Abstract
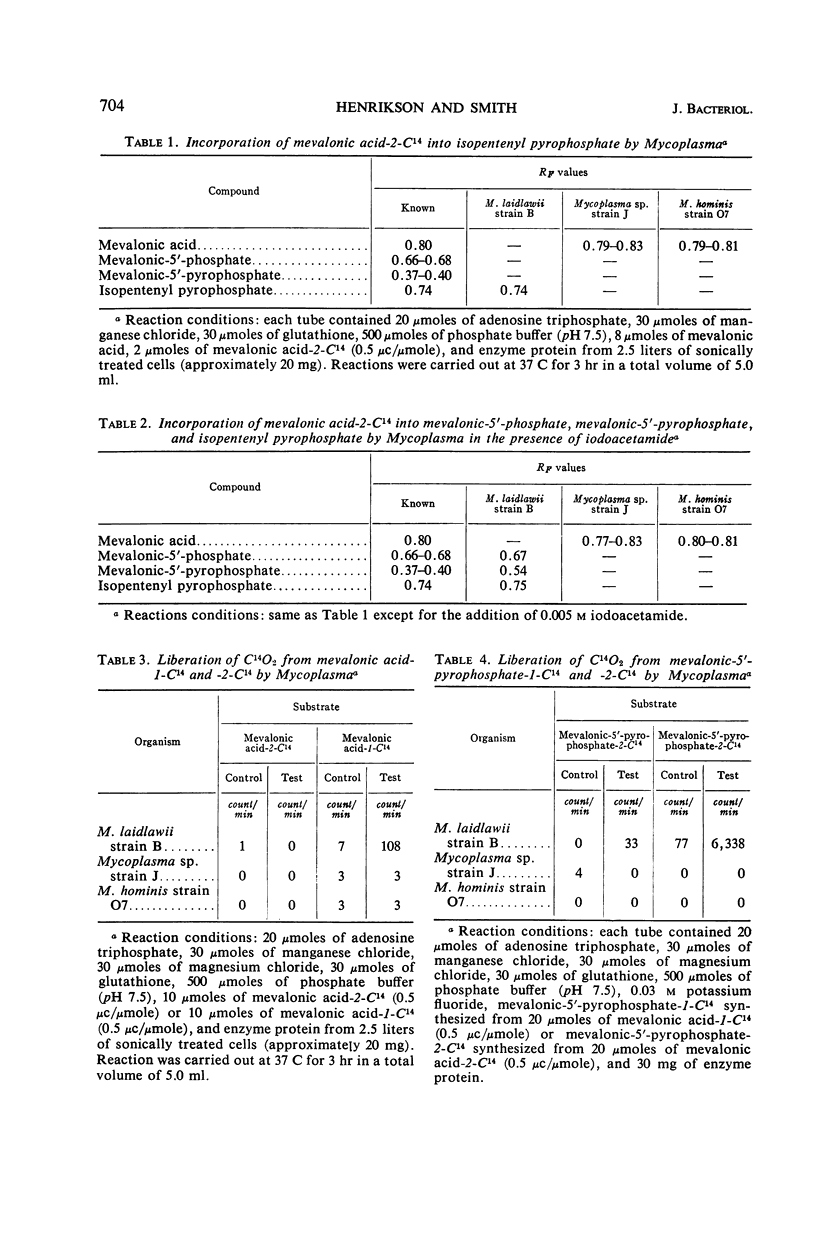
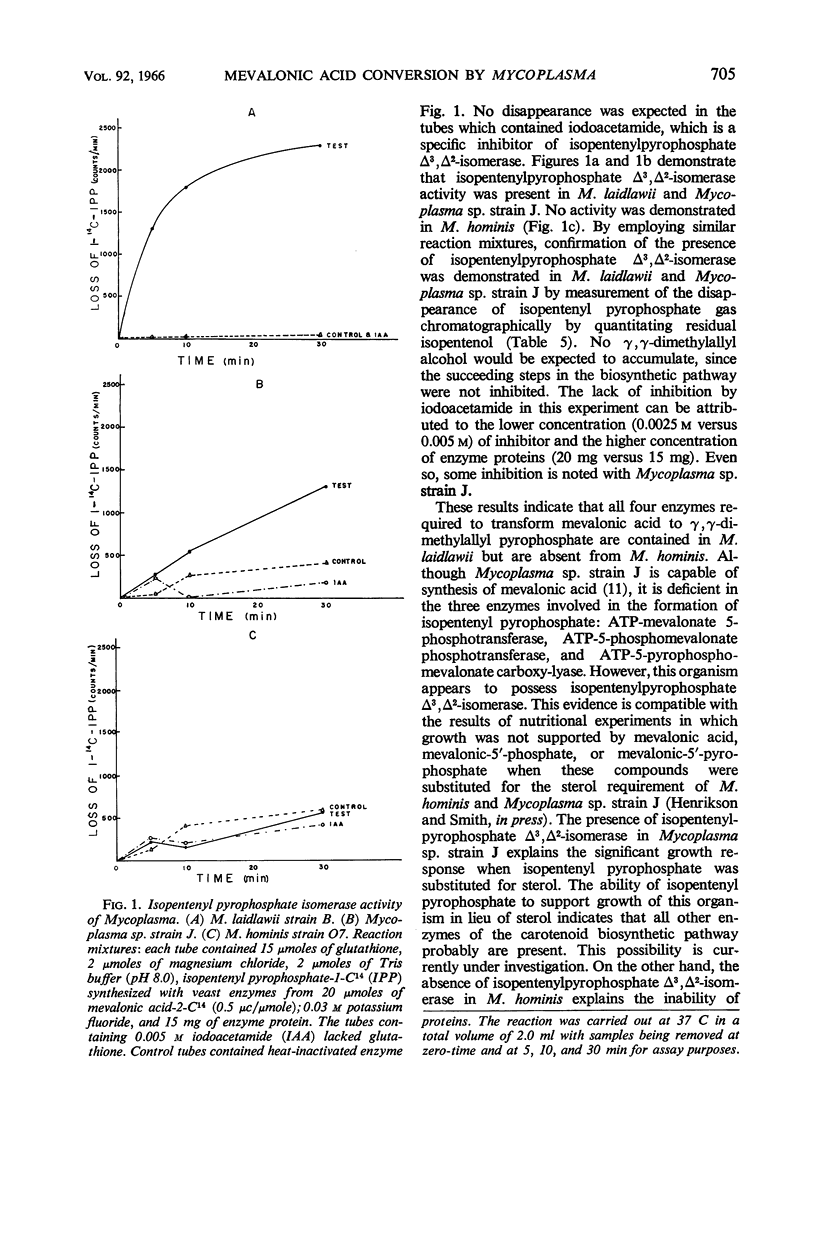
Henrikson, Carl V. (University of South Dakota, Vermillion), and Paul F. Smith. Conversion of mevalonic acid to γ,γ-dimethylallyl pyrophosphate by Mycoplasma. J. Bacteriol. 92:701–706. 1966.—Three representative strains of Mycoplasma, M. laidlawii strain B, Mycoplasma sp. avian strain J, and M. hominis type 2 strain O7, were examined for the presence or absence of enzymes associated with the biosynthetic pathway from mevalonic acid to γ,γ-dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. M. laidlawii served as a control organism, since it is capable of de novo biosynthesis of carotenoids. All four enzymes, namely, adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-mevalonate 5-phosphotransferase (EC 2.7.1.36), ATP-5-phosphomevalonate phosphotransferase (EC 2.7.4.2), ATP-5-pyrophosphomevalonate carboxy-lyase (EC 4.1.1.33), and isopentenylpyrophosphate Δ3,Δ2-isomerase (EC 5.3.3.2), were demonstrated in this organism. Mycoplasma sp. avian strain J, which contains all enzymes necessary for the biosynthesis of mevalonic acid, lacks the first three of the above enzymes but contains isopentenyl pyrophosphate Δ3,Δ2-isomerase. M. hominis, which lacks the enzymes necessary for the biosynthesis of mevalonic acid, also is deficient in the enzymes involved in its conversion to γ,γ-dimethylallyl pyrophosphate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGRANOFF B. W., EGGERER H., HENNING U., LYNEN F. Biosynthesis of terpenes. VII. Isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON D. G., PORTER J. W. The biosynthesis of phytoene and other carotenes by enzymes of isolated higher plant plastids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Jun;97:509–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCH K., CHAYKIN S., PHILLIPS A. H., DE WAARD A. Mevalonic acid pyrophosphate and isopentenylpyrophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2595–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaykin S., Law J., Phillips A. H., Tchen T. T., Bloch K. PHOSPHORYLATED INTERMEDIATES IN THE SYNTHESIS OF SQUALENE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):998–1004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. Amino acid metabolism by pleuropneumonialike organisms. I. General catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1955 Nov;70(5):552–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.5.552-556.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. COMPARATIVE PHYSIOLOGY OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE AND L-TYPE ORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Jun;28:97–125. doi: 10.1128/br.28.2.97-125.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., HENRIKSON C. V. COMPARATIVE BIOSYNTHESIS OF MEVALONIC ACID BY MYCOPLASMA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:146–153. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.146-153.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., NOVELLI G. D., LIPMANN F. Coenzyme A function in and acetyl transfer by the phosphotransacetylase system. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Henrikson C. V. Growth inhibition of Mycoplasma by inhibitors of polyterpene biosynthesis and its reversal by cholesterol. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1854–1858. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1854-1858.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TCHEN T. T. Mevalonic kinase: purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1100–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDEMARK P. J., SMITH P. F. EVIDENCE FOR A TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE IN MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1602–1607. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1602-1607.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTING L. A., PORTER J. W. Intermediates in the conversion of mevalonic acid to squalene by a rat liver enzyme system. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2841–2846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



