Abstract
B cells play a central role in the pathogenesis of multiple autoimmune diseases and the recognition of importance of B cells in these disorders has grown dramatically in association with the remarkable success of B-cell depletion as a treatment for autoimmunity. The precise mechanisms that promote alterations in B cell tolerance remain incompletely defined. There is increasing evidence, however, that TLRs play a major role in these events. Stimulation of B cells via the TLR pathway not only leads to an increase in antibody production but also promotes additional changes including cytokine production and upregulation of activation markers increasing the effectiveness of B cells as APCs. Understanding the role of TLRs in systemic autoimmunity will not only provide insight into the disease pathogenesis but may also lead to the development of novel therapies. This article gives an overview of TLR signaling in B cells and the possible involvement of such signals in autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: B cells, Toll-like receptors, TLR signaling, autoimmunity
Take home message
TLRs can be stimulated by exogenous and endogenous TLR ligands
Stimulation of B cells via TLRs leads to proliferation, up-regulation of co-stimulatory signals, immunoglobulin production, and cytokine secretion.
TLRs are also involved in class switching.
TLR signals can break tolerance in B cells.
Signaling via TLR7 and TLR9 seems to be predominantly involved in breaking tolerance.
TLRs are a potential target for therapeutic intervention in autoimmune diseases.
Introduction
B cells play a central role in the pathogenesis of SLE and other autoimmune diseases. The importance of B cells in these disorders is highlighted by the effectiveness of B cell depletion therapies and the dramatic increase in use for such therapies for additional disorders in recent years (Table 1). There is increasing evidence that B cells promote autoimmune disease not only by the production of auto-antibodies but also by serving as APCs for autoreactive T cells and by secretion of cytokines. Accordingly, remission of lupus nephritis after B cell depletion was associated with a decrease in T cell activation in blood (1). Most healthy individuals possess significant numbers of auto-reactive B cells (2) suggesting that additional events promoting alterations in B cell tolerance are required for initiation of autoimmune symptoms. Mounting evidence suggest that such changes may be mediated by TLR signaling as indicated by the fact that the onset or a flare of an autoimmune disease is often associated with an infection. This review will provide an overview of TLR signaling in B cells and the current ideas of how B cell intrinsic TLR signaling events might impact the development of autoimmunity.
Table 1.
| Autoimmune diseases that have been treated successfully with B cell depletion therapy |
|---|
|
Toll-like receptors and B cells
TLRs are receptors of the innate immune system (reviewed in (3)). In contrast to clonally rearranged antigen-specific T or B cell receptors, TLRs are germline encoded. To date, 10 distinct TLRs have been identified in humans and 11 have been described in mice. TLRs are expressed on both lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells including monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DC), B cells and endothelial cells or cardiac myocytes. TLRs are capable of sensing organisms ranging from bacteria to fungi, protozoa and viruses by recognizing conserved molecular patterns expressed by such organisms (so-called pathogen associated molecular patterns or PAMPs). The best known PAMP is LPS which is recognized by TLR4. In addition to PAMPS several endogenous ligands have also recently been identified and these may be especially important for the development of autoimmunity. Such endogenous ligands include unmethylated CpG DNA (recognized by TLR9), single-stranded RNA (recognized by TLR3, TLR7 and TLR8) as well as diverse products from dying cells (3) (4).
Amongst the cells of the immune system, B cells exhibit a unique status as they express both germline-encoded TLRs and a clonally rearranged, antigen specific receptor, the B cell antigen receptor (BCR). Naïve human B cells do not express significant levels of TLRs unless they are pre-stimulated through the BCR (5) (6). In contrast, human memory B cells constitutively express TRL2, TLR6, TLR7, TLR9 and TLR10. Expression of TLRs on murine B cells has not been analyzed as systematically as in humans. However, most TLRs seem to be expressed constitutively including TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9. As in humans, TLRs are expressed differentially in B cell subsets. In particular, marginal zone B cells express higher levels of TLRs compared to follicular mature B cells (7), consistent with their characterization as innate immune cells (8).
Effect of TLR signaling in B cells
All TLRs, except TLR3, utilize the adaptor molecule, MyD88, for propagation of downstream signaling. MyD88 is recruited to the receptor upon activation (reviewed in (3)) and initiates a signaling cascade that leads to the activation of NFκB and AP-1. These transcription factors function in concert to promote inflammatory responses. In contrast, TLR3 signals via a Myd88–independent pathway use the adaptor molecule TRIF. This pathway, also used by TRL4, leads to activation of the transcription factor IRF-3 (in addition to NFκB) and induction of type I INF expression.
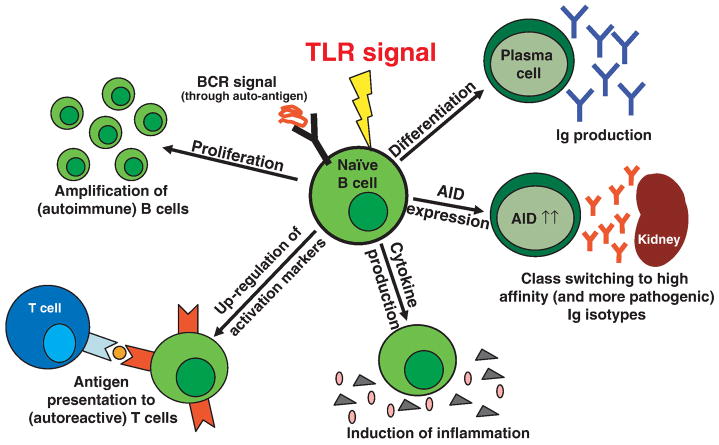
TLR signaling is not a prerequisite for B cell development as demonstrated by normal B cell subpopulations and numbers in MyD88/TRIF double ko mice (9). In general, the outcome of TLR stimulation in B cells depends on TLR ligand and the specific B cell subpopulation. Upon TLR stimulation, B cells increase in size and start to proliferate. Within a few hours, multiple activation markers (CD80, CD86, CD25, CD69, MHC II) are up-regulated thus increasing their potential activity for T cell co-stimulation and antigen presentation. In addition, production of several cytokines is induced including IL-12p40, IL-12p70, IL-6, TNFα, IL-10, INFγ or TGFβ (10). Moreover, stimulation of naïve B cells leads to expression of the plasma cell marker syndecan-1 (CD138) and production of immunoglobulins (11). Activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is also induced enabling immunoglobulin class switching and promoting somatic hypermutation. In particular, switching to IgG2a has been shown to be MyD88 and therefore TLR dependent (12). In addition, CpG but not LPS, up-regulates the expression of T-bet and induces IgG2a whereas IgG1 and IgE production are decreased (13). Thus the sum of this B cell activation cascade (Figure) results not only in an immediate innate immune response but also in initiation and enhancement of adaptive immune responses.
Figure.
Combined stimulation through the TLR and an autoreactive BCR leads to activation of B cells in multiple ways. Autoreactive B cells can then proliferate, or up-regulate co-stimulatory molecules turning them into more efficient APCs. They also secrete cytokines and can differentiate into plasma cells that produce large amounts of immunoglobulins (Ig). In addition, expression of activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is directly induced by TLR signals. This results in class switching to higher affinity immunoglobulins, and -if autoreactivity is retained-, increasingly pathogenic antibodies are generated.
B cell autonomous TLR signals in autoimmunity
The first major evidence suggesting the involvement of B cell intrinsic TLR signals in auto-antibody production came from in-vitro studies from Ann Marshak-Rothstein’s group. These studies utilized B cells from AM14 transgenic mice which express an antigen receptor specific for self-IgG thereby producing a rheumatoid factor (RF) upon stimulation (14). Effective activation of these RF+ B cells could only be obtained in response to DNA or RNA containing immune complexes and required the dual engagement of both the BCR and Toll-like receptors. Proliferation in response to immune complexes of AM14 B cells was abolished in the absence of MyD88, TLR7 or TLR9, or by inhibitors to TLR7 and TL9, indicating that activation of these auto-reactive B cells requires signaling via TLR7 or TLR9 (15) (16).
In-vivo data supporting the requirement for TLRs in autoimmune disease has been mainly obtained via crossing lupus prone mice with mice deficient for MyD88 or various TLRs (17). Surprisingly, whereas TLR7 deficiency led to a marked decrease in antibody production and autoimmune symptoms, other studies have suggested a protective role for TLR9 in these events.
A few studies have begun to address whether B cells play an autonomous role in these processes. Using a model of autoimmunity induced by an anti-DNA BCR transgene and homozygous deficiency of the inhibitory receptor, FcγRIIB, it was shown that class switching of autoreactive B cells to the pathogenic IgG2a and 2b subclasses requires TLR9 and MyD88 signaling; accordingly, TLR9 or MyD88 deficiency resulted in reduced pathology and mortality in this model (4). The genetic modifier, Y-linked autoimmune accelerator (Yaa) has previously been shown to increase the severity of SLE in male mice. Addition of the Yaa modifier to the FcγRIIB deficient model indicated that B cells containing Yaa have an intrinsic bias toward the production of more pathogenic nucleolar autoantibodies. Analysis of the Yaa locus demonstrated a duplication of the TLR7 gene (18). The importance of TLR7 as co-receptor to activate auto-reactive B cells is further supported by a study using a BCR knock-in mouse with specificity for a variety of nuclear antigens. Loss of tolerance and autoantibody production in these mice was largely dependent on TLR7 (19).
Finally, by analyzing chimeric mice where TLR9-deficiency is restricted to the B cell lineage, data from Mark Shlomchik’s group suggests that TLR9 promotes the activation and differentiation of anti-DNA plasmablasts in murine lupus via a B cell-intrinsic mechanism (20).
Concluding remarks
Over the last few years, the understanding of how TLR signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmunity has increased dramatically. In particular, there is now compelling evidence that TLR ligands can directly break B cell tolerance. However, further studies are necessary to analyze the exact mechanisms and the involvement of single TLRs and their ligands in greater detail. This might allow the development of new therapeutic modalities with TLRs as targets.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Sfikakis PP, Boletis JN, Lionaki S, Vigklis V, Fragiadaki KG, Iniotaki A, et al. Remission of proliferative lupus nephritis following B cell depletion therapy is preceded by down-regulation of the T cell costimulatory molecule CD40 ligand: an open-label trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(2):501–13. doi: 10.1002/art.20858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wardemann H, Yurasov S, Schaefer A, Young JW, Meffre E, Nussenzweig MC. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science. 2003;301(5638):1374–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1086907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Uematsu S, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. J Mol Med. 2006;84(9):712–25. doi: 10.1007/s00109-006-0084-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ehlers M, Fukuyama H, McGaha TL, Aderem A, Ravetch JV. TLR9/MyD88 signaling is required for class switching to pathogenic IgG2a and 2b autoantibodies in SLE. J Exp Med. 2006;203(3):553–61. doi: 10.1084/jem.20052438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bernasconi NL, Onai N, Lanzavecchia A. A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: up-regulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. Blood. 2003;101(11):4500–4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-11-3569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bourke E, Bosisio D, Golay J, Polentarutti N, Mantovani A. The toll-like receptor repertoire of human B lymphocytes: inducible and selective expression of TLR9 and TLR10 in normal and transformed cells. Blood. 2003;102(3):956–63. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-11-3355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gunn KE, Brewer JW. Evidence that marginal zone B cells possess an enhanced secretory apparatus and exhibit superior secretory activity. J Immunol. 2006;177(6):3791–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.6.3791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bendelac A, Bonneville M, Kearney JF. Autoreactivity by design: innate B and T lymphocytes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1(3):177–86. doi: 10.1038/35105052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gavin AL, Hoebe K, Duong B, Ota T, Martin C, Beutler B, et al. Adjuvant-enhanced antibody responses in the absence of toll-like receptor signaling. Science. 2006;314(5807):1936–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1135299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wagner M, Poeck H, Jahrsdoerfer B, Rothenfusser S, Prell D, Bohle B, et al. IL-12p70-dependent Th1 induction by human B cells requires combined activation with CD40 ligand and CpG DNA. J Immunol. 2004;172(2):954–63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Won WJ, Kearney JF. CD9 is a unique marker for marginal zone B cells, B1 cells, and plasma cells in mice. J Immunol. 2002;168(11):5605–11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jegerlehner A, Maurer P, Bessa J, Hinton HJ, Kopf M, Bachmann MF. TLR9 signaling in B cells determines class switch recombination to IgG2a. J Immunol. 2007;178(4):2415–20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu N, Ohnishi N, Ni L, Akira S, Bacon KB. CpG directly induces T-bet expression and inhibits IgG1 and IgE switching in B cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(7):687–93. doi: 10.1038/ni941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leadbetter EA, Rifkin IR, Hohlbaum AM, Beaudette BC, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature. 2002;416(6881):603–7. doi: 10.1038/416603a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Viglianti GA, Lau CM, Hanley TM, Miko BA, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A. Activation of autoreactive B cells by CpG dsDNA. Immunity. 2003;19(6):837–47. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lau CM, Broughton C, Tabor AS, Akira S, Flavell RA, Mamula MJ, et al. RNA-associated autoantigens activate B cells by combined B cell antigen receptor/Toll-like receptor 7 engagement. J Exp Med. 2005;202(9):1171–7. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Marshak-Rothstein A. Toll-like receptors in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(11):823–35. doi: 10.1038/nri1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pisitkun P, Deane JA, Difilippantonio MJ, Tarasenko T, Satterthwaite AB, Bolland S. Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science. 2006;312(5780):1669–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1124978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Berland R, Fernandez L, Kari E, Han JH, Lomakin I, Akira S, et al. Toll-like receptor 7-dependent loss of B cell tolerance in pathogenic autoantibody knockin mice. Immunity. 2006;25(3):429–40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Christensen SR, Shlomchik MJ. Regulation of lupus-related autoantibody production and clinical disease by Toll-like receptors. Semin Immunol. 2007;19(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2006.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]