy of Listeria monocytogenes-infected mouse spleen. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1346–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1346-1355.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONRAD M. E., Jr, CROSBY W. H. INTESTINAL MUCOSAL MECHANISMS CONTROLLING IRON ABSORPTION. Blood. 1963 Oct;22:406–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTZIAS G. C. Manganese versus magnesium: why are they so similar in vitro and so different in vivo? Fed Proc. 1961 Sep;20(3):98–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H. THE CONTROL OF IRON BALANCE BY THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Blood. 1963 Oct;22:441–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMULDER R. Iron: metabolism, biochemistry, and clinical pathological physiology; review of recent literature. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958 Aug;102(2):254–301. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1958.00260200082010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M. E., KAUTTER D. A. Effect of nutrition on the respiratory virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:456–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.456-462.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD K. F., SBARRA A. J., BARDAWIL W. A. Serology of Listeria monocytogenes. I. Characteristics of the soluble hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:349–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.349-355.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI A. N., ADAMS E. W. PURIFICATION OF THE SOLUBLE HEMOLYSINS OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.418-424.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAYE D., HOOK E. W. THE INFLUENCE OF HEMOLYSIS OR BLOOD LOSS ON SUSCEPTIBILITY TO INFECTION. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:65–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEELER R. F., GRAY M. L. Antigenic and related biochemical properties of Listeria monocytogenes. I. Preparation and composition of cell wall material. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:683–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.683-692.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. K., HEDBERG M. EFFECTS OF CORTISONE ON SUSCEPTIBILITY OF MICE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Mar;43:248–250. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/43.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHADE A. L., OYAMA J., REINHART R. W., MILLER J. R. Bound iron and unsaturated iron-binding capacity of serum; rapid and reliable quantitative determination. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Nov;87(2):443–448. doi: 10.3181/00379727-87-21407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHADE A. L. SIGNIFICANCE OF SERUM IRON FOR THE GROWTH, BIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS, AND METABOLISM OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem Z. 1963;338:140–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade A. L., Caroline L. An Iron-binding Component in Human Blood Plasma. Science. 1946 Oct 11;104(2702):340–341. doi: 10.1126/science.104.2702.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade A. L., Caroline L. RAW HEN EGG WHITE AND THE ROLE OF IRON IN GROWTH INHIBITION OF SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE, STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, ESCHERICHIA COLI AND SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Science. 1944 Jul 7;100(2584):14–15. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2584.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sword C. P. Serum protein alterations induced by Listeria monocytogenes infections. J Immunol. 1966 May;96(5):790–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSHIMER H. J. VITAMIN REQUIREMENTS OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1156–1159. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1156-1159.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



